🌱Plants BIO153
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
How did leaves allow plants to live on land?
they provide a surface area to acquire sunlight and CO2 from above the ground
How did roots allow plants to live on land?
they anchor plants to the ground and absorb water and nutrients from the soil
What does the vascular system do?
transports water and minerals throughout plant body
What are the primary tissues of the vascular system?
xylem and phloem
What is the benefit of being tall and elevated for plants?
taller plants have better exposure to light and more reproductive success
Xylem
transports water and minerals from roots to leaves
Phloem
transports sugars from storage/production sites to other parts of the plant body
Cuticle
waxy polymer covering plant body for protection against desiccation
Stomata
pores on outer layer of leaves and stems allowing for O2 and CO2 exchange, closes in dry conditions to preserve water
What did mosses develop to survive on land?
anti-desiccation mechanisms
What did ferns develop to survive on land?
vascular system and tissue specialization
What did gymnosperms develop to survive on land?
pollen, ovule, and seed
What did angiosperms develop to survive on land?
flowers and fruit
What is the dominant life cycle in mosses?
gametophyte
What is the dominant life cycle in ferns?
sporophyte
What is the dominant life cycle in gymnosperms?
sporophyte
What is the dominant life cycle in angiosperms?
sporophyte
Sporophyll
specialized leaves of vascular plants which have been modified to produce spores
Sporangium
structures located on the sporophyll that produce and contain spores
How are moss attached to the ground?
by rhizoids, which do not transport water unlike real roots
What is distinctive about gymnosperms?
they form pollen and seeds but not flowers
What does “micro” refer to?
male reproductive structure
What does “mega” refer to?
female reproductive structure
What do microspores grow into?
microspores grow into the male gametophyte and produce sperm (pollen)
What do megaspores grow into?
megaspores grow into female gametophyte and produce eggs
How many sets of chromosomes does a sporangium have?
It is a diploid cell with two sets of chromosomes (2n)
How many sets of chromosomes do the spores produced by sporangium have?
They are haploid cells with one set of chromosomes (n)
What does sporangium do?
it produces spores via meiosis
What is the ovule made up of?
integument + megasporangium + megaspore
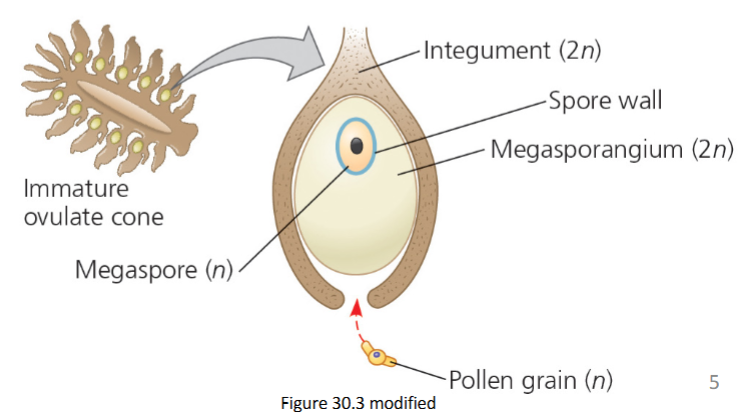
What does the ovule develop into?
the ovule develops into a seed after pollination
What does the integument do?
it becomes the seed coat after fertilization
How does pollination lead to fertilization?
The pollen grain attaches to the ovule through pollination and the pollen tube delivers sperm to egg, fertilizing it and forming a zygote. The zygote forms into an embryo which will later form a sporophyte.
What is the difference between the ovule in gymnosperms and in angiosperms?
In gymnosperms, the ovule is exposed to the environment. In angiosperms, the ovule is encased inside the ovary.
What happens to the ovule in angiosperms upon pollination?
The ovule develops into a seed and the ovary develops into a fruit.
Septal
base of the flower, encloses the flower before it opens
Petal
brightly colored and attracts pollinators
Stamen
male reproductive organ of flowers
Anther
part of the stamen, contains microsporangia to produce pollens
Filament
part of the stamen, supportive structure of the anther
Carpal
female reproductive organ made up of the stigma, style and ovary
Stigma
sticky tip of the carpal that captures pollens
Style
connects stigma to ovary
Ovary
the base of the carpal that contains the ovules
What occurs to the ovule and ovary after pollination?
The ovule develops into a seed and the ovary develops into a fruit.
Where does the pollen land during pollination in angiosperms?
on the stigma of the carpel
How is pollen produced?
The microsporangium in the anther produces microspores which develop into male gametophytes that eventually get packaged in pollen alongside sperm.
What is the pollen tube and how is it formed?
The pollen tube delivers sperm to the ovule and begins to grow after pollen is delivered to the stigma.
Simple fruit
derived from a single carpel or several fused carpals (eg. peas)
Aggregate fruit
derived from a single flower with a group of carpels forming a cluster (eg. raspberries)
Multiple fruit
derived from a group of flowers clustered together, each segment developing from the carpal of one flower (eg. pineapple)
Accessory fruit
contains tissue from plant parts other than the ovary (eg. apples)
What is the first step of pollination?
The pollen grain attaches to the ovule and the pollen tube delivers sperm to egg, fertilizing it and forming a zygote
What happens after the zygote is formed in pollination?
the zygote grows into the embryo which will later form a sporophyte
What is the symbiotic relationship between Rhizobium and plants?
Nodules develop in plant roots for Rhizobium to live inside, which provides anaerobic environment for bacteria to fix nitrogen.
What are some similarities between plants and algae?
-Photoautotrophic
-Alternation of generation
-Plastid DNA
-Cellulose cell walls
PGDC (photosynthesis, generation, DNA, cellulose)
What does moss have to protect against desiccation?
sporopollenin covering the spores
What do moss spores grow into?
protonema
What does the protonema do?
it produces buds which grow into full male or female gametophytes
Why is the moss life cycle dependent on water?
moss lack vascular tissue and thus all parts of a moss gametophyte need to directly absorb water from the environment
What do fern spores grow into?
a hermaphrodite gametophyte that produces both sperm and eggs
What supports the zygote while it develops into a sporophyte?
the gametophyte
What is contained within the seed?
the sporophyte embryo
Cones
scaly sporophylls produced by gymnosperms
What is distinctive about the gymnosperm life cycle?
They can reproduce without water since their pollen is dispersed by the wind
Sporocyte
a cell produced inside the sporangium which undergoes meiosis to produce haploid spores