Glycolysis Exam #2
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
Glycolysis
purpose?
body location?
cell location?
energy production?
purpose: use glucose for energy
biosynthesis/intermediates for different pathways in the body
catabolic reaction (generates energy)
body location: all tissues
cell location: cytosol
energy production: net 2 ATP + 2 NADH
Glycolysis deficiencies
hemolytic anemia
decreased RBC lifespan
disrupted shape
decreased or no oxygen delivery
side effects: fatigue/shortness of breath
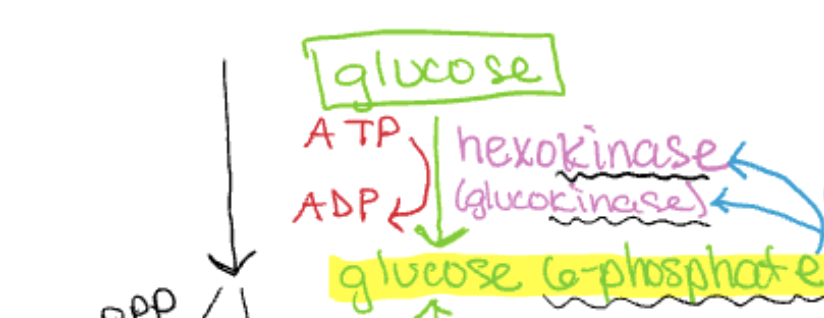
Glycolysis pathway (first step)
glucose → glucose 6 phosphate
this occurs by the phosphorylation of glucose (catalyzed by enzyme hexokinase)
uses one molecule of ATP (turned into ADP) and is irreversible
Glycolysis pathway (second step)
glucose 6 phosphate (G6P) → fructose 6 phosphate (FSP)

Glycolysis pathway (third step)
fructose 6 phosphate → fructose 1,6 phosphate
uses ATP (ATP→ADP), caused by enzyme PFK-1
rate limiting step (irreversible)

What is PFK-1 activated/inhibited by? (3rd step of glycolysis)
activated: AMP (low energy), F2,6BP, insulin (well fed state), glucagon (starve state)
inhibited: citrate, ATP (high energy)
Glycolysis (step 4)
fructose 1,6 phosphate → phosoenolpyruvate (PEP) x2

Glycolysis (step 5/final step)
phosoenolpyruvate (PEP) x2 → pyruvate x2
uses enzyme pyruvate kinase (PK)
irreversible step
2 ADP→2 ATP

