AP Environmental Science Chapter 16: Waste Generation and Waste Disposal
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Waste
Material outputs from a system that are not useful or consumed
Humans
Only ________________ generate waste
Municipal Solid Waste (MSW)
Refuse collected by municipalities from households, small businesses, and institutions
Wealthier
______________ societies generate more waste
Residences
Sixty percent of MSW comes from ____________
Commercial and institutional facilities
Forty percent of MSW comes from _______________
Seasons of the year, status of person generating waste, and geographic location within country
Waste generation varies by _____________________
Waste Stream
The flow of solid waste that is recycled, incinerated, placed in a solid waste landfill, or disposed of in another way
Paper
What makes up the most of the waste stream (30%)
Reduce, reuse, recycle
A popular phrase promoting the idea of diverting materials from the waste stream
Source reduction
An approach to waste management that seeks to cut waste by reducing the use of potential waste materials in the early stages of design and manufacture
Reuse
Using a product or material that was intended to be discarded
Recycling
The process by which materials destined to become municipal solid waste are collected and converted into raw materials that is then used to produce new objects
Closed-loop recycling
Recycling a product into the same product
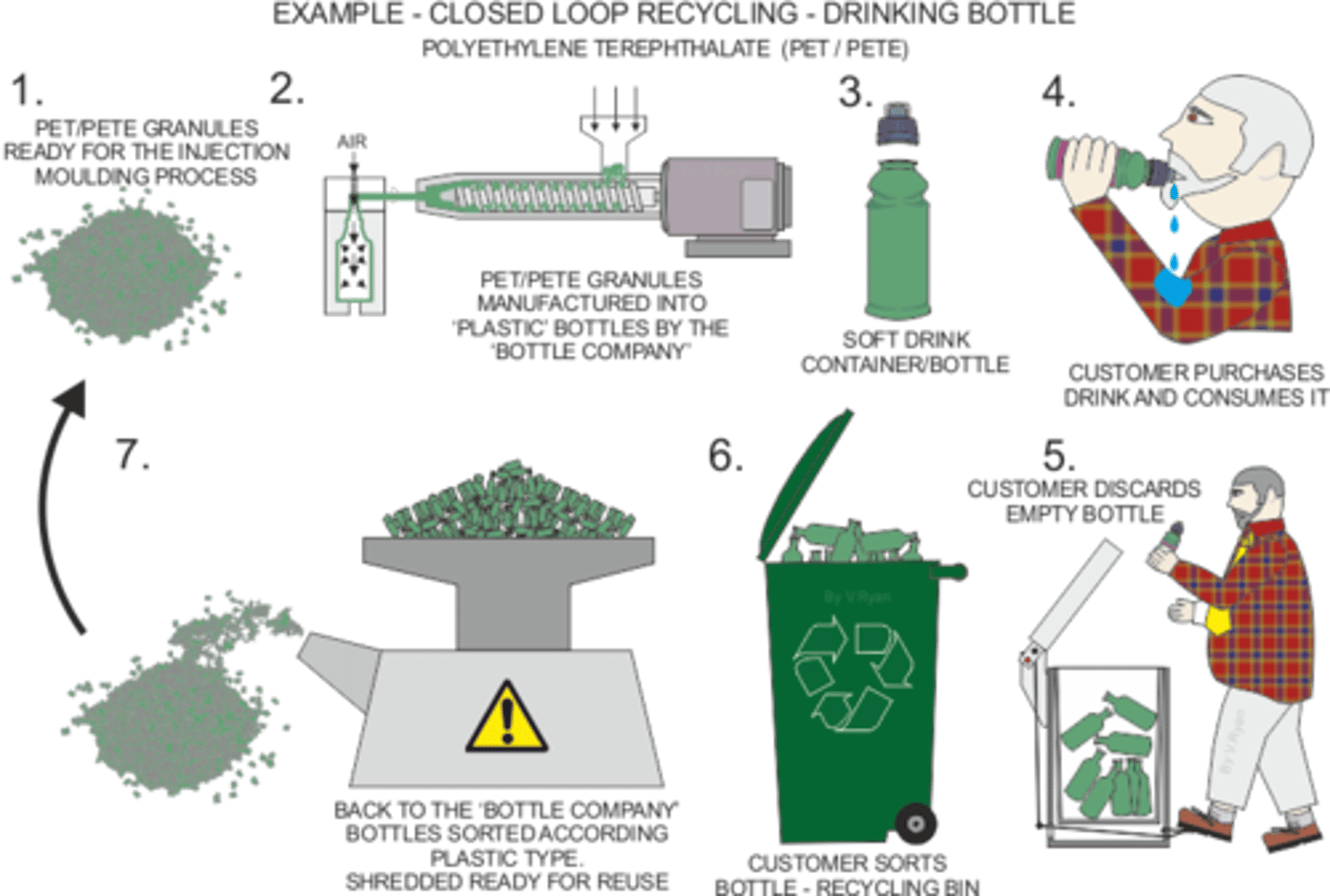
Open-loop recycling
Recycling one product into a different product
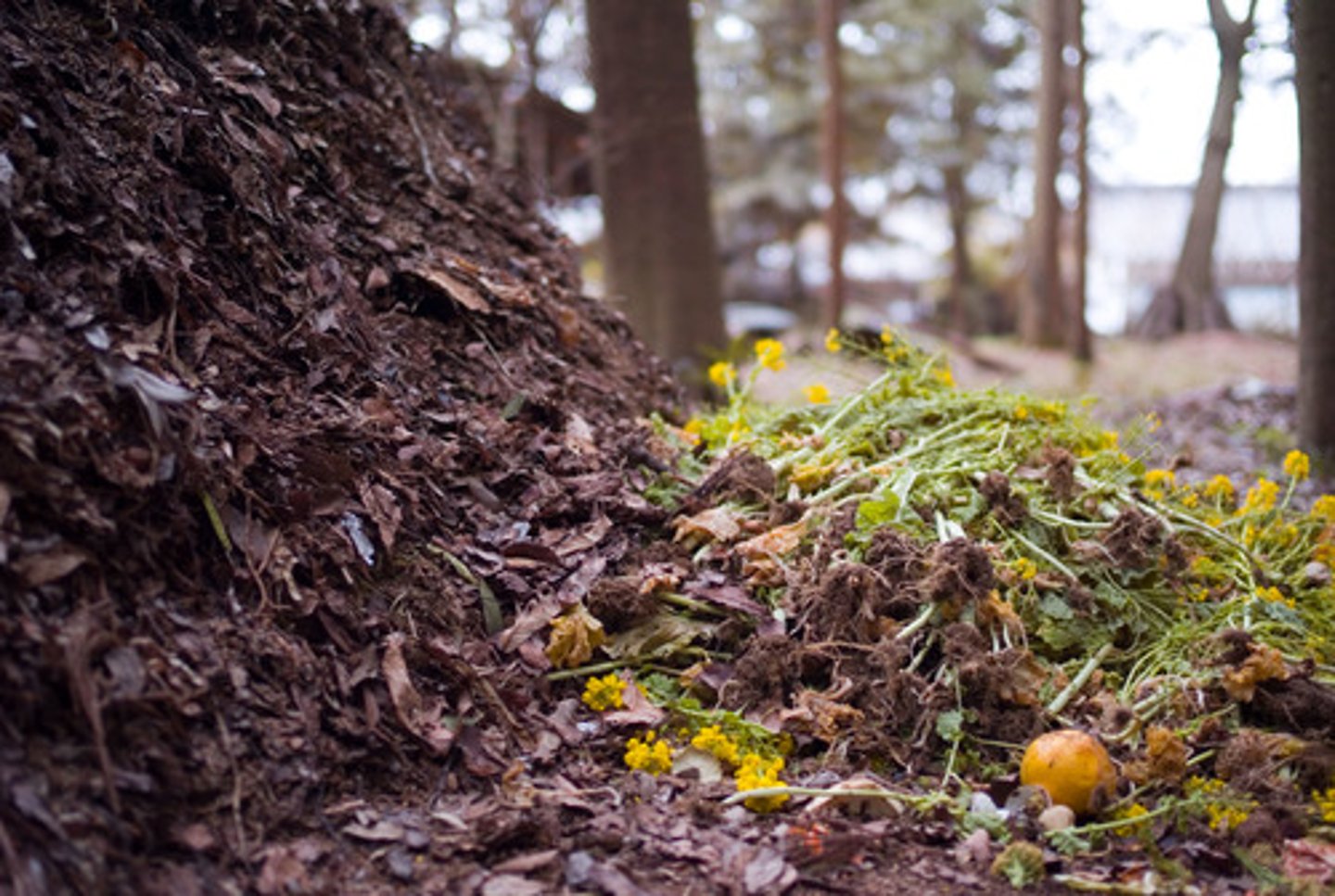
Composting
