CIS 2200 Quiz 1
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Porter’s five forces
A framework for analyzing the competitive forces within an industry, including the intensity of rivalry among competitors, the threat of new entrants, the threat of substitute goods or services, the bargaining power of buyers, and the bargaining power of suppliers.
Value Chain
A set of activities through which a product or service is created and delivered to customers.
Inbound Logistics
The process of getting needed materials and other inputs into the firm from suppliers.
Operations
The activities involved in turning inputs into products or services.
Outbound Logistics
The activities involved in delivering products or services to consumers, retailers, or other partners.
Marketing and Sales
Activities related to customer engagement, pricing, promotion, and transaction.
Support
Service, maintenance, and customer support activities within the value chain.
Firm Infrastructure
Functions that support the whole firm, including general management, planning, information systems, and finance.
Human Resource Management
The process of recruiting, hiring, training, and developing employees.
Tech/Research and Development
Activities focused on new product and process design.
Procurement
The sourcing and purchasing functions within a company.
Operational Effectiveness
Performing the same tasks better than rivals perform them.
Danger of Operational Effectiveness
The risk of 'sameness' which can lead to a lack of differentiation and make it hard for a company to stand out.
Strategic Positioning
Performing different tasks than rivals or the same tasks in a different way.
Resource-Based View of Competitive Advantage
The concept that for a firm to maintain sustainable competitive advantage, it must control resources that are valuable, rare, imperfectly imitable, and nonsubstitutable.
Sustainable Competitive Advantage
Financial performance that consistently outperforms industry averages.
Greige
Goods that are to be further customized based on designer or manager collaboration.
Straddling
A firm's attempt to occupy more than one position while failing to match the benefits of a more efficient, singularly focused rival.
Omnichannel
An approach to retail that offers consumers an integrated set of shopping, sales, and return experiences across online and offline platforms.
Economies of Scale
Cost advantages achieved when costs can be spread across increasing units of production or serving multiple customers.
Experiential Products
Items that need to be seen and experienced in person before a buyer can make a decision.
Fast Follower Problem
The situation where rivals learn from a pioneer’s efforts and enter the same market with a comparable or superior product at a lower cost.
Information Asymmetry
A situation where one party has more or better information than its counterparty.
Price Transparency
The degree to which complete information about prices is available.
Switching Cost
The cost a consumer experiences when moving from one product to another.
Commodity
A basic good that is interchangeable with near identical offerings by others.
Brand
The symbolic embodiment of all the information connected with a product or service.
Product-Market Fit
The degree to which a product satisfies market demand.
Inventory Turns
The number of times inventory is sold or used during a given period; also known as turnover rate.
Disintermediation
The elimination of the need for a salesperson or intermediary in a transaction.
Showrooming
The practice of customers examining products in a physical store and then purchasing online from a lower-cost rival.
Vertical Integration
When a single firm owns several layers in its value chain.
Tactical Information Systems
Information systems that do not create or add value, but are important for business operations.
Strategic Information Systems
Systems used to support or shape competitive strategy and defined by objectives rather than functionality.
Barriers of Entry
Obstacles that make it difficult for new competitors to enter an industry.
Differentiation
The process of making products appear different through various marketing strategies.
Supply Chain for Physical Retailers
The process consisting of production, warehousing, and selling products in-store.
Supply Chain for Online Retailers
The process starting with customer research and ending with delivery to the customer.
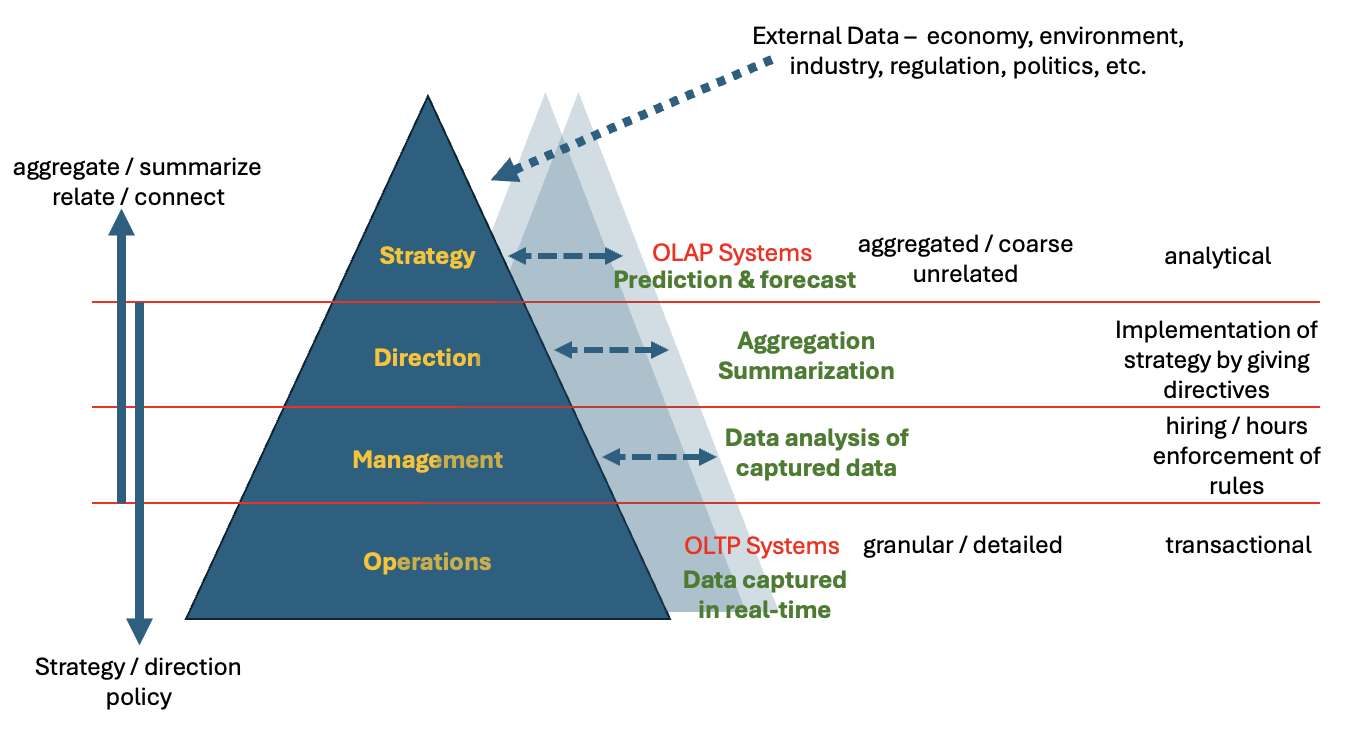
Online Analytical Processing (OLAP) Systems
Systems used for predicting and forecasting business outcomes.
OLTP Systems
Systems that capture data in real time.
Information Flow in an Organization
The way information moves through various levels and departments of an organization.