CDEP 2017 (Building Construction for Interior Design)
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
One-way slab
A concrete slab of uniform thickness reinforced in one direction and cast integrally with parallel supporting beams

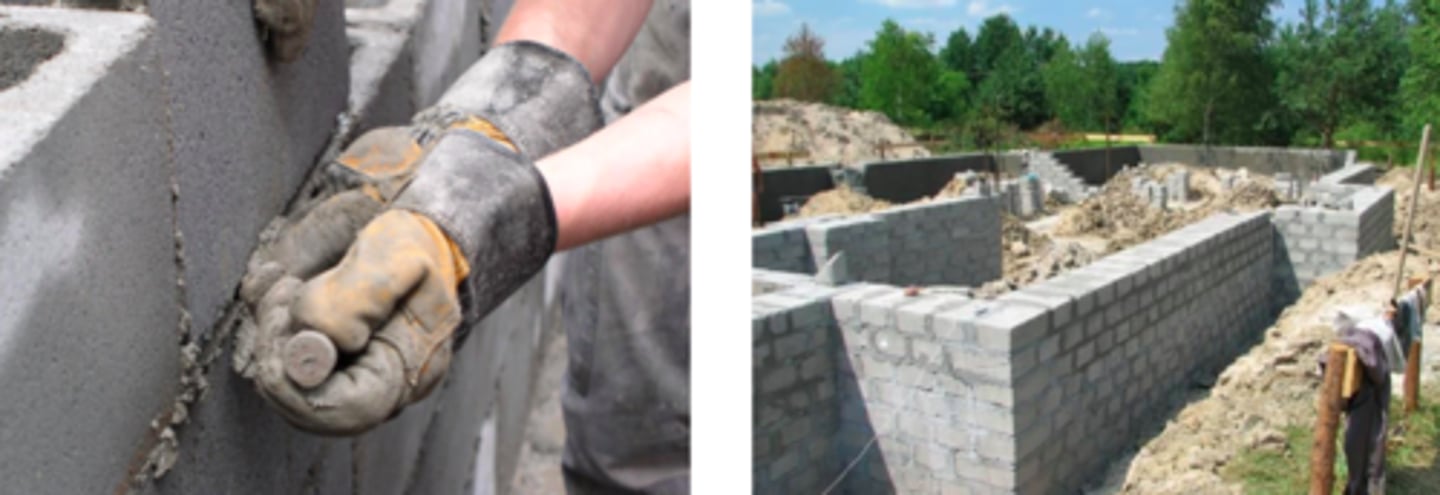
Mortar
Cement mix used to glue masonry units to each other, or other surface finishing materials like tiles, bricks, and stones to a receiving structure like a wall or floor.

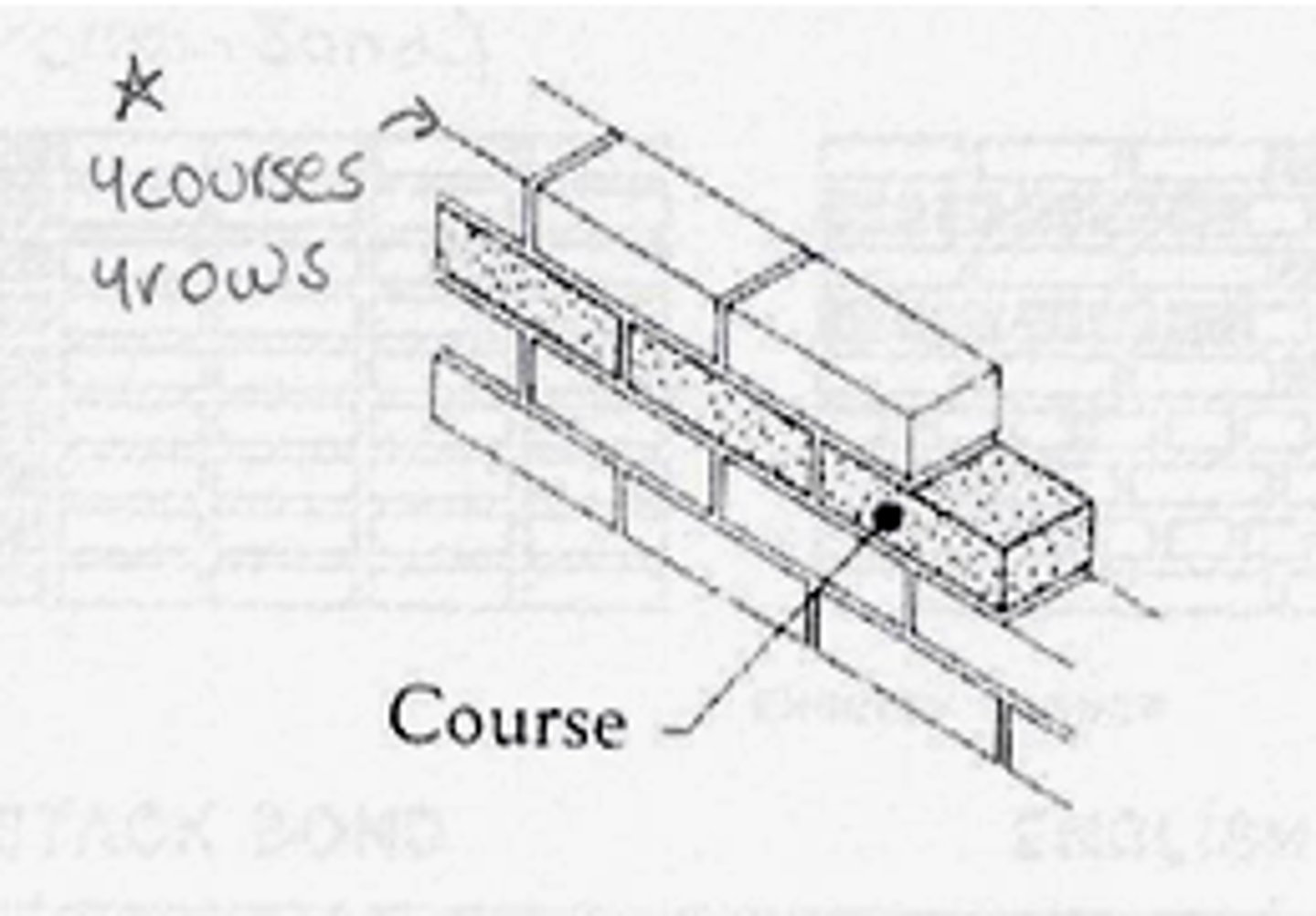
Course
A continuous layer of bricks, stones, or other masonry units.
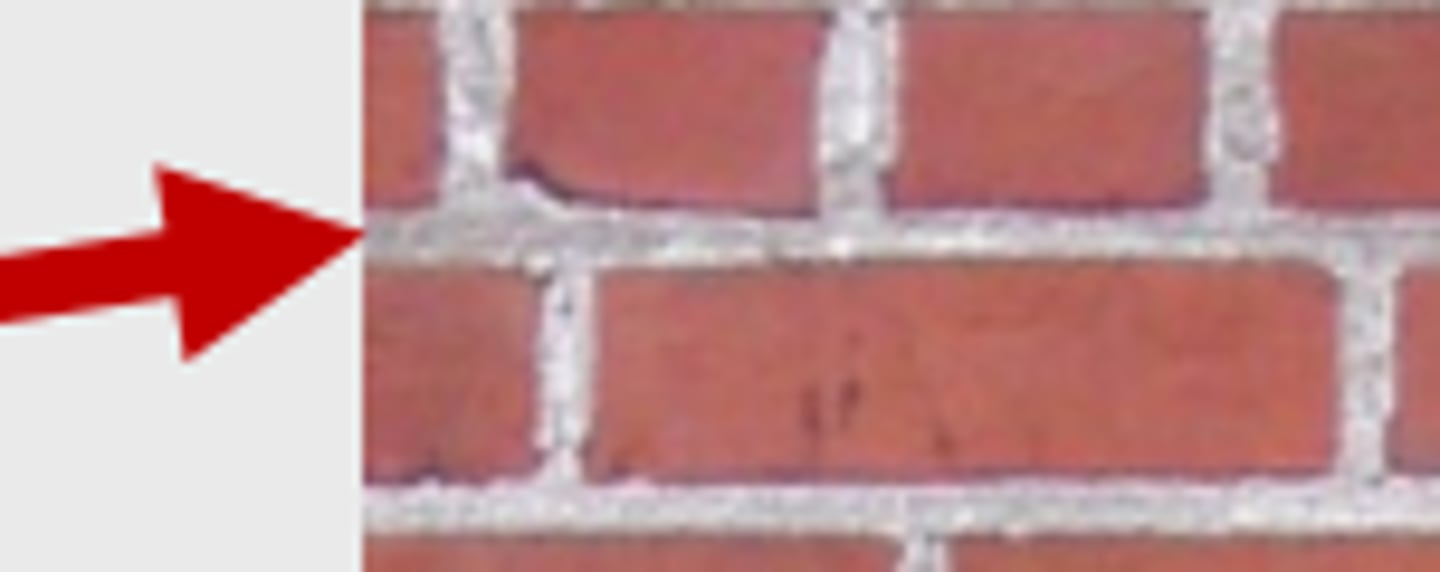
Bed
The horizontal surfaces on which the stones or bricks of walls lie in the courses.

