Chapter 16: Long-Run Economic Growth Principles
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
output growth
The growth rate of the output of the entire economy.
per-capita output growth
The growth rate of output per person in the economy.
labor productivity growth
The growth rate of output per worker.
catch-up
The theory stating that the growth rates of less developed countries will exceed the growth rates of developed countries, allowing the less developed countries to catch up.
convergence theory
The idea that gaps in national incomes tend to close over time.
advantages of backwardness
The phenomenon of less developed countries leaping ahead by borrowing technology from more developed countries.
production possibility frontier (ppf)
Shows all the combinations of output that can be produced if all society's scarce resources are fully and efficiently employed.
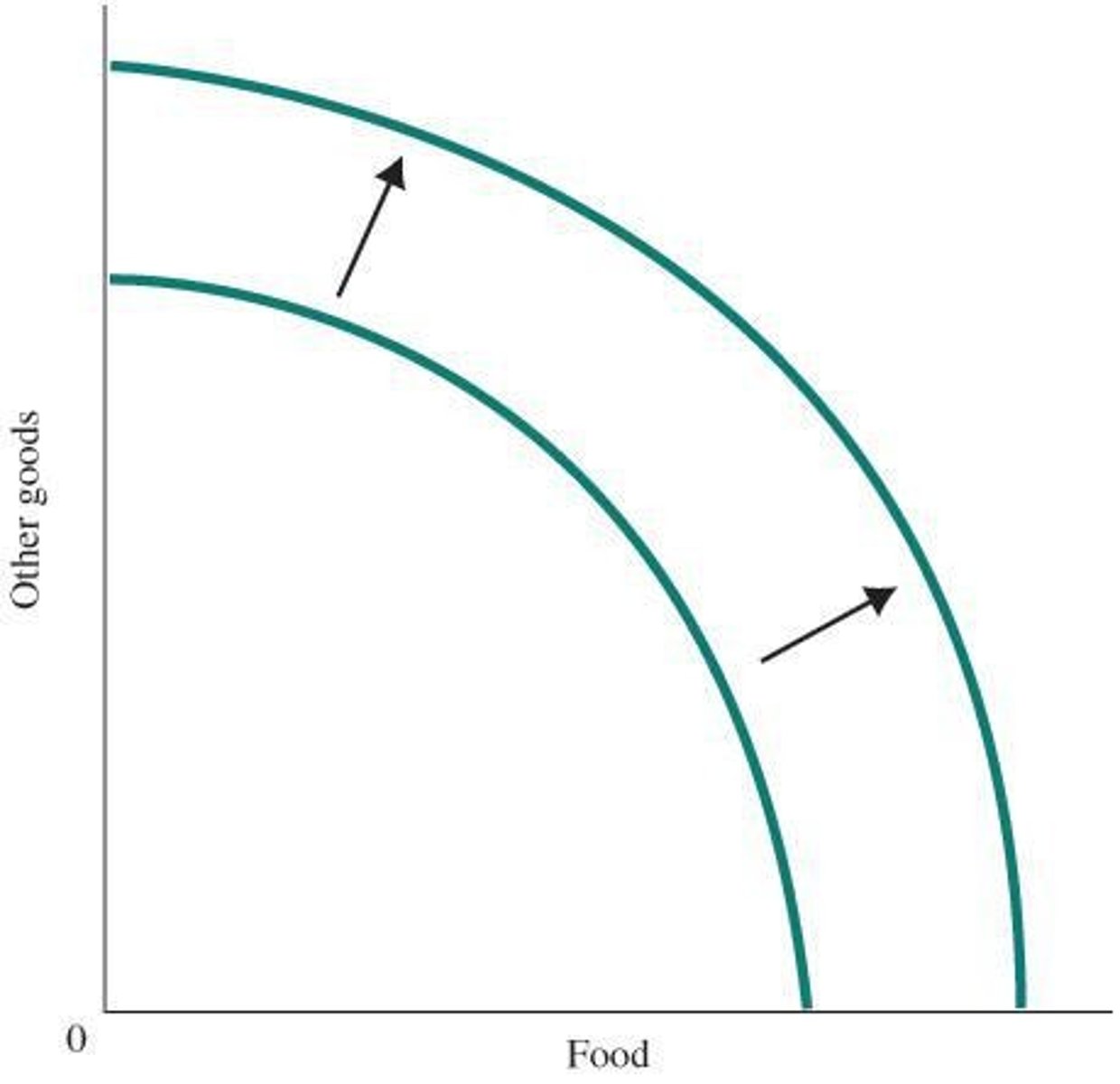
economic growth
Expands society's production possibilities, shifting the production possibility frontier up and to the right.
