Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Concepts
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
77 Terms
Study of internal and external structures of the body and their physical relationships.
Anatomy
Study of the functions of body parts and how they work.
Physiology
Body's tendency toward stability.
Homeostasis
Structures not visible without magnification.
Microscopic Anatomy
Study of internal structures of cells.
Cytology
Study of tissues that make up the body.
Histology
Structures visible without magnification.
Gross Anatomy
Study of superficial anatomical markings (morphology).
Surface Anatomy
Study of structures in a specific body area.
Regional Anatomy
Study of organ systems that function together.
Systemic Anatomy
99.5% of the body is composed of: Hydrogen (62%), Oxygen (26%), Carbon (10%), Nitrogen (1.5%).
Elements
Smallest unit of life; contain organelles.
Cells
Similar cells performing a common function.
Tissues
Four types: Epithelial, Connective, Muscle, Neural (Nerve).
Types of Tissues
Combination of tissues performing a common function (e.g., the heart contains all four tissue types).
Organs
Combination of organs performing a common function.
Organ Systems
The complete living body, made up of all organ systems.
Organism
Atom, Molecule, Macromolecule, Organelle, Tissue, Organ, Organ System, Organism.
Proper Order of Organization
Ability to react to environmental stimuli.
Responsiveness
Cells grow larger and become specialized.
Growth & Differentiation
Ability to produce offspring.
Reproduction
Internal (blood, food) and external movement.
Movement
Chemical reactions for survival.
Metabolism & Excretion
Breakdown of molecules.
Catabolism
Synthesis of molecules.
Anabolism
Intake and removal of materials.
Absorption & Excretion
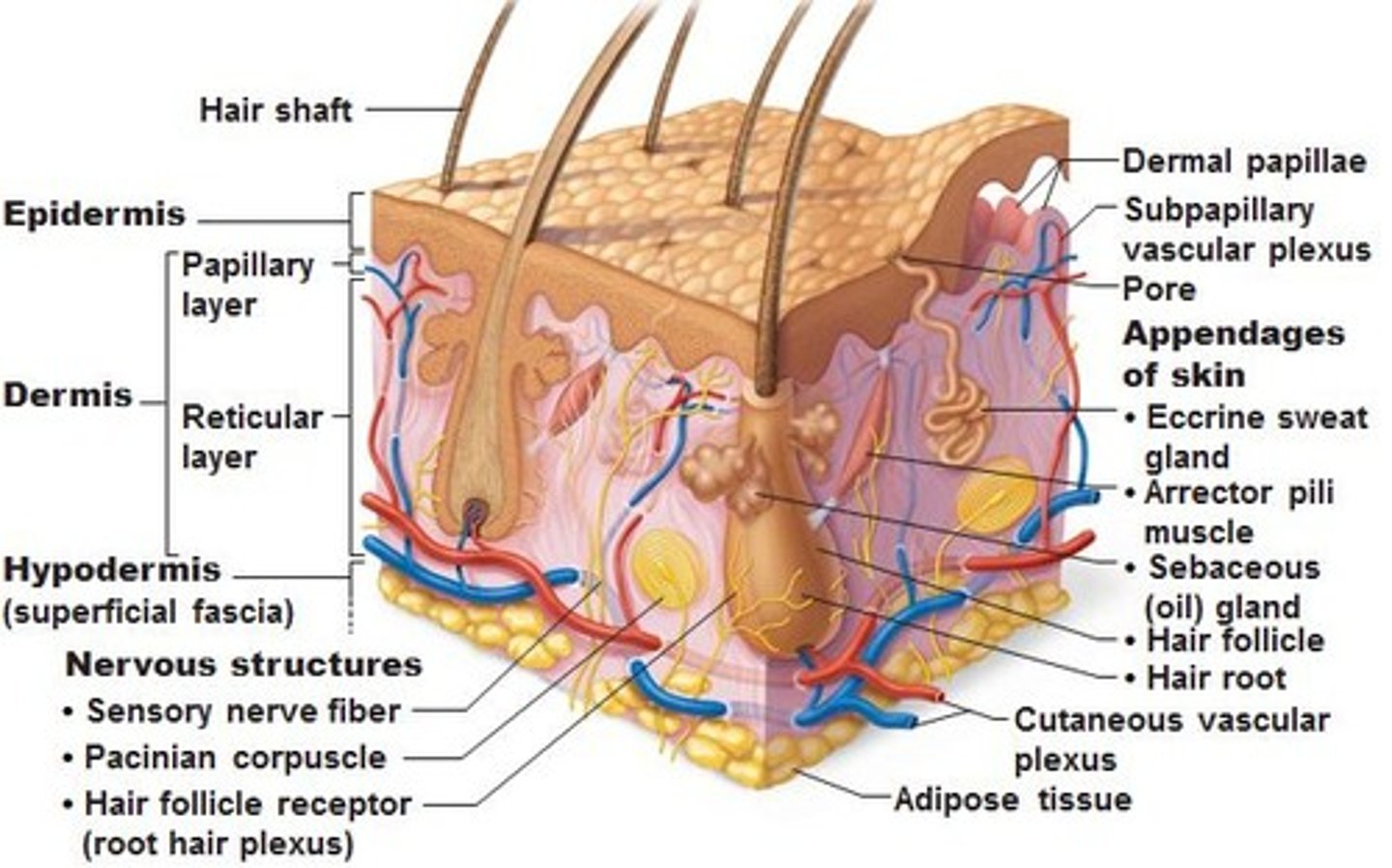
Skin and accessory organs.
Integumentary System
Bones, cartilage, joints.
Skeletal System
Skeletal muscles for movement.
Muscular System
Brain, spinal cord, nerves, special senses.
Nervous System
Glands regulating bodily functions.
Endocrine System
Heart, blood vessels, blood.
Cardiovascular System
Spleen, thymus, lymph nodes, vessels.
Lymphatic System
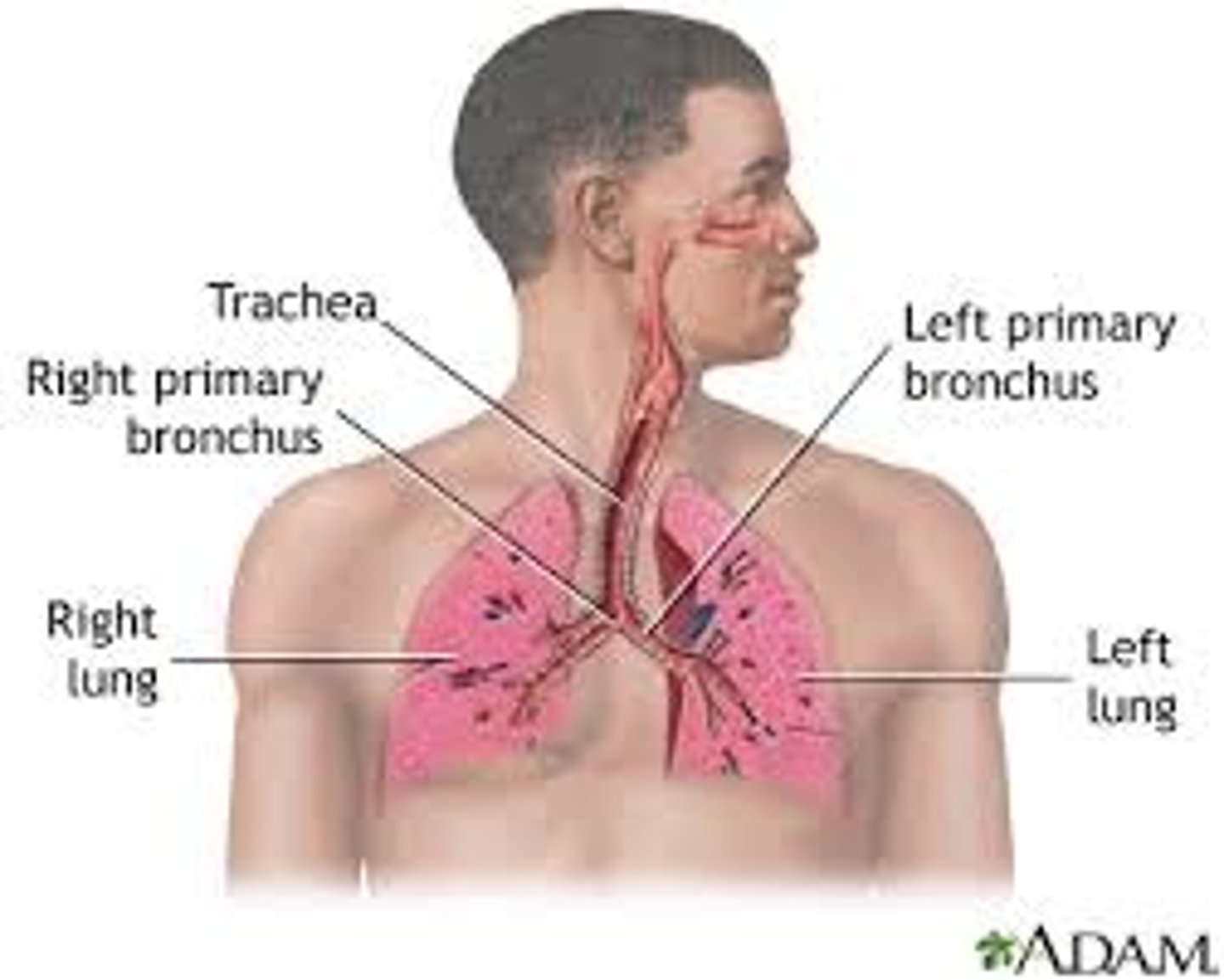
Lungs, trachea, larynx, pharynx, nasal cavity.
