Human Physiology Final
1/118
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
119 Terms
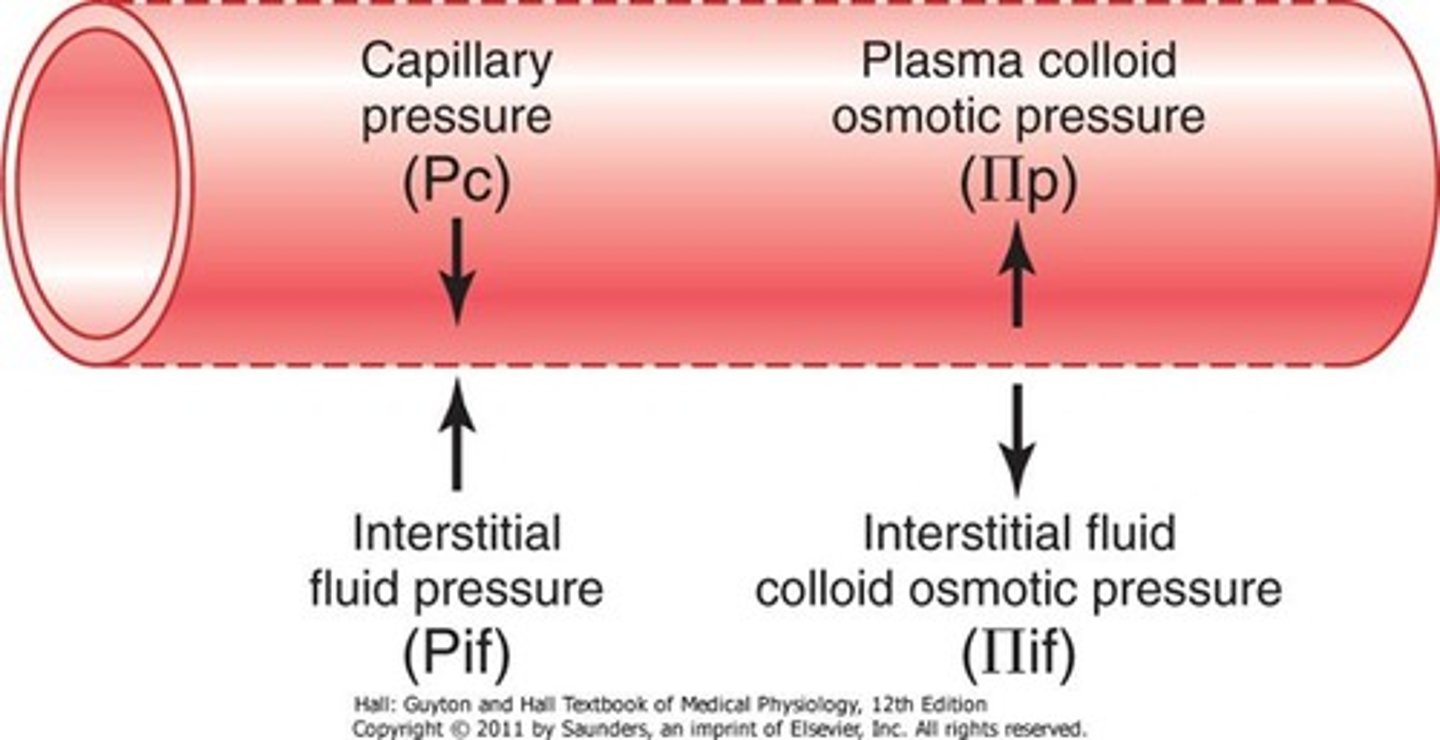
Capillary Hydrostatic Pressure
-pushes fluid out