Creation of organic matter (humus) by decomposition under controlled conditions to produce an organic-rich material that enhances soil structure, cation exchange capacity, and fertility.

Nitrogen
What are the greens in compost?
Carbon
What are the browns in compost?
30:1
What is the best ratio of carbon to nitrogen?
Greens
Grass clippings, weeds, fruit peels, and leftover veggies are examples of
Browns
Sawdust, fallen leaves, and wood clippings are examples of
Open dumps
These are where villages of people used to leave their waste in a shared open area, the waste is exposed, attracts wildlife, and an eyesore. These are illegal in most developed countries
Landfills and Incineration
What are the two options for waste disposal?
Leachate
Liquid that contains elevated levels of pollutants as a result of having passed through municipal solid waste or contaminated soil
Sanitary landfill
An engineered ground facility designed to hold MSW with as little contamination of the surrounding environment as possible
Can hold A LOT of waste, cuts down on contamination, inexpensive to build BUT causes an environmental injustice issue, produces methane
What are the pros and cons of landfills?
Incineration
The process of burning waste materials to reduce volume and mass, sometimes to generate electricity or heat
Ash
The residual nonorganic material that does no combust during incineration
90%
An effective incinerator can reduce the volume of solid waste by up to _________ and the weight by 75%
Waste-to-energy
A system in which heat generated by incineration is used as an energy source rather than released into the atmosphere *Concentrates toxins into ash and may release harmful gases just like coal