Respiratory System
Organs for nutrient absorption.
Digestive System
Kidneys, ureters, bladder, urethra.
Urinary system
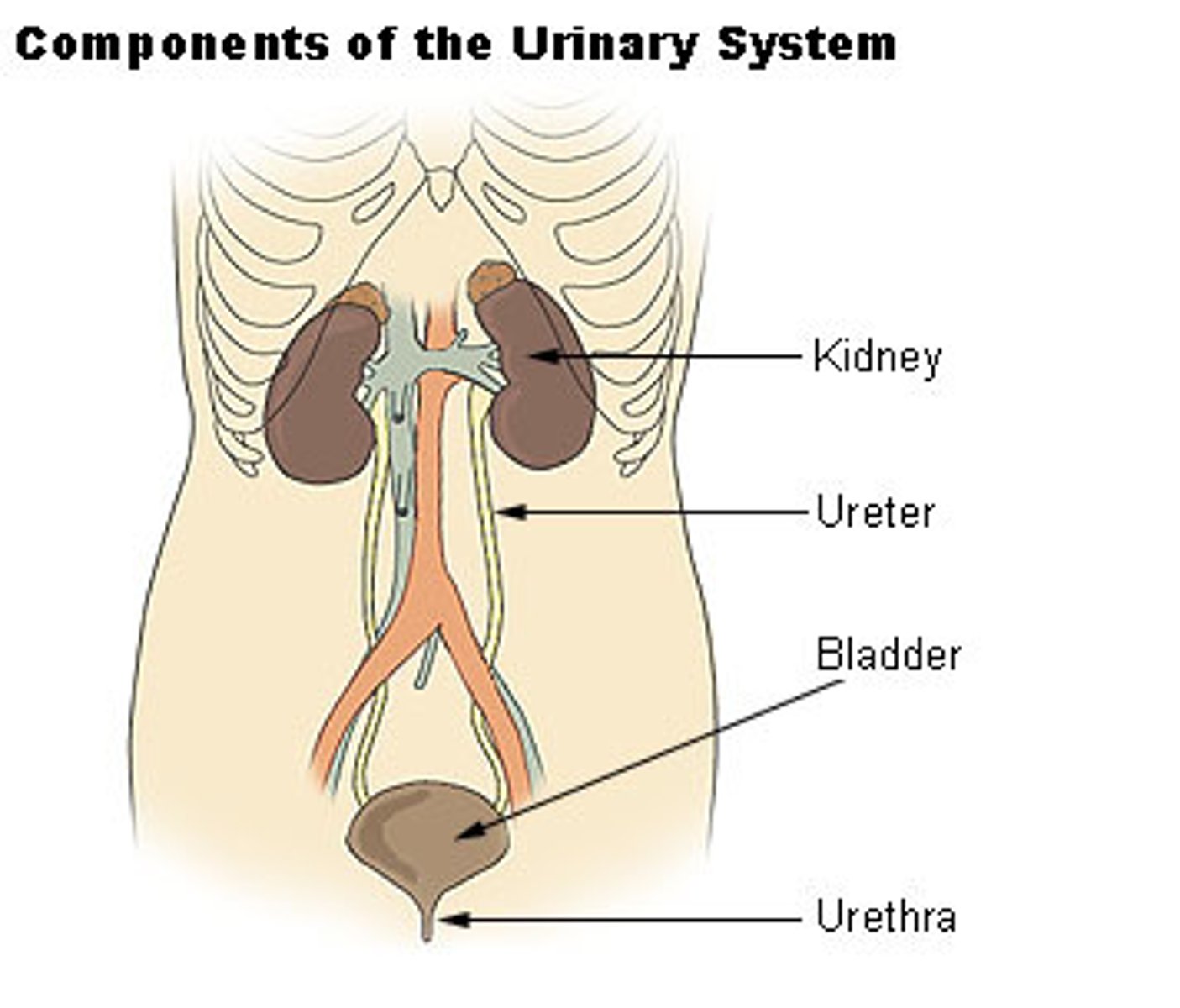
Organs for reproduction and fetal development.
Reproductive System
Body erect, face forward, arms at sides, palms forward.
Anatomical Position
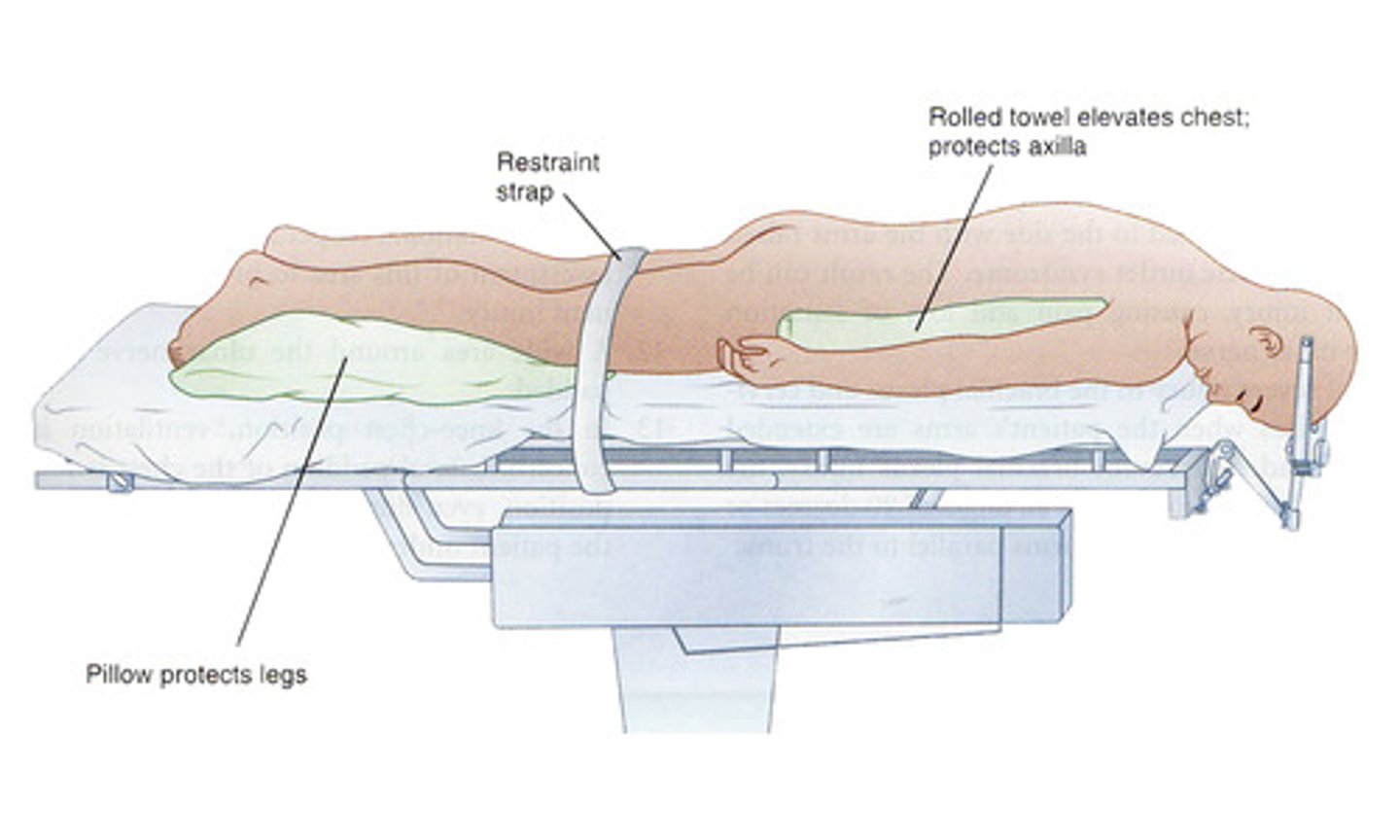
Lying face down.