-Force exerted by fluid against a wall
- 20L of fluid is pushed out each day
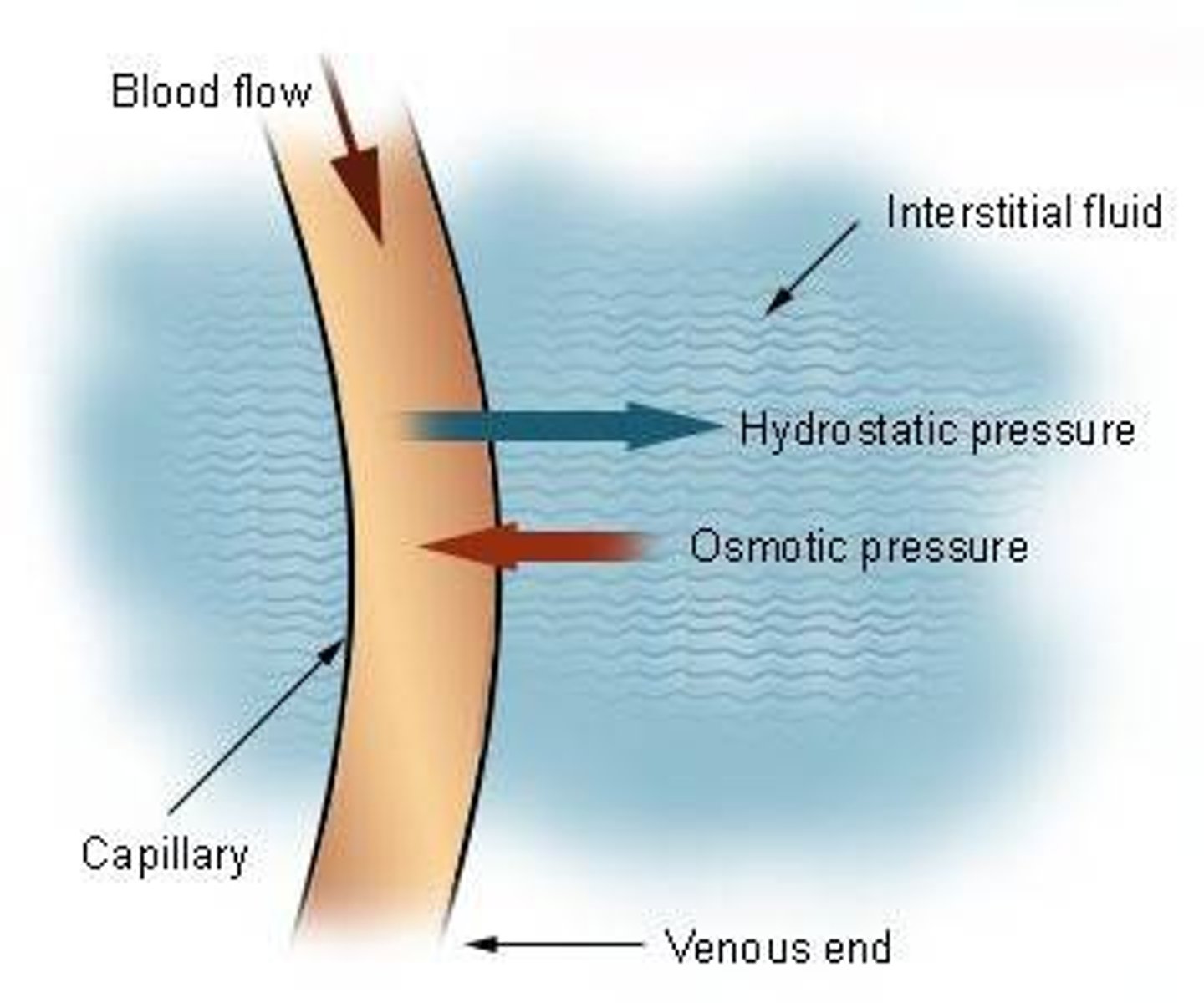
Colloid osmotic pressure
created by non-diffusible molecules that draw some fluid back.
