Fluid Compartments and Renal Overview
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
what are 4 things the kidneys regulate?
1. waste removal (through urine)
2. water regulation
3. ion regulation
4. acid-base balance
____% of the human body is water
60
blood is ___% plasma and ___% cells
60, 40
sodium is (low/high) in extracellular fluid while potassium is (low/high)
high, low
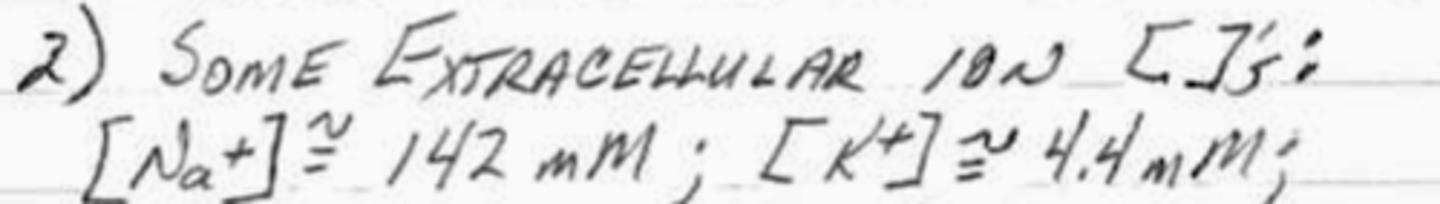
what is the total extracellular concentration of HCO₃⁻ in the body? what is the total osmolarity?
24 mM; 300 mOsm
what are 4 steps of estimating body fluid compartments by volume dilution?
1. select an appropriate indicator
2. inject a known volume of the indicator
3. allow the indictor to distribute evenly
4. take plasma sample and determine the indicator concentration
(t/f) an indicator must be able to be measured in a fluid samples and distribute evenly through the compartments by being metabolized and then being excreted
false; the indicator should not metabolize or be excreted
what are 2 indicators that will distribute to the total body water?
1. tritum (³H₂O)
2. antipyrine
which indicator will distribute to the extracellular fluid?
inulin
what 2 indicators will distribute to the plasma?
1. albumin
2. evan's blue
how can the total volume of plasma be calculated with an indicator? how can the total volume of blood be calculated?
Vplasma = ((volume of the indicator) * [indictor])/final concentration of the indicator in the body
Vblood = Vplasma / (1-0.4)
![<p>Vplasma = ((volume of the indicator) * [indictor])/final concentration of the indicator in the body</p><p>Vblood = Vplasma / (1-0.4)</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/61c240b8-05b3-4332-b249-31e5e5ed28ee.png)
the renal arteries give rise to ______________ arteries which give rise to ______________ arteries
interlobular, arcuate
what is the function of the glomerulus in bowman's capsule?
plasma filtration
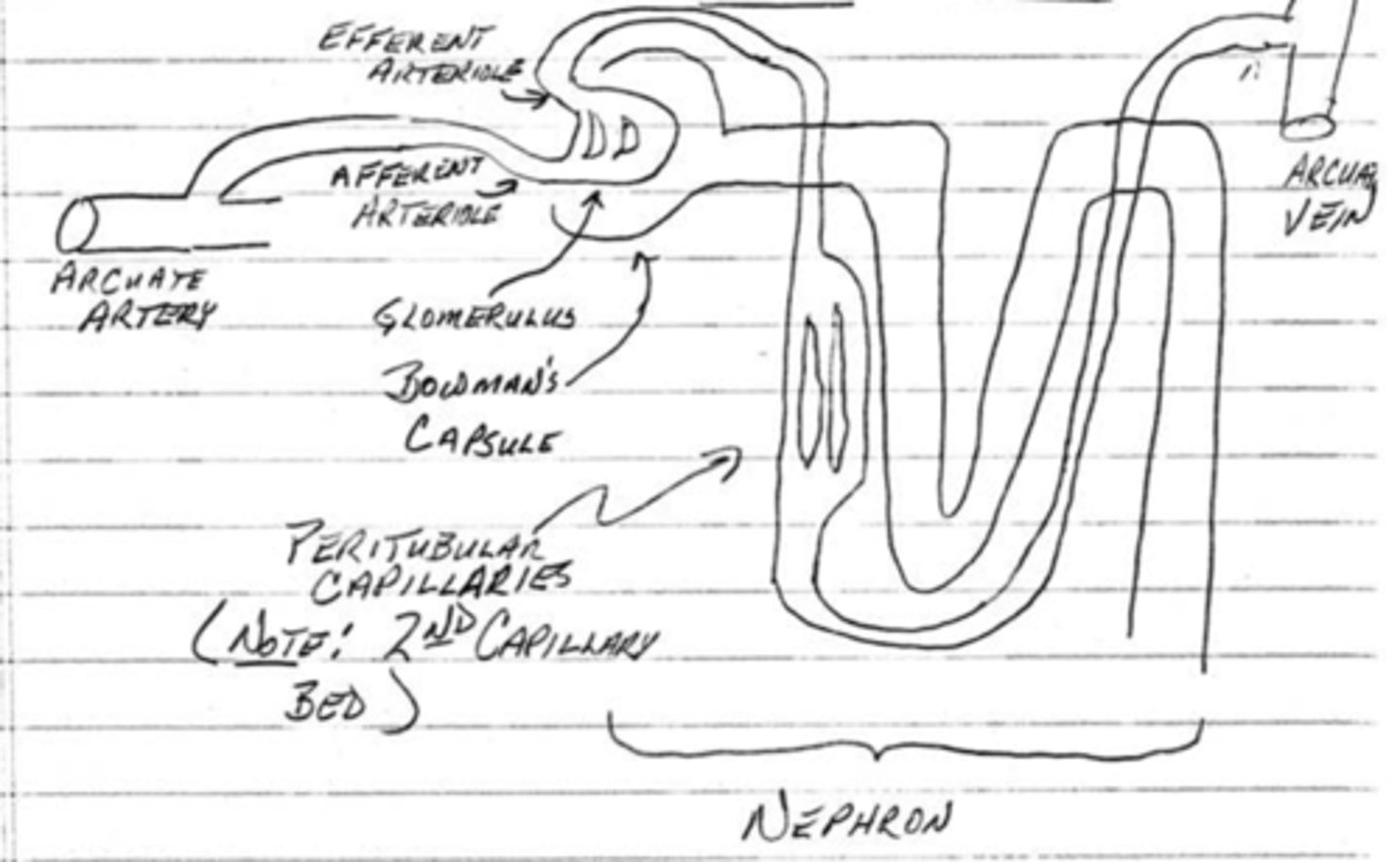
what is the function of the peritubular capillaries?