Prone
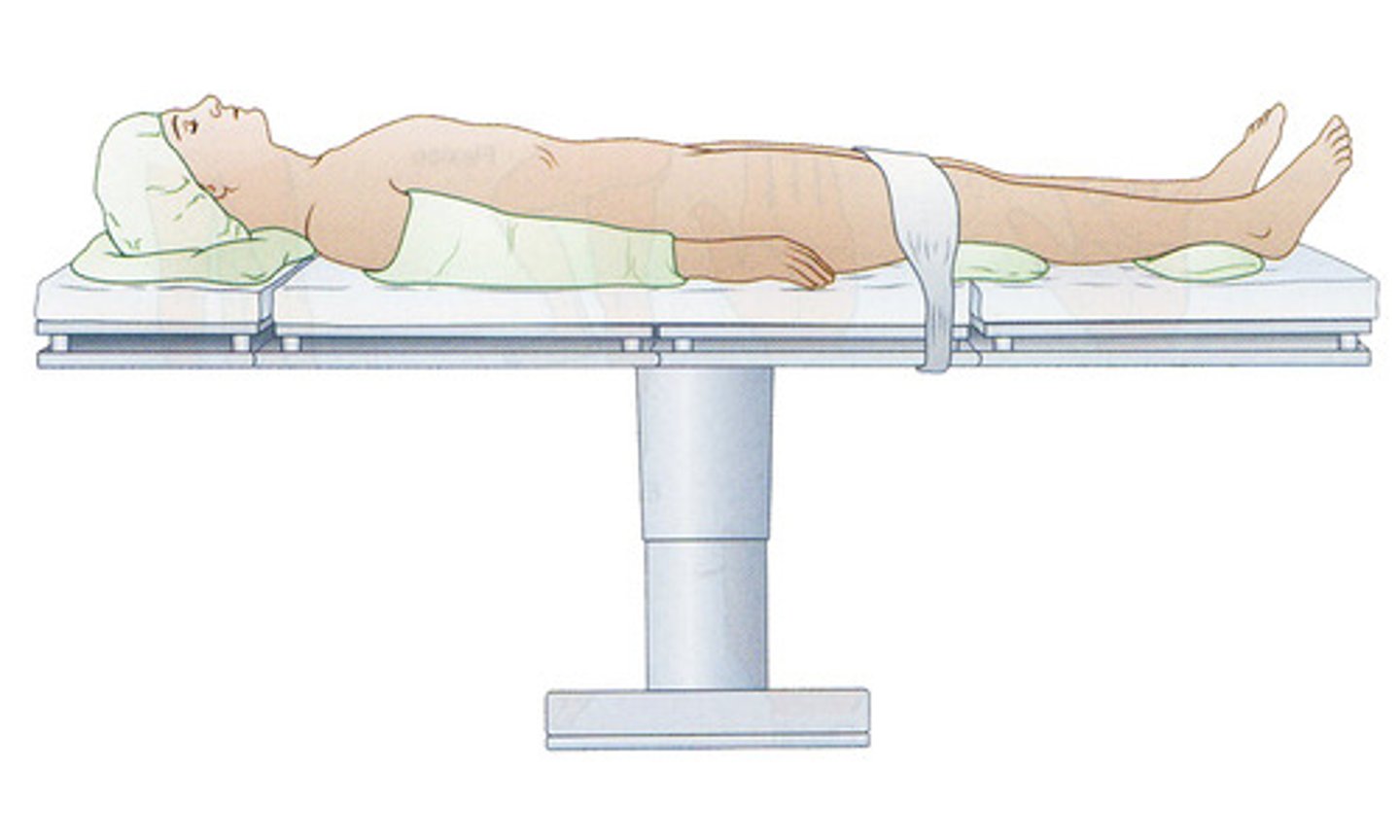
Lying face up.
Supine
Above / Below.
Superior / Inferior
Front / Back.
Anterior / Posterior
Toward the midline / Away from midline.
Medial / Lateral
Closer to attachment / Farther from attachment.
Proximal / Distal
Near the surface / Deeper in the body.
Superficial / Deep
Both sides / Same side / Opposite sides.
Bilateral / Ipsilateral / Contralateral
Toward the head / Toward the tail.
Cephalic / Caudal
Right lobe of liver, gallbladder, right kidney, portions of stomach, small/large intestine.
Right Upper Quadrant (RUQ)
Left lobe of liver, stomach, pancreas, left kidney, spleen, portions of large intestine.
Left Upper Quadrant (LUQ)
Cecum, appendix, portions of small intestine, reproductive organs (right ovary in females, right spermatic cord in males), right ureter.
Right Lower Quadrant (RLQ)
Most of small intestine, portions of large intestine, left ureter, reproductive organs (left ovary in females, left spermatic cord in males).
Left Lower Quadrant (LLQ)
Divides body into right/left parts.
Sagittal Plane
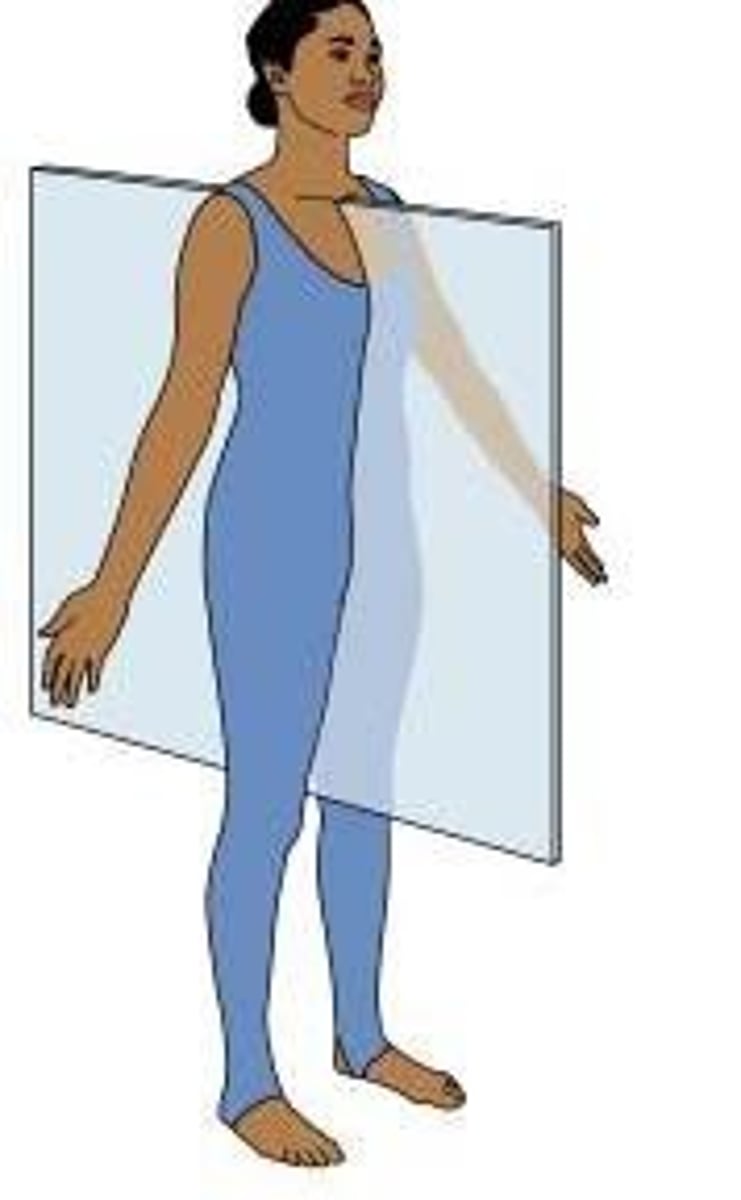
Equal halves.
Midsagittal
Unequal halves.
Parasagittal

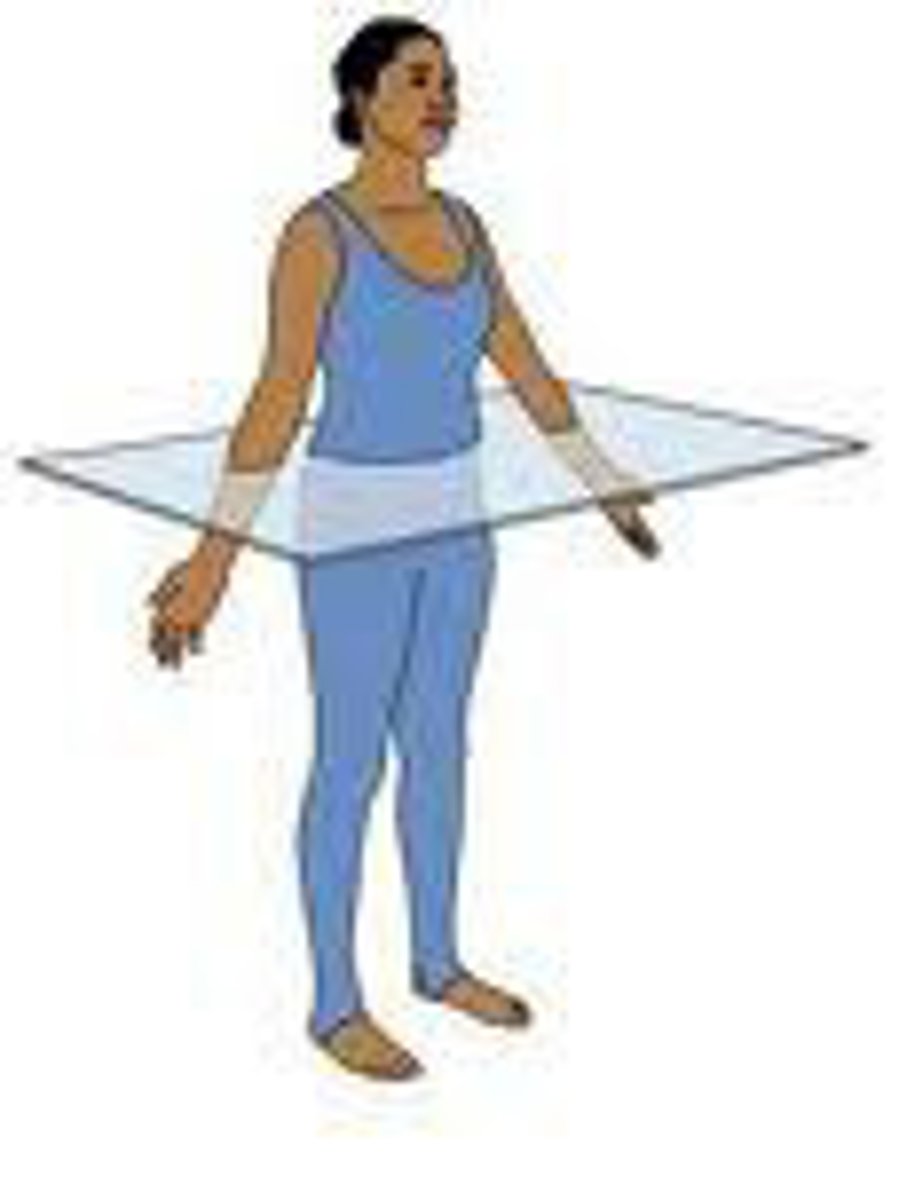
Divides into superior and inferior parts.
