HESI- A2 A&P
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
Transverse plane
top and bottom
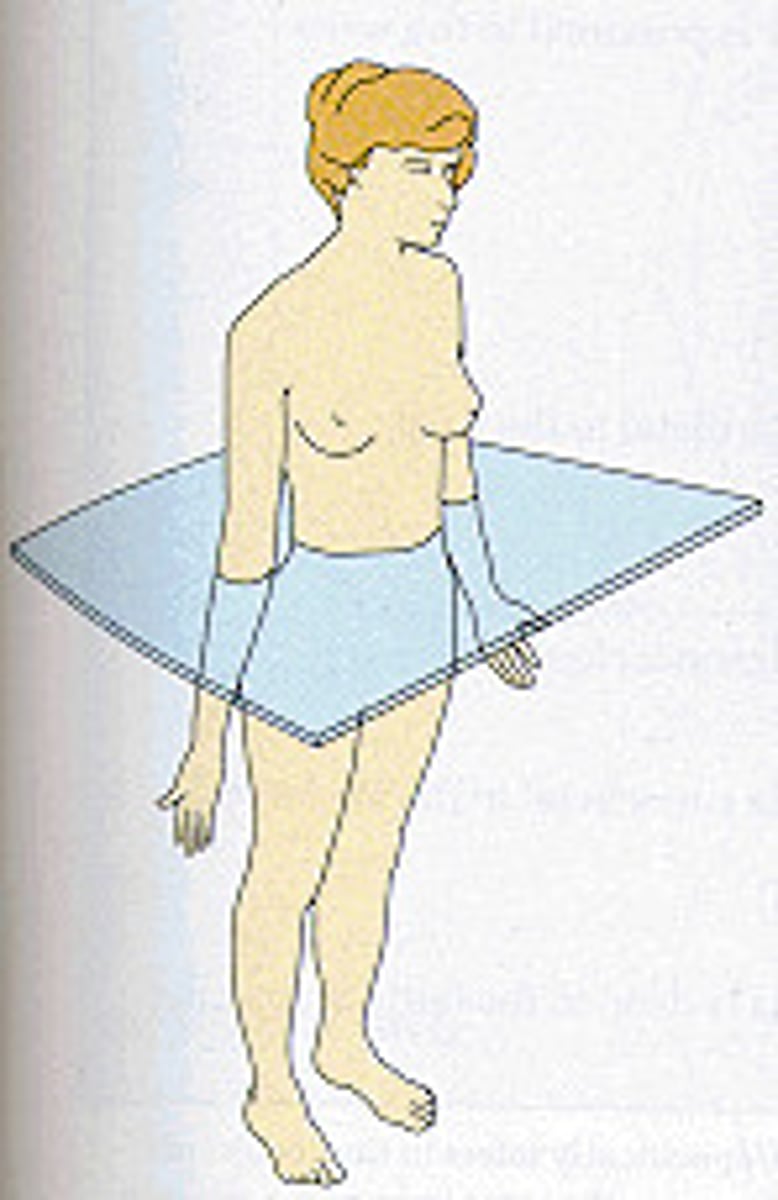
Median plane
Into right and left side
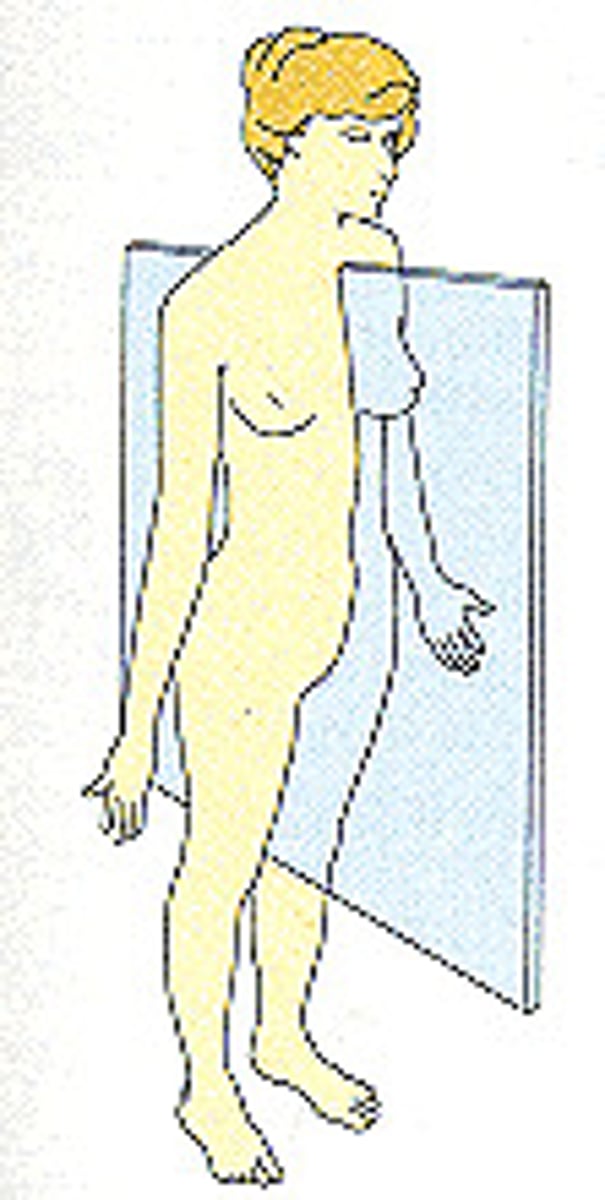
Sagital Plane