reabsorption from the nephron
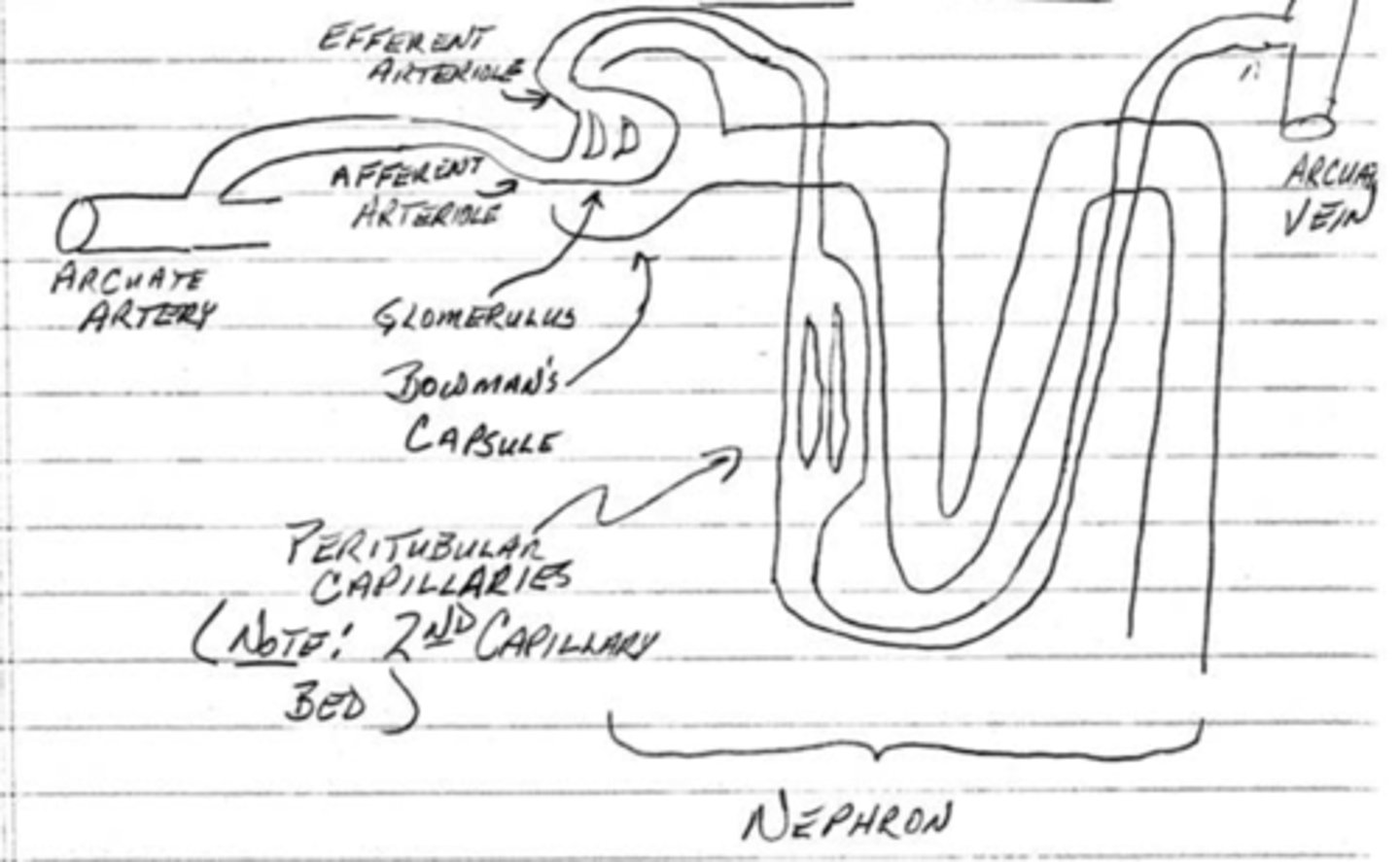
what is the function of the afferent and efferent arterioles?