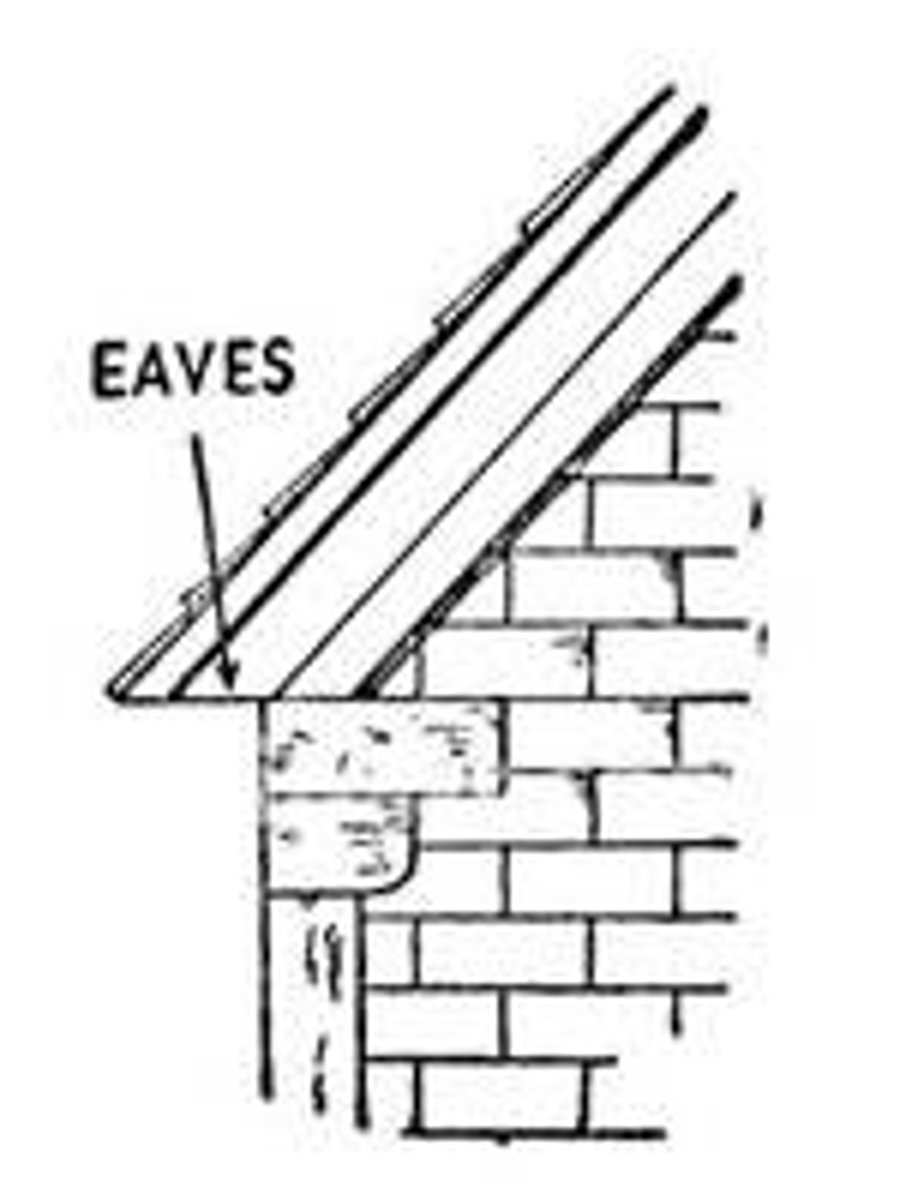
Eave
The lower edge of a sloping roof; that part of a roof of a building which projects beyond the wall.
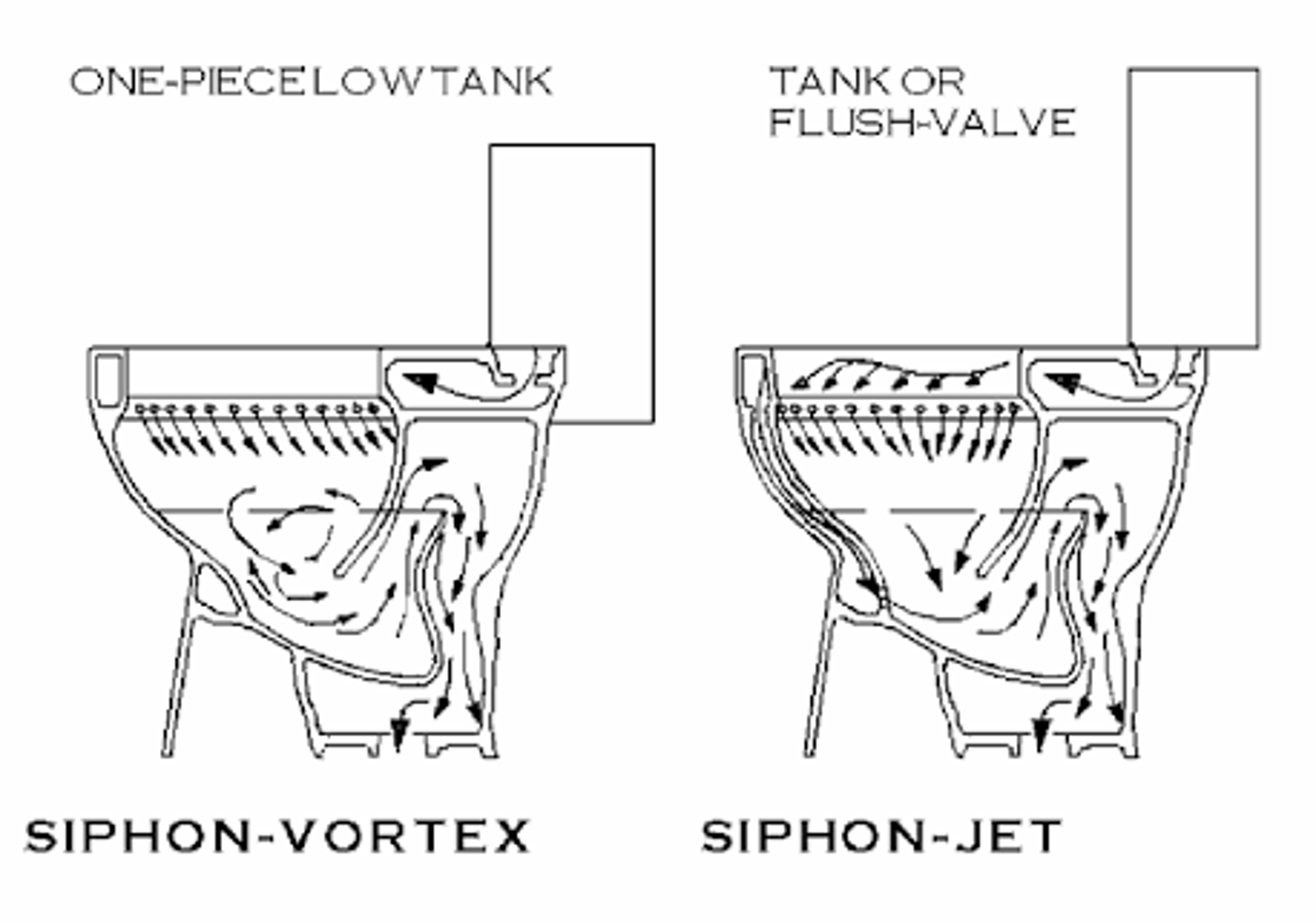
Siphon Vortex
This type of toilet bowl develops its flushing action through the water entering through diagonal holes around the rim which creates a swirling action.
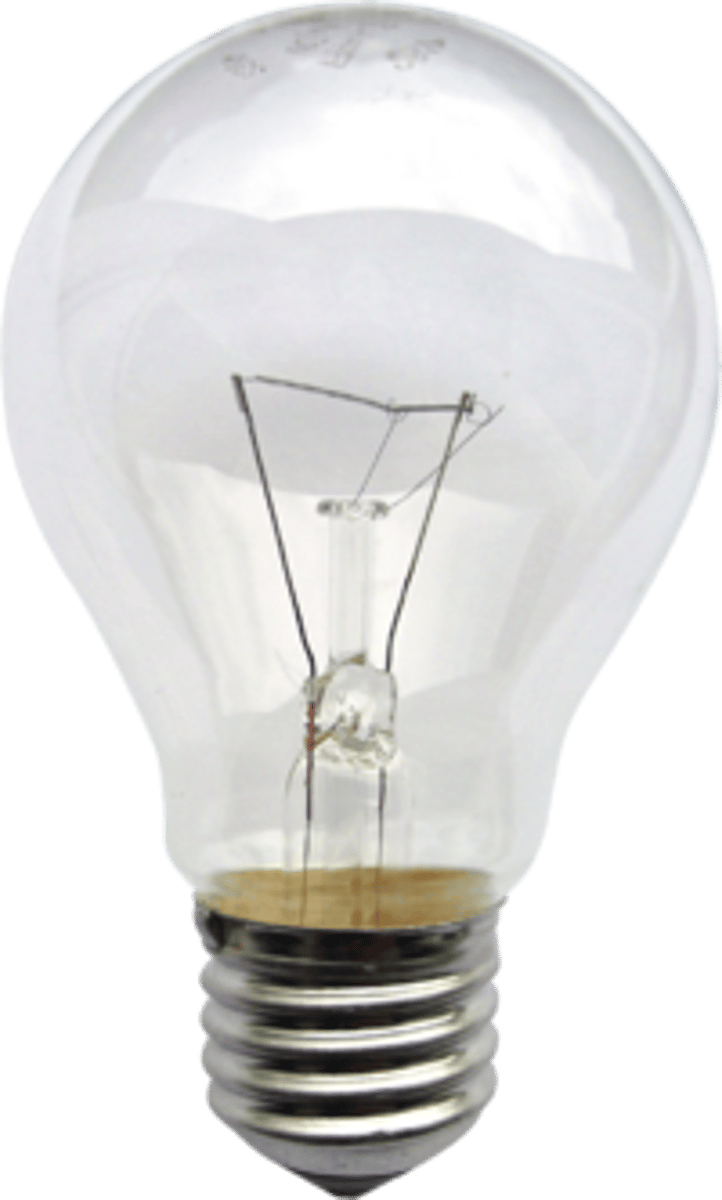
Incandescent Lamp
A lamp in which a filament gives off light when heated by an electric current.

