Organic Chemistry 2: Need to Know
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms
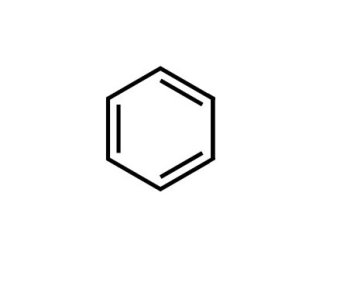
Benzene
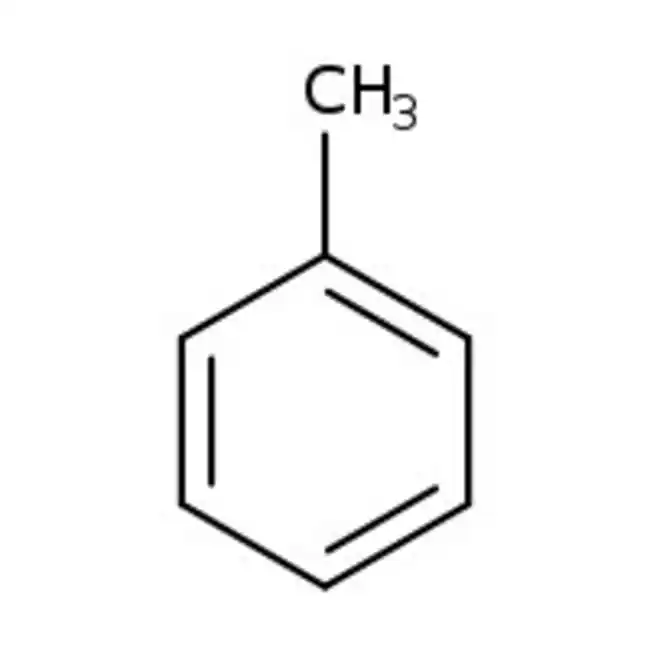
Toluene
benzene + CH3
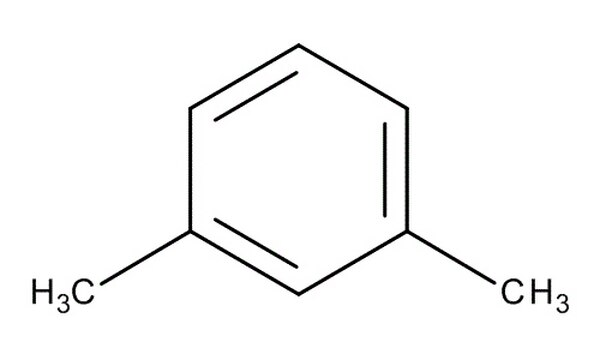
Xylene
benzene + 2CH3
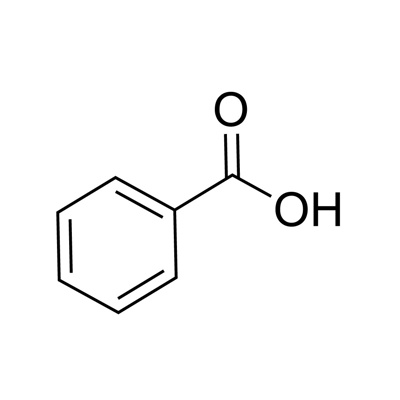
Benzoic acid
benzene + C=O OH
Acetylphenone
benzene + C=O CH3
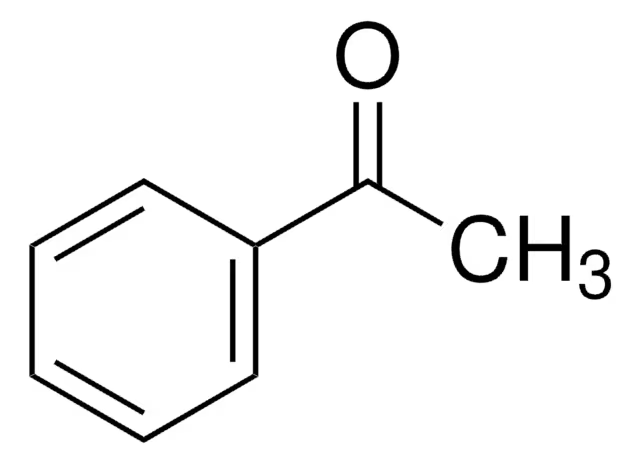
Anisole
benzene + O—CH3
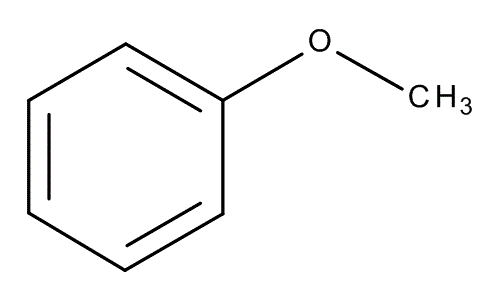
Aniline
benzene + NH2
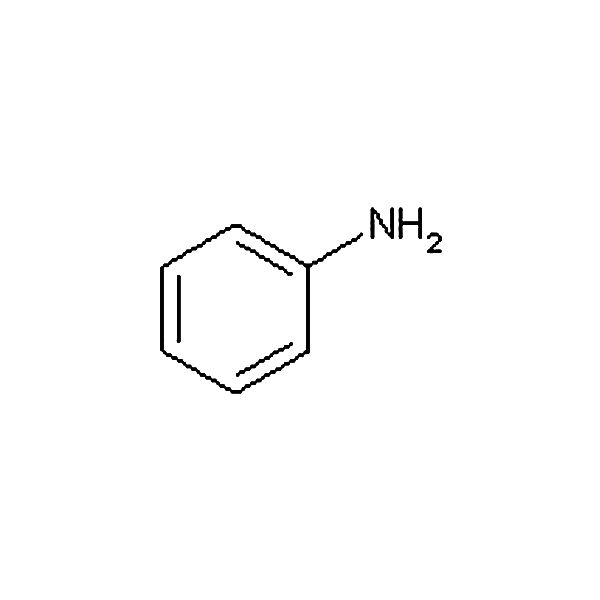
Anilide
benzene + C=O NH2
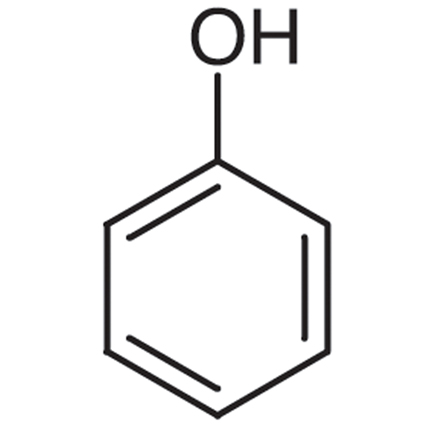
Phenol
benzene + OH
Markovnikov
The bigger compound goes on the more substituted carbon
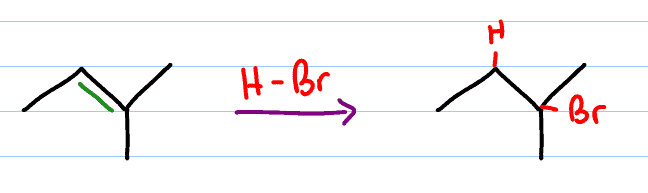
Hydrohalogenation reagents
HX (X: halogen)
Hydrohalogenation mechanism
markovnikov addition
Acid-Catalyzed Hydration reagents
H3O+ Or H2O/H2SO4
Acid-Catalyzed Hydration mechanism