regulate the capillary hydrostatic pressure in the glomerulus
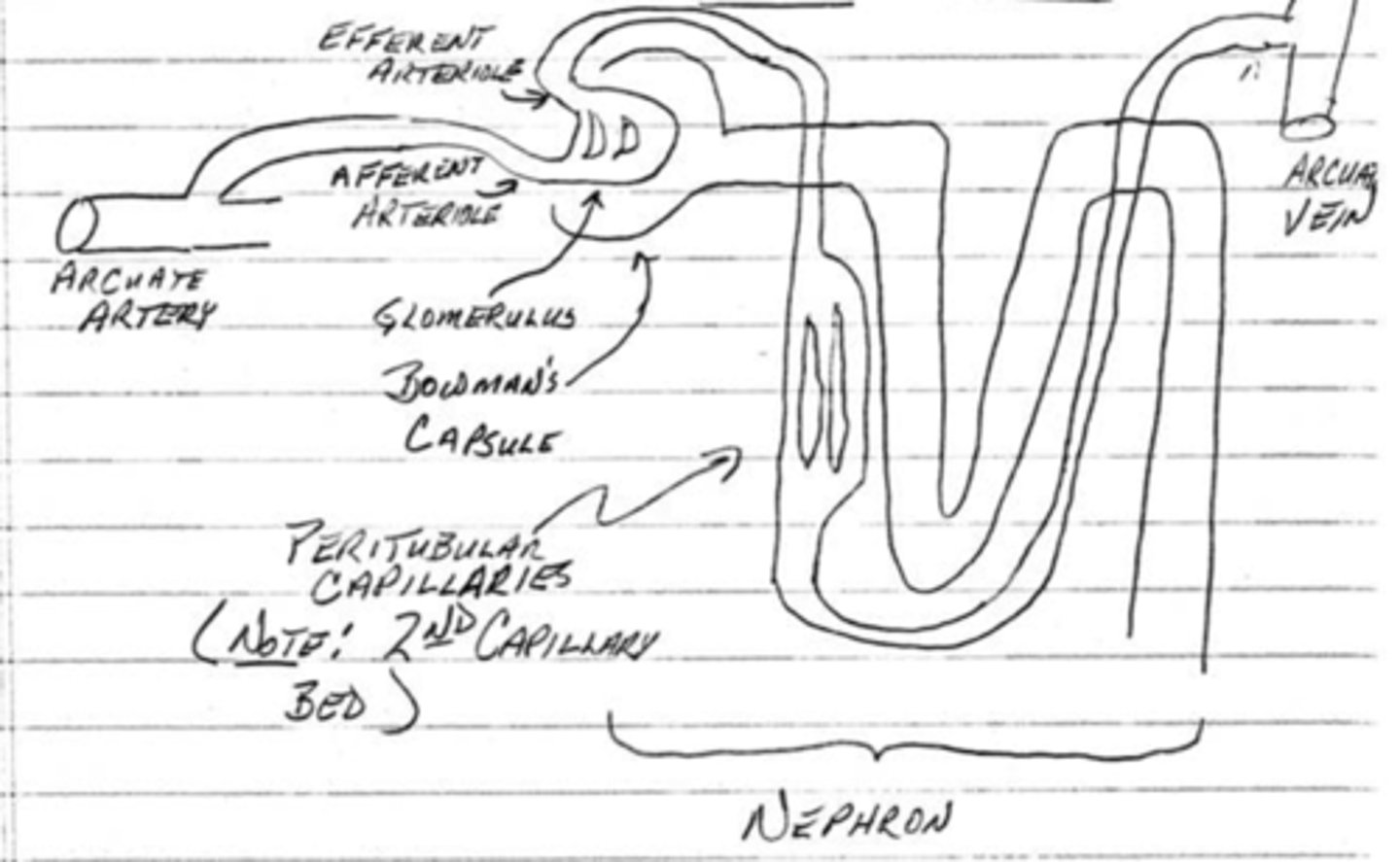
what is the filtration pressure of the arterioles? what is the reabsorption pressure of the peritubular capillaries?
60 mmHg; 13 mmHg

which component of the nephron does filtration take place?
bowman's capsule
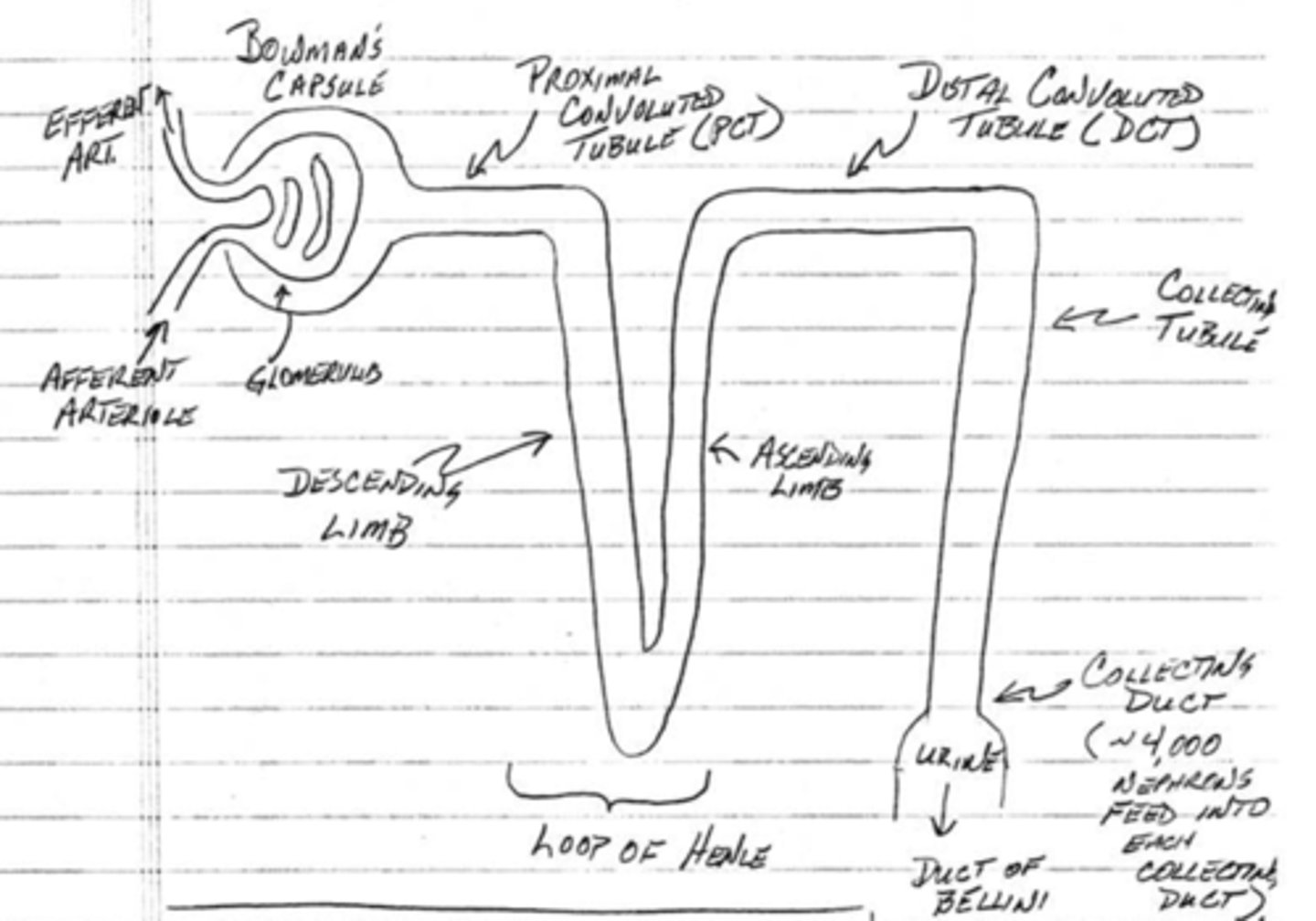
which component of the nephron does bulk reabsorption?