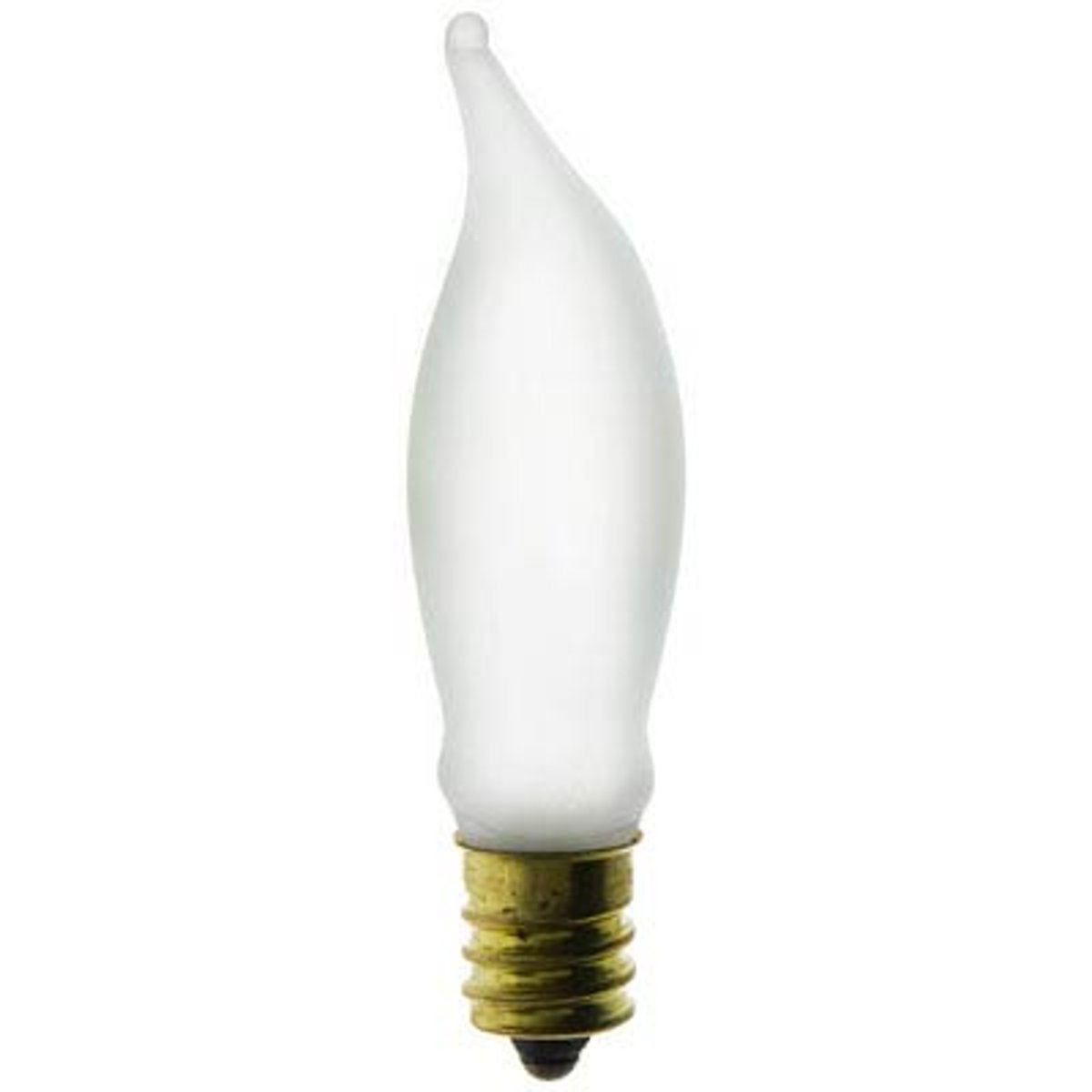
CA bulb
A candle-shaped bulb for low-wattage, decorative incandescent lamps.

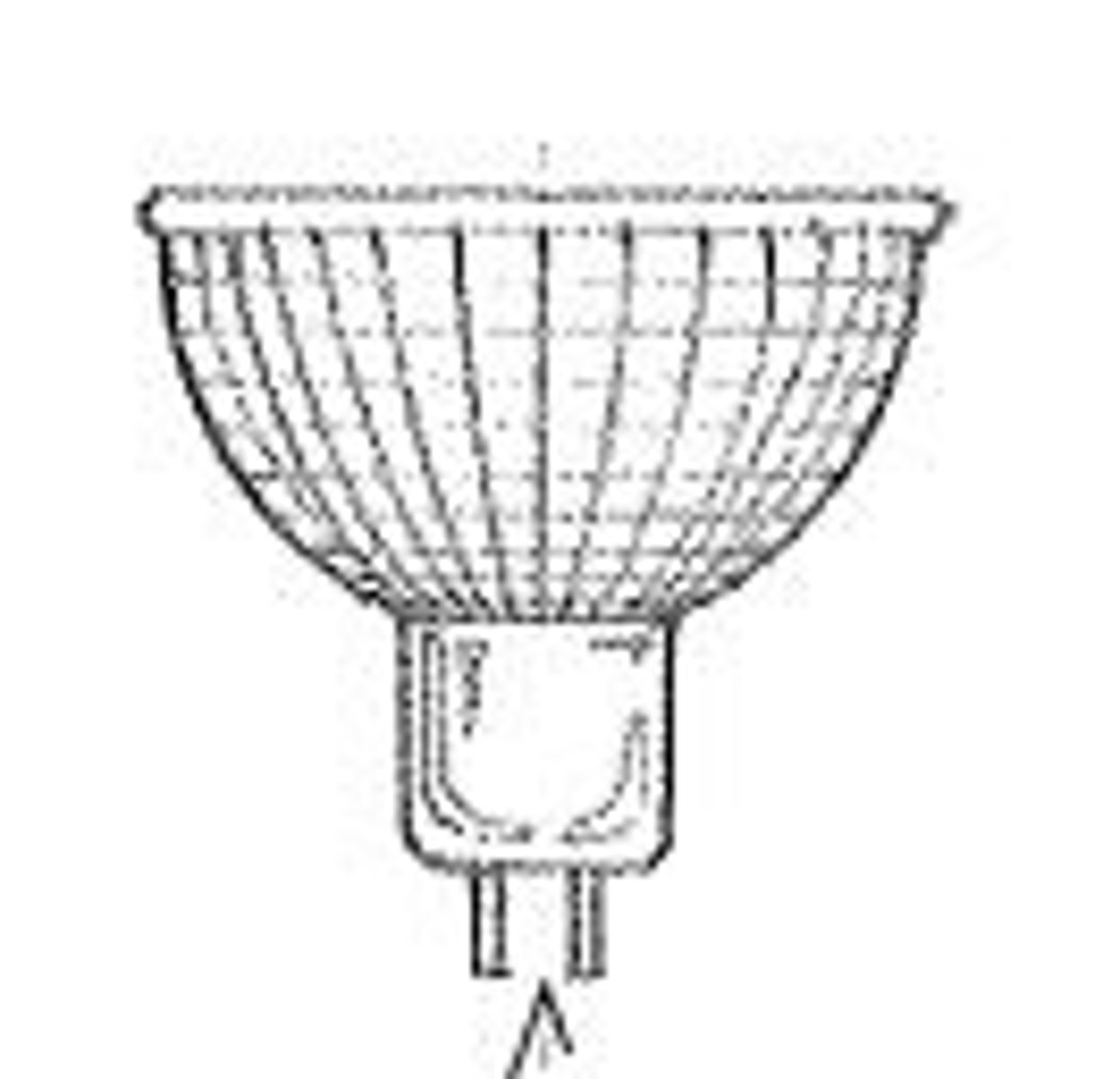
MR bulb
A multifaceted reflector bulb for tungsten-halogen lamps, having highly polished reflectors arranged in discrete segments to provide the desired beam spread.
1) Produces light by the discharge of electricity between electrodes in a gas-filled glass enclosure.
2) Uses starter and ballast to function properly.
3) More efficient and have a longer life than incandescent lamps.
4) Available in variety of colors (warm white, cool white, day light).
Characteristics of Fluorescent Lamps
Bolts
Threaded metal pins or rods, usually having a head at one end, designed to be inserted through holes in assembled parts and secured by a mating nut.

