BIOCHEM EXAM 2
1/183
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
184 Terms
Carbohydrates
Biomolecules that serve as a primary source of energy, structural components, and signaling molecules in cells.
Glycolysis
The metabolic pathway that converts glucose into pyruvate, producing ATP in the process.
Pentose Phosphate Pathway
A metabolic pathway that generates ribose for nucleic acid synthesis and NADPH for biosynthetic reactions.
Homeostasis
The ability of a cell or organism to maintain stable internal conditions.
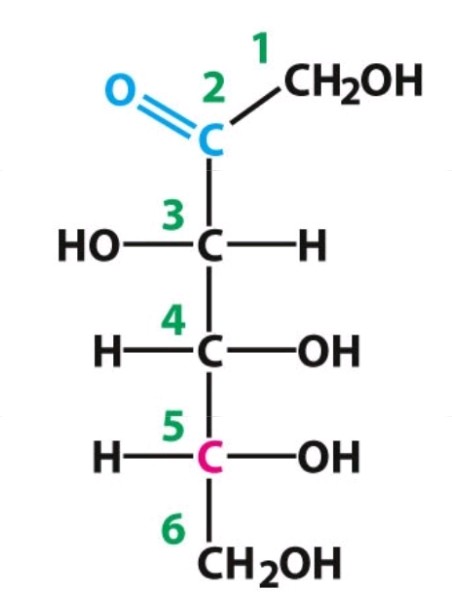
D-Fructose
Ketose
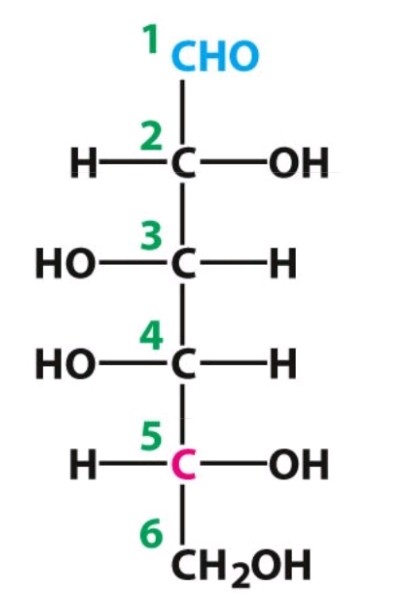
D-galactose
Aldose
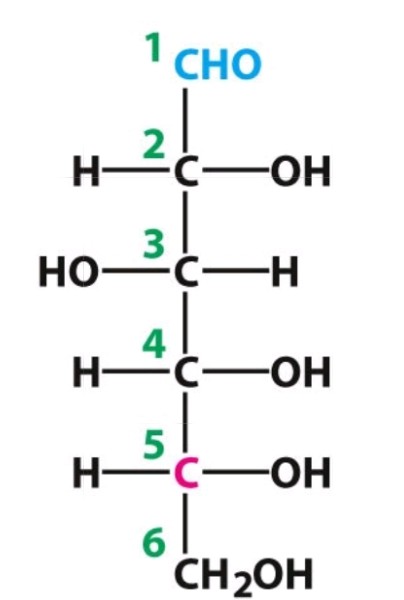
D-glucose
Aldose
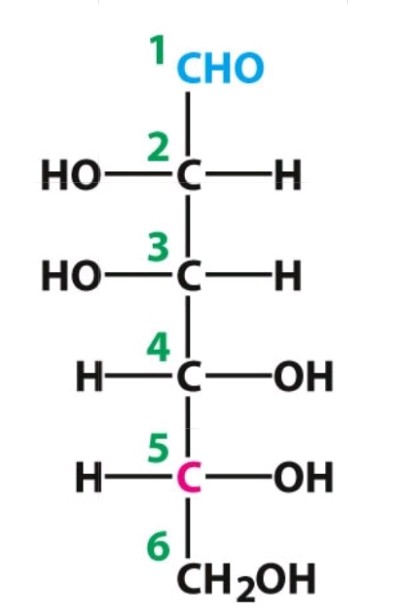
D-Mannose
Aldose
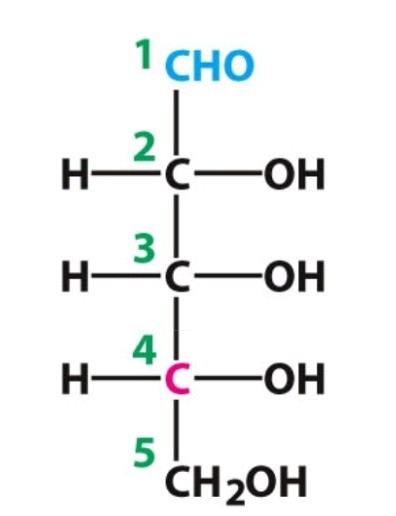
D-ribose
Aldose
Name