proximal convoluted tubule
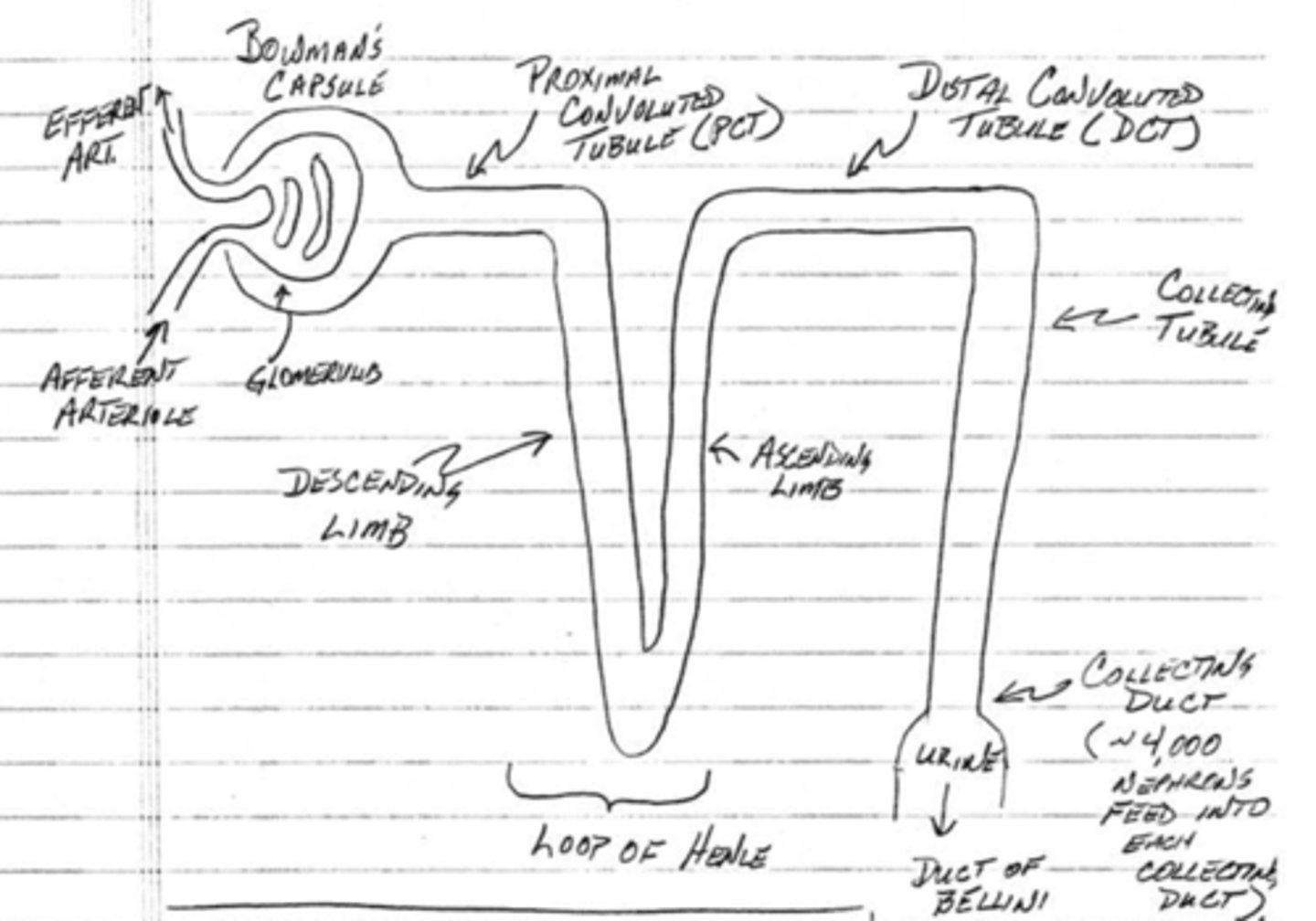
which component of the nephron produces an osmotic gradient?
