AP Bio Midterm Review (copy)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/62
Last updated 1:59 PM on 10/5/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
1
New cards
1) What is the maximum number of covalent bonds that an oxygen atom with an atomic number 8 can make with hydrogen?
2
2
New cards
A covalent chemical bond is one in which _____
outer-shell electrons of 2 atoms are shared so as to satisfactorily fill their respective orbitals.
3
New cards
Bonds between 2 atoms that are equally electronegative are___
nonpolar covalent bonds
4
New cards
What results from an unequal sharing of electrons between atoms?
a polar covalent bond
5
New cards
What is the difference between covalent bonds and ionic bonds?
Covalent bonds involve the sharing of electrons between atoms; ionic bonds involve the electrical attraction between charged atoms
6
New cards
Water molecules can form hydrogen bonds with____
compounds that have polar covalent bonds
7
New cards
Hydrophobic substances such as vegetable oil are___
nonploar substances that repel water molecules.
8
New cards
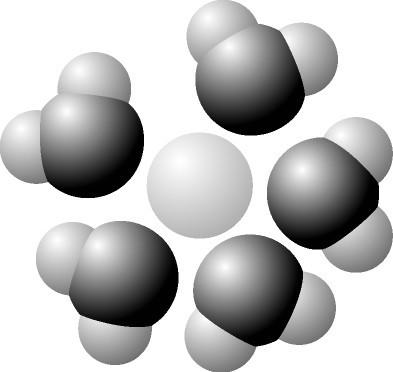
Based on your knowledge of the polarity of water molecules, the solute molecule depicted here is most likely ___
positively charged
9
New cards
the element present in all organic molecules is___
carbon
10
New cards
Differences among organisms are caused by differences in the ___
types and relative amounts of organic molecules synthesized by each organism
11
New cards
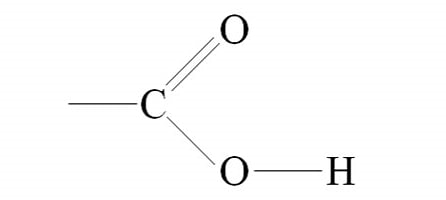
what is the name of the functional group sown in the figure below?
carboxyl
12
New cards
which of the following is true of carbon?
it can form both polar and nonpolar bonds
13
New cards
which 2 functional groups are always found in amino acids
carboxyl and amine groups
14
New cards
which of the functional groups below acts most like an acid in water?
Carboxyl
15
New cards
why are hydrocarbons insoluble in water?
the majority of their bonds are nonpolar carbon-to-hydrogen linkages
16
New cards
which molecule above can form a cross linkage
sulfhydryl
17
New cards
which of these classes of biological molecules does NOT include polymers?
Lipids
18
New cards
which of these is NOT a polymer?
glucose
19
New cards
how many molecules of water are used to completely hydrolyze a polymer that is 11 monomers long?
10
20
New cards
a glycosidic linkage is analogous to which of the following in proteins?
a peptide bond
21
New cards
how do phospholipids interact with water molecules?
the polar heads interact with water; the nonpolar tails do not
22
New cards
phospholipids and triglycerides both___
have a glycerol background
23
New cards
which of the following is the best explanation for why vegetable oil is liquid at room temperature when animal fats are solid?
vegetable oil has more double bonds than animal fats
24
New cards
which of the following statements is FALSE? saturated fats___
have many double bonds in the carbon chains of their fatty acids
25
New cards
saturated fatty acids___
are the principle molecules in lard and butter
26
New cards
steroids are considered to be lipids because they___
are not soluble in water
27
New cards
which one of the following is NOT a component of each monomer used to make proteins
a phosphorus atom,P
28
New cards
you disrupt all hydrogen bonds in a protein. what level of structure will be preserved?
primary structure
29
New cards
Lipids___
are insoluble in water
30
New cards
which of the following is the strongest evidence the protein structure and function are correlated?
denatured (unfolded) proteins do not function normally
31
New cards
Proteorhodopsin consists of single polypeptide chain. what is the highest level of structure found in this protein?