Transverse (Horizontal) Plane
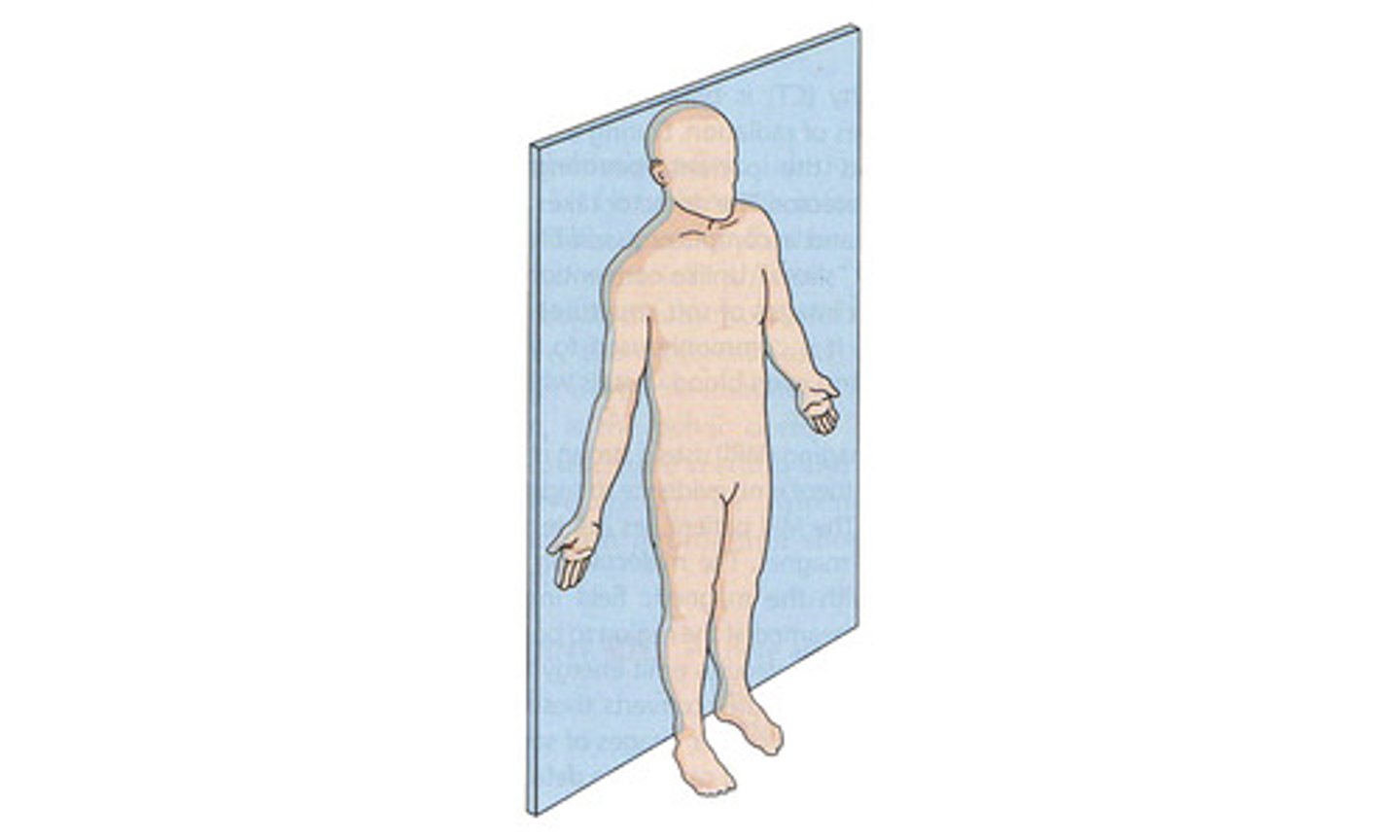
Divides into anterior and posterior parts.
Frontal (Coronal) Plane
Perpendicular slice.
Cross Section
Angled slice.
Oblique Section
Lengthwise slice.