loop of Henle
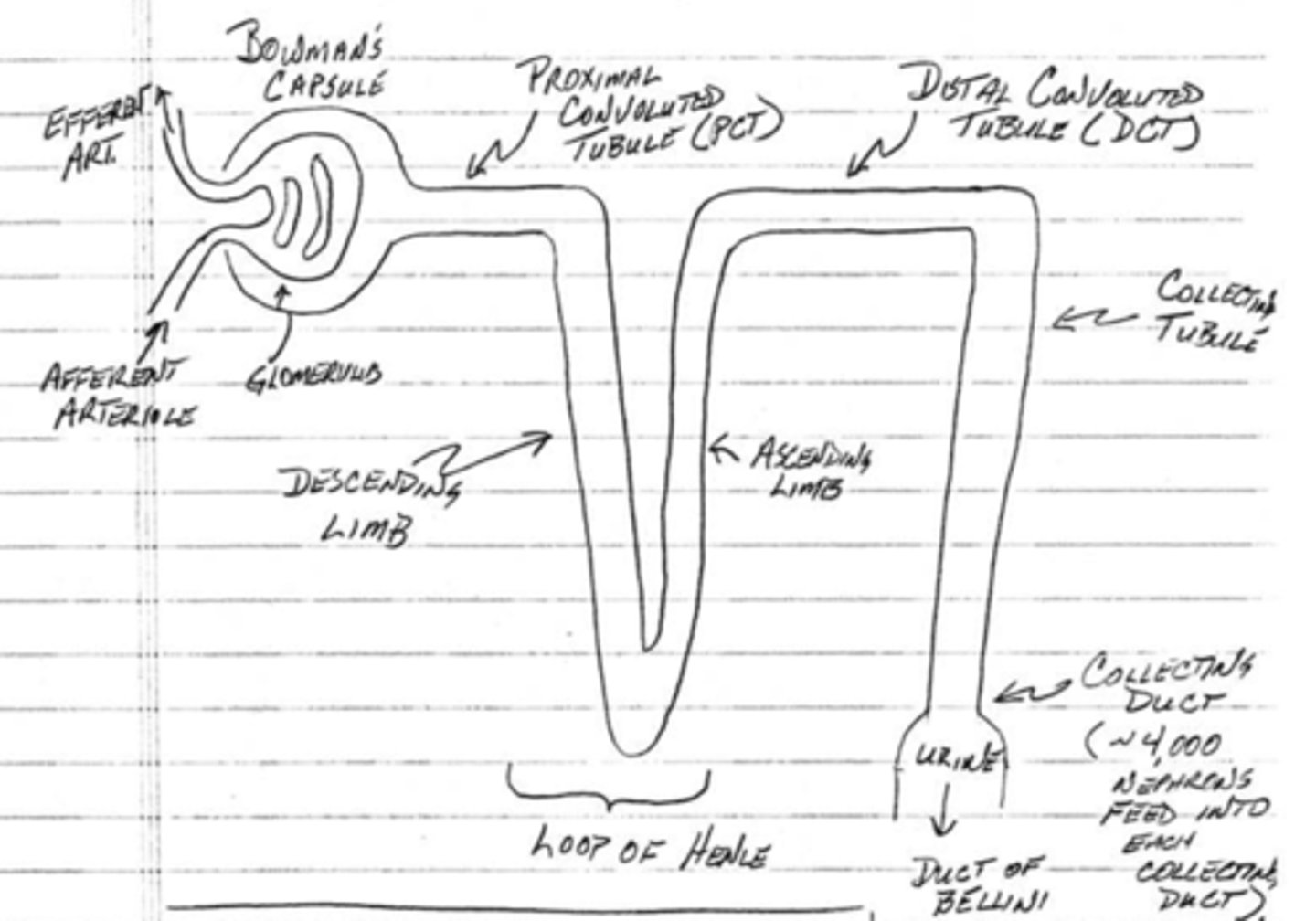
which component of the nephron fine-tunes reabsorption without water reabsorption?
distal convoluted tubule
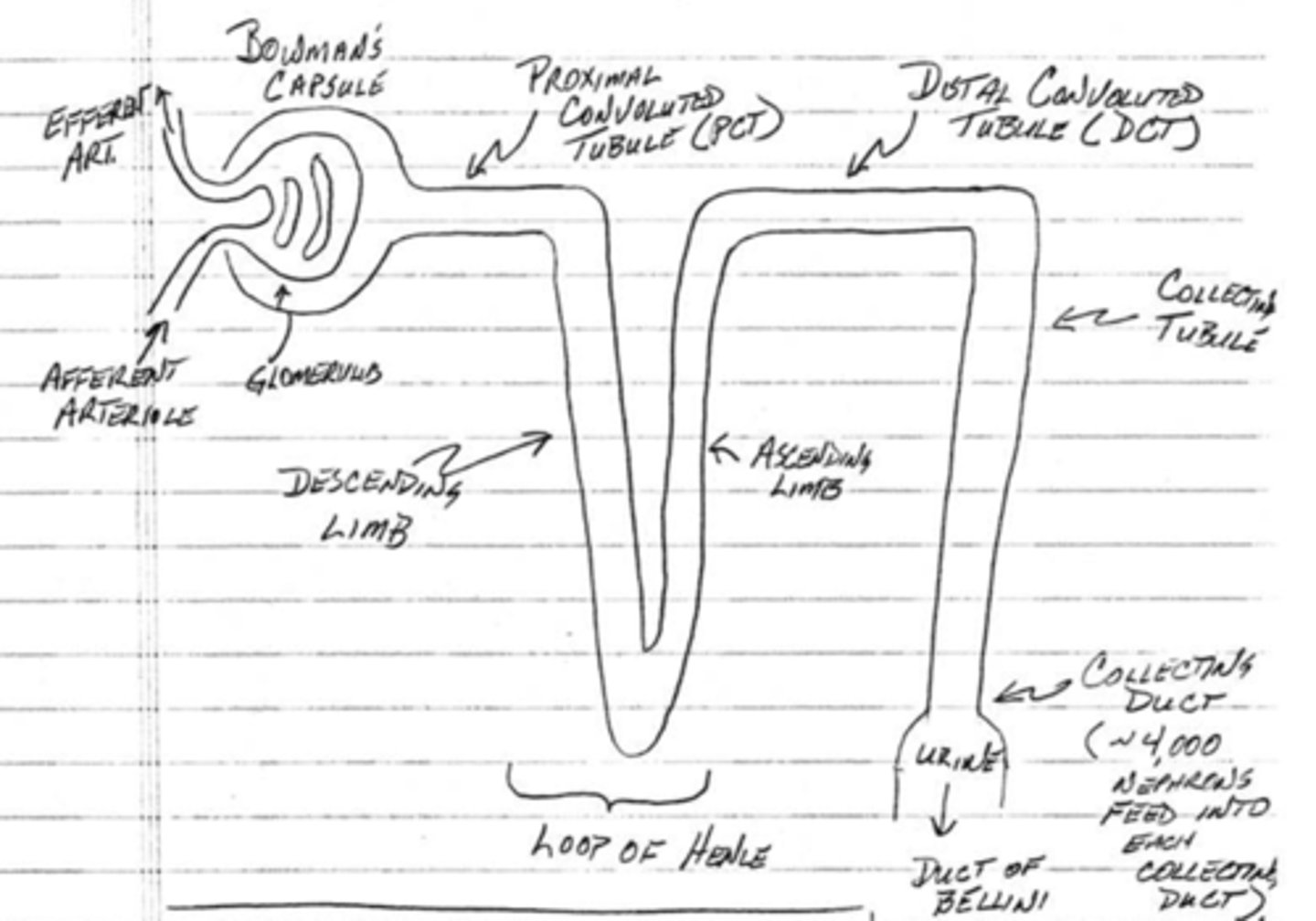
which component of the nephron fine-tunes reabsorption with water reabsorption?