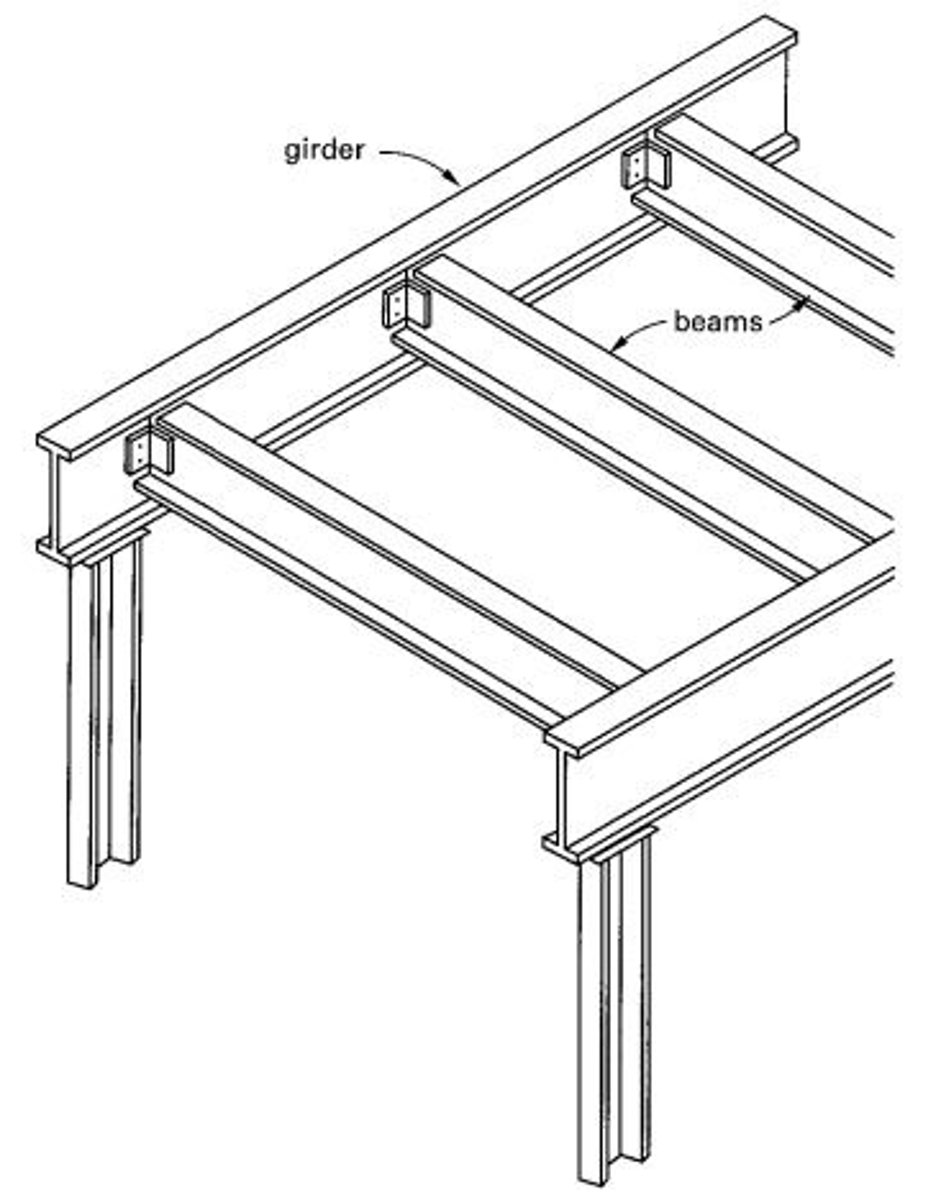
Girder
A term applied to a beam that supports one or more smaller beams.
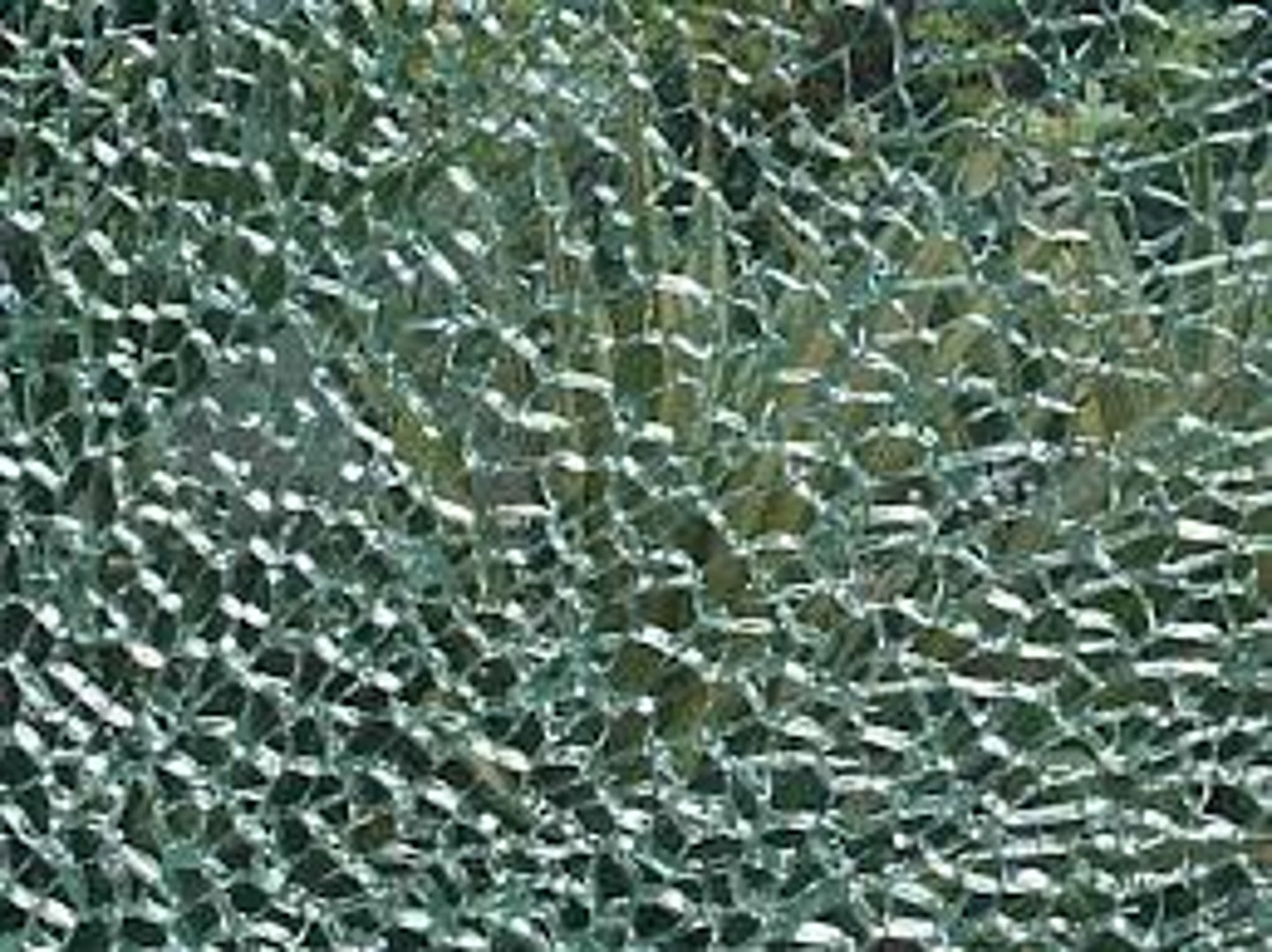
Tempered Glass
A type of annealed glass that is reheated to just below the softening point and then rapidly cooled induce compressive stresses in the surfaces and edges of the glass and tensile stresses in the interior. This has three to five times the resistance of annealed glass to impact and thermal stresses but cannot be altered after fabrication. When fractured, it breaks into relatively harmless pebble-sized particles.

Storey
The space in a building between floor levels or between a floor and a roof above.
Water Proofing
Method of making building surfaces impervious to water.
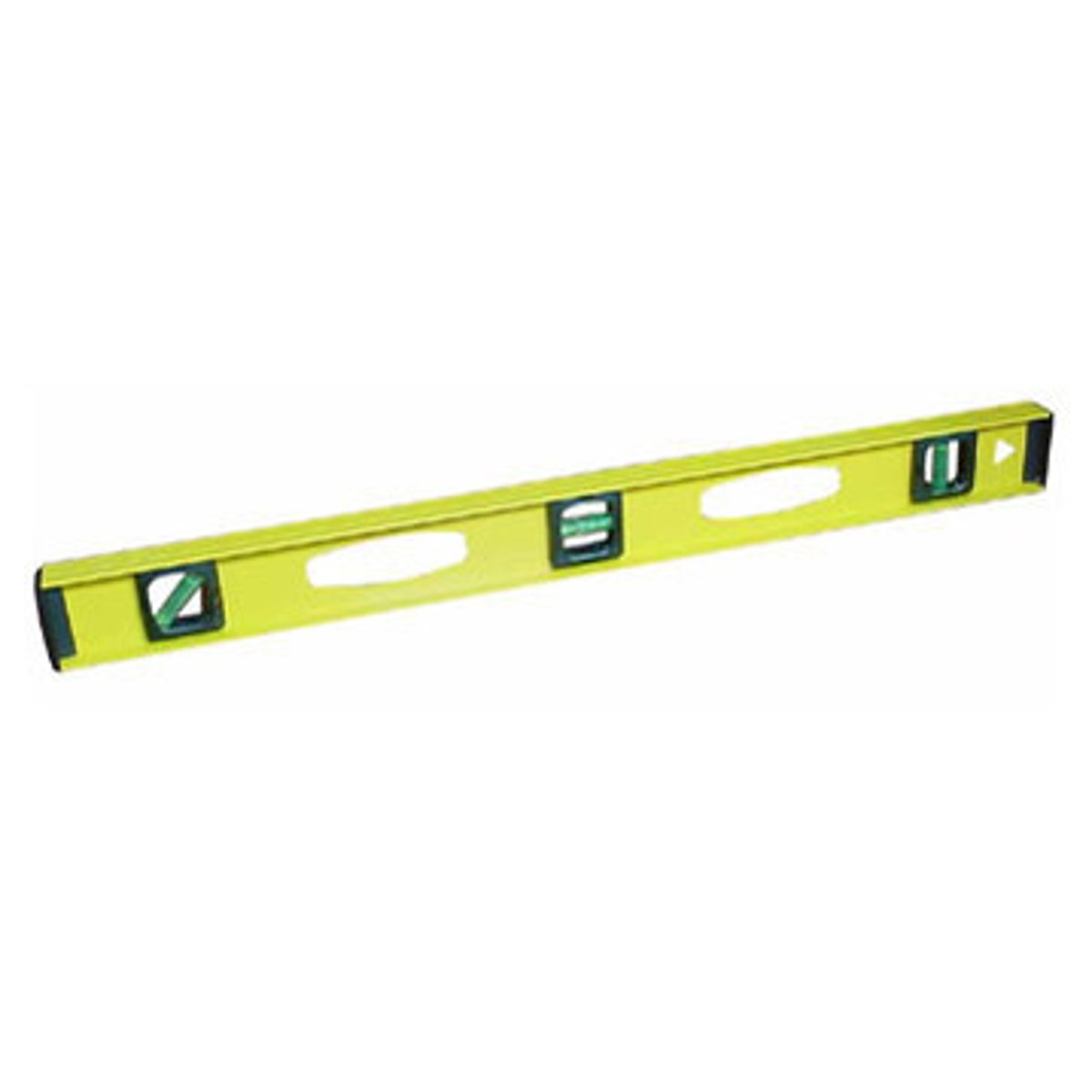
Spirit Level
A long, straight tool that contains one or more vials of liquid and used to determine if the horizontal or vertical is exact.