Longitudinal Section
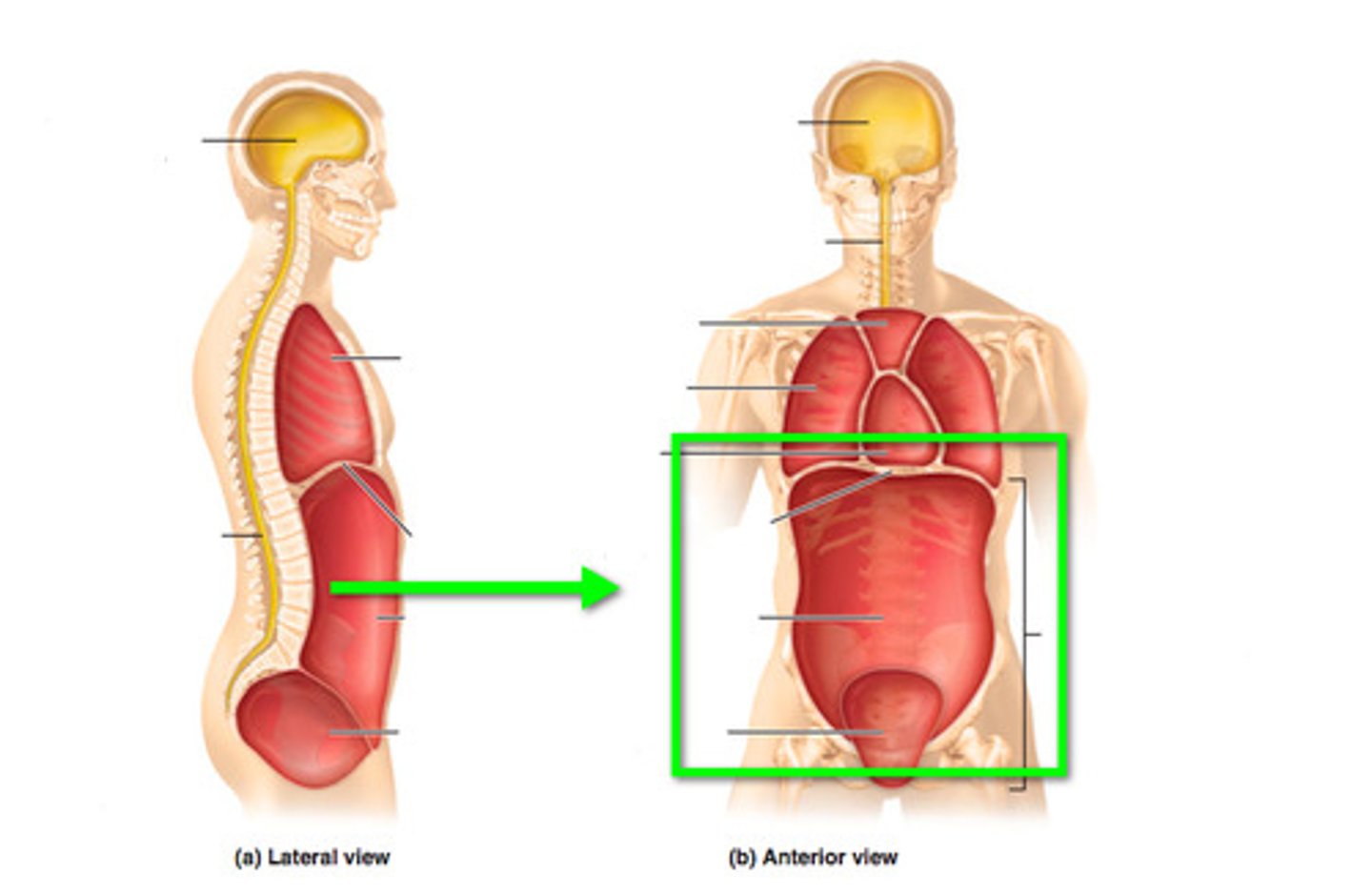
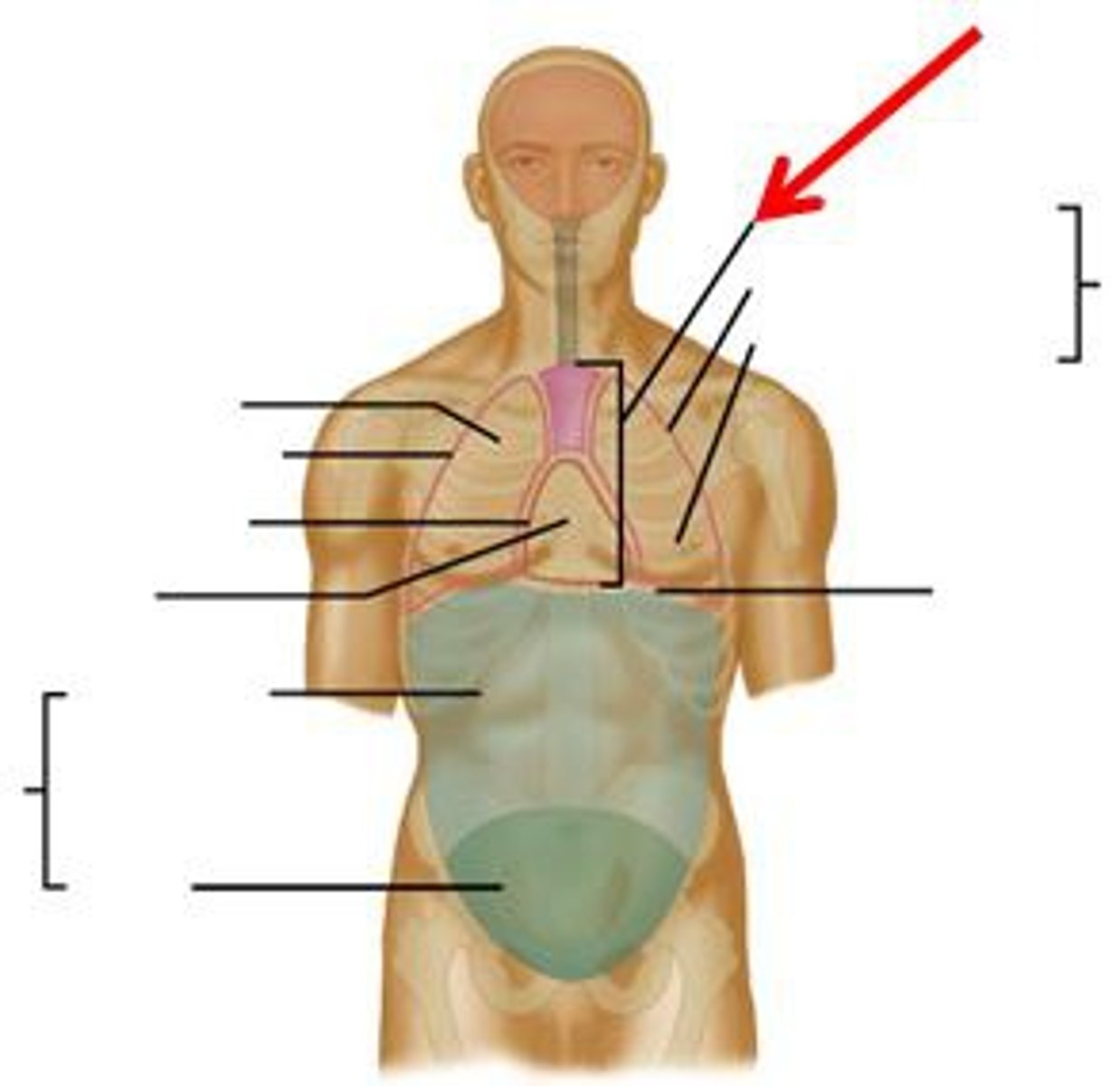
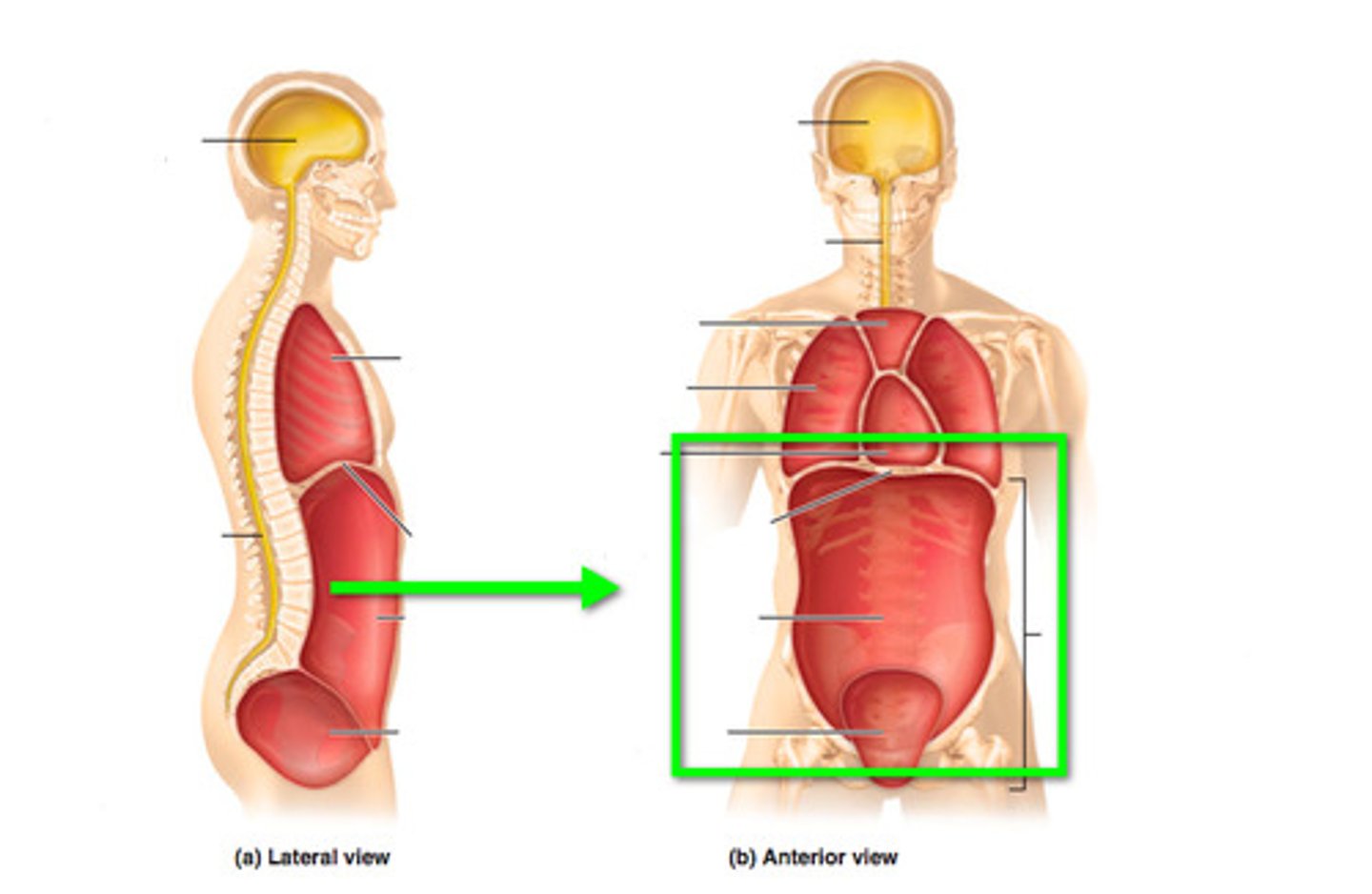
Contains brain.
Cranial Cavity
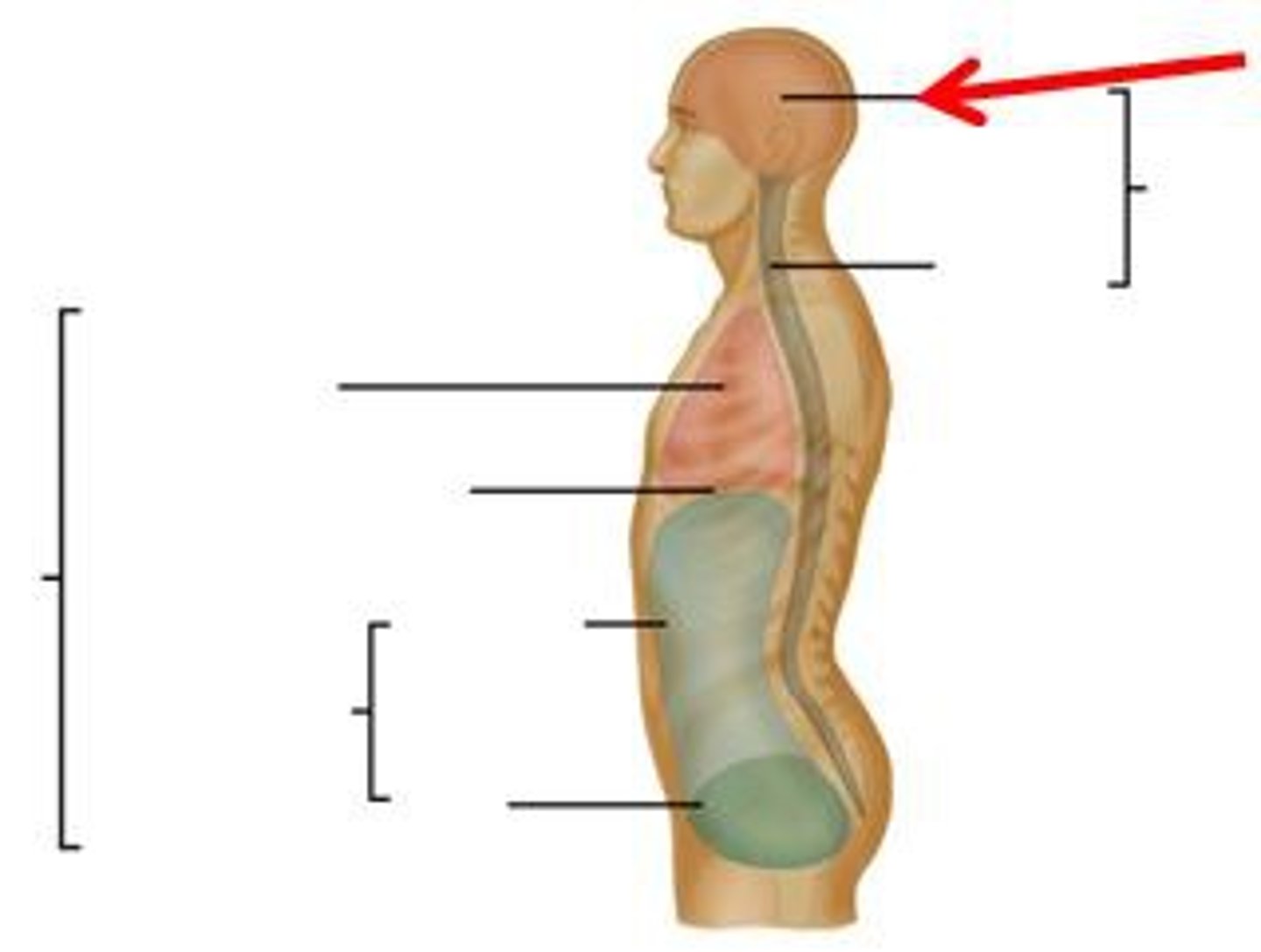
Contains spinal cord.
