chapter 41: Neural Signaling and Neuron Function Overview
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
Functional regions of a neuron
receptive region (dendrites and cell body), conducting region (axon), and secretory region (axon terminal)
neuron function
produce and transmit electrical signals (nerve impulses or action potentials)
multipolar neuron
A type of neuron characterized by multiple extensions from the cell body.
cytoplasmic extensions (processes)
dendrites: receive stimulation, conduct toward cell body
axon: conduct impulses away from cell body to effector
axon hillock
sufficient stimulation initiates action potential along axon
myelin sheath
insulating membrane around axon - separate cell
node of ranvier
gap in myelin
axon collateral
branches at end of axon - along length
terminal branches
division at end of axon
synaptic terminal
end of terminal branches, transmits signal to effect
synapse
junction between a synaptic terminal and effector (neuron, muscle, gland)
afferent neurons
sensory neurons
bringing thing in - toward CNS
Major structural types of neurons
pseudounipolar, bipolar, and multipolar.
multipolar
multiple extensions off of cell body
single axon and multiple dendrites
99% of all neurons
bipolar
one axon and one dendrite and cell body between them
eye and olfactory epithelium (nasal cavity)
pseudounipolar
cell body off to side
single short process that splits into two axons
Interneuron (associated neuron)
in CNS (brain and spinal cord)
efferent neuron
Motor neuron
information going out
Glial cells
Supportive cells in the nervous system that perform various functions.
astrocytes
large, star-shaped cells with many processes
anchor neurons and blood vessels in place
transport nutrients and gasses between blood vessels and neurons
regulate extracellular environment of brain
form blood brain barrier
repair damaged tissue
ependymal cells
line internal cavities of the CNS and have cilia
function: produce and circulate of CSF
microglial cells
found near blood vessels
specialized macrophages, remove bacteria and cell debris
CNS
Central Nervous System, consisting of the brain and spinal cord.
