Climate and Surface Processes
1/5
Earn XP
Description and Tags
- Recognize how changes in temperature, moisture, and vegetation throughout Earth's history produce diagnostic landscape features - Explain how chemical weathering regulates global climate - Articulate how a space-for-time substitution can (or cannot!) reveal the impact of climate change on landscapes
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
6 Terms
How chemical weathering affects climate
Regulates atmospheric and terrestrial carbon pools
Calcium Silicate Weathering —> Biomineralization
CO2, Water, and Calcium Silicate turned to bicarbonate, calcium ions, and silica
The bicarbonate and calcium is then turned into calcium carbonate in the shells of animals, which is then STORED AS A SINK
SILICATE WEATHERING IS A CARBON SINK
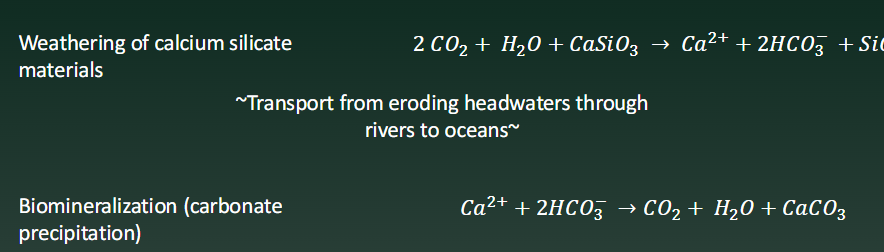
Chemical weathering carbon neutral, sink, or source
Carbonate weathering —> Neutral
Aformentioned Silicate Weathering —> Sink
Carbonate rocks cooked in lithosphere —> Source
Ex. Volcanic eruptions releasing carbon
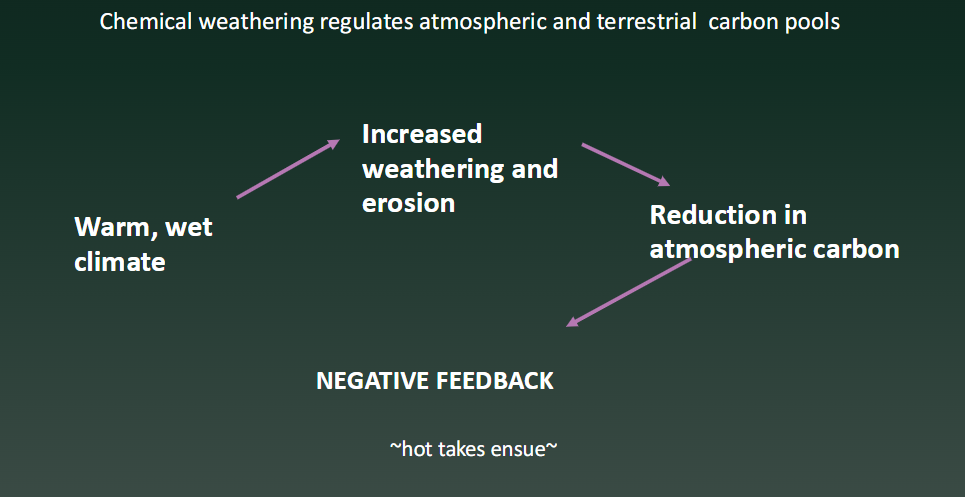
Idea regarding carbonate weathering and global climate effects
As it gets warmer, more weathering occurs of calcium silicate minerals, ultimately resulting in the biomineralization and storage of CO2, cooling global climate
Need to understand degree of weathering and erosion under warm/wet climates
Diagnostic Landform Examples
Moraines, Eskers, Drumlins, etc. — Presence of glaciers and colder climate; ELA with moraines
Pingos — Evidence of permafrost presence
Large outwash canyons from glacial outburst floods
Fjords with glacial carving
Ideally study landforms representative of a snapshot of climate; or a single relatively constant period of climate
Space-for-Time Substitution
Using landforms from different stages of development or similar landforms under different environmental conditions to determine how certain climate processes act on landforms
Ex. Using modern climate gradients to ascertain how climate (precipitation and temperature) is linked to erosion and chemical weathering of landforms
However, for past climate, limits extent of use due to it being much colder 20K years ago for example