Vertebral Cavity
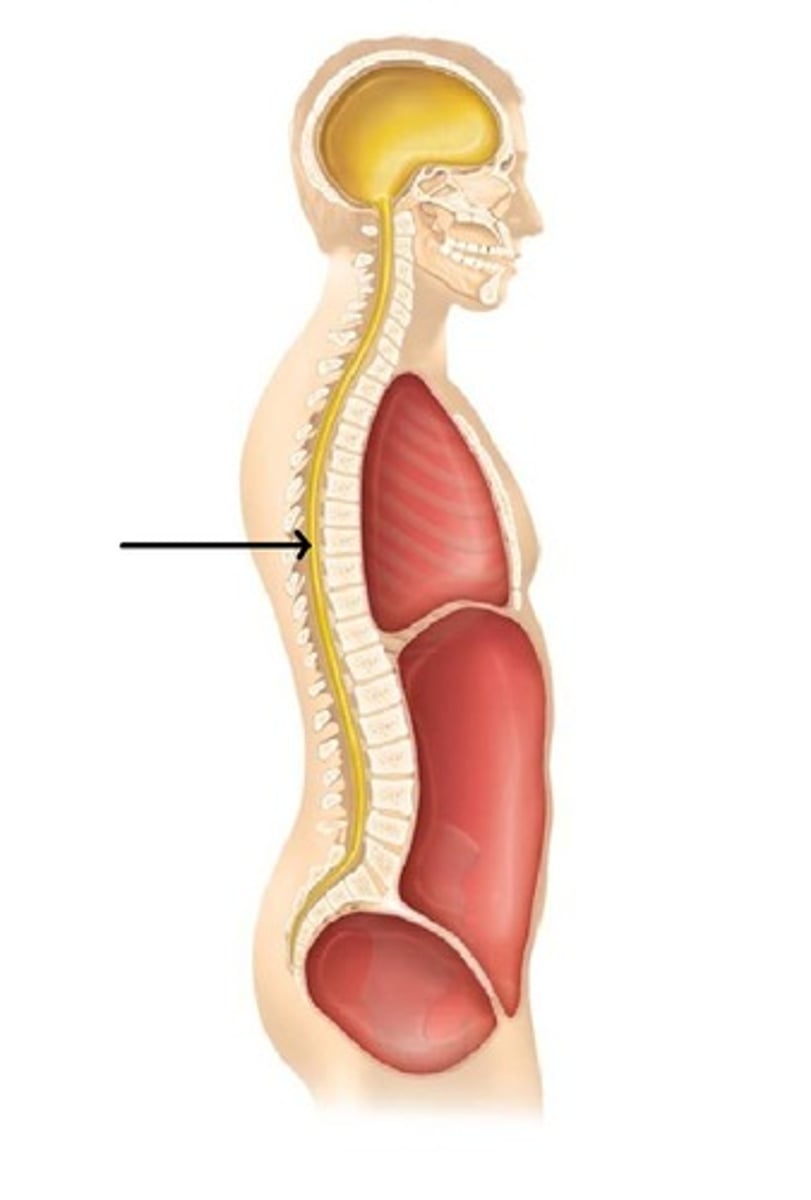
Contains lungs, heart, thymus, esophagus.
Thoracic Cavity
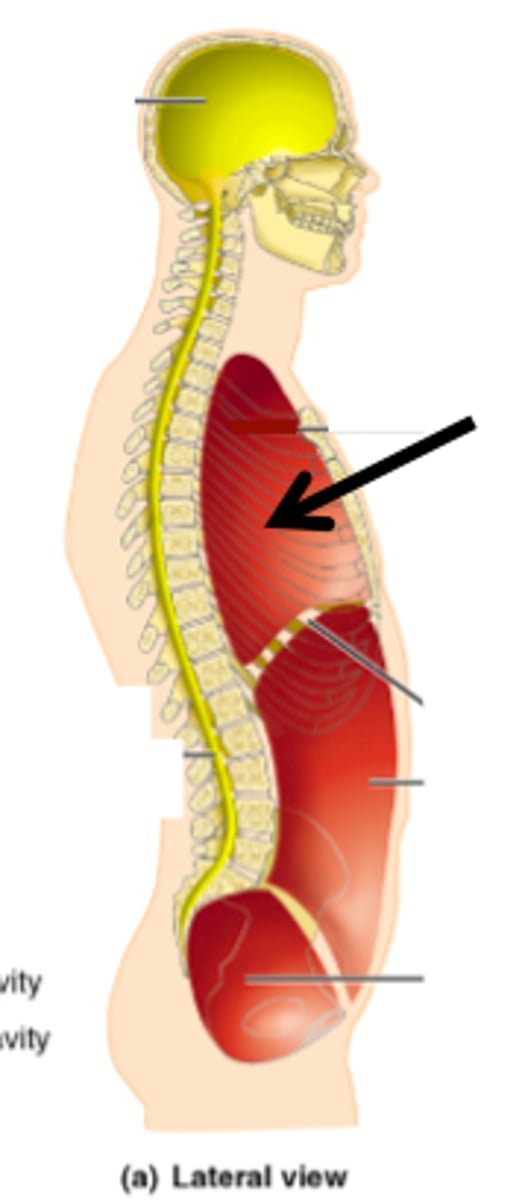
Contains digestive, urinary, reproductive organs.
Abdominopelvic Cavity
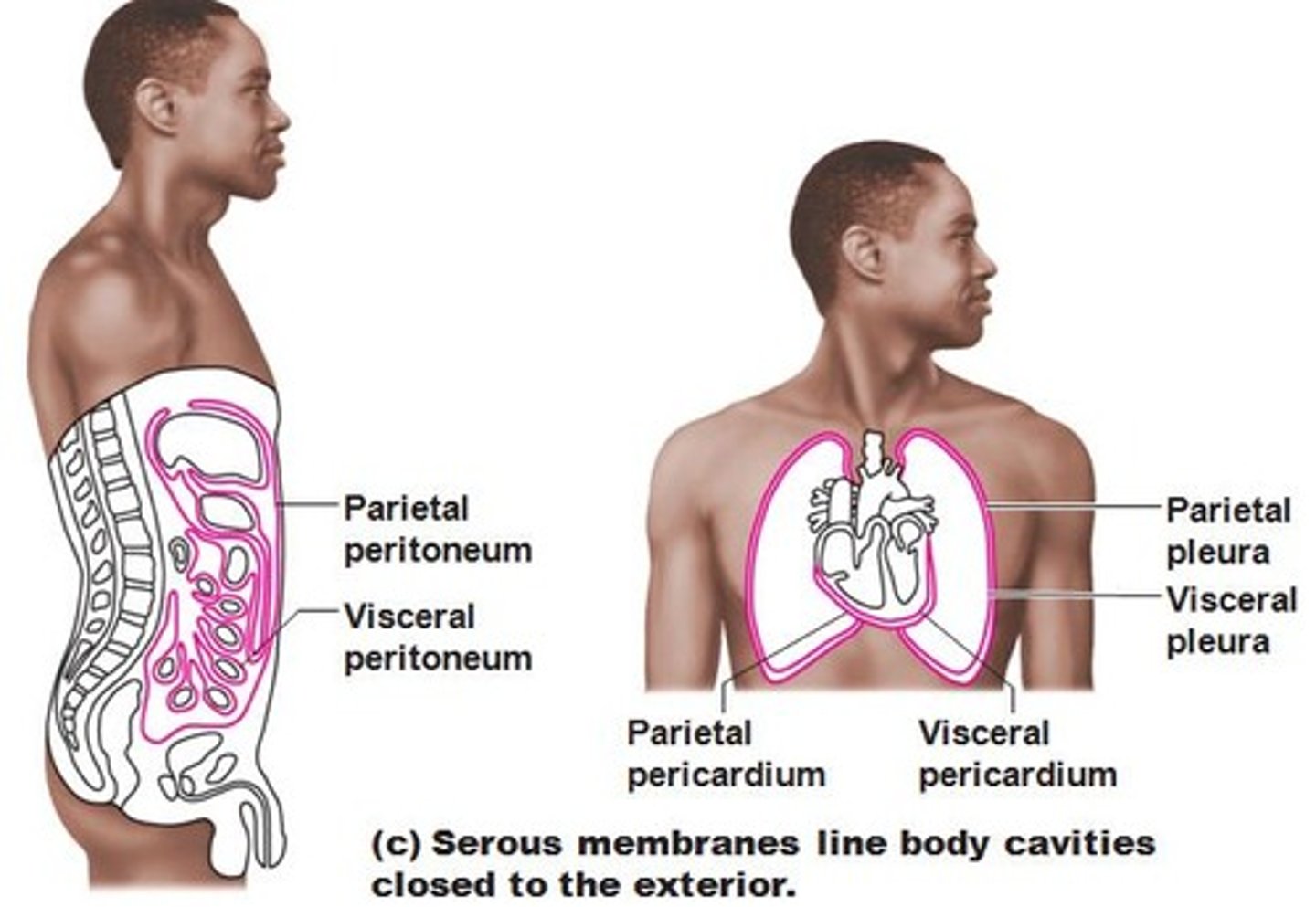
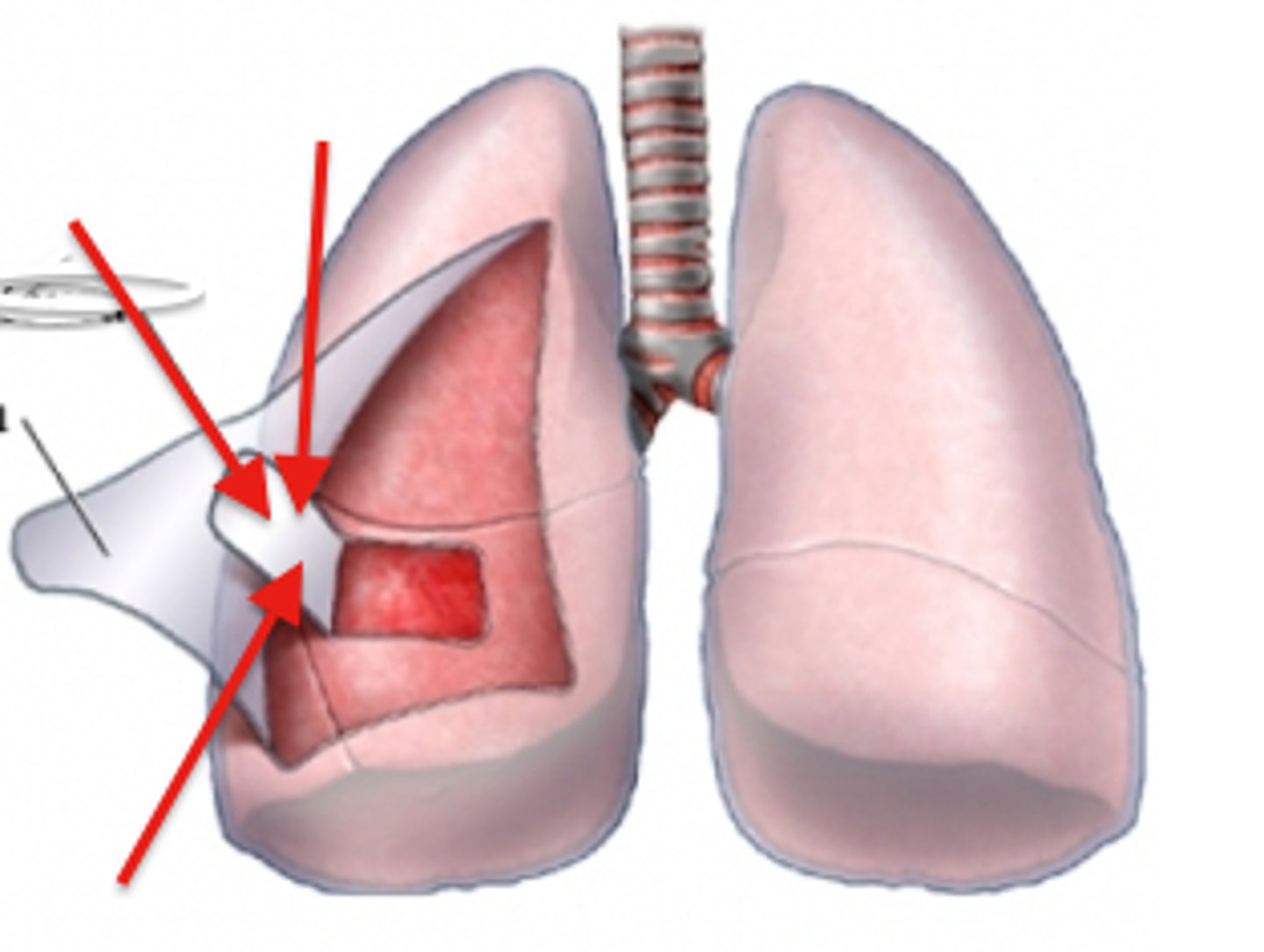
Lines lung compartments.
Parietal pleura