left and right of trunk
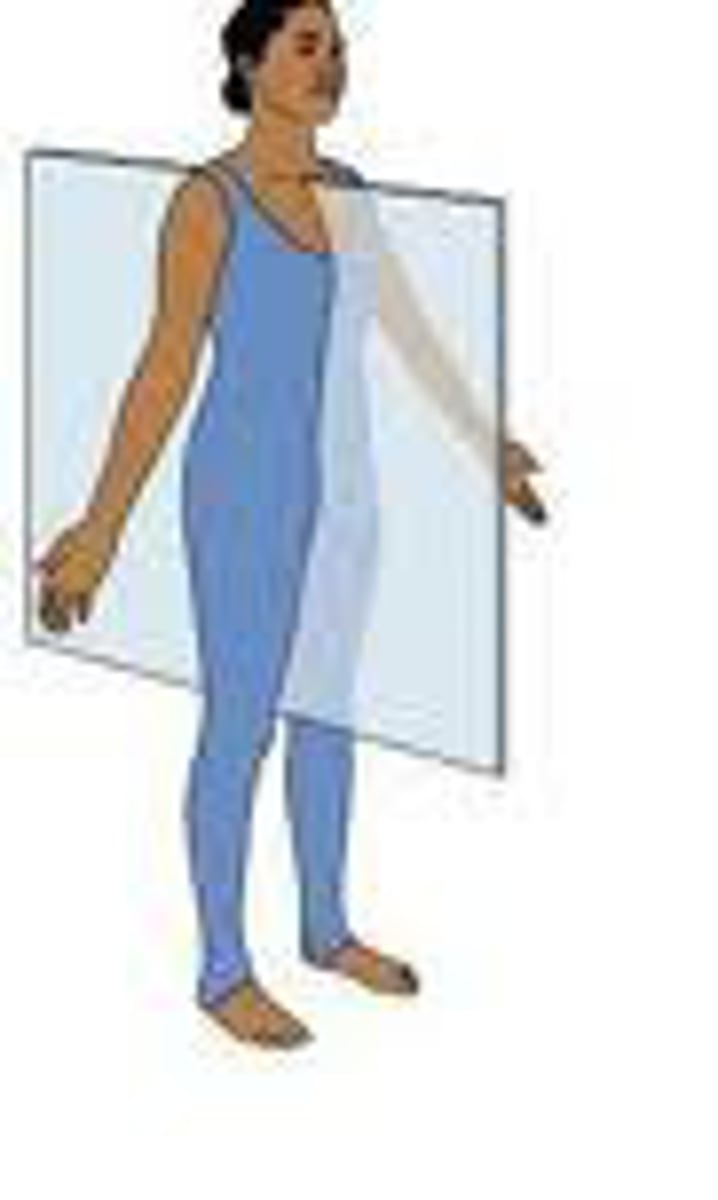
coronal plane
front and back only pertaining to torso area
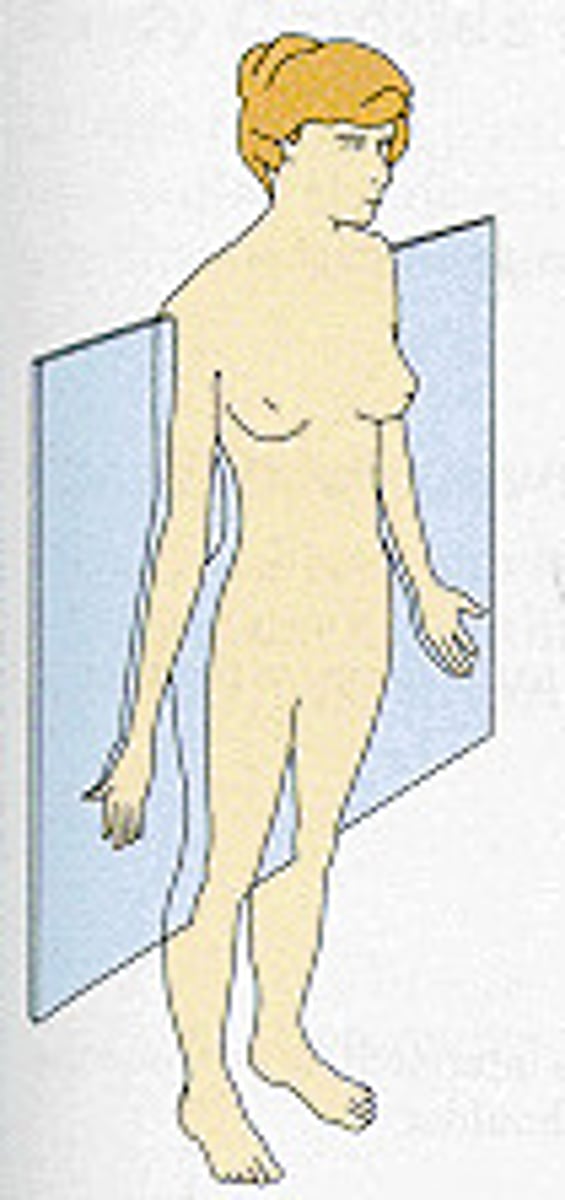
frontal plane
front and back
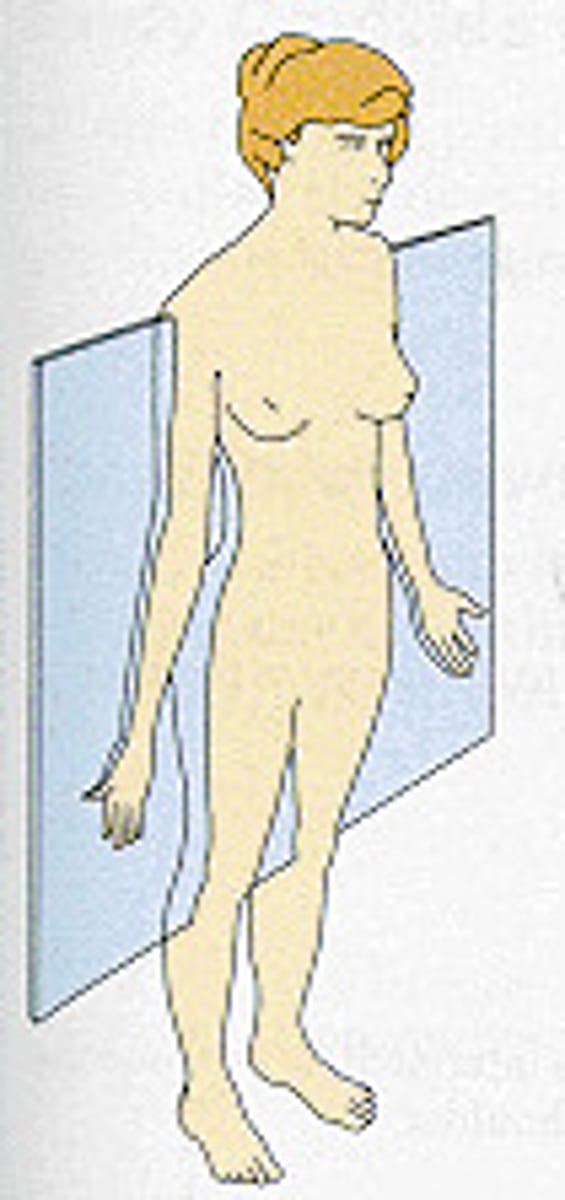
anatomic position
superior
above
inferior
below
posterior
back, toward the back, behind
medial
toward the midline
lateral
away from the midline or toward the sides
proximal
closer to a point of attachment
distal
further away from the point of attachment.