What is PK activated/inhibited by? (5th/final step of glycolysis)
activated (phosporylated): PP1, insulin (beta)
inhibited (dephosphorylated): PKA, glucagon (alpha)
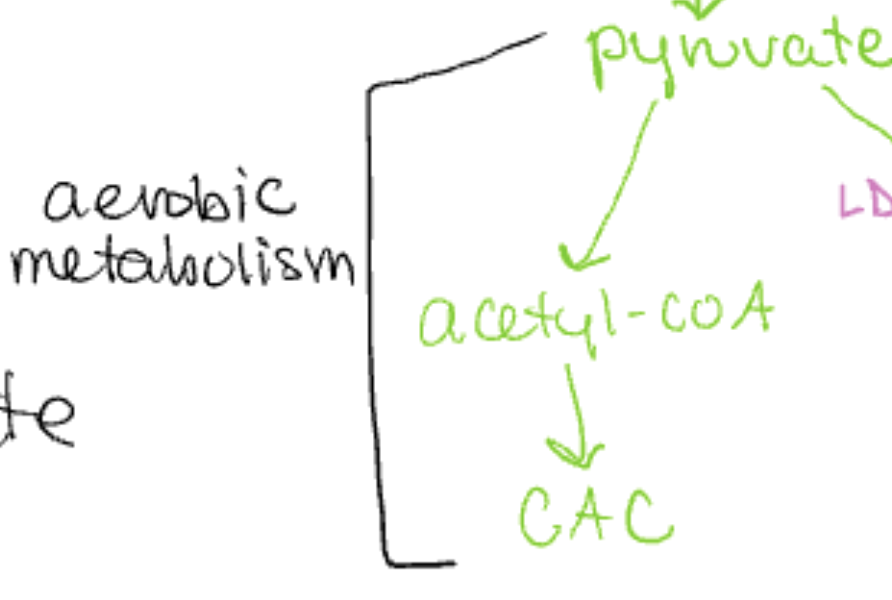
Aerobic metabolism
pyruvate → acetyl CoA → CAC
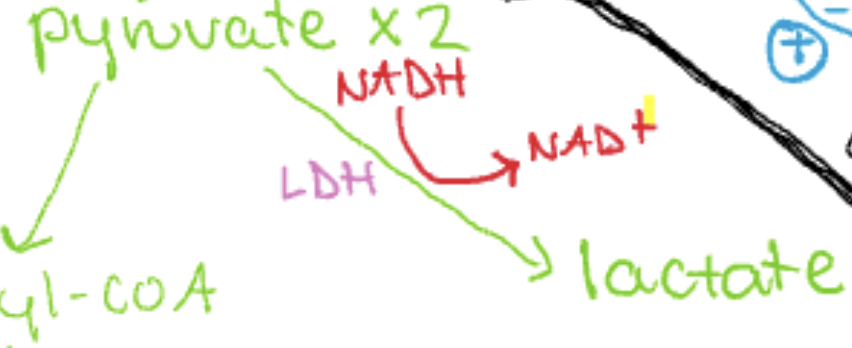
Anaerobic metabolism
process?
cells?
Warburg effect?
process: pyruvate → lactate
enzyme LDH is used
NADH → NAD+
cells: eye, RBC, skeletal muscle in extreme exercise
Warburg effect: occurs in cancer cells
pyruvate → lactate even with O2 present
increased production of growth intermediates
increased lactate production → increased acids → acidic environment around tumors
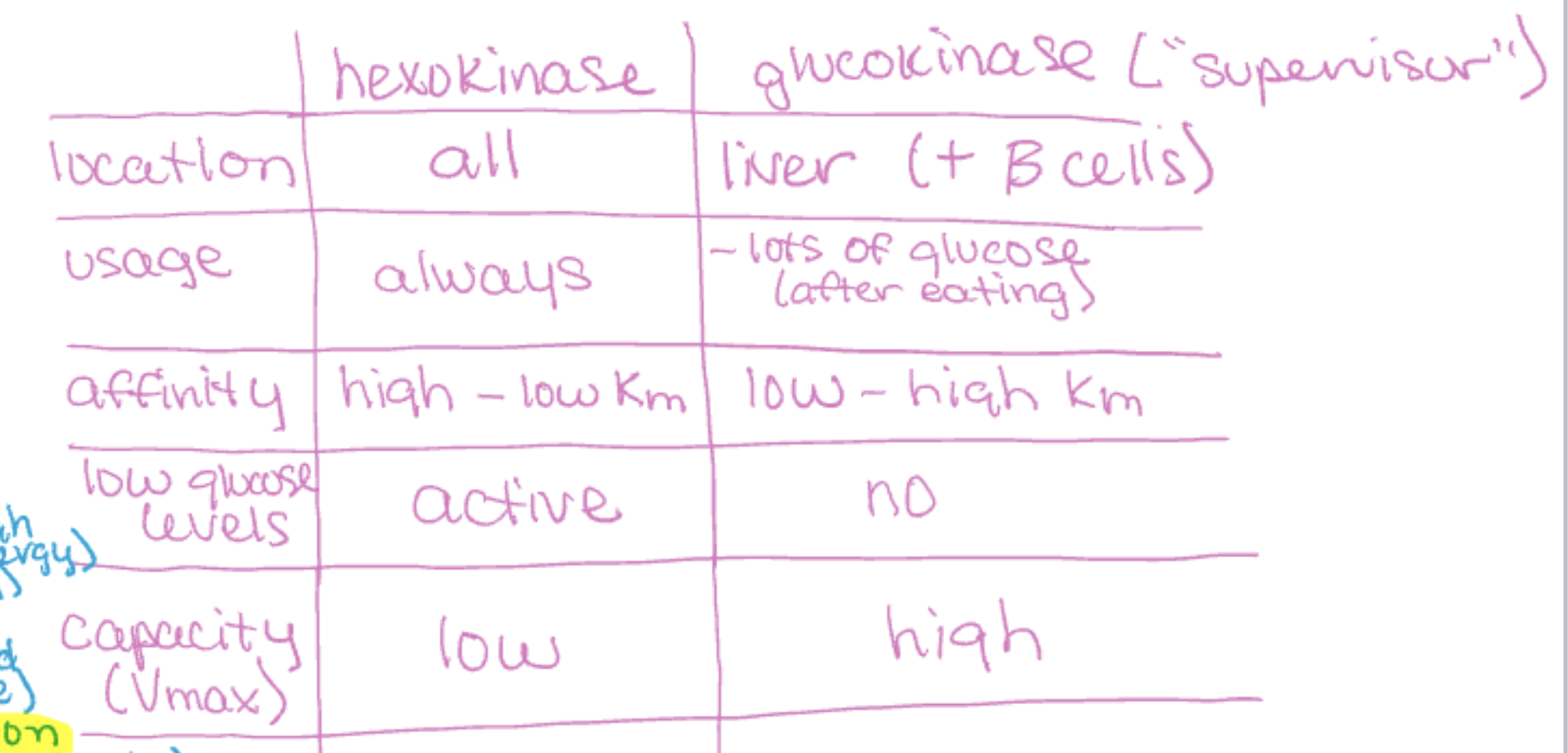
hexokinase vs glucokinase (involved in 1st step of glycolysis)