markovnikov addition
sometimes a hydride shift will be necessary
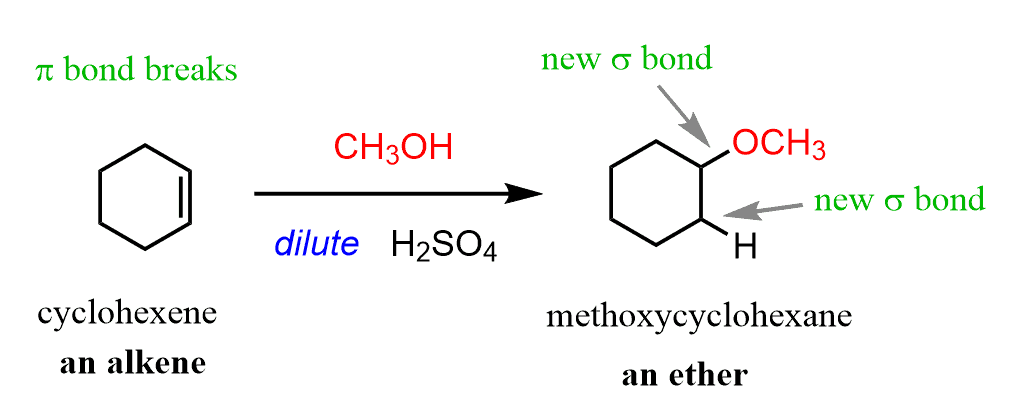
Acid-Catalyzed addition of an alcohol reagents
CH3OH/H+
Acid-Catalyzed addition of an alcohol mechanism
markovnikov
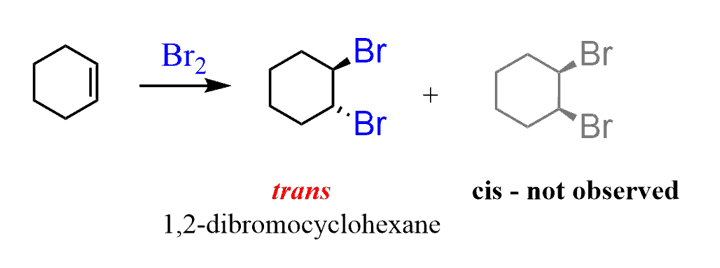
Halogenation reagents
X2/CCl4 (X: halogens)
Halogenation mechanism
anti addition (one wedged other dashed)
Halogenation in H2O reagents
X2/H2O (X: halogens)
Halogenation in H2O mechanism
markovnikov
anti addition
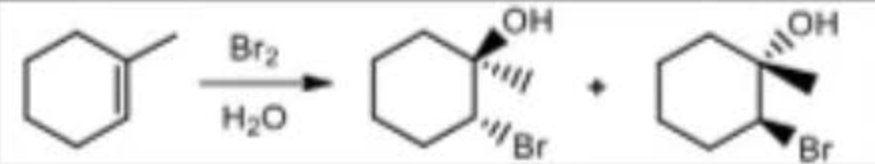
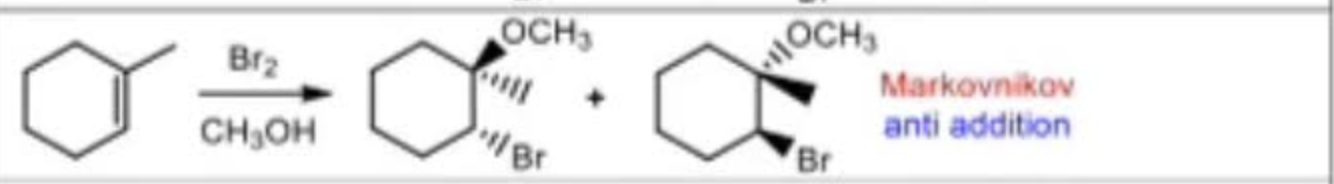
Halogenation in alcohol reagents
X2/CH3OH (X: halogens)
Halogenation in alcohol mechanism
markovnikov
anti addition
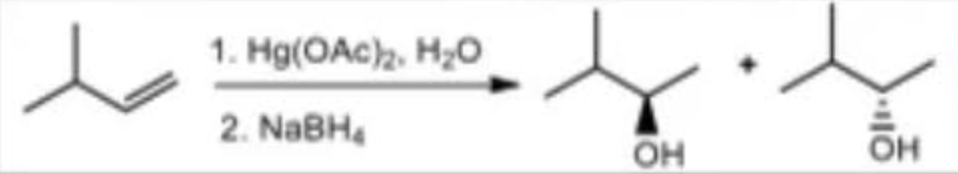
Oxymercuration-Demurcuration reagents
Hg(OAc)2, H2O / NaBH4
Oxymercuration-Demurcuration mechanism
markovnikov
anti addition
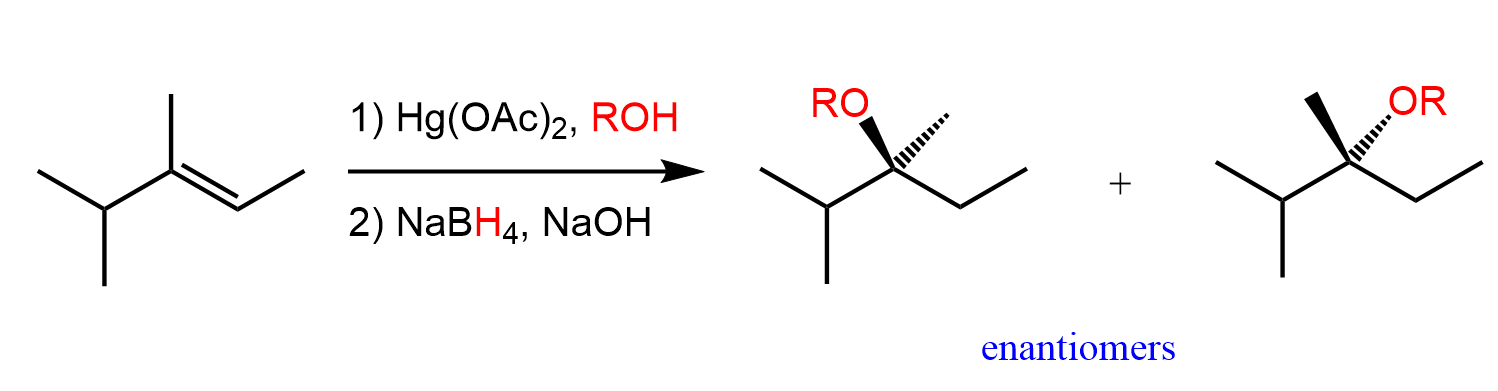
Alkoxymercuration-Demurcuration reagents