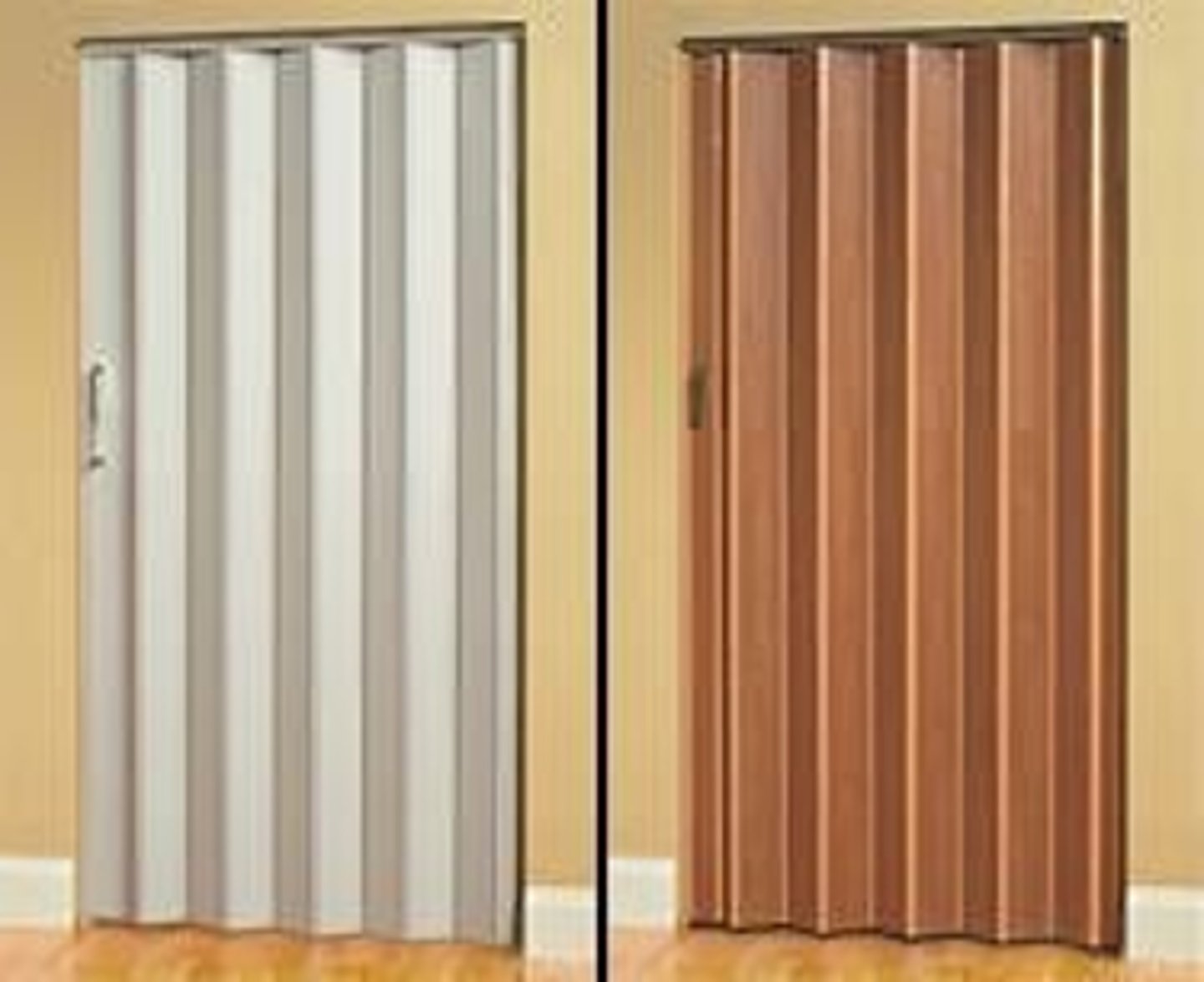
Accordion Door
A hinged door consisting of a system of panels which are hung from an overhead track. When the door is open, the faces of the panels close flat against each other; when the door is closed, the edges of adjacent panels butt against (or interlock with) each other to form a solid barrier.

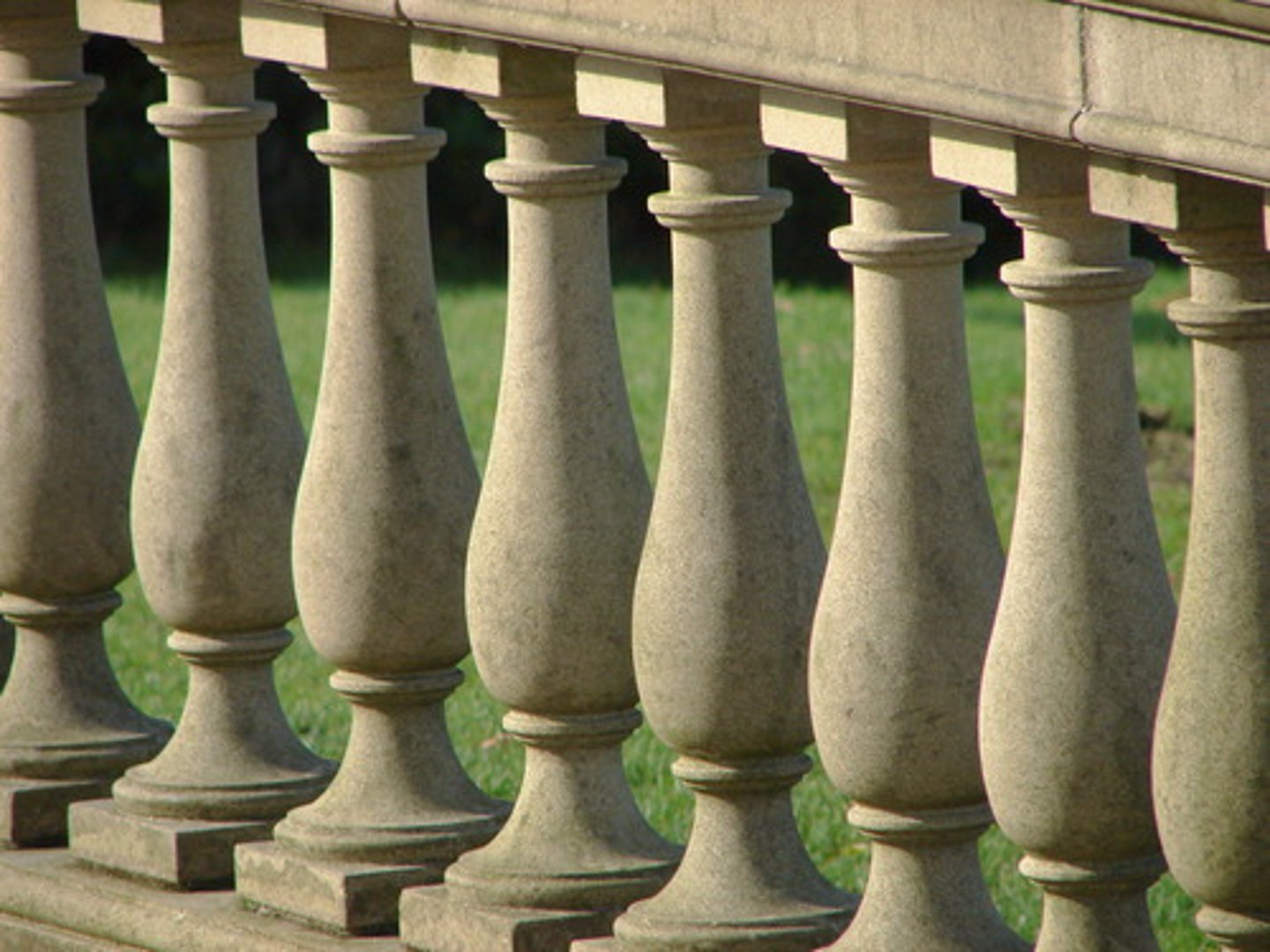
Baluster/Banister
One of a number of short vertical members, often circular in section, used to support a stair handrail or a coping.

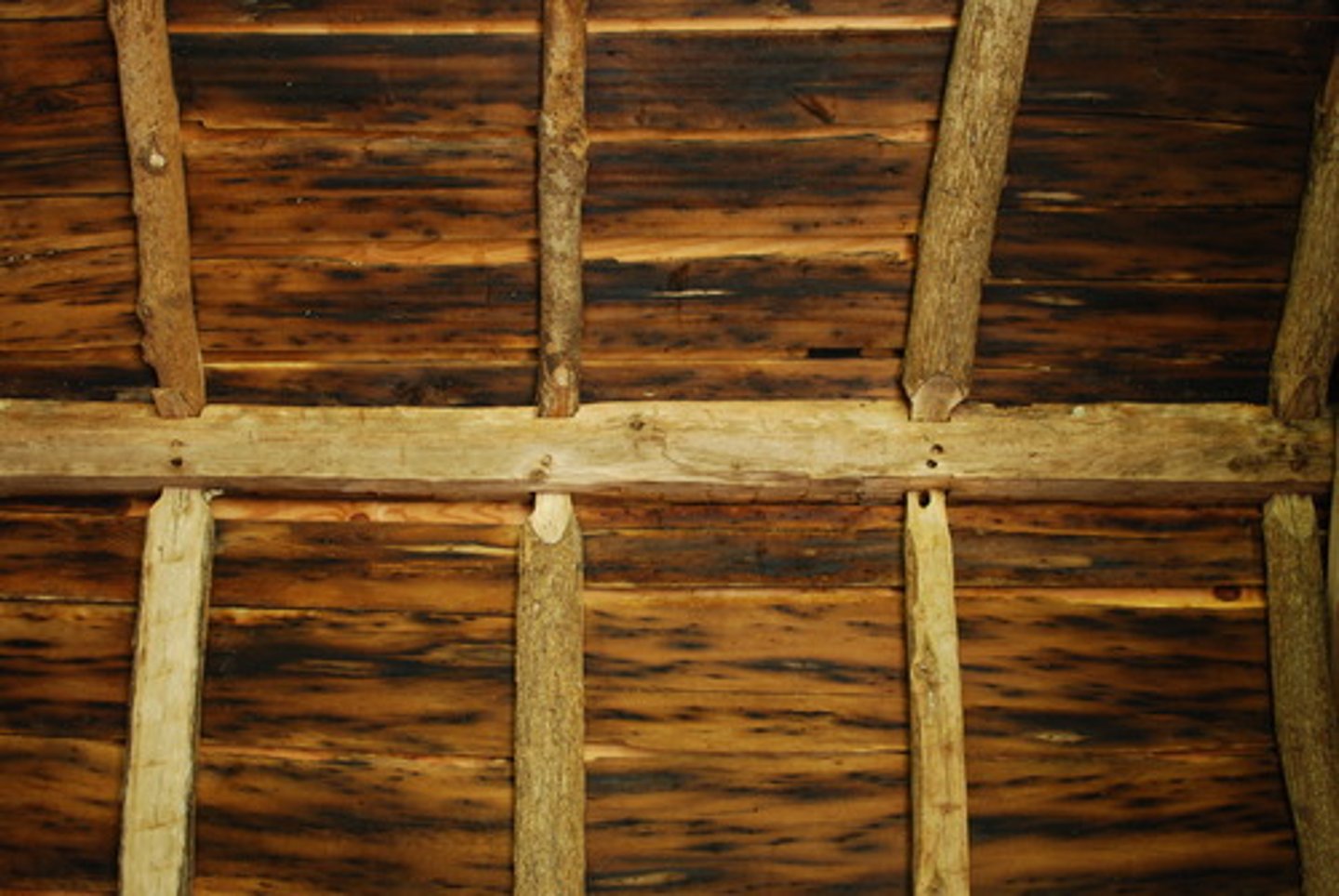
Beam
A structural member whose prime function is to carry transverse loads, as a joist, girder, rafter, or purlin.