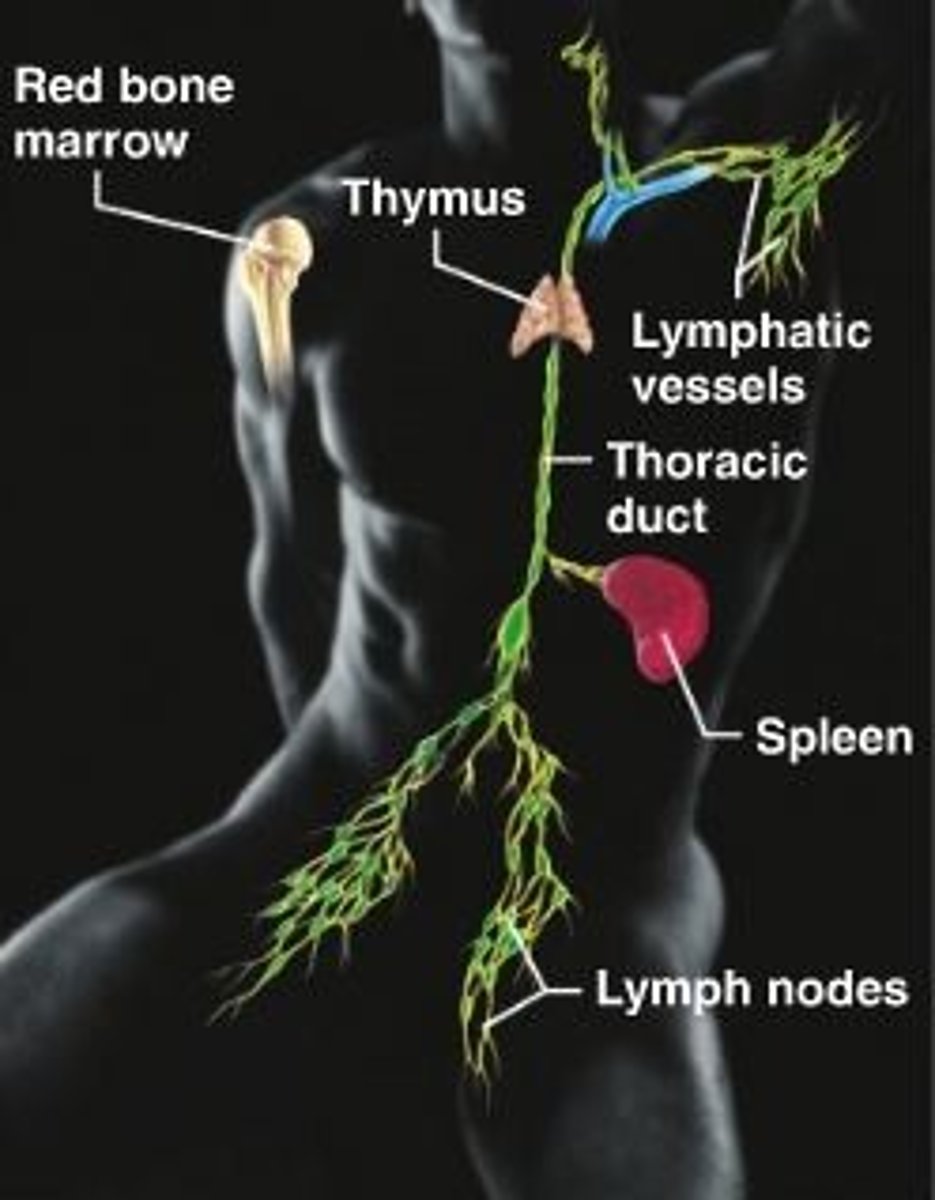
Lymphatic system
A network of vessels that take up fluid from the interstitial space and return it to the blood.