Hg(OAc)2, CH3OH / NaBH4
Alkoxymercuration-Demurcuration mechanism
markovnikov
anti addition
Hydroboration-Oxidation reagents
BH3 THF / H2O2 , NaOH
Hydroboration-Oxidation mechanism
anti-markovnikov
syn addition
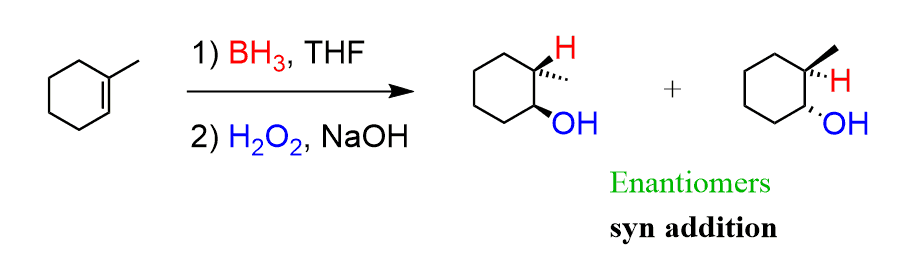
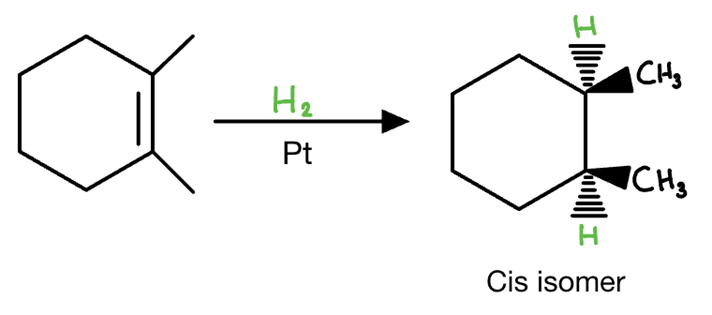
Catalytic Hydrogenation reagents
H2 / Pd/c
Catalytic Hydrogenation mechanism
syn addition
meso
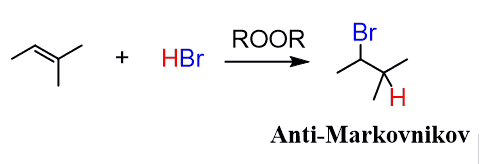
Hydrobromination with peroxide reagents
HBr / ROOR
Hydrobromination with peroxide mechanisms
anti-Markovnikov
Epoxidation reagents
RCO3H or MCPBA
Epoxidation mechanism
syn addition

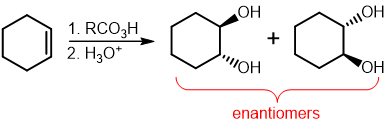
Anti-Hydroxylation reagents
RCO3H / H3O+
Anti-Hydroxylation mechanism
anti addition
Syn-Hydroxylation (1) reagents
OsO4 / H2O2
Syn-Hydroxylation (1) mechanism
syn addition
meso
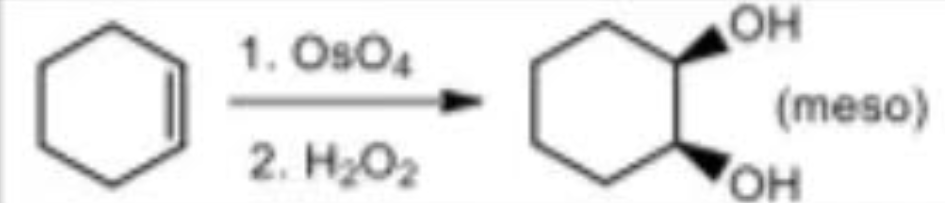
Syn-Hydroxylation (2) reagents