PNS
Peripheral Nervous System, consisting of all nerves outside the CNS.
Nerve regeneration
The process by which nerves repair themselves after injury.
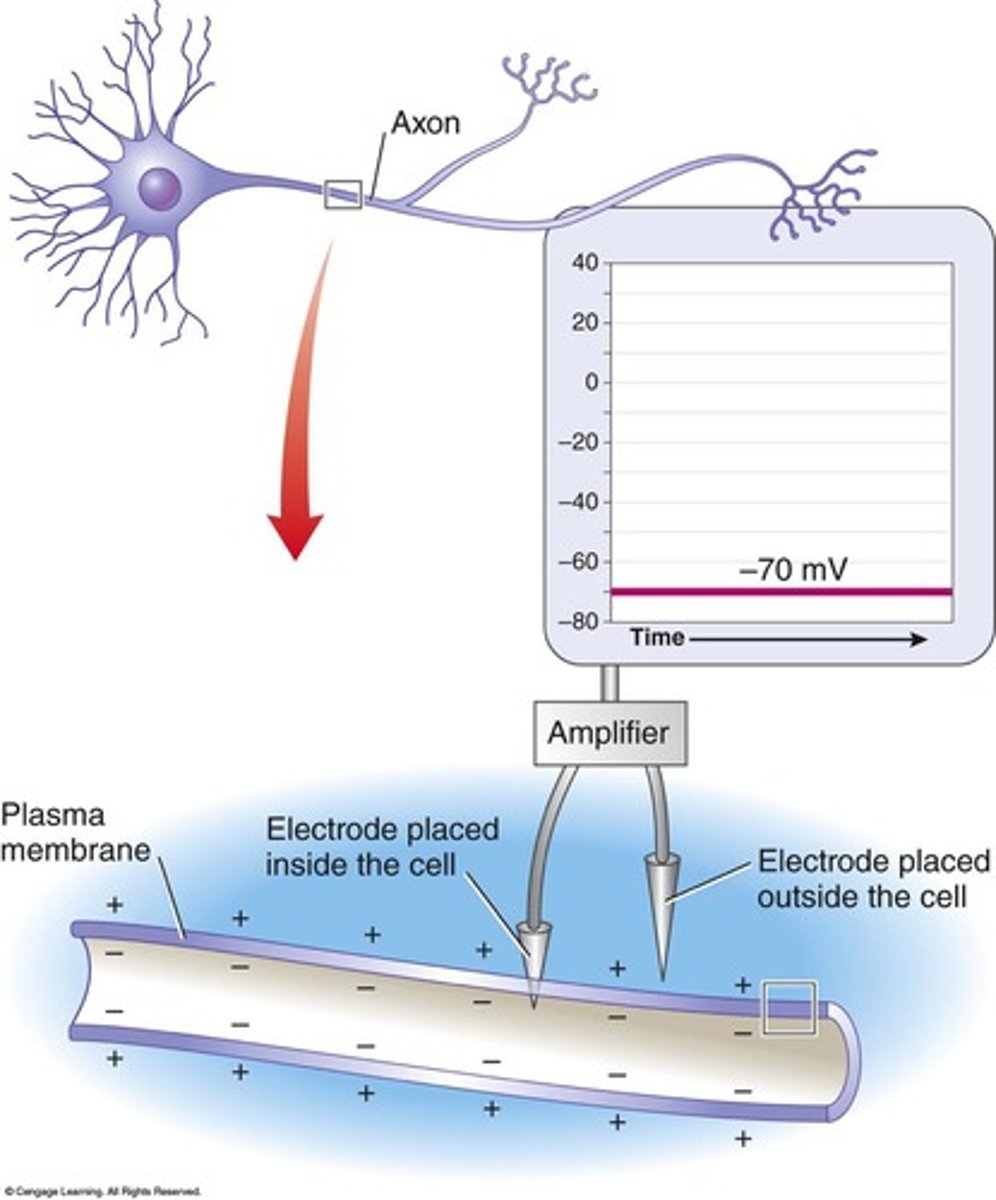
Resting potential
The transmembrane potential of a neuron when it is not actively transmitting signals.
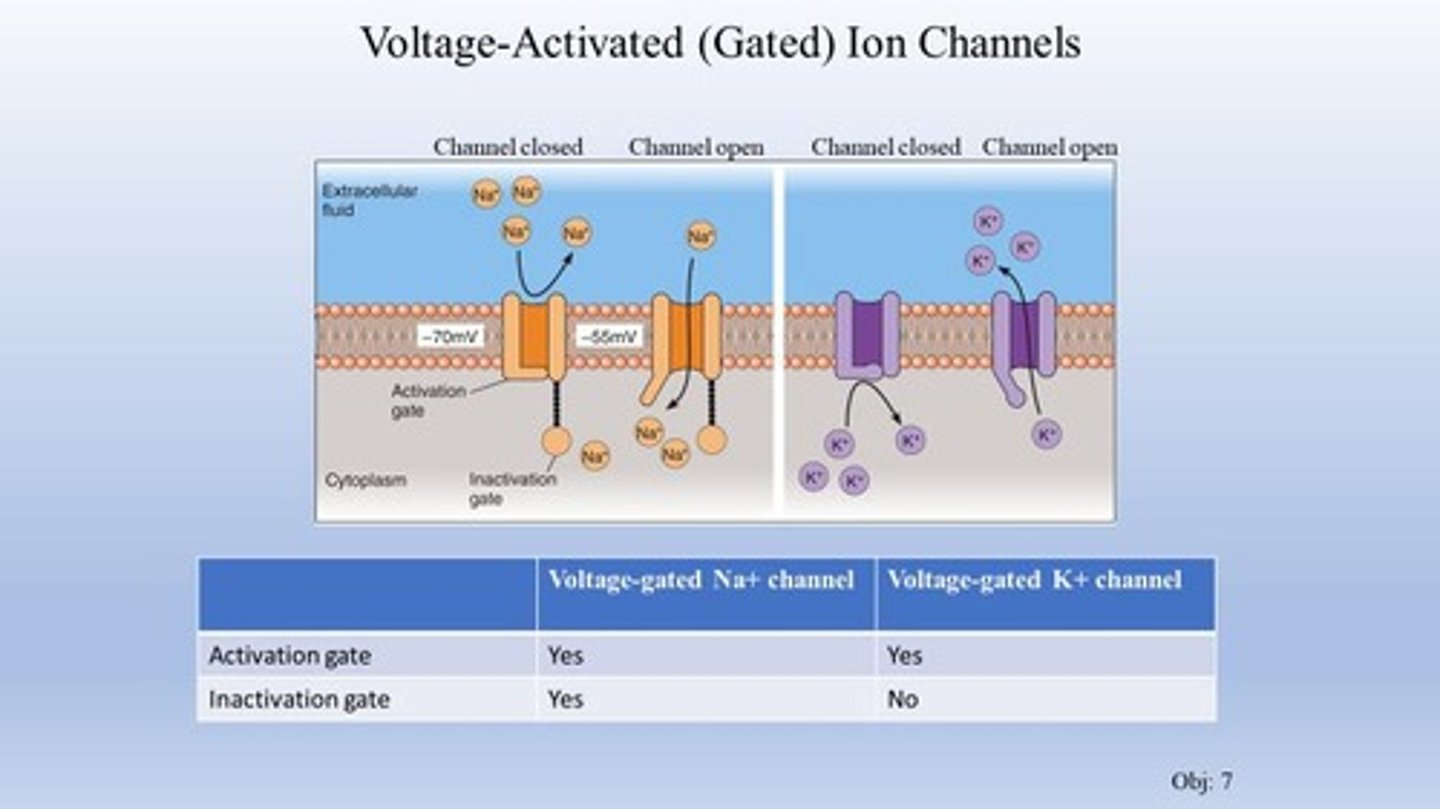
Ion channels
Proteins that allow ions to pass through the neuron's membrane.
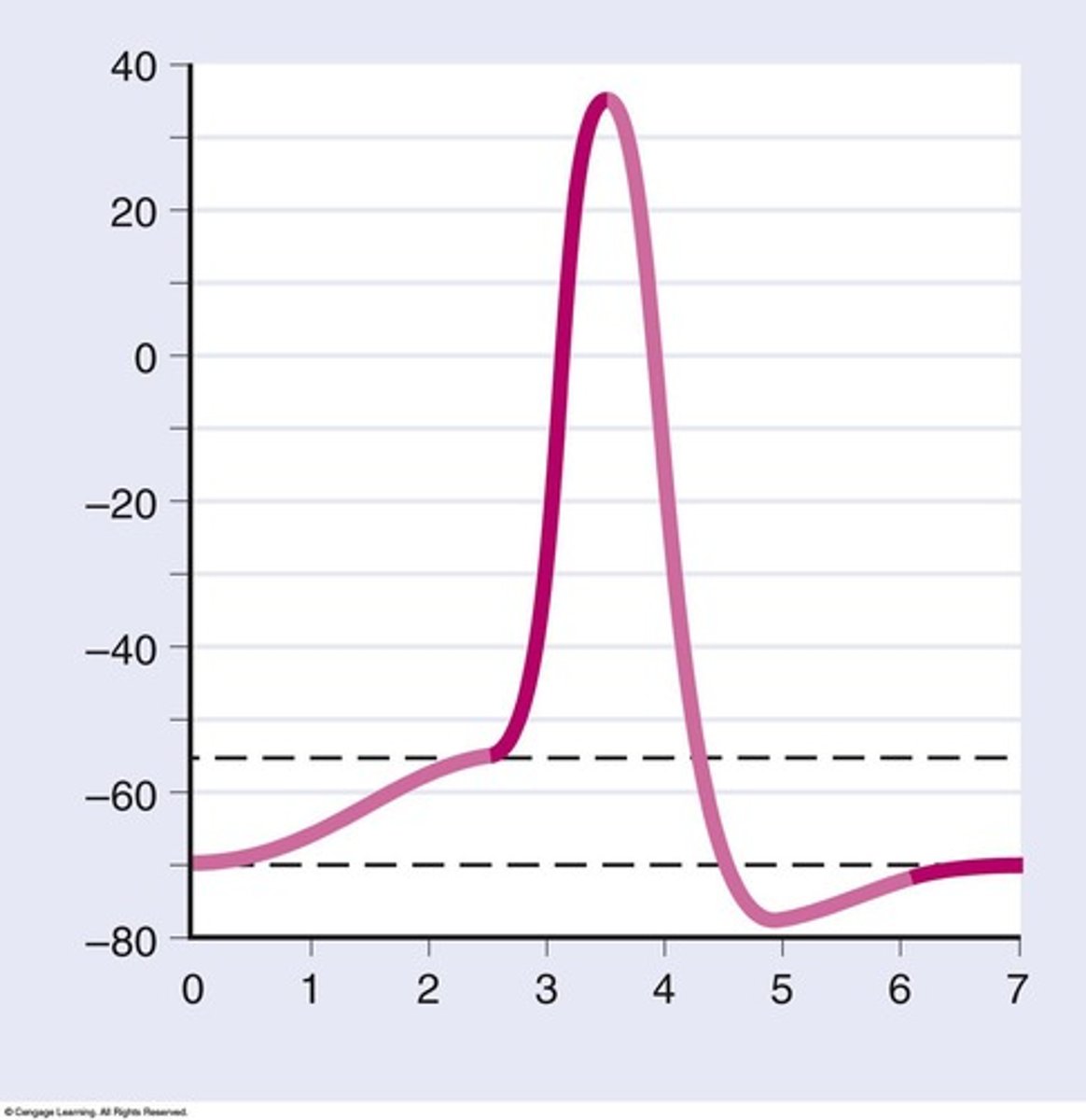
Action potential
A rapid change in membrane potential that propagates along the neuron.
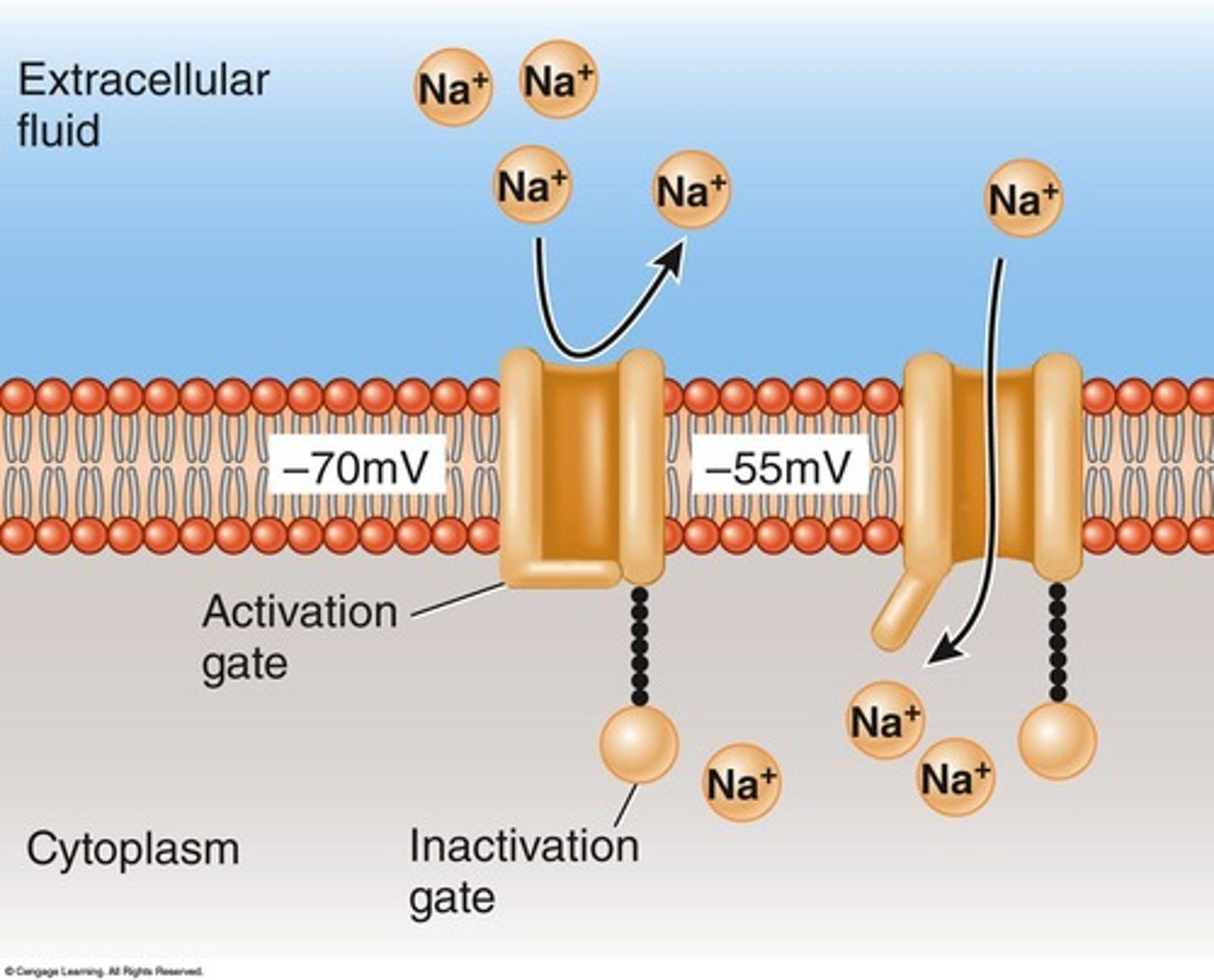
Sodium voltage-gated channels
Channels that open in response to membrane depolarization, allowing sodium ions to enter the neuron.