Escalator
A power driven stairway consisting of steps attached to a continuously circulating belt, used for moving passenger up and down between floors.

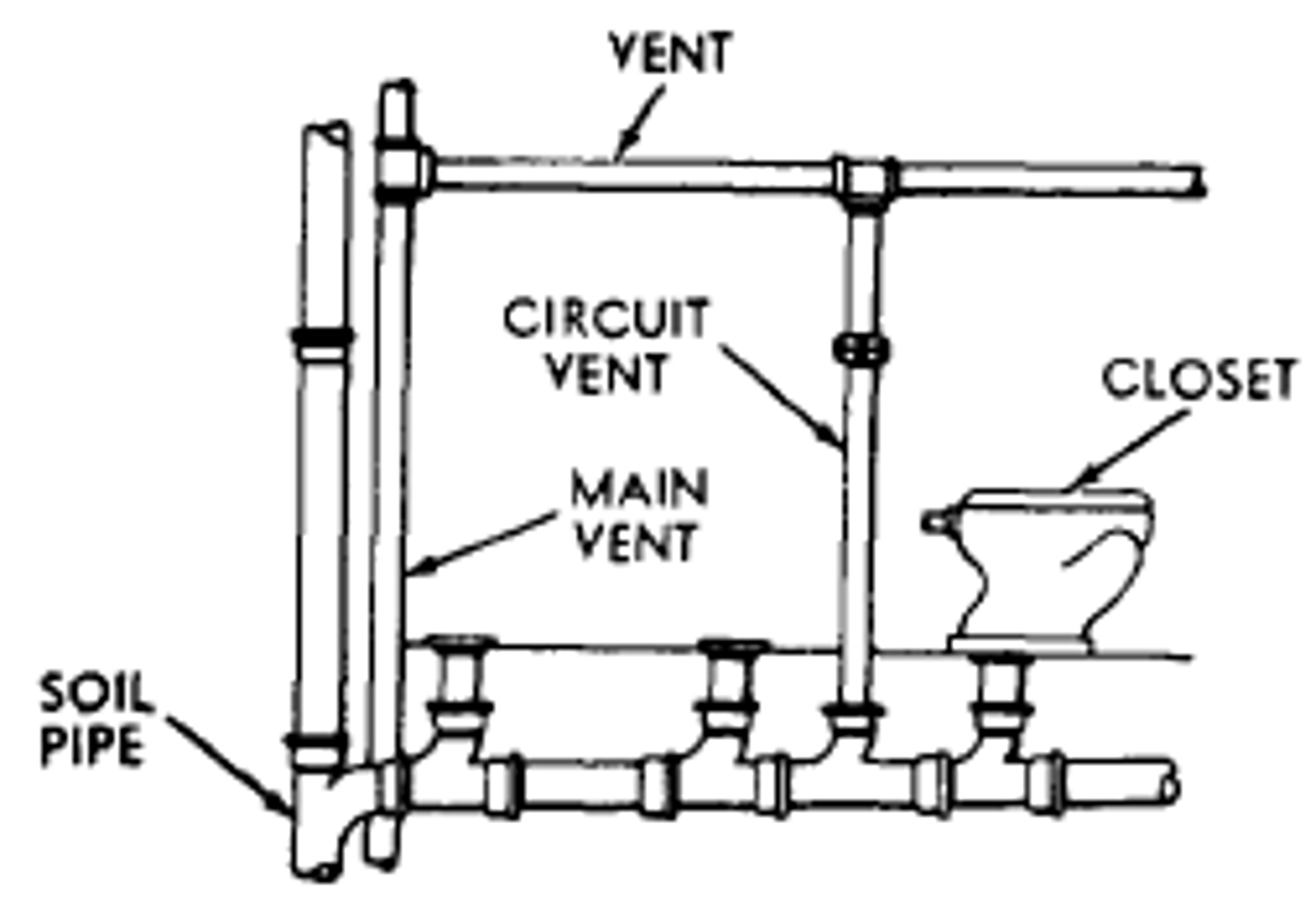
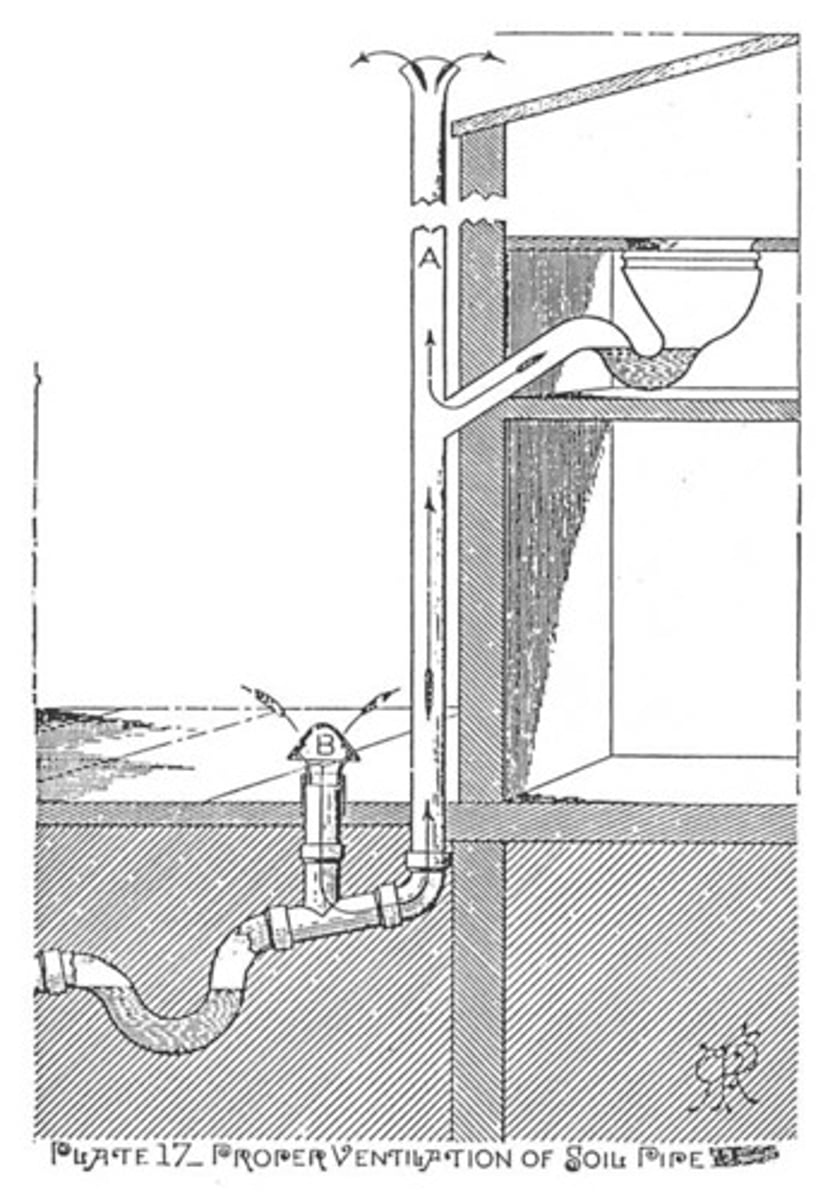
Vent Pipe
Any pipe in the plumbing system provided to ventilate a house drainage system and to prevent trap siphonage and back pressure.
Circuit Vent
A vent used in a battery of plumbing fixtures where the vent is installed in-front of the last fixture of the battery.
Water distribution pipes
The general term for the hot and cold water pipes containing potable water supplying the different plumbing fixtures.
Soil Pipe
A pipe in the plumbing system, which conveys the discharge of liquid and solid wastes with or without discharge from other fixtures to the house drains.
Dormer
A projecting structure built out from a sloping roof, usually housing a vertical window or ventilating louver.

Board foot
A unit quantity for lumber equal to the volume of a piece whose nominal dimensions are 12 inches square and 1 inch.
Concrete
An artificial, stone like building material made by mixing cement and various mineral aggregates with sufficient water to cause the cement to set and bind the entire mass.
Framing Square
A layout tool that is used to measure 90-degree angles at the corners of framework and joints. They can also be employed to determine cutting angles on dimension lumber.

Hack Saw
A type of saw used to cut metals.

Service Entrance
The point of delivery of electricity to a building by a public utility company.
Terrazzo
A mixture of cement, marble chip aggregates and water laid as a topping or as a wall finish, and ground to a fine, smooth surface. It is used for floor and bases where durability, resistance to wear, and minimal maintenance are necessary. It is available either in precast form e.g. tile, or cast-in-place form, with either a smoothly polished or non-slip surface. For non-slip surfaces, abrasive granules are added to the mixture.