KMnO4 (cold, dilute) / OH-
Syn-Hydroxylation (2) mechanism
syn addition
meso

Ozonolysis under reducing conditions reagents
O3 / Zn/H2o
Ozonolysis under reducing conditions mechanism
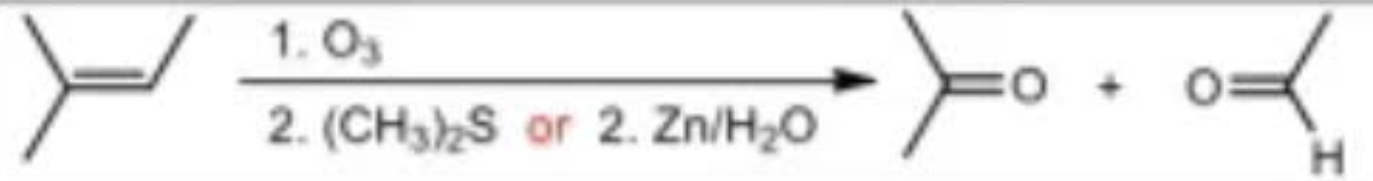
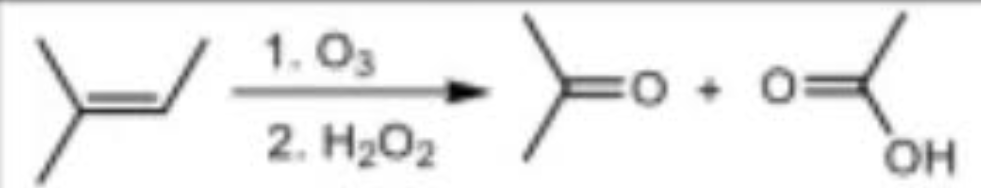
Ozonolysis under oxidizing conditions reagents
O3 / H2O2
OR
KMnO4 (hot,conc.) / H3O+
Ozonolysis under oxidizing conditions mechanism
THE FOLLOWING MECHANISMS FOR ALKYNES (triple bonds)
THE FOLLOWING MECHANISMS FOR ALKYNES (triple bonds)
Dehydrohalogenation of vicinal dihalides reagents
KOH, ethanol
OR
NaNH2, NH3
Dehydrohalogenation of vicinal dihalides mechanism
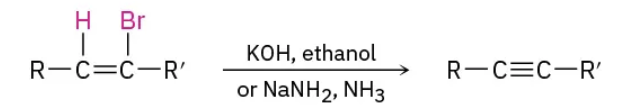
Alkylation of acetylide anions reagents
1) NaNH2 then 2) RCH2Br
Alkylation of acetylide anions mechanism
if it starts off as terminal triple bond then product becomes internal and vice versa
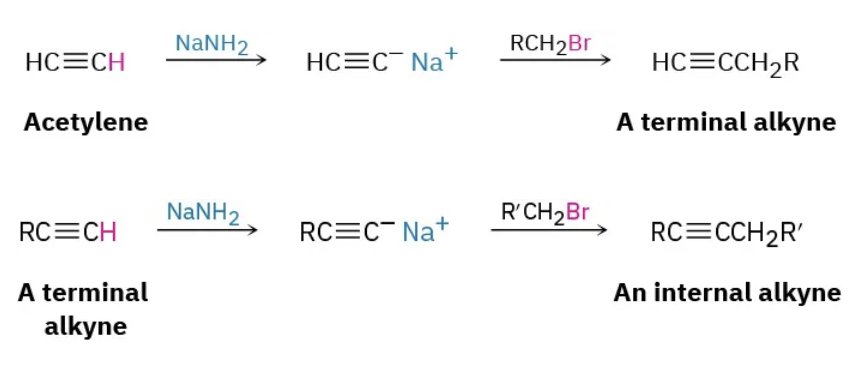