Potassium voltage-gated channels
Channels that open to allow potassium ions to exit the neuron, helping to repolarize the membrane.
Positive feedback in nerve conductance
A process where an initial stimulus leads to an amplification of the response.
Negative feedback in nerve conductance
A process that counteracts changes, helping to stabilize the system.
Absolute refractory period
The period during which a neuron cannot fire another action potential, regardless of stimulus strength.
Local potentials
Small changes in membrane potential that occur in a localized area of the neuron.
All-or-none response
The principle that a neuron either fires an action potential or does not, with no intermediate states.
Velocity of an action potential
Factors that influence how fast an action potential travels along a neuron.
Self-propagating action potentials
The ability of action potentials to continue along the neuron without additional input.
Continuous conduction
A type of action potential propagation that occurs along unmyelinated axons.
Saltatory conduction
A type of action potential propagation that occurs along myelinated axons, jumping between nodes of Ranvier.
Nerve to effector synapses
Connections between neurons and their target effectors, such as muscles or glands.
Inhibitory post synaptic potentials (IPSP)
Changes in membrane potential that make a neuron less likely to fire an action potential.
Excitatory post synaptic potentials (EPSP)
Changes in membrane potential that make a neuron more likely to fire an action potential.
Temporal summation
The process where multiple signals arrive at a neuron in quick succession to increase the likelihood of firing.
Spatial summation