Battery of fixtures
Term applied to the interconnection of the same fixtures in one soil or waste branch with one branch vent.
Circuit Breaker
An over-current protective device designed to function as a switch, or it can be manually tripped and thus, act as a circuit switch. It breaks a circuit with an automatic tripping device without injury to itself. It is not self-destructive on operation, as the fuse is, and it can be reset after tripping by merely operating its handle.
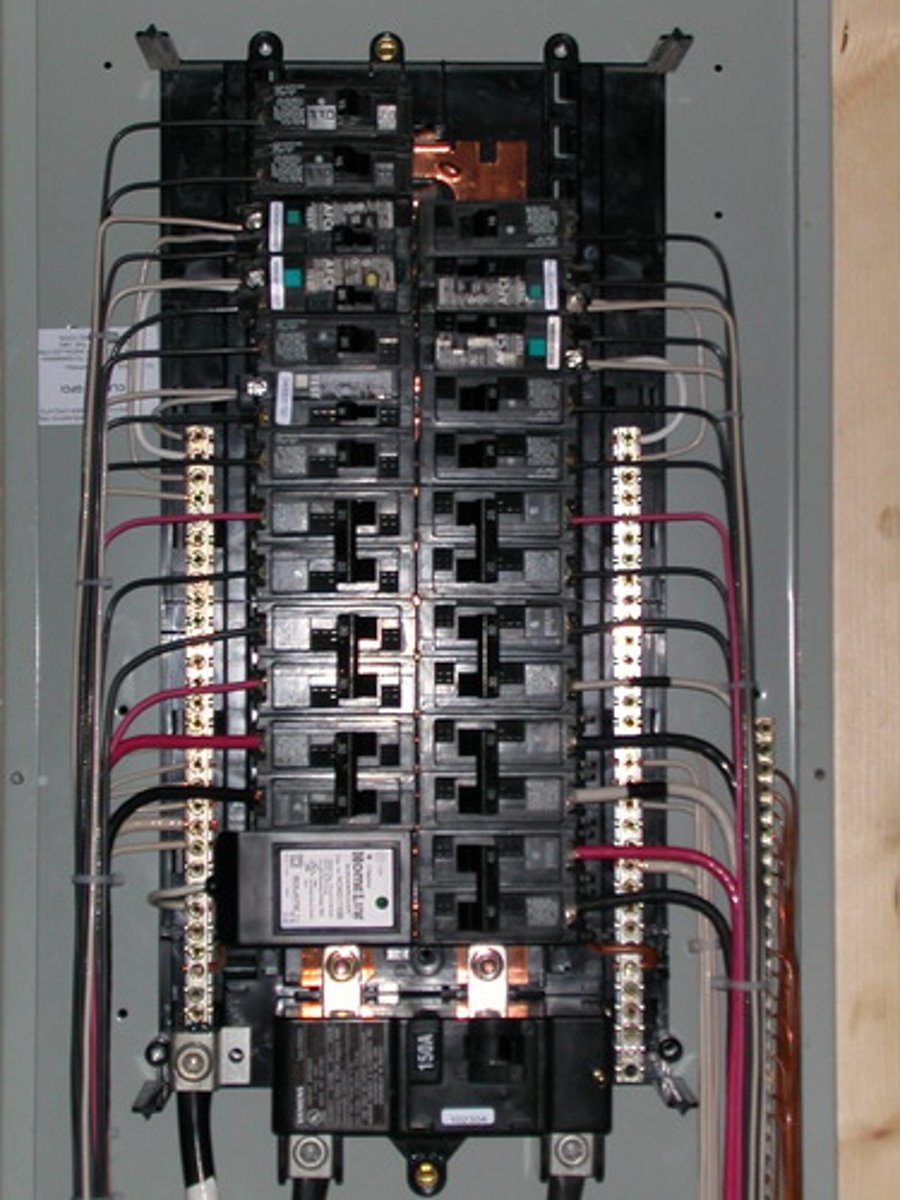
Ampacity
Conductor current carrying capacity is the maximum operating temperature that its insulation can stand continuously.
Current carrying capacity.
Foundation
The lowest division of a building or other construction, partly or wholly below the surface of the ground, designated to support and anchor thee superstructure and transmit its loads directly to the earth.
Isolated Footing
A single spread footing supporting a freestanding column or pier.
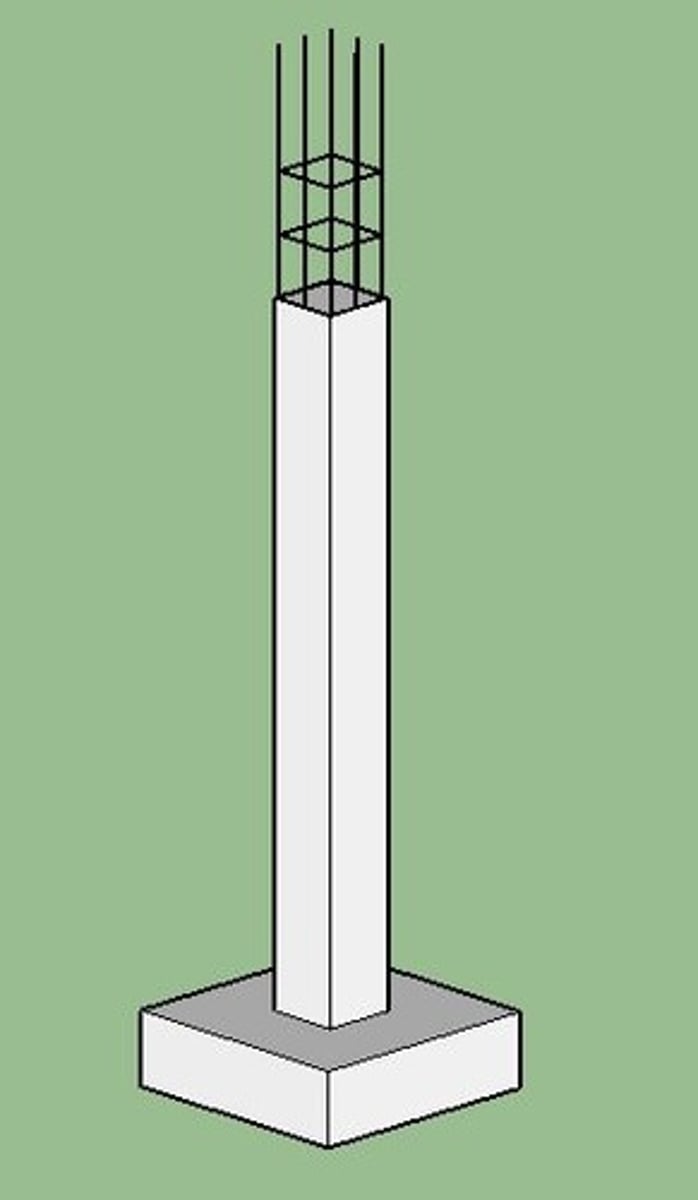
Column
A rigid, relatively slender structural member designed primarily to support axial, compressive loads applied at the member ends.
Girder
A large, principal beam designed to support concentrated loads at isolated points along its length.
Truss
A structural frame based on the geometric rigidity of the triangle and composed of linear members subject only to axial tension or compression, used to support the roof of a building.
Machine-Room Less Elevator
Utilize a gearless traction machine located in the hoist way.
Four-way switch
When you want to control a light fixture from 3 points, you will need to install a ____.
Winder
Refers to the tapered treads used in circular and spiral stairs. Quarter-turn and half-turn stairways also use this to conserve space when changing directions.
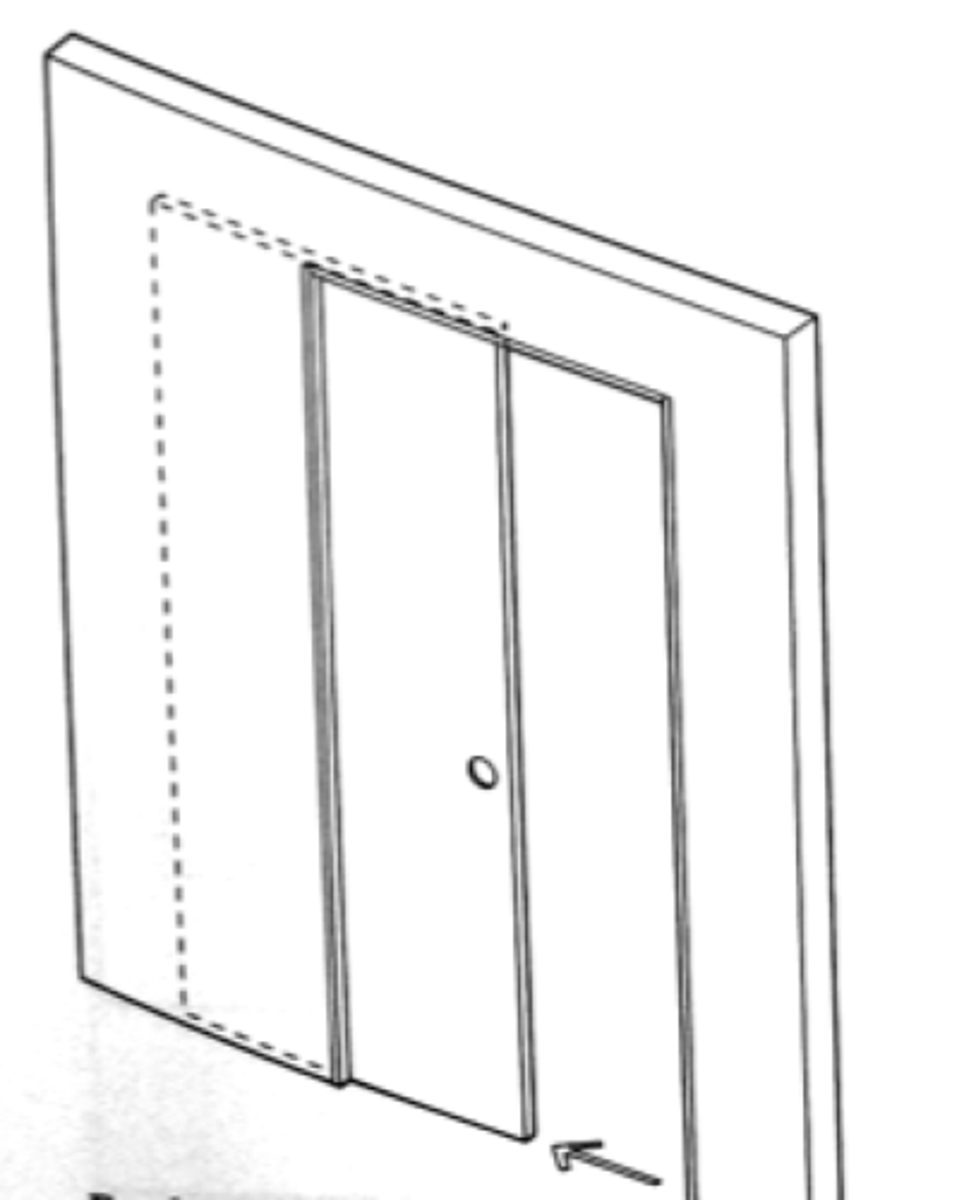