Covers lungs.
Visceral pleura
Contains esophagus, trachea, major blood vessels of the heart.
Mediastinum
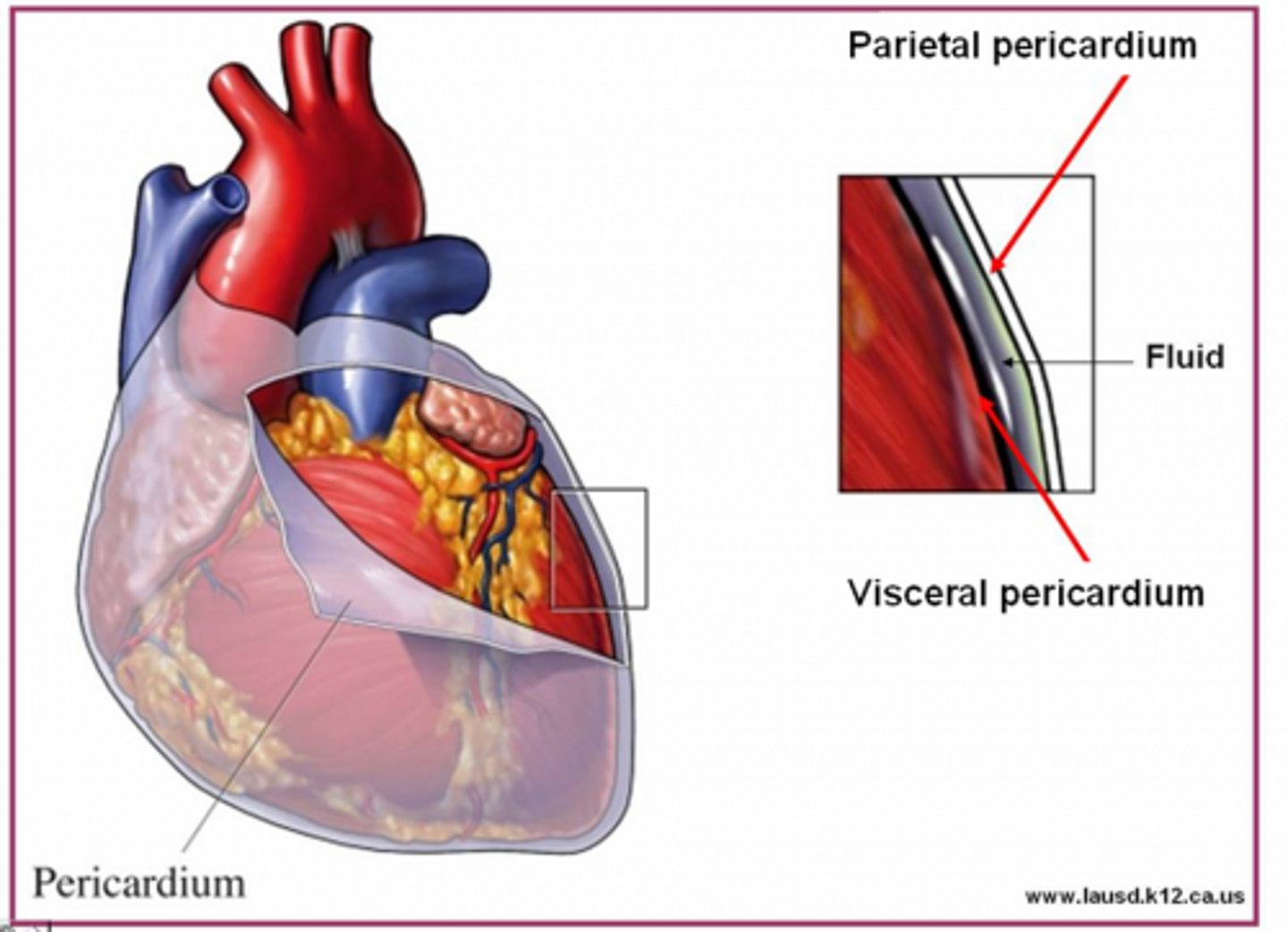
Lines cavity.
Parietal pericardium
Covers heart.
visceral pericardium
Contains digestive and urinary organs.
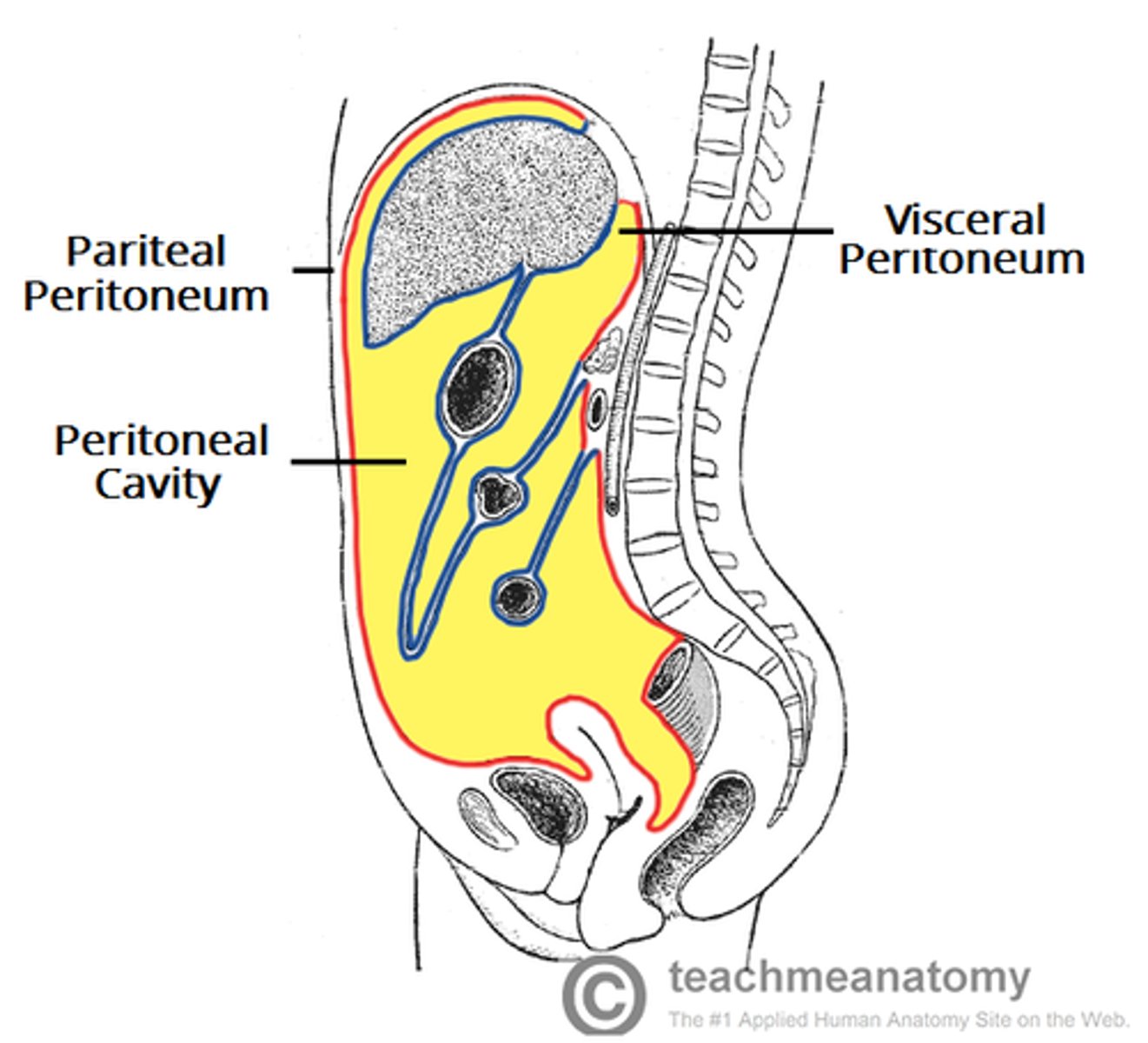
Abdominal Cavity
Holds most digestive organs.