The process where signals from multiple neurons arrive at a neuron simultaneously to increase the likelihood of firing.
Neural circuits
Networks of interconnected neurons that process specific types of information.
Convergence of neural circuits
The process where multiple neurons synapse onto a single neuron.
Divergence of neural circuits
The process where a single neuron synapses onto multiple neurons.
Continuous conductance
occurs in unmyelinated axons and is continuous along the length of the axon
Neurolemmocyte
cell that myelinates neurons in PNS
Oligodendrocyte
cell that myelinates neurons in the CNS
Postsynaptic neuron
the neuron leaving a synapse
Presynaptic neuron
the neuron leading up to a synapse (the one coming into the synapse)
Relative refractory period
stage in the repolarization time of an action potential when an additional depolarization event is possible, but the threshold level will be higher than during a resting transmembrane potential
Saltatory conductance
movement of an action potential along a myelinated axon where the action potential only occurs at the nodes
Threshold
electrical value at which the voltage-gated sodium channels will be stimulated to open resulting in depolarization
Transmembrane potential
electrical charge difference across a membrane
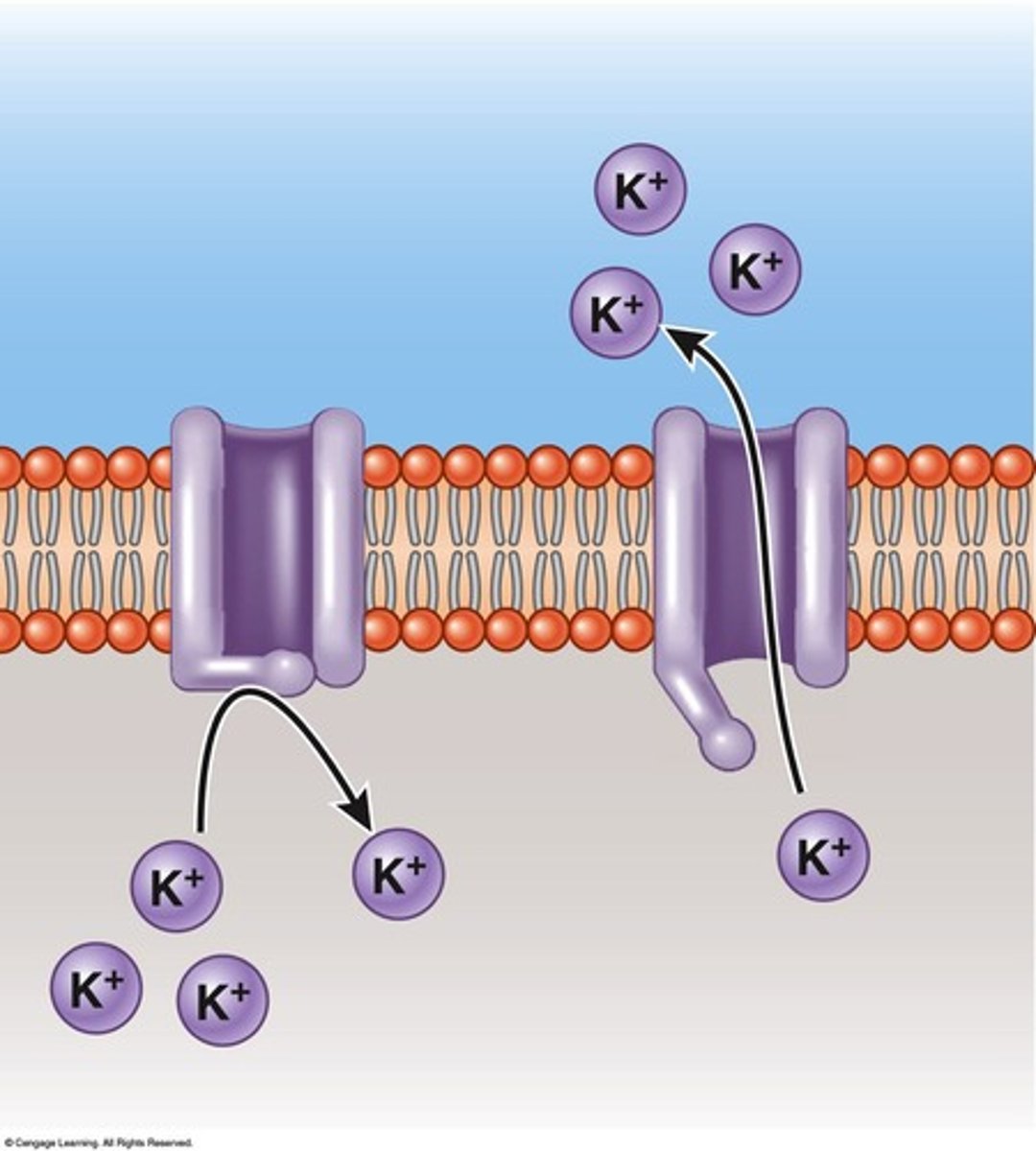
Voltage-activated channels
channels that open and close based upon the charge difference across the membrane
Satellite cells
Glial cells that surround the cell bodies of neurons in the PNS and provide supportive functions.
Nuclei
Clusters of neuron cell bodies in the CNS.
Tracts
Bundles of axons in the CNS.
Ganglia
Clusters of neuron cell bodies in the PNS.
Nerves
Bundles of axons in the PNS.