Pocket Sliding
Kind of door that is hung on track, and slides within the width of the wall.
Glazing
Panes or sheets of glass set in frame of a window.
Zaguan
It would have a vapor barrier (damp proofing) should it be constructed today.
Verandillas
Where would you connect the handrails so to that it can be supported?
Lock Set
Assembly of parts making up a complete locking system including knobs, plates, and locking mechanism.
Oil or Spring Buffers
These are placed at the bottom of the elevator pit, not to stop a falling car, but to bring it to a partially cushion stop if the car should overshoot the lower terminal.
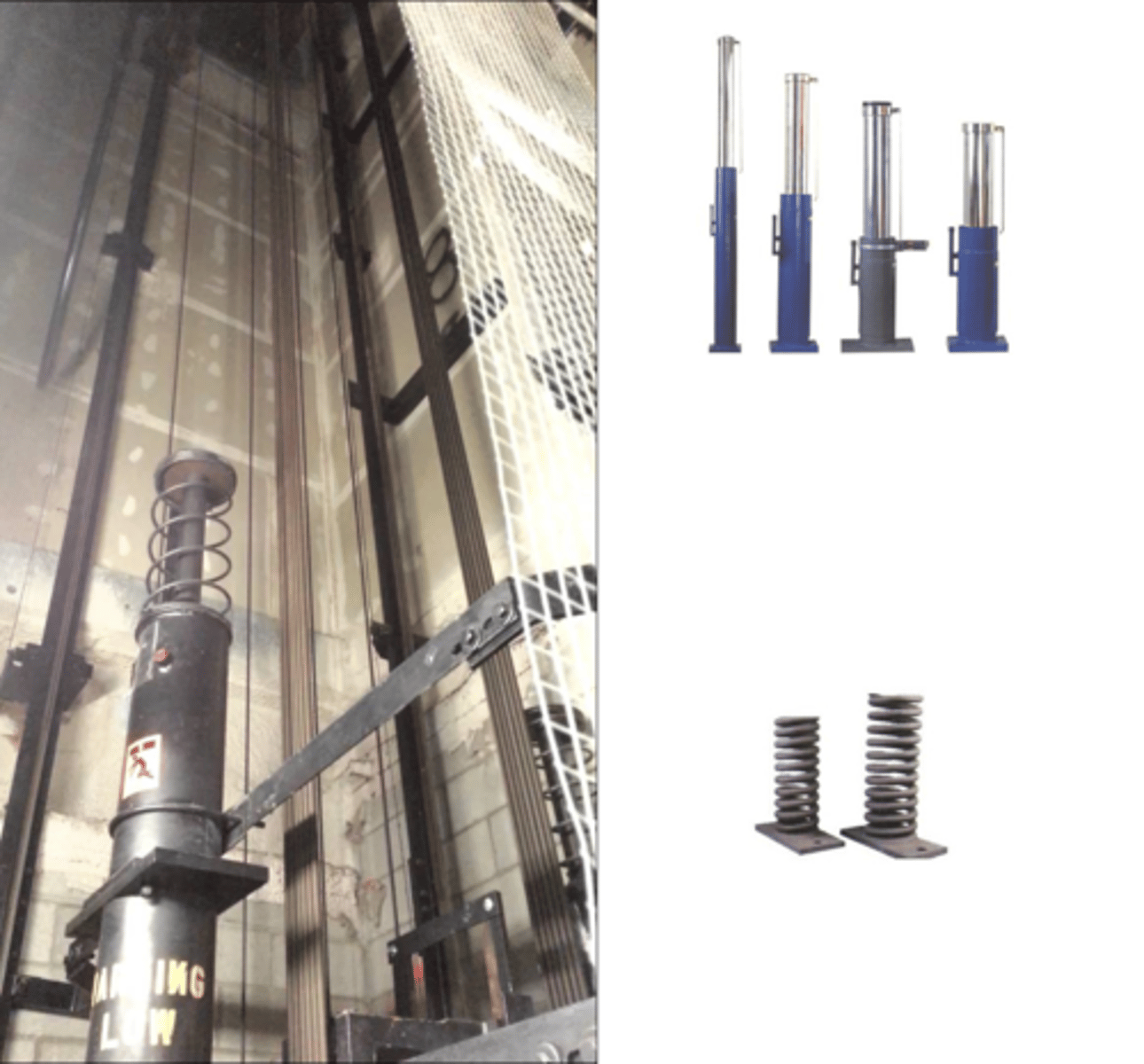
Buffer
A piston or spring device for absorbing the impact of a descending elevator car or counterweight at the extreme lower limit of travel.
Tracks
Steel angles attached to the truss on which the steps rollers are guided thus controlling the motion of the steps in an escalator.
Driving Machine
This provides the motive power for the escalator unit.
Extension Bolt
A bolt flush with the face or edge of a door.
Escutcheon
Protective plate surrounding the key hole of a door or a light switch.
Panic Bolt
Door opening mechanism to put in a fire exit door.
Astragals
Vertical members used between double doors to seal the opening, act as a door stop, or provide extra security when the doors are closed.
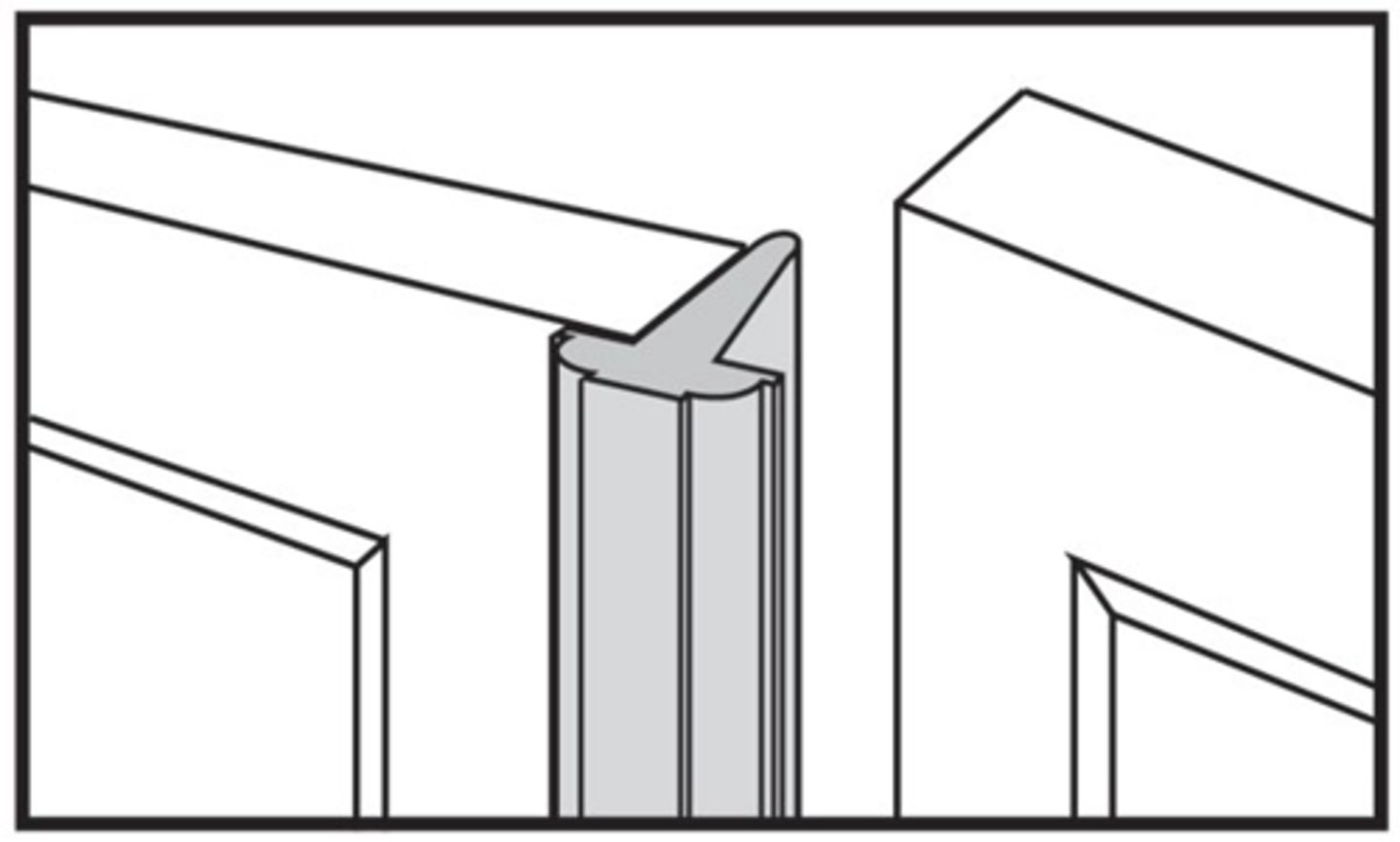
Miter
Made by cutting the two ends at angles complementary to each other, usually 45deg. And then buffing them together.
Bridging
A brace or system of braces placed between joist to stiffen them, to hold them in place and to help distribute the load.
Plaster
A composition of gypsum, or lime, water, sand, and sometimes hair or other fiber in a pasty form to the surfaces of walls or ceilings in a plastic state and allowed to harden and dry.