tertiary
32
New cards
which level of protein structure do the a-helix and the b-pleated sheet represent?
secondary
33
New cards
what is the term used for a protein molecule that assists in the proper folding of other proteins?
chaperonin
34
New cards
the chemical reaction illustrated in the accompanying figure___
results in a peptide bond
35
New cards
nucleic acids are polymers made up of which of the following monomers?
nucleotides
36
New cards
all of the following are part of the prokaryotic cell except___
an endoplasmic reticulum
37
New cards
cell size is limited by___
surface to volume ratios
38
New cards
A cell with an extensive area of smooth endoplasmic reticulum is specialized to
synthesize large quantities of lipids
39
New cards
which structure i common to plant AND animal cells?
mitochondrion
40
New cards
which structure is NOT part of the endomembrane system
chloroplast
41
New cards
the golgi apparatus has a polarity, or sidedness, to its structure and function. Which of the following statements correctly describes this polarity?
All of the listed responses are correct.
42
New cards
Suppose a cell has the following molecules and structures: enzymes, DNA, ribosomes,plasma membrane, and mitochondria. It could be a cell from___
nearly any eukaryotic organism
43
New cards
In a plant cell, DNA may be found ___
in the nucleus, mitochondria, and chloroplasts
44
New cards
which structure is the site of the synthesis of proteins hat may be exported from the cell?
rough er
45
New cards
for a protein to be an integral membrane protein, it would have to be ___
amphipathic, with at least one hydrophobic region
46
New cards
what kinds of molecules pass through a cell membrane most easily
small and hydrophobic
47
New cards
when a plant cell, such as one from a rose stem, is submerged in a very hypotonic solution, what is likely to occur?
the cell will become turgid
48
New cards
cell membranes are asymmetrical. Which of the following statements id the most likely explanation for the membranes asymmetrical nature?
the two sides of a cell membrane face different environments and carry out different functions
49
New cards
according to the fluid mosaic model of cell membranes, phospholipids___
can move laterally along the plane of the membrane
50
New cards
you have a planar bilayer with equal amount of saturated and unsaturated phospholipids. after testing the permeability of this membrane to glucose, you increase the proportion of unsaturated phospholipids in the bilayer. what will happen to the membranes permeability to glucose?
permeability to glucose will increase.
51
New cards
which of the following membrane activities requires energy from atp?
movement of Na+ ions form a lower concentration in a mammalian cell to a higher concentration in the extracellular fluid
52
New cards
ions diffuses across membranes through specific ion channels down___
their electrical chemical gradients
53
New cards
white blood cells engulf bacteria using___
phagocytosis
54
New cards
in receptor mediated endocytosis, receptor molecules initially project to the outside of the cell. where do they end up after endocytosis?
on the inside surface of the vesicle
55
New cards
the difference between pinocytosis and receptor mediated endocytosis is that
pinocytosis is nonselective in the molecules it brings into the cell, whereas receptor mediated endocytosis offers more selectivity
56
New cards
the force driving simple diffusion is___, while the energy source for active transport is___
the concentration gradient;ATP
57
New cards
which of the following would increase the electrochemical gradient across a membrane?
a proton pump
58
New cards
a bacterium engulfed by a white blood cell through phagocytosis will be digested by enzymes contained in___
lysosomes
59
New cards
an organism with a cell wall would most likely be unable to take in materials through
phagocytosis
60
New cards
several epidemic microbial diseases of eariler centuries incurred high death rates because they resulted in severe dehydration due to vomiting and diarrhia. today they are usually not fatal because we have developed which of the following?
hydrating drinks with high concentrations of salts and glucose.
61
New cards
what will happen to a red blood cell (RBC) which has an internal ion concentration of about 0.9 percent, if it is paced into a beaker of pure water?
the cell would swell because they water in the beaker is hypotonic relative to the cytoplasm of the RBC
62
New cards
which of the following statements correctly describes the normal tonicity conditions for typical plant and animal cells? the animal cell is in___
an isotonic solution, and the plant cell is in a hypotonic solution
63
New cards
which of the following allows water to move much faster across cell membranes?
aquaporins