collecting tubule/duct
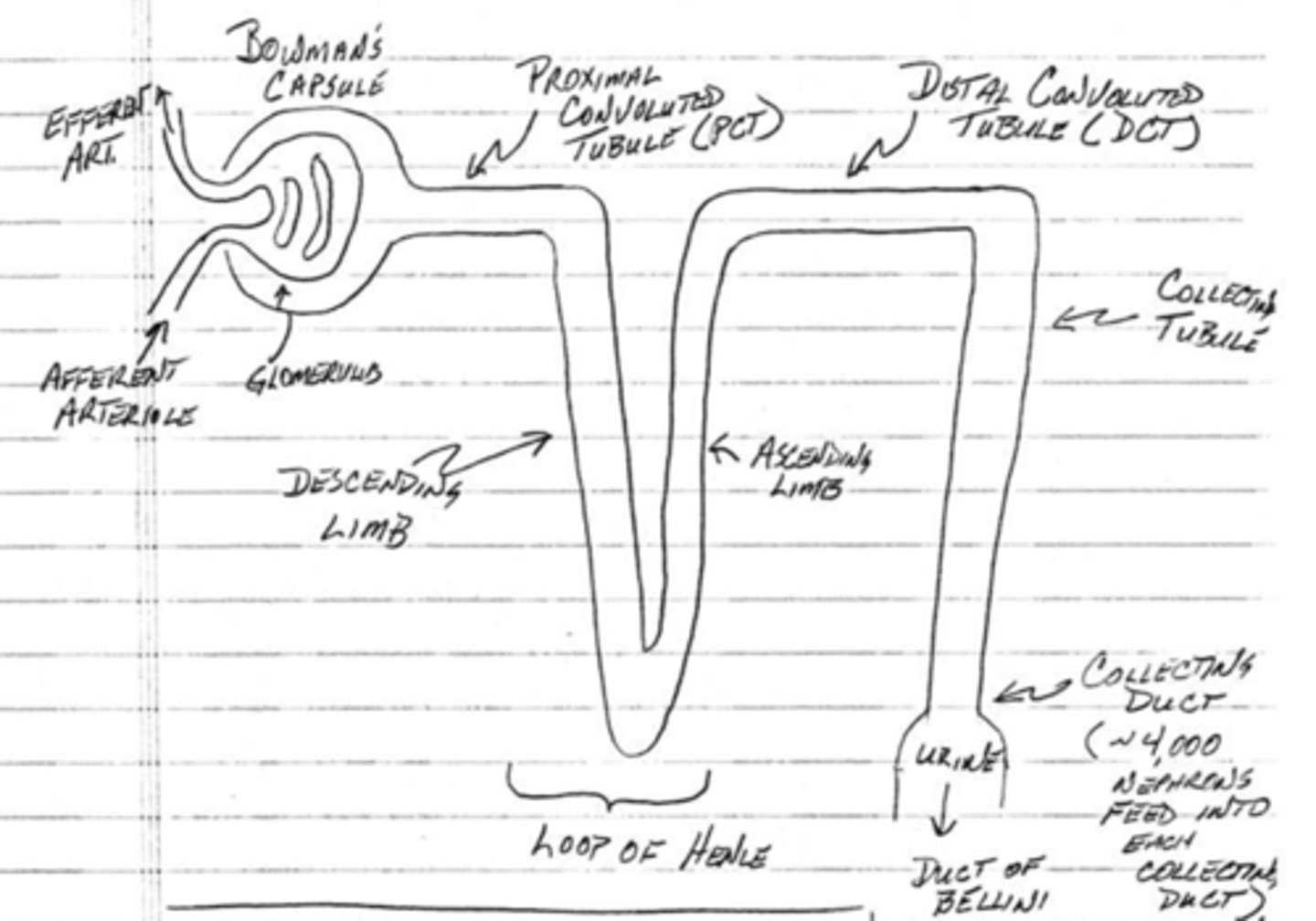
(t/f) most nephrons are cortical nephrons
true; 70-80% of nephrons are cortical nephrons
what is the purpose of a juxtamedullary nephron's long loop of Henle?
to produce an osmotic gradient that can concentrate urine
what are vasa recta?
