A patient presenting with bullous lesions in general dental practice
How do you describe a clinical lesion? (7)
1. site
2.size
3. margins
4. surface
5. type (white/ red/ mixed/ pigmented/ lump/ ulcer
6. surrounding tissues
7. palpate- firm/ soft
What should be included in a secondary care referral? (4)
1. clinical lesion description
2. relevant MH and social history
3. test results and previous investigations
4. urgency of referral
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
How do you describe a clinical lesion? (7)
1. site
2.size
3. margins
4. surface
5. type (white/ red/ mixed/ pigmented/ lump/ ulcer
6. surrounding tissues
7. palpate- firm/ soft
What should be included in a secondary care referral? (4)
1. clinical lesion description
2. relevant MH and social history
3. test results and previous investigations
4. urgency of referral
What needs to be discussed with the patient in terms of the referral? (3)
1. need their consent
2. should outline the referral process and expected timeline
3. should outline who and what specialists will now be looking after them
What are the 2 forms of pemphigoid?
1. Bullous pemphigoid- tends to be present on the skin and last 5 years
2. Mucous membrane pemphigoid- MMP-tends to be present in the mouth
What causes MMP?
It is an autoimmune condition with antibodies directed against antigens in the epithelial basement membrane resulting in a split and blister formation at this level.
How does mucous membrane pemphigoid present? (6)
1. mucosal inflammation
2. mucosal erosion and ulceration
3. blister formation
4. desquamative gingivitis
5. scaring
6. can also occur on the eye and genitals but not always
How can we diagnose mucous membrane pemphigoid? (2)
1. clinically - can see a blister forming
2. Histological findings- direct immunofluorescence (either direct or indirect) (highlights the antibodies bound to the antigens in basement membrane.
What are the 5 possible areas that can be affected by Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid and what are the possible consequences in these regions?
1. skin involvement - blistering and ulceration
2. genital involvement: scaring/deformities and ulceration
3. pharyngeal involvement: blistering and ulceration and scaring which can lead to dysphagia
4. oral involvement: blistering, ulceration and perio (due to painful to clean)
5. eye:
can have tethering of conjunctiva to sclera
What topical treatment can you give for mucous membrane pemphigoid? (2)
1. topical steroids- eg: clobetasol
2. topical immunosuppressants
What systemic treatment can you give for mucous membrane pemphigoid? (2)
1. prednisolone (corticosteroid)
2. mycophenolate mofetil/azithoprine - non glucocorticoid immunosuppression
What is pemphigus Vulgaris?