dorsal cavity
cranial and spinal cavities
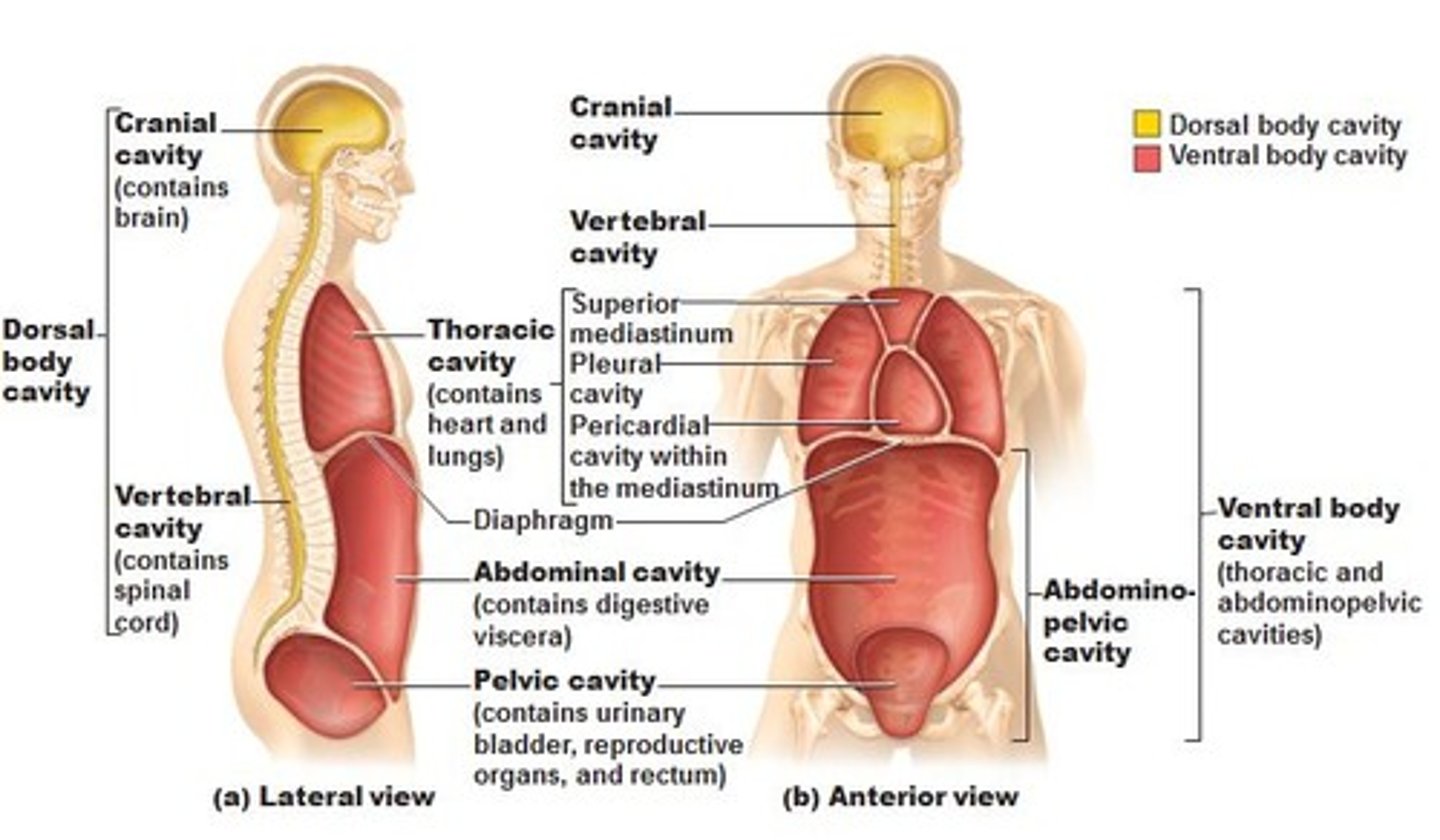
ventral cavity
orbits, nasal, oral, thoracic, and abdominopelvic cavities
histology
the study of tissues
4 types of tissues
epithelial, cognitive, muscle,and nerve
epithelial tissue
cover, line and protect the body and internal organs
connective tissue
provides the framework support and structure.
nerve tissue
nerves and connective tissue cells called neurolgia
muscle tissue
voluntary(skeletal) and involuntary(smooth and cardiac)muscle
Skin
largest organ of the body. two layers epidermis: outermost protective layer. Dermis: layer of connective tissue with blood vessels, nerve endings, and other skin structures.