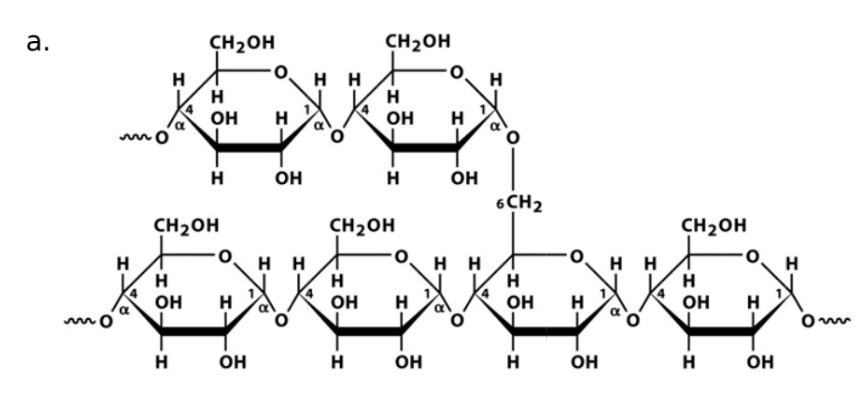
Glycogen
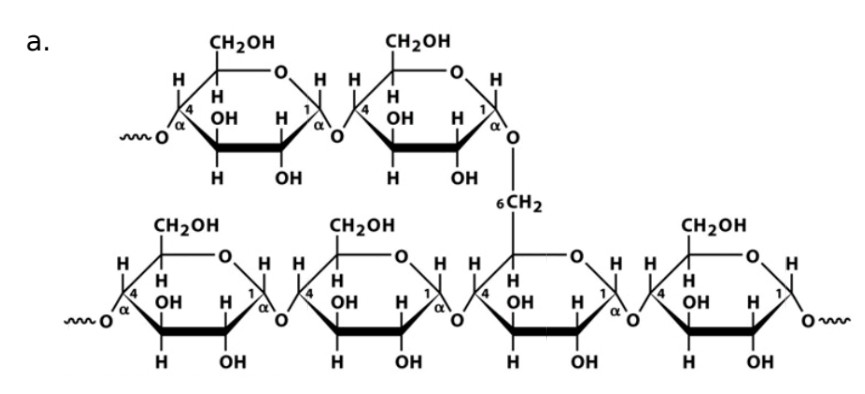
Monosaccharide
Glucose
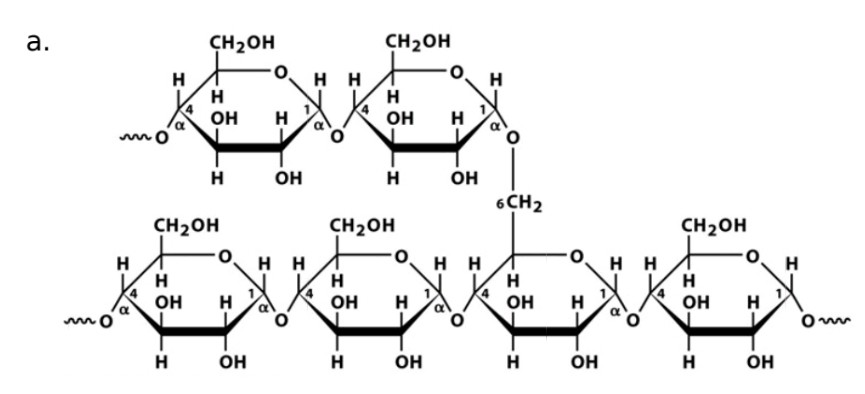
Linkage
a-1,4-glycosidic bonds linked by a-1,6-glycosidic bond forms every 12 glucose units
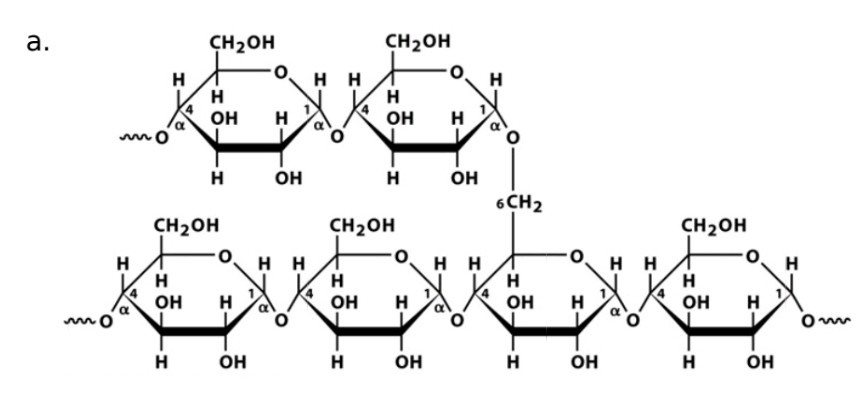
Name of enzyme to breakdown
a-amylase, glycogen phosphorylase
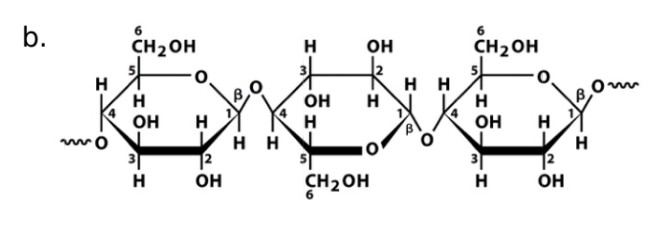
Cellulose
Name
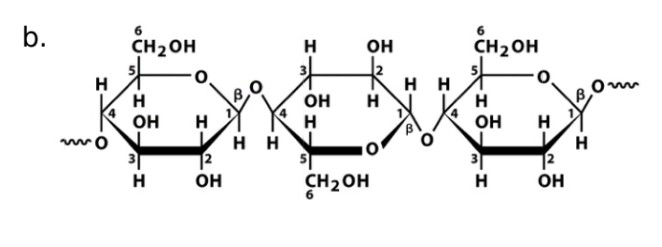
Glucose
Monosaccharide
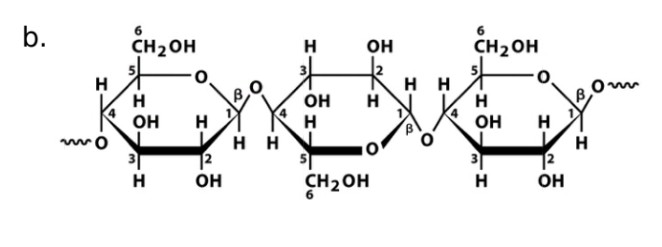
Beta-1, 4-glycosidic bonds
Linkage
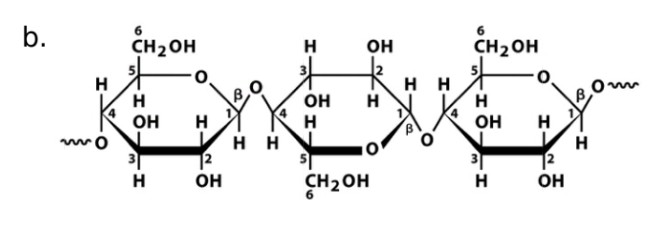
Cellulase
Name of enzyme to breakdown
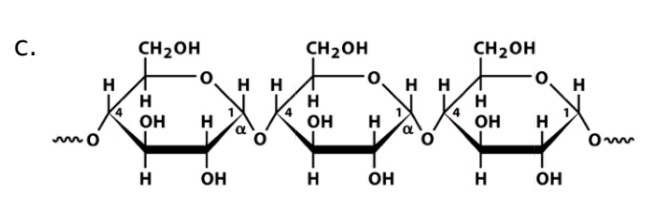
Starch (amylose)
Name
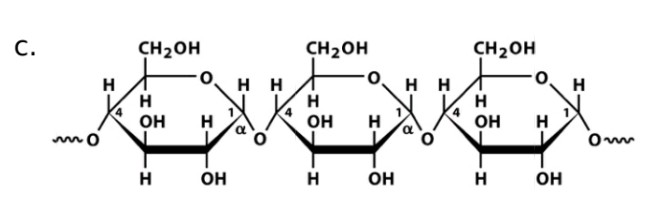
Glucose
Monosaccharide
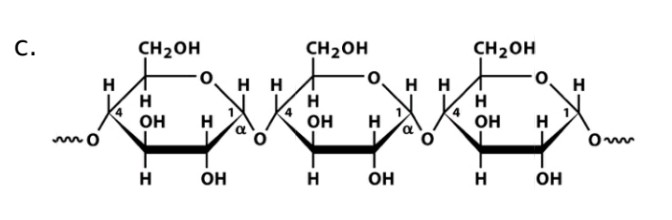
a-1,4-glucosidic bonds
Linkage