Lymphatic capillary
a close-ended microscopic lymphatic vessel that begins in the interstitial spaces between cells, takes in interstitial fluid, and begins its transport through the lymphatic system
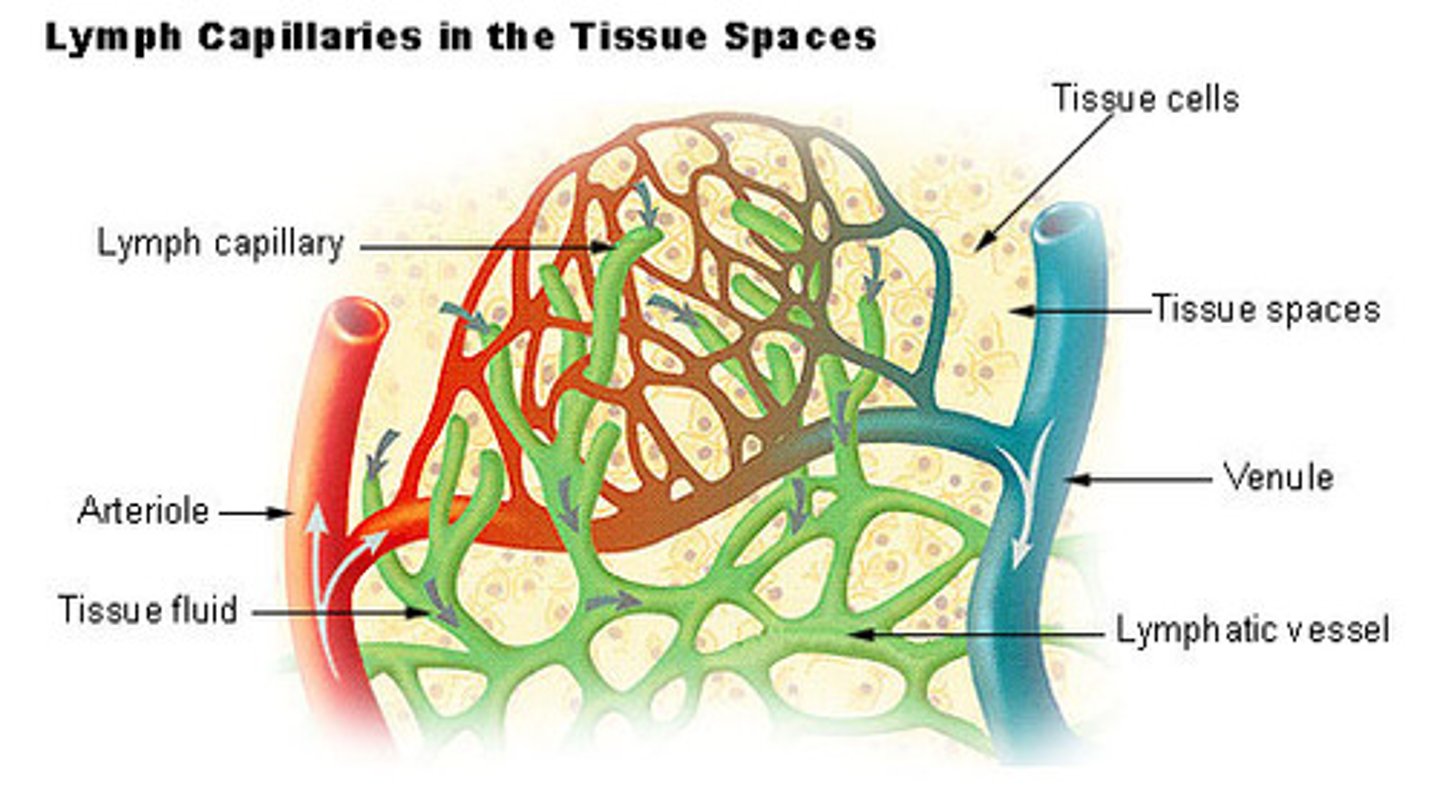
Lymph Vessels
vessels that receive lymph from the lymph capillaries and circulate it to the lymph nodes (everywhere)
Where Does Lymph Go?
Back to the blood to become plasma again (heart)
Lymph
is cleansed of debris and surveyed for pathogens.
Lymph Nodes
Solid spherical bodies that cluster along lymphatic vessels.