Skeletal system
bone, cartilage, ligaments and joints. support movement, blood cell formation.
axial skeleton
consists of skull, vertebral column, 12 pairs of ribs, sternum.
appendicular skeleton
girdles and limbs
muscular system
produce movement. muscle contraction results from the sliding together of actin and myosin filaments
what must be present in the cell for a muscle to contact
calcium and ATP
voluntary muscles
aka: skeletal muscles. muscles that are under copious control.
the functional unit of the nervous system
nerve cells
main parts of a neuron
Body, axon and dendrites
what do dendrites do?
transmit the impulse toward the cell body
what do axons do?
transmit the impulse away from the cell body.
what is the CNS comprised of?
spinal cord and brain
what is the PNS comprised of?
all other neurons in the body
sensory of afferent neurons
transmit nerve impulses toward the CNS
motor or efferent neurons
neurons transmit nerve impulses away from the CNS toward the the effector organs
major parts of the brain
cerebrum(associated with movement and sensory input), cerebellum(responsible for muscular coordination) and the medulla oblongata(controls vital functions)
what does the endocrine system do?
helps the nervous system in homeostasis. Play an important role in growth and sexual maturation.
What does the Hypothalamus govern?
the pituitary gland. Which in turn is controlled by feedback hormones in the blood. Nicknamed the "Master gland"
where are hormones during stress released and what do they do to the body?
From the adrenal cortex, hypothalamus, posterior and anterior pituitary gland. Cortisol; reduces inflammation, raises blood sugar, and inhibits release of histamine.
What does blood consist of ?
55% plasma and 45% formed elements
RBC's
transport 02 via hemoglobin
WBC's- leukocytes
are responsible for defense from diease and have 5 different kinds that look different.
Platlets
are needed for blood clotting.Also has 10% proteins, ions,nutrients, waste products, and hormones.
external respiration
refers to the exchange of gases between the atmosphere and the blood through the alveoli.
internal respiration
refers to the exchange of gases between the blood and the body cells.
Chyme
a bolus of food that has mixed and churned into a soupy substance.
Which plane would separate the abdominal cavity from the thoracic cavity?
Transverse
What tissue is Pillar-shaped cells arranged tightly together?
Columnar epithelium
The Epidermis is classified as a
Tissue
What type of tissue provides support and structure for the organs?
Connective
Within which epidermal layer of the skin does mitosis occur?
Stratum germinative
The cells that form compact bone are?
Osteoblasts
What is true about skeletal muscle?
Skeletal muscle attaches to bone by tendons, Muscle contraction helps keep the body warm, skeletal muscle continuously contract to maintain posture.
what is needed for muscle to contract?
Calcium and ATP
what does the parathyroid hormone regulate?
Calcium
Bile is recreated where?
Small intestine
What is the role of progesterone in the female reproductive system?
Stimulates the development of the endometrium.
What are the glands of the skin that produce thin watery recreation?
eccrine gland
Tissue that that has open spaces partially filed by an assemblage of needle like structures?
Spongy Bone
Mineral responsible for regulating fluid in the body
Sodium
All of the actions of the nervous system depend on the transmission of nerve impulses over what?
Neurons
Monocytes
become macrophages
Neutrophils
phagocytize Microorganisms
Nephrons
are the functional unit of the kidneys
What separates the thoracic cavity from the abd
the diaphragm
what are chemical messengers that control growth, diffrentiatation and metabolism of specific target cells
Hormones
Most of the C02 in the blood does what?
Is converted into bicarbonate ions by canonic anhydrase in the plasma.
What valve is responsible for preventing back flow from the right ventricle to the right atrium
Tricuspid
which type of cellular connection is characterized by openings in adjacent animal cells for inter cellular exchange to take place
gap junctions
what is the main function of calcitonin?
decreasing calcium concentration in the blood.
Which muscle is responsible for the adduction of the shoulder?
Latissimus dorsi
What type of joint is the elbow
hinge
the lobe of the brain responsible for producing olfactory information
temporal
section of the spine that has 5 vertebrae?
Lumbar