G202 Exam 1 Content
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Topics 1-4 from Spotlight Slides
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Both Pe and Qe are _______ of government action
independent
Rule 1 for Social Efficiency: Produce and sell product that has consumer value ______ production costs
greater than or equal to
Rule 2 for Social Efficiency: Avoid producing and selling product that has consumer value _______ production costs
less than
Net benefit given up by society when
below Qe
Net cost incurred by society when
above Qe
Taxes on sellers cause an _______ shift of the supply curve by _______ production costs
inward; increasing
What determines how much of the tax and subsidy can be passed to the consumer
elasticity
Taxes will increase efficiency in an ________ market
overproducing
For taxes: ________ price to buyers → ________ consumer surplus
increased; decreased
For taxes: _____ seller price→_____ producer surplus
decreased; decreased
Subsidies given to sellers cause an _______ shift of the supply curve by _______ production costs
outward; decreasing
Because the buyer’s price _________ from a subsidy, ______ will be consumed, so the market ________.
decreased; more; expands
Subsidies are efficient in what kind of market
underproducing
For a subsidy: ______ prices to buyers → consumer surplus ________
decreased; increases
For a subsidy: ______seller price → producer surplus ______
increased; increased
productive regulations imposed on sellers cause an _______ shift of the supply curve by forcing the seller to ______
inward; incur compliance costs
For a productive regulation: because the buyer’s price _______, ______ will be consumed, so the market _______
increased; less; shrinks
Taxes and Productive Regulations act the same, so what is the only difference between the two?
Who keeps the revenue. For PR - the rev is kept somewhere in the supply chain
Lobbying (Rent Seeking)
devoting resources to influence public policy formation in order to bring more income/support to your group
Special interest effect
small group of people, with the incentive to take political action, receive benefits at the expense of a large unorganized group of people
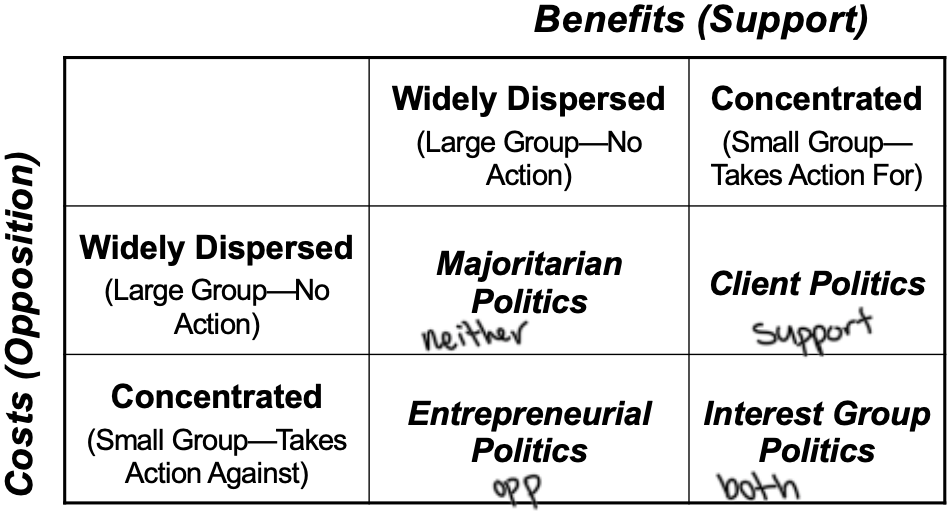
Majoritarian Politics
Widely dispersed costs and benefits
Ex: Social Security
Lobbying does not occur
Client Politics
concentrated benefits and widely dispersed costs
Ex: USDA Foreign Advertising Funds (MAP)
Lobbying will likely be successdul
Interest Group Politics
Concentrated benefits and costs
Ex: Legalizing Marijuana (NORML [pro] vs CALM [anti]) and UBER!
Lobbying success depends on relative strength of either side
Entrepreneurial politics
Concentrated costs and widely dispersed benefits
ex: nuclear waste dumps
Successful lobbying will be costly: You have to convince a large group to give up their benefits
Logrolling
politicians trading support on regional projects that they each care about
risky
Pork Barrel Legislation
politicians bundling different regional politics together into a package to vote on collectively
less risk
Consumption Rule (QD) for imports: Domestic consumers should consume as long as value DUS is ____________ production cost (PW)
greater than or equal to
Production Rule (QS) for imports: Domestic producers should produce as long as their production costs (SUS) are _________ the world’s cost (PW)
less than or equal to
Foreign Gains Formula:
(quota price - original price - licensing fee)*quota = foreign gains
Tariff
Tax on imports
Quota
Physical limitation on imports
True or False: Quota Price is impacted by the licensing fee
FALSE. Licensing fee only change foreign gains and gov revenue
The _____ that imports are restricted, the _______ that under consumption and over production will become.
more; bigger
When is a tariff more inefficient than a quota
If the tariff has more restrictions and the quota has no foreign gains
Communal Property
No single owner, everyone has access while it lasts
Over-utilization occurs (tragedy of the commons)
Government Property
property decisions made by a small group of elected political representatives (lots of power in hands of few)
Private Property gives owners incentive to:
create ______ value with property and benefit others
maintain property and conserve _____ for the future
innovate ____ and create new technologies
engage in _____ voluntary exchange
all more
Private property rights incentivizes
benefitting others w property
conservation for the future
innovation
voluntary exchange
Patent
Right to exclude all other from using, producing, or selling an invention (everyone benefits from patents)
Trademark
a work, name, symbol, or device that is used in trade with goods to indicate their source
Copyright
Right to exclude all others from reproducing, distributing, or performing a work
The sharing economy
an economic system in which assets or services are shared between private individuals, either for free or for a fee, typically by means of internet
may increase crime rates bc the notion of IP ownership is unclear
Equation for Becker’s Crime Model
Expected Utility = (probability of success)*(current income + gain)+(probability of failure)*(current income-fine)
Expected Utility MUST be greater than current utility to commit the crime