• Provide a meeting, surveillance, and proliferation site for immune cells
Lymphoid Organs
Lymphocytes, Antigen Presenting Cells
Lymphocytes (the soldiers)
T cells (T lymphocytes): manage response, can attack infected cells.
- B cells (B lymphocytes): produce antibodies
Antigen Presenting Cells (the intelligence)
Macrophages phagocytose foreign substances and present antigens
- Dendritic Cells capture antigens in tissues and bring them back to the lymph node
Cortex
-Dividing B cells (germinal centers)
- T cells in transit
Medulla
Draining sinuses that allow lymph efflux
Spleen
Immune surveillance of blood (- Removal of old RBCs (Red pulp)
Thymus
T Cell education/maturation
• No B cells
Atrophies with age
Tonsils
Trap and remove pathogens entering throat.
Produce memory cells for later.
Appendix
Off-shoot of large intestine
Thought to survey/store gut bacteria
Peyer's Patches
Nodules in small intestine
survey gut bacteri
First Line of Defense
Skin and Membranes are physical barriers.
Acid (skin, stomach = inhibit bacterial growth)
Enzymes (Lysozyme in saliva, tears = destroy bacteria)
Second Line of Defense
Innate Immune cells
Macrophages
Derived from blood monocytes • Search tissue and "eat" debris or foreign invader
What is the first step in phagocytosis?
Phagocyte adheres to pathogens or debris
What do phagocytes form to engulf particles during phagocytosis?
Pseudopods
What is formed when a phagocyte engulfs particles?
Phagosome
What fuses with the phagocytic vesicle to form a phagolysosome?
Lysosome
What do lysosomal enzymes do in the phagolysosome?
Digest the particles, leaving a residual body
What process removes indigestible and residual material from the phagocyte?
Exocytosis of the vesicle
What is inflammation?
Aggressive steps the body takes to fix a problem.
What triggers inflammation?
Tissue injury or infection.
What type of receptors do macrophages and dendritic cells use to detect problems?
Toll-like receptors (TLRs).
What do Toll-like receptors (TLRs) do?
They detect problems and 'sound the alarm'.
Why is edema beneficial?
Sweeps foreign material into lymphatics
Calling For Back up
Chemical "alarm" recruits immune cells to injured or infected area.
Neutrophils
A type of white blood cell that engulfs invading microbes and contributes to the nonspecific defenses of the body against disease.
Extravasation
escape of blood from the blood vessel into the tissue
- Blood vessels and immune cells upregulate adhesion molecules.
Diapedesis
Neutrophils enter tissue.
Chemotaxis
Movement up a chemical gradient (to injury/infection)
Interferons
"Interfere" with viral replication
Complement System
20 plasma proteins that circulate in blood.- Activation triggers cascade that lyses bacteria and cells.
T Cells
Cells created in the thymus that produce substances that attack infected cells in the body.
B Cells
produce antibodies
What are foreign antigens?
Foreign antigens originate from outside the body.
What are self antigens?
Self antigens are produced by the body and rarely initiate an immune response.
What can self antigens trigger in other people?
Self antigens can trigger an immune response in other people, as seen in the rejection of transplanted tissues and organs.
Bubble boy
Severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID)
What is required for T cell activation?
T cells require two signals.
What do Antigen Presenting Cells (APCs) do?
APCs present antigens to T cells.
Where do dendritic cells present antigens to T cells?
Dendritic cells present antigens to T cells in lymph nodes.
What happens to co-stimulation molecules on APCs when they encounter pathogens?
APCs upregulate co-stimulation molecules.
MHC Class II Proteins
present these antigens to Helper T Cells.
CD4 Helper T Cells (2 signals)
T Cell receptor (TCR) binds antigen in MHC-II complex
Alveoli
tiny sacs of lung tissue specialized for the movement of gases between air and blood
Pleurae
Double layered membrane
- Fluid between laye
Parietal
covers chest wall and diaphragm
Visceral
covers lung surface
Lung Expansion
Increase in lung volume during inhalation.