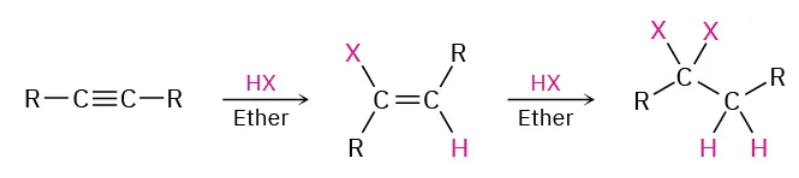
Addition of HX to alkyne reagents
HX / ether (X: halogen)
Addition of HX to alkyne mechanism
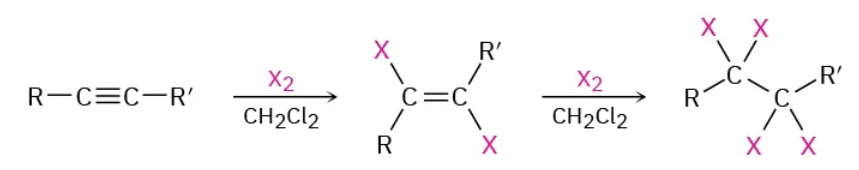
Addition of X2 to alkyne reagents
X2 / CH2Cl2
Addition of X2 to alkyne mechanism
do it twice to go from triple bond to single bond
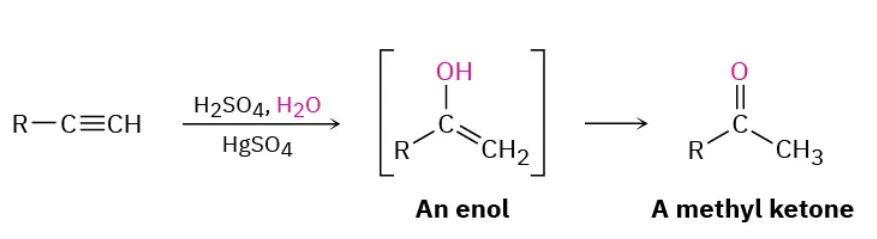
Mercuric sulfate catalyzed hydration reagents
H2SO4, H2O / HgSO4
Mercuric sulfate catalyzed hydration mechanism
Hydroboration-oxidation of alkyne: hydration (reagents)
BH3 / H2O2
Hydroboration-oxidation of alkyne: hydration (mechanism)
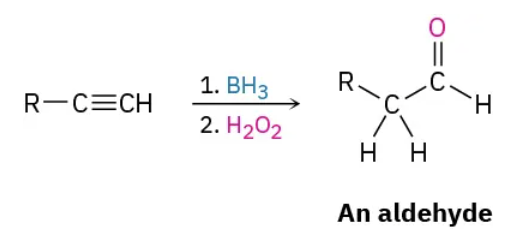
Catalytic hydrogenation (1) : reduction (reagents)
2 H2 / Pd/c
Catalytic hydrogenation (1) : reduction (mechanism)
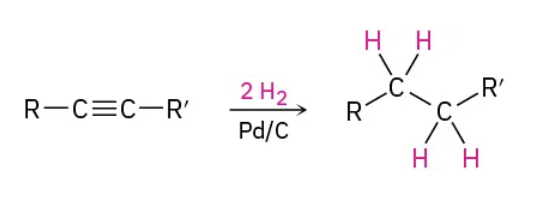
Catalytic hydrogenation (2) aka Lindlar : reduction (reagents)
H2 / Lindlar catalyst
Catalytic hydrogenation (2) aka Lindlar : reduction (mechanism)