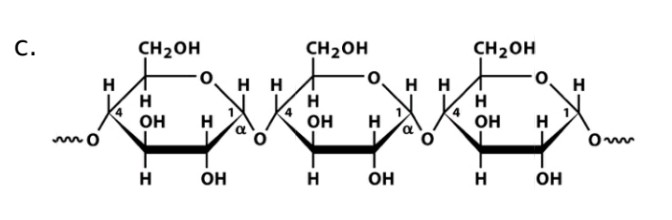
a-amylase
Name of enzyme to breakdown
Glucose-6-phosphate
In glycolysis Glucose becomes what in step 1
Frucotse-6-phosphate
In glycolysis Glucose-6-phosphate becomes what in step 2
Frucotse-1,6-biphosphate
In glycolysis fructose-6-phosphate becomes what in step 3
Glyceraldheyhde-3phosphate and dihydroxyacetone phosphate
In glycolysis fructose-1,6-biphosphate becomes what in step 4
What are the end products of glycolysis?
2 molecules of pyruvate, 2 ATP, and 2 NADH.
What is NADH's role in glycolysis?
It acts as an electron carrier, transferring electrons to the electron transport chain.
What happens to pyruvate after glycolysis?
It can be converted into either acetyl-CoA or lactate, depending on oxygen availability.
What is the structure of glycogen?
Glycogen is a branched polysaccharide made up of glucose units.
All mammalian tissue
Glut1 tissue distribution
Liver and pancreatic Beta Cells
Glut2 tissue distribution
All mammalian tissues-pt2
Glut3 tissue distribution
Muscle and fat cells
Glut 4
Small intestine
Glut5
Glut4
Transporter responsible for transporting glucose into muscle and fat cells
Insulin
Molecule that regulates tranpost of GLUT protein to the cell surface in muscle and fat cells
How does gluconeogenesis differ from glycolysis?
Gluconeogenesis is the reverse of glycolysis but involves distinct enzymes at key steps.
Which enzyme catalyzes the eighth step of glycolysis?
Phosphoglycerate mutase.
Which enzyme catalyzes the ninth step of glycolysis?
Enolase.
Which enzyme catalyzes the tenth step of glycolysis?
Pyruvate kinase.
What is the first step of gluconeogenesis?
Conversion of pyruvate to oxaloacetate.