Boyle's Law- Volume changes lead to pressure changes
Recoil
Recoil expels air • Lungs sticking to chest wall prevents collapse
Pneumothorax
Presence of air pleural cavity.-
Seal broken.
- Can't breathe!
collapsed lung
Diaphragm
Parachute-shaped muscle
• Contraction (Down) increases chest volume
Intercostal muscles
Muscles between ribs
• Raises rib cage
. • "Bucket Handle" movement.
Intercostal muscles + Diaphragm =
Inspiration
Lung Recoil
Expiration
Passive proces
Muscles relax...- Major driving forces Lung elasticity and Surface tension
Forced Expiration
Contract abdominal muscles
CD4 Helper T Cells
Promote B Cell Activation and Antibody Synthesis
MHC-I Presents Intracellular Proteins
Random sampling of recycled proteins sent to ER. • Peptides bind MHC-I and present what is being made.
MHC-I
is expressed by ALL cells.
Cytotoxic CD8 T cells Scan MHC-I Molecules
CD8 cells recognize foreign antigens presented by MHC-I. • Release toxic enzymes killing target cell.
Natural Killer (NK) Cells:
a Back-up plan for those Sneaky Viruses
CAR T-Cell Therapy for Cancer
CAR (Chimeric Antigen Receptor)- Synthetic receptor- Allows T cells to recognize and attack cancer cells
What is the role of MHC in organ transplantation?
MHC must match between donor and recipient to reduce rejection.
What types of cells are involved in rejecting mismatched tissue?
CD8 and NK cells.
What is the effect of immunosuppressive drugs on transplant rejection?
They can reduce the rate of rejection.
What percentage of patients reject a transplant within 10 years under the best conditions?
50%.
Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome
Caused by Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)
• Infects and kills CD4 T cells
• Virus always X mutating ("new" molecules/antigens)
Autoimmunity
Immune system destroys own cells
- Antibodies or CD8 T Cells
• Most prevalent in women.
Rheumatoid Arthritis
(joints)
Multiple Sclerosis
myelin sheath destruction. disruptions in nerve impulse conduction
Grave's Disease
thyroid gland stimulation
Diabetes Mellitus
destroys insulin producing cells
Molecular mimicry
Pathogen antigens look like our own
treatments of autoimmune diseases
metabolic control therapy
immunosuppressive therapy
targeted treatments
oral tolerance
What is the first step in the activation of CD4 Helper T Cells?
An APC encounters and ingests a microorganism, processing the antigen into short peptides that combine with MHC class II molecules.
What happens after the MHC-antigen complex is formed on the APC?
A receptor on the surface of the CD4 T cell binds to the MHC-antigen complex, providing two signals that activate the Th cell.
What do activated CD4 Helper T Cells produce?
Cytokines.
What is the result of cytokine production by activated CD4 Helper T Cells?
The Th cell proliferates and develops its effector functions.
What is required for a T cell to become activated by a dendritic cell?
The T cell must recognize a dendritic cell that is producing costimulatory molecules.
FAB Region (2 Ends)
Binds antigens
FC Region (Tail)
Binds macrophage receptors
Active immunity (Induce)
Vaccines
weakened or attenuated pathogen
mRNA vaccines
Plasma Cells
Short-lived "Antibody factories
Helper T Cells promote B Cell activation
by providing cytokines
cytokines
Chemicals released by the immune system communicate with the brain.
Guardians of the Nostrils
Lined with hair follicles- Filter large particles (dust, pollen)
Respiratory System Lined with
mucus membranes and ciliated cells
When Large Particles Sneak Through
Nasal mucosa lined with sensory nerve endings.
• Contact with particles triggers reflex
Cold air
makes nose engorged with blood.
- Blood circulation provides heat
• Moisture = humidity
thin-walled air sacs in lungs
Alveoli
Asthma
Inflammation triggers muscle contraction
• Epinephrine relaxes muscle
Inside Alveoli
Thin epithelium
- Fuses with vessels
- Diffusion of gase