TMOD (Vitreous)
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
Posterior Vitreous Detachment (PVD)
Liquefaction of vitreous gel (collagen clumping) that cause dehiscence of posterior hyaloid from retina
Risk factors: high myopia, old age
New PVD may be accompanied by retinal break or detachment
May complain of flashes, floaters, blur associated with eye movement
Usually temporal VF and sudden onset
Shafer’s sign is sometimes present
Weiss Ring is diagnostic
Posterior Vitreous Detachment (PVD) Treatment/Manageme
No tx if isolated
NdYAG for chronic bothersome floaters
If new, could be a precursor for a RD
FU in 1,3,6 months after onset
Educate on symptoms of RD
If no retinal breaks but a mild vitreous heme is present, FU in 1 week, 1,3,6 months
If no retinal breaks but significant vitreous heme is present, urgent referral to retinal specialist within 24 hours
Asteroid Hyalosis
Calcium-phosphate soaps within vitreous associated with aging >60
Presents as yellow-white “asteroids” in vitreous
Moves with eye movement but stays suspended (does not settle inferiorly)
Astroid Hyalosis Treatment/Management
No tx
Vitrectomy in severe cases
Synchysis Scintillians
Rare, usually occurs in a blind eye after chronic vitreous hemorrhage, trauma, or uveitis
Cholesterol crystal
Brownish-yellow refractile crystals
Settles inferiorly (“snow globe effect”)
Synchysis Scintillians Treatment/Management
Observation and possible vitrectomy
Manage high cholesterol
Vitreous Hemorrhage
Occurs when retinal neo grows into the vitreous
Painless vision loss, flashes, floaters
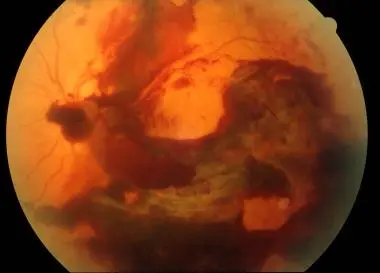
Vitreous Hemorrhage Treatment/Management
If retinal tear or break is present, tx it immediately
Observe bedrest for 2-3 days with head elevated
Avoid anticlotting agents (aspirin and NSAID)
If hemorrhage persist >3 months, tx with vitrectomy