Proteins
1/47
Earn XP
Description and Tags
This deck contains content from 3.1.4 Proteins
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
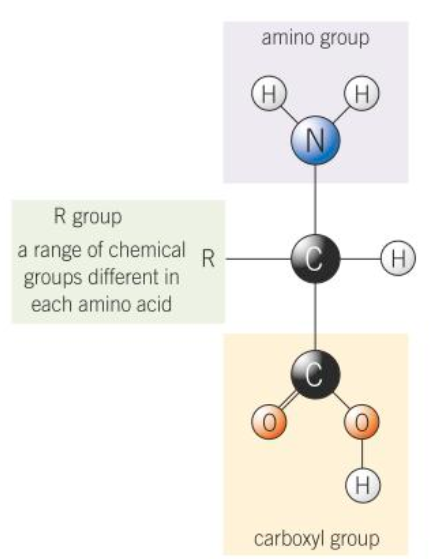
What is the structure of an amino acid?
Amino group
Carboxyl group
Central carbon and hydrogen atom
Variable R-group
What is the biological term for proteins?
Polypeptide
What is the monomer for proteins?
Amino acids
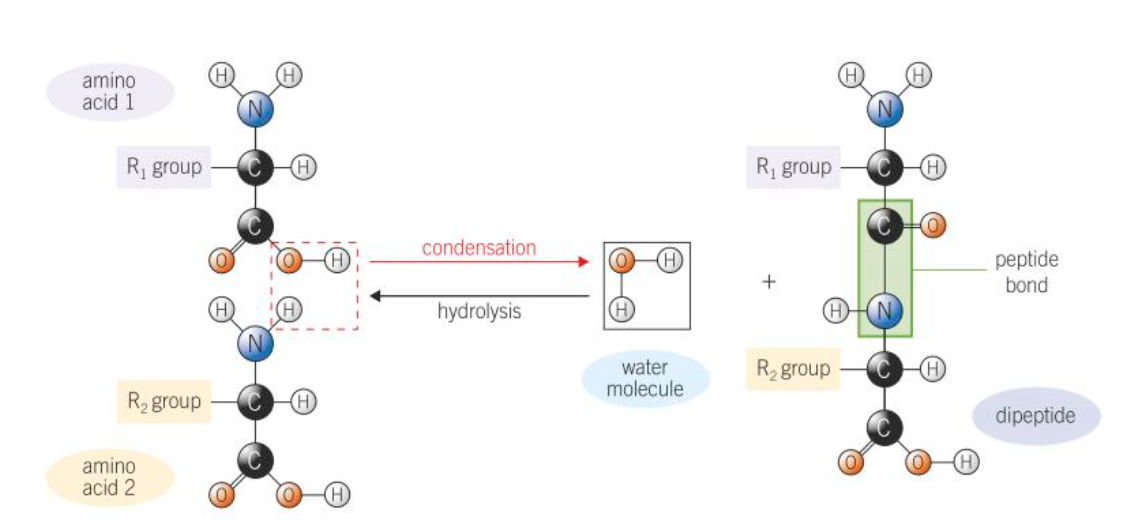
What bond is formed between the monomers of proteins?
Peptide bond
Where does the peptide bond form?
Between the hydroxyl from the OH from the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the H from the amino group of another one
How does a peptide bond form to make a dipeptide?
Condensation reaction
What are the four structures of proteins?
Primary
Secondary
Tertiary
Quaternary
What is the primary structure of a protein?
The specific sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain
What bonds are present in the primary structure?
Only peptide
What does the primary structure determine?
The shape and function of the protein
What is the primary structure determined by?
The sequence of DNA bases
What is the secondary structure of proteins?
The basic level of folding in a protein
What bonds are within the secondary structure?
Hydrogen bonds
Peptide bonds
Where did the hydrogen bonds form in the secondary structure?
Between the carboxyl groups and the amino groups in the polypeptide backbone
What are the two types of secondary structure?
alpha-helix
beta-pleated sheet
What is the tertiary structure of proteins?
The further folding of the alpha-helix into a complex, 3D structure
When is a polypeptide classified as a protein?
In the tertiary structure
What bonds are within the tertiary structure?
Peptide bonds'
Hydrogen bonds
Ionic bonds
Disulfide bonds
Hydrophobic interactions
What do the positions of the bonds depend on?
The primary structure
What are stronger, Ionic bonds or disulfide bonds?
Disulfide bonds
What is the quaternary structure of a protein?
More than one polypeptide chain with a prosthetic group
What is a prosthetic group?
Non-protein groups associated with the molecule
What are the two types of protein?
Fibrous
Globular
What are fibrous proteins?
Structural proteins
What are globular proteins?
Functional proteins
What are the four functions of proteins?
Enzymes
Antibodies
Transport Proteins
Structural Proteins
What is the test for proteins called?
The Biuret Test
What is the method for the test for proteins?
Place a sample in a test tube and add NaOH
Add a few drops of biuret solution and mix gently
What is the positive result for the test for proteins?
A colour change from blue to lilac
What shape are globular proteins?
Roughly circular
What shape are fibrous proteins?
Long strands
What is the amino acid sequence of globular proteins like?
Irregular, with a wide range of R-groups
What is the amino acid sequence of fibrous proteins like?
Repetitive, with a limited range of R-groups
What is the functionality of globular proteins?
Physiological/functional
What is the functionality of fibrous proteins?
Structural
What are some examples of globular proteins?
Haemoglobin
Enzymes
Insulin
Immunoglobin
What are some examples of fibrous proteins?
Collagen
Keratin
Actin
Myosin
Are globular proteins soluble?
Yes, generally
Are fibrous proteins soluble in water?
Generally no
How many polypeptide chains are in collagen?
3 (triple helix)
What is the shape of collagen?
Long and thin
What type of protein is collagen?
Fibrous
What is the main function of collagen?
Structural (connective tissue)
Does collagen contain a prosthetic group?
No
What is haemoglobin made up of?
4 polypeptide chains, 2 alpha-globin and 2 beta-globin
What shape is haemoglobin?
Spherical
What is the function of haemoglobin?
Functional (transport of oxygen)
Does haemoglobin contain a prosthetic group?
Yes, a haem group