An autoimmune disease, in which there is an antibody mediated disease directed against desmoglein 1+3 which holds epithelial cells together.
How does pemphigus vulgaris present?
It presents initially with oral lesions/ followed by skin involvement later.
- more widespread than MMP- affects the skin more than MMP
- it is also has more surface level blisters which are more likely to rupture and cause erosions whereas MMP blisters are deeper and are less likely to rupture
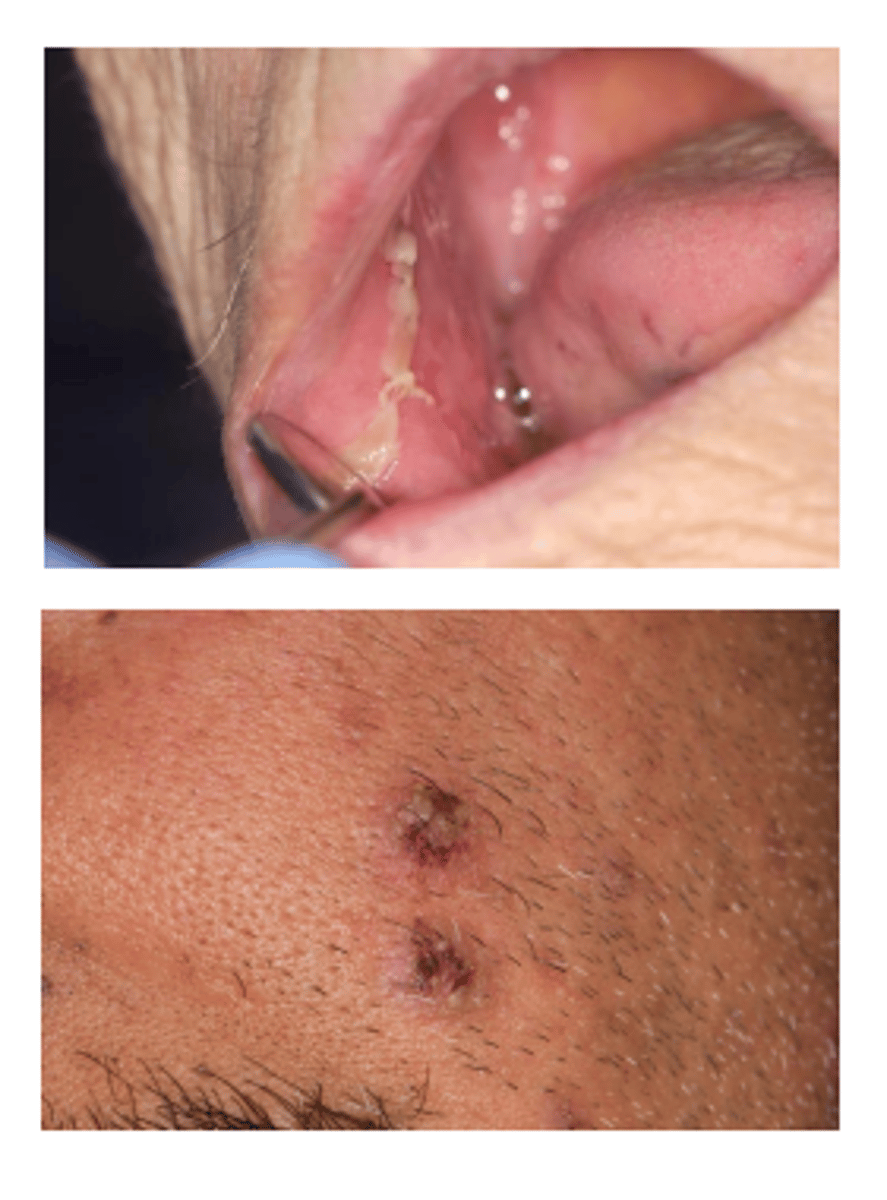
How does pemphigus vulgaris present intra orally? (3)
1. mucosal erosion and ulceration
2. blisters- tend to burst on presentation
3. desquamative gingivitis
What are the 3 extra oral signs of Pemphigus vulgaris?
1. skin lesions
2. genital lesions
3. pharyngeal lesions
How is Pemphigus Vulgaris diagnosed? (3 steps)
1. first need a thorough history and exam of extra and intra oral
2. then need to make a list of differential diagnosis
3. then special investigations to rule out other diagnosis
What 3 special investigations may be used for Pemphigus vulgaris?
Following a biopsy need to conduct:
1. histopathological examination see what cells are present and their structure
2. direct IF - where you can view antibodies in the sample attacking the desmoglein. this is using the patients own tissue sample from a biopsy and binding to the auto antibodies present
3. indirect IF - where blood samples are taken, serum is extracted and then incubate with a substrate that mimics the patients tissues and you see if the antibodies present in the serum bind to the substrate
What type of drugs may induce pemphigus oral ulcerations?
Drugs which contain a sulphydrl group- tell them to use SLS free toothpaste
What is paraneoplastic pemphigus?
This is pemphigus related oral ulcerations in association with malignancy- it may be known or unknown.
How can we treat pemphigus vulgaris? (3)
1. acute control of symptoms - systemic and topic steroids eg prednisolone
2. maintenance of immune response e- topical and systemic steroids + non sterioidal immunosuppressants eg azithoprine and mycophenolate mofetil
3. REFER
What 4 tissues can be affected by Pemphigus vulgaris and what complications can occur in these tissues as a result?
1. skin- blistering, ulceration, fluid loss
2. genital involvement - blistering and ulceration
3. pharyngeal involvement - blistering, ulceration and scaring can lead to dysphagia
4. oral involvement - blistering, ulceration, loss of perio tissues (cannot clean
What are 5 differential diagnosis to Pemphigus Vulgaris and Mucous Membrane Pemphigus for bullous lesions?
1. dermatitis herpetifromis - linked to coeliac disease
2. linear IG A disease - common in children
3. epidermolysis bullosa acquisita - v rare
4. erythema multiforme
5. viral infections