aggregate production function
A mathematical relationship stating that total GDP (output) depends on the total amount of labor used and the total amount of capital used.
Production Function
A mathematical representation of the relationship between inputs (capital and labor) and output.
Diminishing Returns
A phenomenon where increasing one input (like labor) while holding others constant leads to smaller increases in output.
Labor Productivity
The amount of output produced per worker.
Marginal Return to Labor
The additional output produced by adding one more unit of labor.
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)
Investment in enterprises made in a country by residents outside that country.
Fragile Countries
Countries with poor institutions, corruption, and inadequate protection for lenders and investors.
Economic Growth from Labor Increase
An increase in labor supply can lead to more output but at a declining rate due to diminishing returns.
Economic Growth from Capital Increase
An increase in physical capital can lead to more output and higher labor productivity, but with diminishing returns.
Total Output
The overall amount of goods and services produced in an economy.
Quantity of Labor
The total number of workers available for production.
Quantity of Capital
The total amount of capital available for production.
Output per Worker
The total output divided by the number of workers.
Period
A specific time frame used to measure economic data.
Labor Supply Growth
An increase in the number of workers available for production.
Investment Sources
New capital can come from the saving of a country's residents and/or from the investments of foreigners.
Capital Stock
The total amount of capital available in an economy at a given time.
Innovation
The process of developing new technologies or methods to improve production.
Entrepreneurship Policies
Government strategies aimed at supporting new business ventures and innovation.
Technological Frontier
The highest level of technology available in the world at a given time.
Fixed Private Nonresidential Net Capital Stock
The total value of fixed private nonresidential capital stock in billions of 2009 dollars from 1960 to 2016.
Growth of capital relative to labor
Capital has grown relative to labor as indicated by larger growth rates of capital compared to labor.
Human Capital
The level of educational attainment in the United States has risen significantly since 1940, leading to increased labor productivity.
Years of School Completed by People Older Than 25 Years
Data showing the educational attainment of individuals older than 25 from 1940 to 2017.
German Jewish Émigrés Contribution to U.S. Growth
More than 133,000 Jewish émigrés contributed considerable human capital to the U.S. economy before World War II.
Increase in patent rates due to émigrés
New U.S. citizens may have increased patent rates in their fields by more than 30%.
Embodied Technical Change
Technical change that results in an improvement in the quality of capital, leading to increased labor productivity.
Disembodied Technical Change
Technical change that results in a change in the production process, often leading to increased labor productivity.
Educational attainment concern
Policymakers in many developed economies are concerned about their ability to continue to generate growth through human capital improvements.
invention
An advance in knowledge.
innovation
The use of new knowledge to produce a new product or to produce an existing product more efficiently.
fraction of GDP spent
A commonly used measure of inputs into research.