Peritoneal Cavity
Lines cavity.
Parietal peritoneum
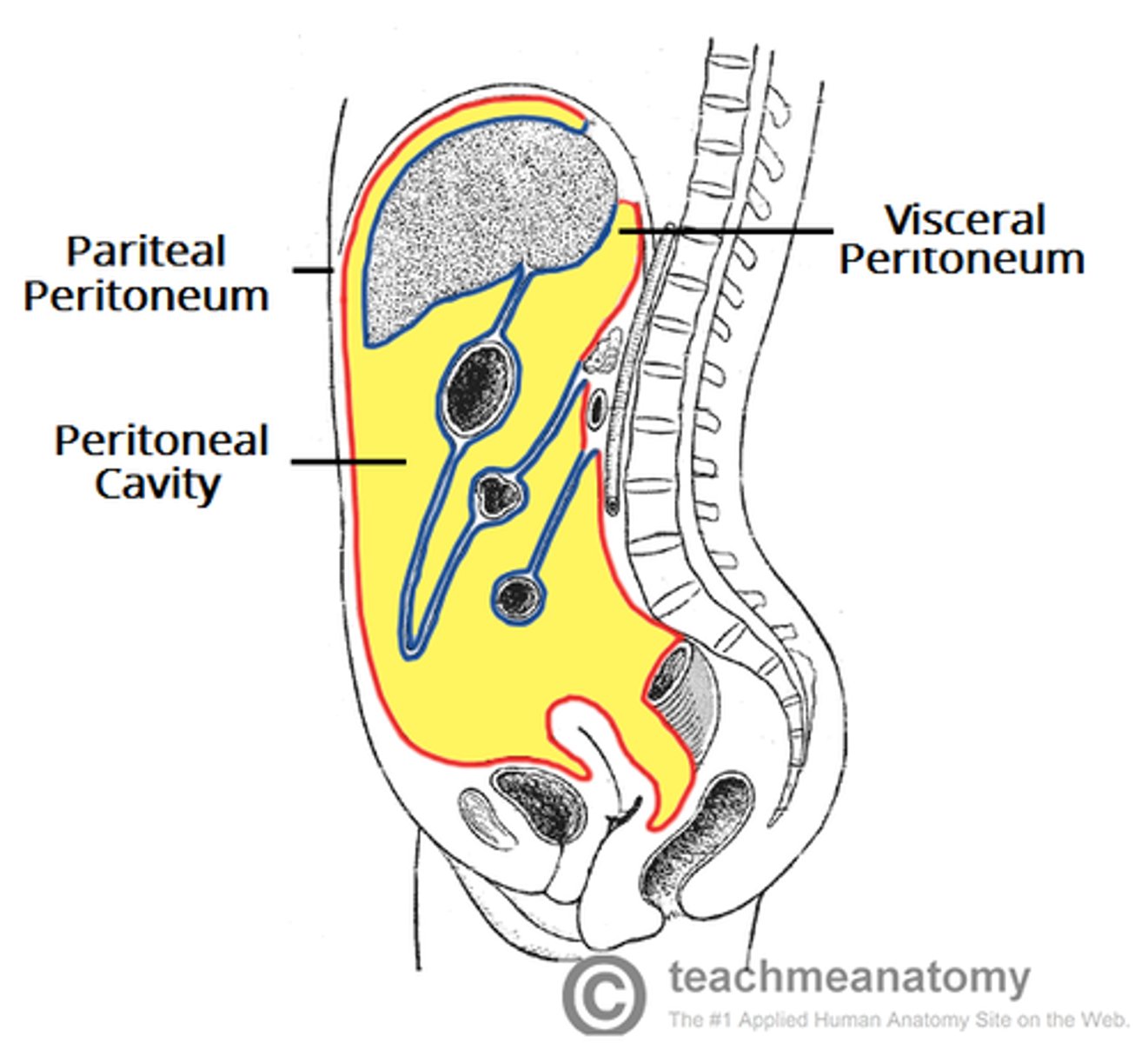
Covers organs.
Visceral peritoneum
Hold organs in place.
Mesenteries
Contains parts of digestive system, urinary bladder, reproductive organs.
Pelvic Cavity
Reduce friction between body cavities and organs by secreting transudate fluid.
Serous Membranes
Line body cavities.
Parietal Membranes
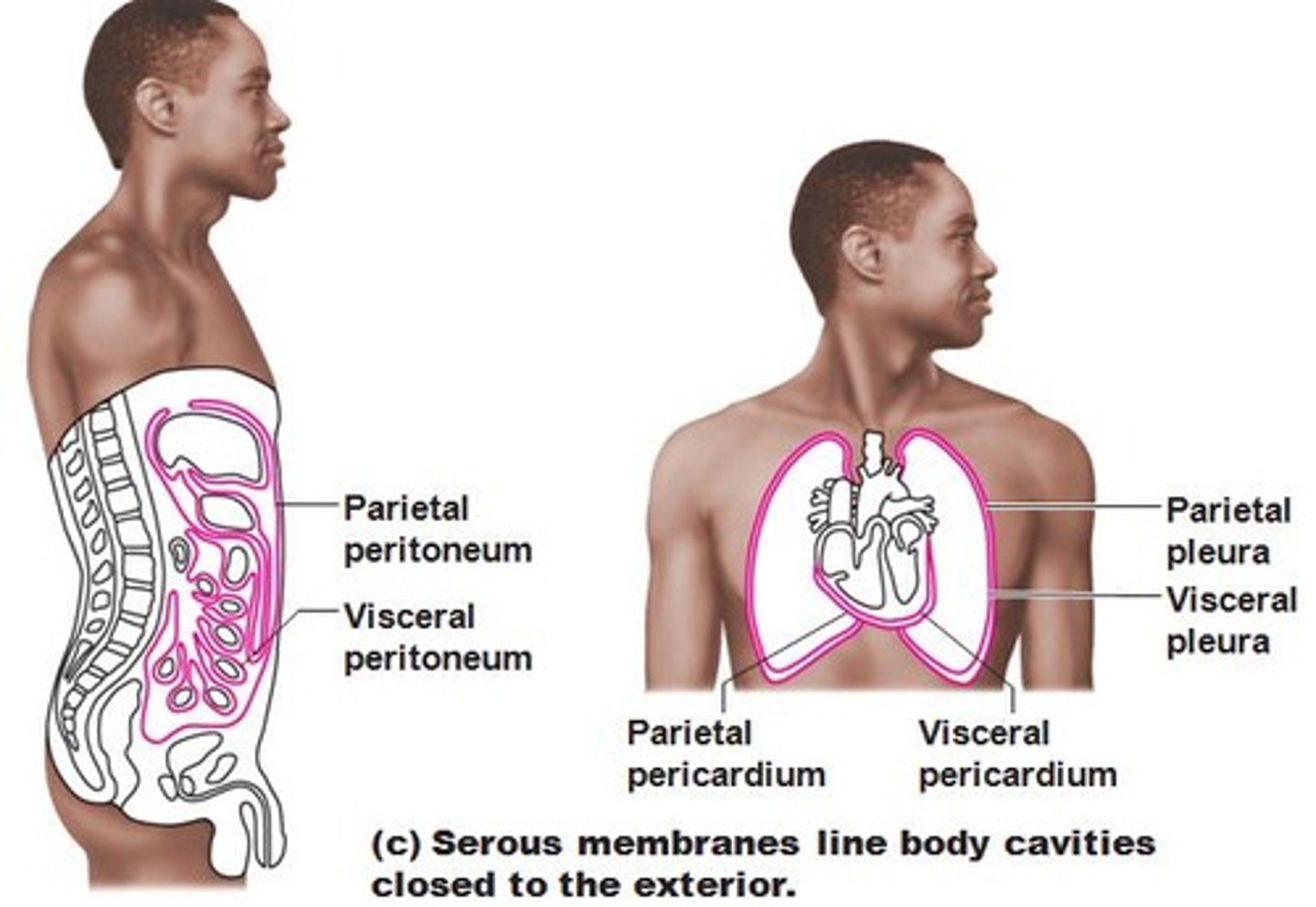
Cover organs within cavities.
Visceral Membranes