cis product
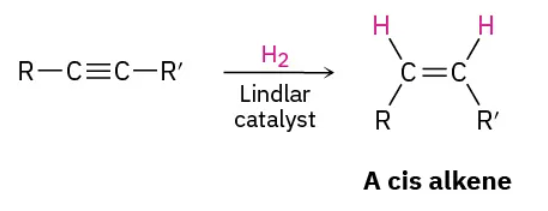
Lithium in liquid ammonia: reduction (reagents)
Li / NH3
Lithium in liquid ammonia: reduction (mechanism)
trans product
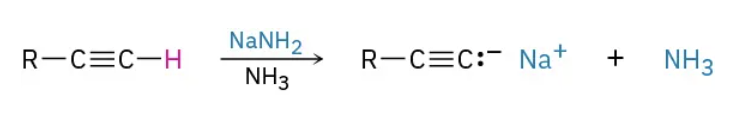
Conversion into acetylide anions reagents
NaNH2 / NH3
Conversion into acetylide anions mechanism
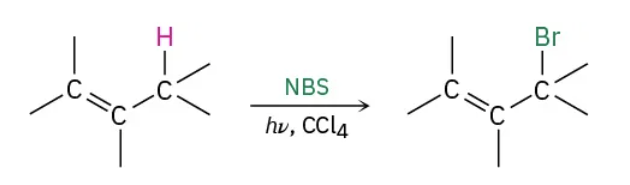
Alkene to Alkyl halides using allylic bromination reagents
NBS / light,CCl4
Alkene to Alkyl halides using allylic bromination mechanism
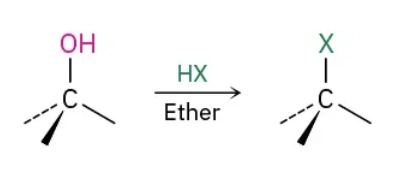
Alcohols to Alkyl halides using HX reagents
HX / ether (X: halogens)
Alcohols to Alkyl halides using HX mechanism
reactivity order 3o > 2o > 1o
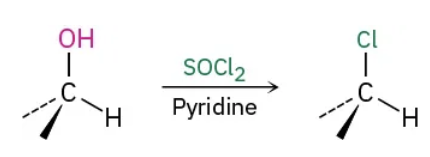
1o and 2o Alcohols to Alkyl halides using SOCl2 reagents
SOCl2 / Pyridine
1o and 2o Alcohols to Alkyl halides using SOCl2 mechanism
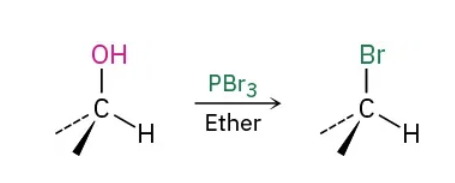