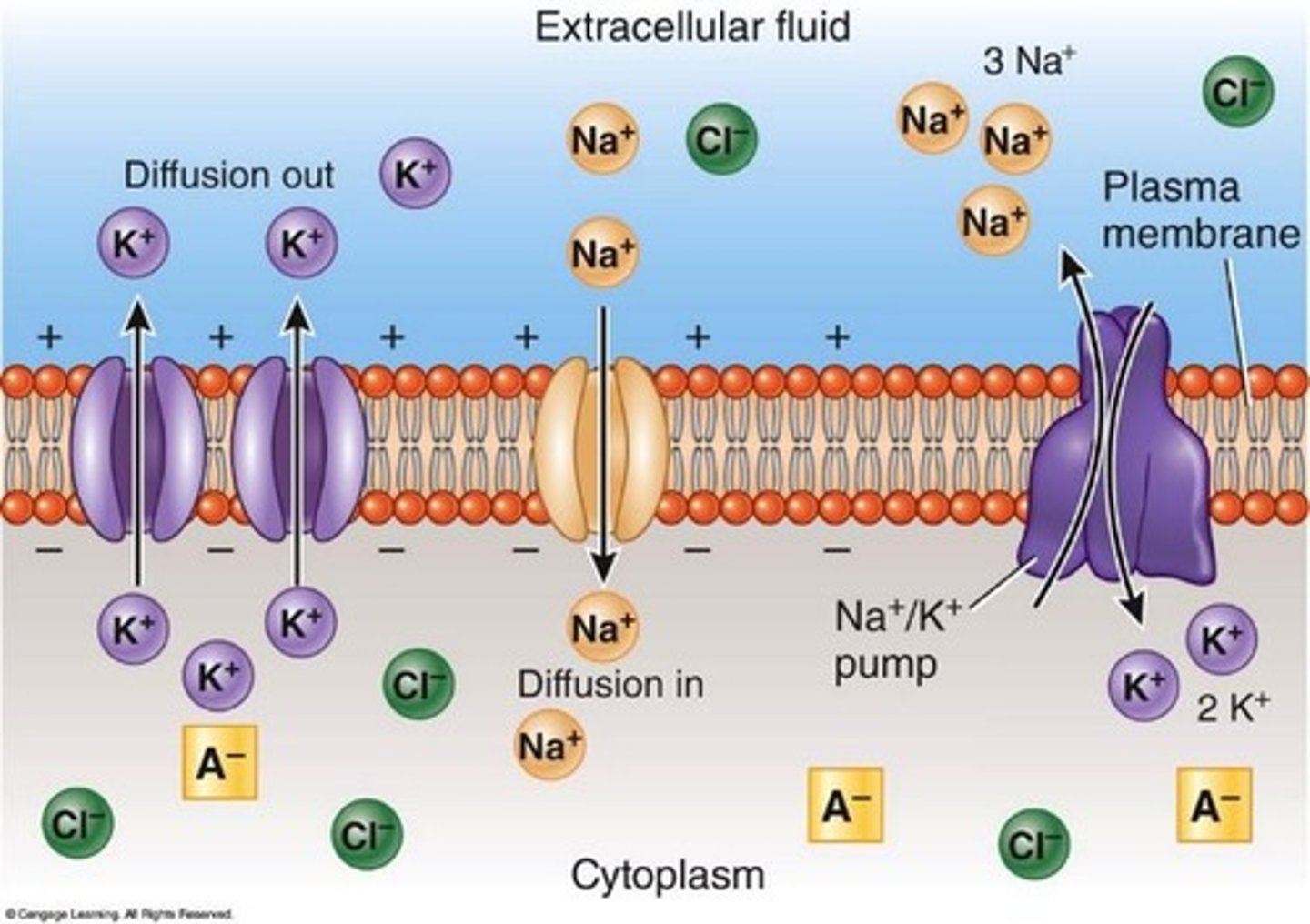
Resting membrane potential
The electrical gradient established by the separation of charges across the plasma membrane, typically around -70mV.
Sodium-potassium pump
Transport mechanism that moves 3 Na+ out and 2 K+ into the cell, requiring ATP.
Graded potentials
Local changes in membrane potential that are reversible and decrease in strength over short distances.
Electrical synapses
Synapses where two cells are connected by protein channels (gap junctions) allowing fast, bidirectional communication.
Chemical synapses
Synapses that involve neurotransmitter release from the presynaptic neuron to the postsynaptic neuron across a synaptic cleft.
Neural integration
The process by which EPSPs and IPSPs are added together to determine if an action potential will be generated.