capillary beds around the loops of henle of juxtamedullary nephrons
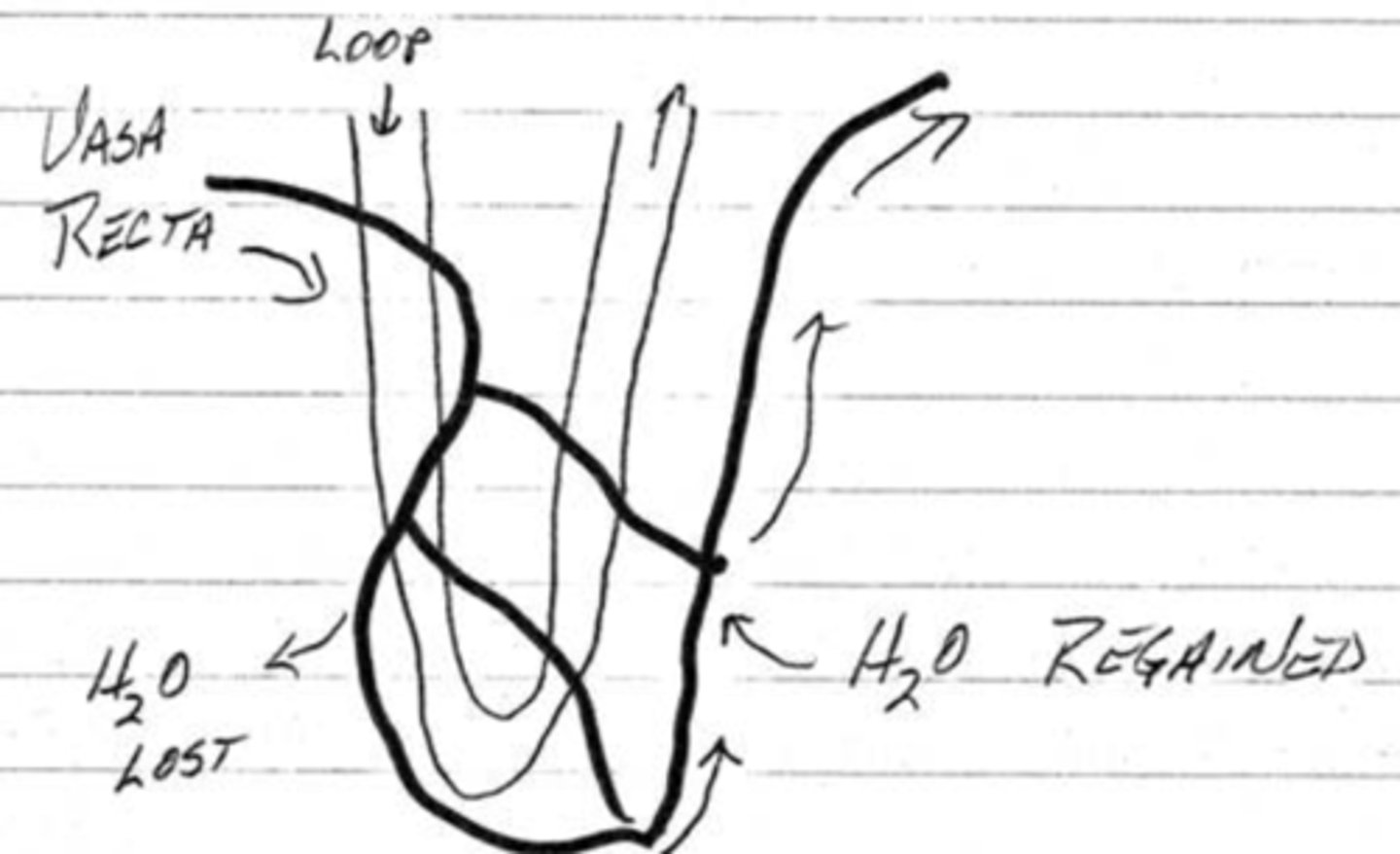
how does blood from the vasa recta regain water after descending into the medulla?
blood flow to the loop cells in the medulla cause water loss so the blood vessels will rise back into the cortex where it can regain the lost water
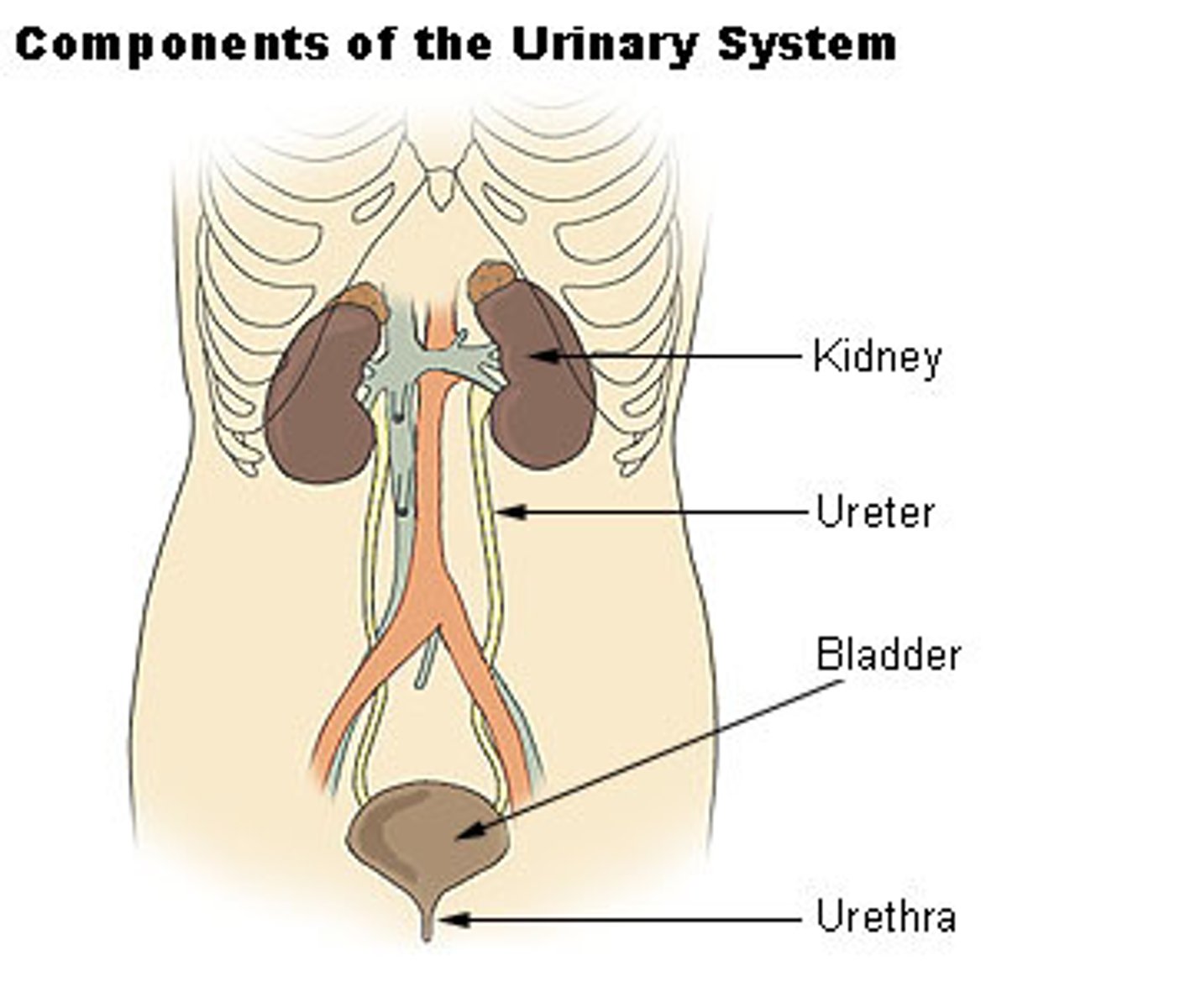
urine enters the bladder from the kidneys through the __________
ureters
(t/f) the bladder is a multi-unit of skeletal muscles
false; the bladder is a single unit of smooth muscle
what muscle will try to prevent micturition of the bladder?