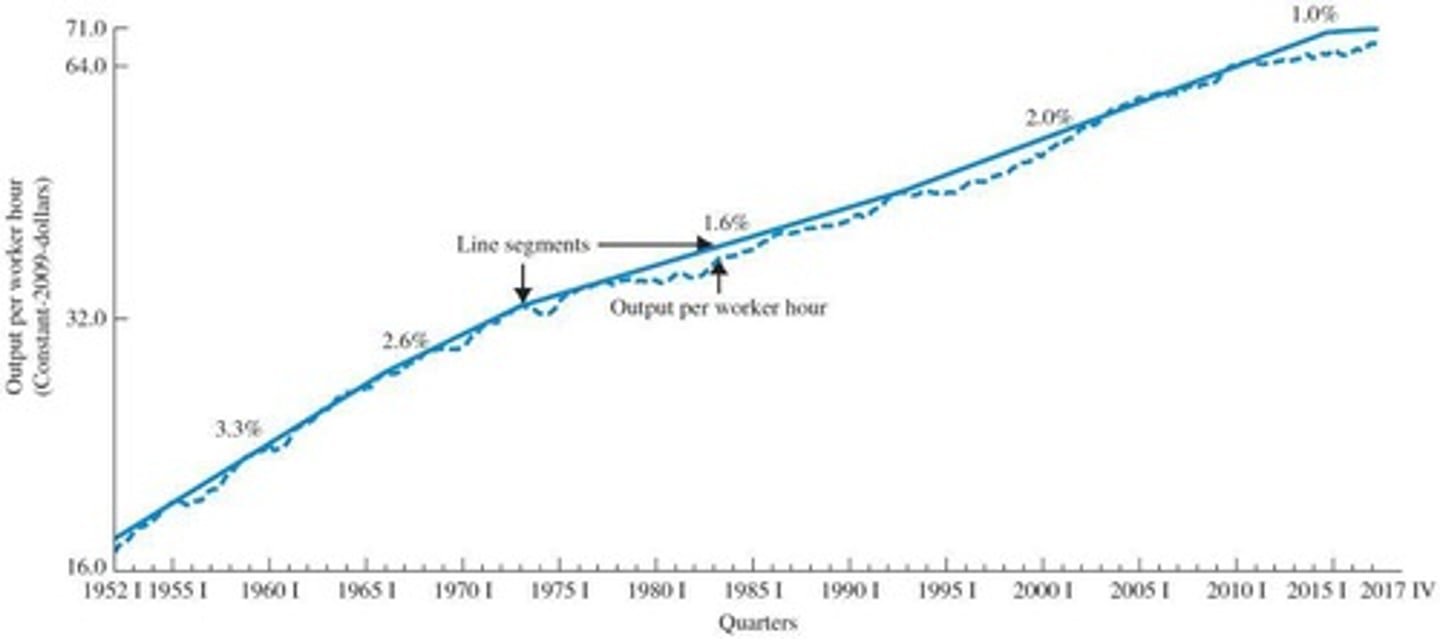
U.S. Labor Productivity: 1952 I-2017 IV
Output per Worker Hour (Productivity), 1952 I-2017 IV.
slowdown in productivity growth
There was a slowdown in productivity growth in the 1970s due to a low rate of saving, environmental and government regulation, and little spending on R&D.
productivity rise
Productivity rose to 2.0% between 1993 and 2010.
export-led manufacturing
Much of Southeast Asia has fueled its growth through export-led manufacturing.
resource extraction
For countries that have based their growth on resource extraction, public investment in infrastructure is especially important.
natural resource base limits
The question of whether the natural resource base imposes strong natural limits on growth has been debated since the time of Malthus.
air pollution measure
One measure of air pollution is smoke in cities.
relationship between smoke and GDP
The relationship between smoke concentration and per-capita GDP is an inverted U: As countries grow wealthier, smoke increases and then declines.
The Limits to Growth
In 1972, the Club of Rome released a study suggesting that the entire world economy would reach its limits sometime after the year 2000.
collapse due to resource depletion
Collapse occurs because of nonrenewable resource depletion, leading to an inability to keep up with depreciation and resulting in industrial base collapse.
industrial capital stock
The industrial capital stock grows to a level that requires an enormous input of resources.
population decrease
Population finally decreases when the death rate is driven upward by the lack of food and health services.