1o and 2o Alcohols to Alkyl halides using PBr3 reagents
PBr3 / ether
1o and 2o Alcohols to Alkyl halides using PBr3 mechanism
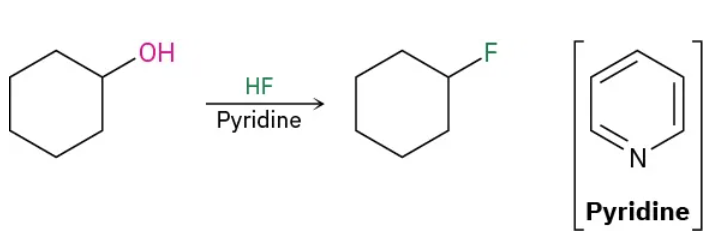
1o and 2o Alcohols to Alkyl halides using HF reagents
HF / Pyridine
1o and 2o Alcohols to Alkyl halides using HF mechanism
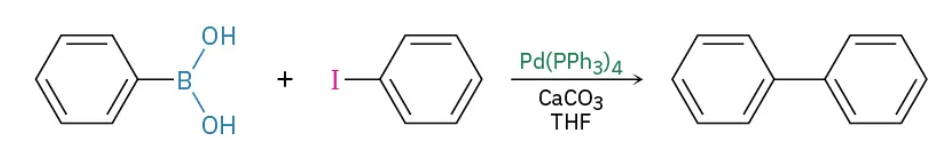
Palladium-catalyzed Suzuki-Miyaura reagents
Pd(PPh3)4 / CaCO3 THF
Palladium-catalyzed Suzuki-Miyaura mechanism
Grignard reagents
R-Mg-X , ether / H2O or H3O+
Grignard mechanism
adds the R to reactant
makes the O into OH
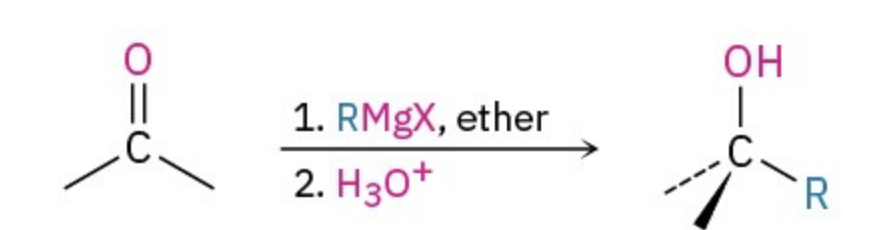
IR range 3200-3500
O-H
IR range 3000-3050
Csp2 - H
IR range 2900-3000
Csp3 - H
IR range 1650-1750
C=O
IR range 1600-1650
C=C
IR range 1050-1250
C-O
IR range 1650-1680
amides
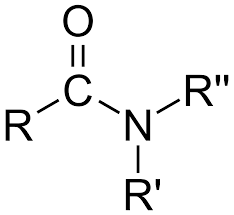
IR range 1685-1715
aldehyde/ketone
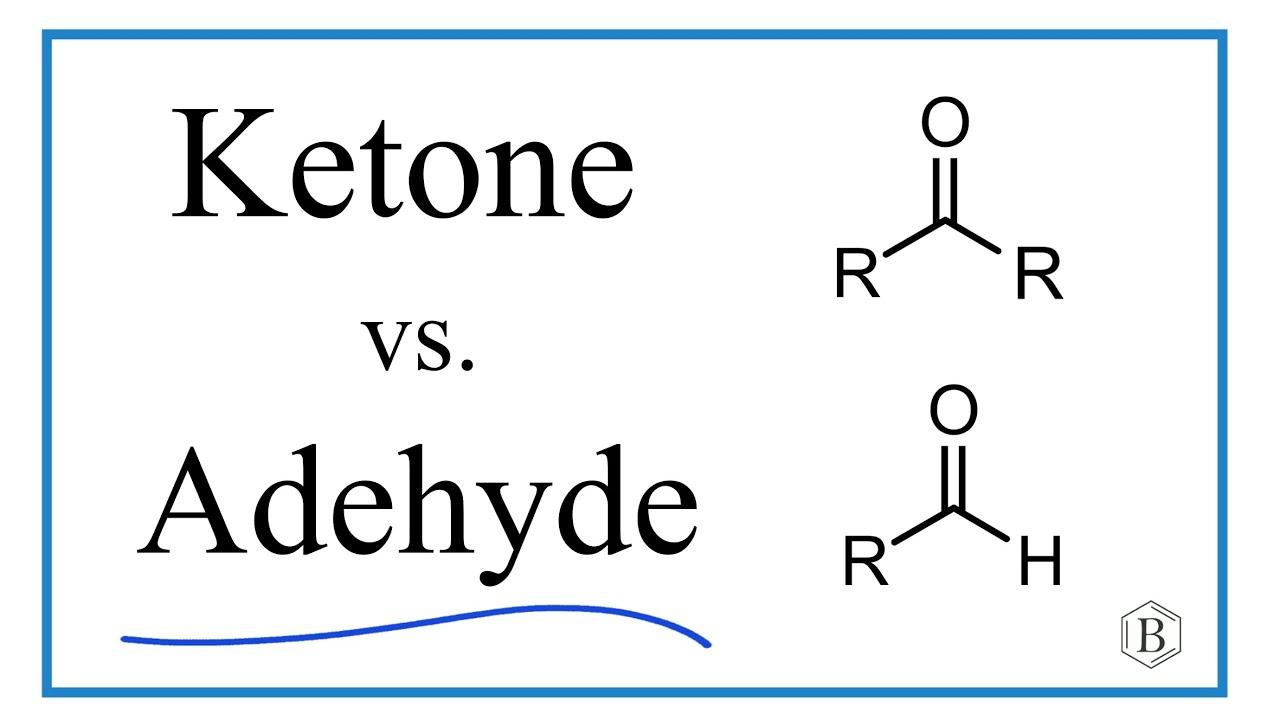
IR range 1680-1710
Carboxylic acids