the internal sphincter in the neck of the bladder
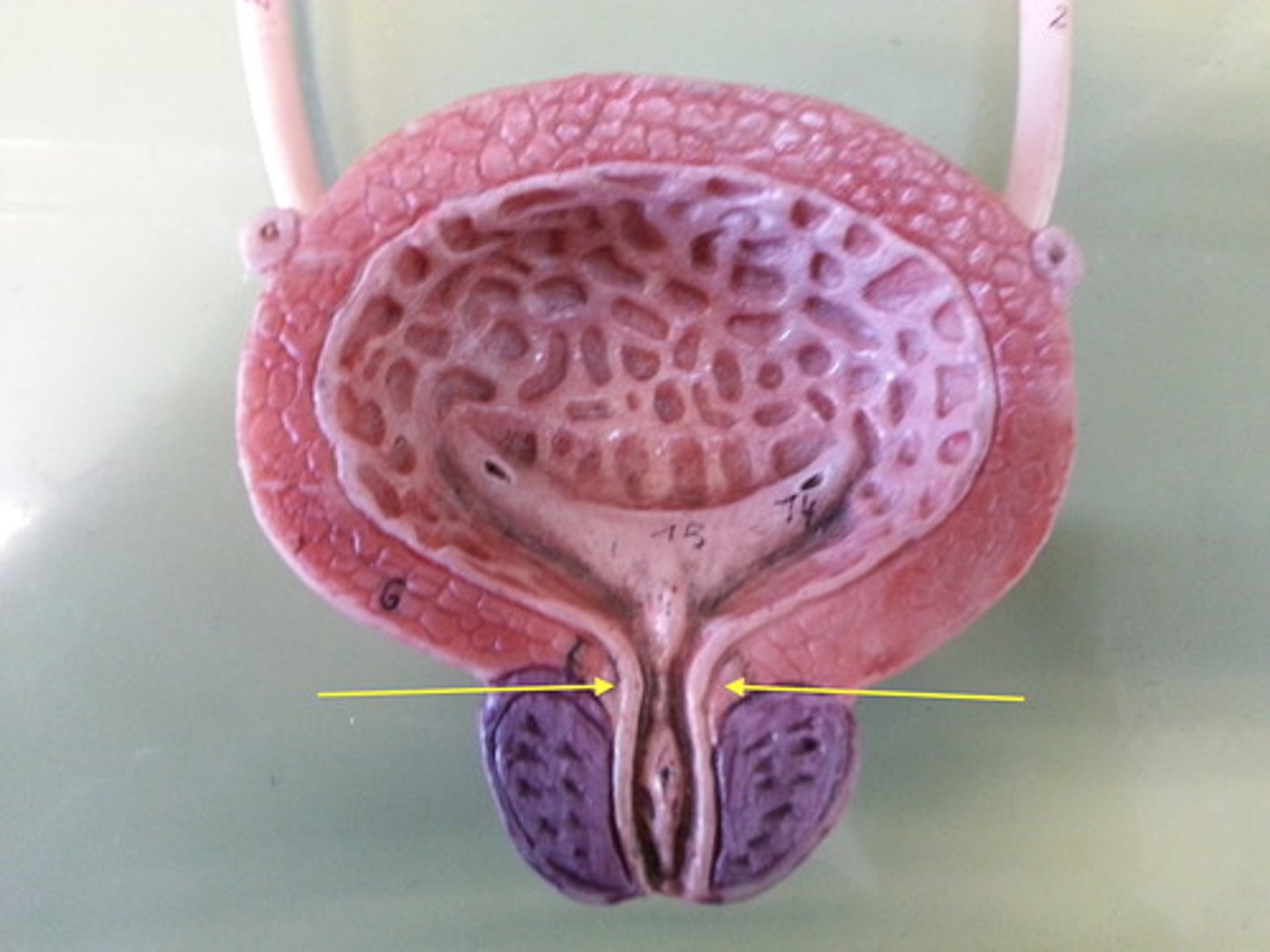
(t/f) the internal sphincter in the neck of the bladder is tonically contracted
true
(t/f) the external sphincter is made of smooth muscle and not under conscious control. where is it found?
false; the external sphincter is made of skeletal muscle and under conscious control
urethra
what does an increase in stretching of the bladder cause?
stimulates afferent fibers in the pelvic nerve which generates a reflex that causes the bladder to contract; this will lead to an increase in pressure which exceeds contracted strength of the internal sphincter causing urination
the contraction of the bladder is caused by (sympathetics/parasympathetics)
parasympathetics
the bladder is innervated by fibers in the (pelvic/pudendal) nerve while the external sphincter is innervated by fibers in the (pelvic/pudendal) nerve
pelvic, pudendal
consciously contracting and relaxing the (internal/external) sphincter is a learned process
external
(t/f) initiation of bladder emptying through an increase in pressure and a triggering of the micturition reflex can only done by the muscles of the bladder
false; abdominal muscles can contract to initiate bladder emptying by increasing pressure and triggering the micturition reflex
when the bladder contains _______-_______ mL, we get the urge to urinate. at the end of the urination, the bladder contains only 5-10 mL.
300-400
spinal damage, pudendal nerve damage, or pelvic nerve damage can result in urinary _______________
incontinence (the inability to control urine release)