Reduces waste by up to 90%, energy can be generated BUT toxic ash must be disposed of and metals and toxins are released into air
What are the incineration pros and cons?
Hazardous waste
Liquid, solid, gaseous, or sludge waste material that is harmful to humans or ecosystems at high doses
Fatal to organisms in low doses, alters genes, ignitable at less than 60°C (140°F), corrosive, explosive or highly reactive
What are characteristics of hazardous waste?
Superfund Act
The common name for CERCLA; a 1980 U.S. federal act that imposes a tax on the chemical and petroleum industries, funds the cleanup of abandoned and nonoperating hazardous waste sites, and authorizes the federal government to respond directly to the release or threatened release of substances that may pose a threat to human health or the environment
Superfund sites
Areas deemed by CERCLA to be the highest priority to clean up as they are a direct threat to humans
Brownfields
Contaminated industrial or commercial sites that may require environmental cleanup before they can be redeveloped or expanded (EPA assists in cleaning of these sites) -Less of a priority than Superfund sites
Cradle-to-grave analysis
A systems tool that looks at the materials used and released throughout the lifetime of a product-from the procurement of raw materials through their manufacture, use, and disposal
Integrated waste management
An approach to waste disposal that employs several waste reduction, management, and disposal strategies in order to reduce the environmental impact of MSW