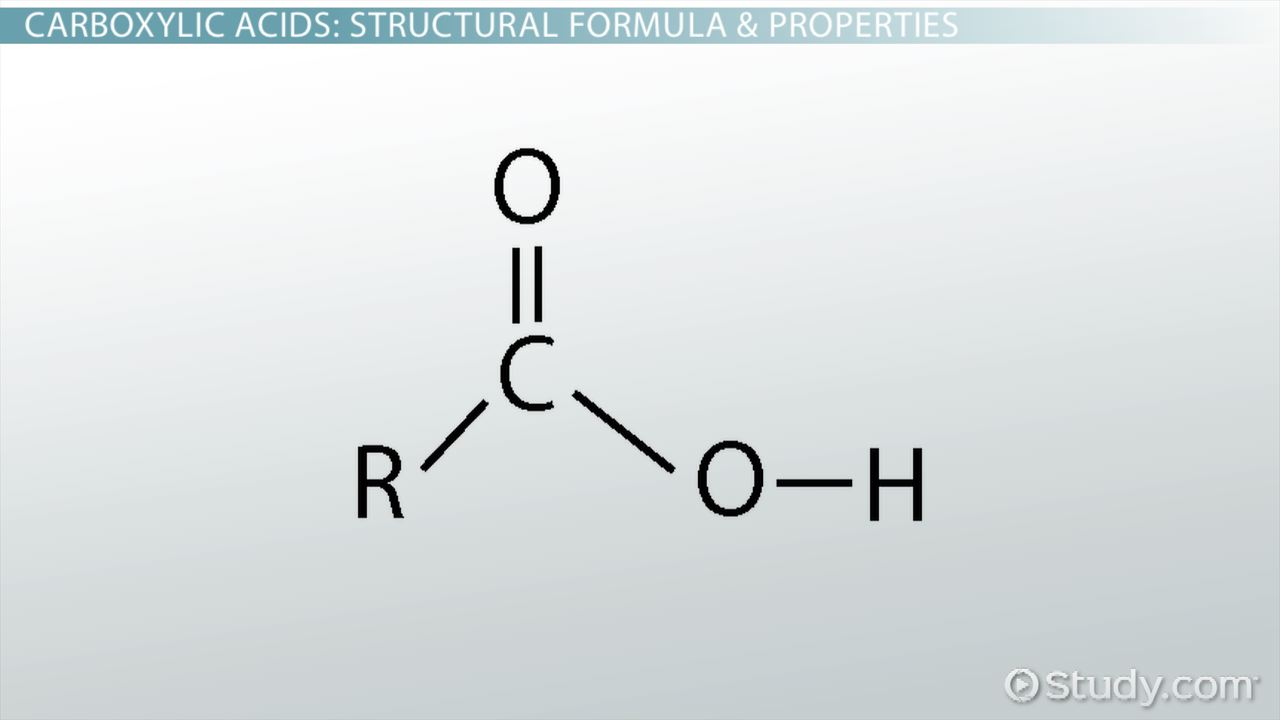
IR range 1735-1760
esters/lactones
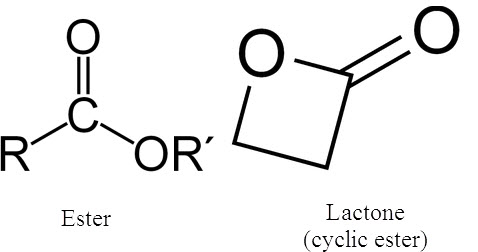
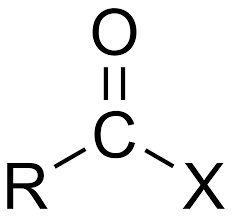
IR range 1760 and 1820
Anhydrides
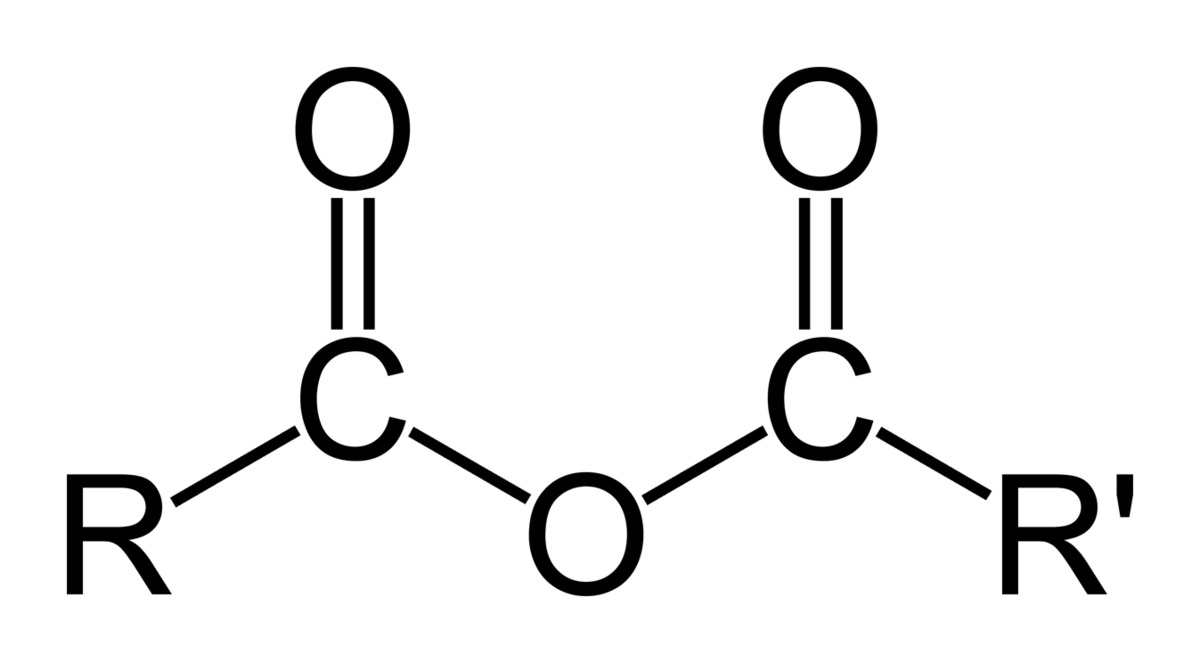
IR range 1800
acyl halides
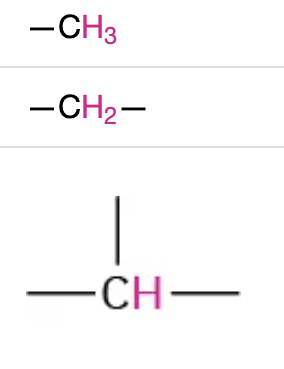
NMR range 0.8-2.0
hydrogen is on an alkyl chain
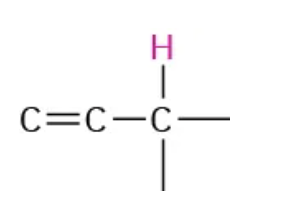
NMR range 2.0-2.5
hydrogen is attached to an allylic carbon
NMR range 3.0-4.5
electronegative atom is attached to the same carbon as the hydrogen
NMR range 5.0-6.0
hydrogen is attached to an alkene carbon
NMR range 7.0-8.0
hydrogen is attached to an aromatic carbon
NMR range 9.7-10.0
aldehyde
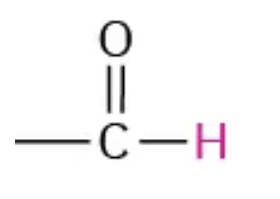
NMR range 11.0-12.0
carboxylic acid
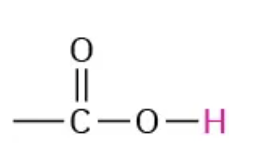
IR range 690-710 and 730-770
monosubstituted benzene ring
IR range 735-770
o-disubstituted benzene ring