MIDDLE GRADE SCIENCE SOL
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
All the units involved in the 7th grade science SOL in a reviewed and summarized set of information. Please note that the best way to go through the flashcards is directly in order, it starts with 6th grade and progressively works towards 7th, going out of order would be difficult due to how the questions are phrased. :)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
What does Mitosis mean/do?
Mitosis is the process of cell division in which a single cell divides to produce two genetically identical daughter cells, ensuring that each new cell receives a complete set of chromosomes.
What is the differences between Mitosis and Meiosis?
Mitosis results in two identical daughter cells, whereas meiosis produces four genetically diverse gametes. Mitosis is for growth and repair, while meiosis occurs for sexual reproduction.
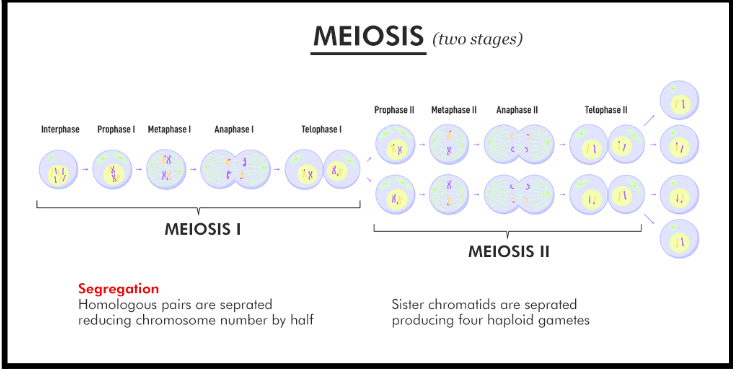
What is the acronym for the process of Mitosis (and Meiosis)?
PMAT
Prophase - Metaphase - Anaphase - Telophase (includes cytokineis which is the cell division after mitosis). (Meiosis includes two rounds: PMAT I and PMAT II.)
What occurs during Prophase?
During prophase, chromatin condenses into visible chromosomes, the mitotic spindle begins to form, and the nuclear envelope breaks down, allowing the spindle fibers to attach to the chromosomes.
What occurs during Metaphase?
During metaphase, chromosomes align at the cell's equatorial plane, attached to spindle fibers, ensuring proper separation during the next phase.
What occurs during Anaphase?
During anaphase, sister chromatids are pulled apart by the spindle fibers towards opposite poles of the cell, ensuring each new cell will receive an identical set of chromosomes.
What occurs during Telophase (including cytokineis)?
During telophase, the separated chromosomes reach the poles of the cell, decondense back into chromatin, nuclear envelopes reform around each set, and the cell prepares to divide.
What happens after this process?
Following telophase and cytokinesis, two daughter cells form, each with an identical set of chromosomes, effectively completing cell division and are currently in interphase, waiting to start the process again.
What does Meiosis mean/do?
Meiosis is a type of cell division that reduces the chromosome number by half, producing four genetically diverse gametes from one original cell, essential for sexual reproduction.
What is “Crossing Over”?
Homologous chromosomes pair up (AKA a tetrad). Non-sister chromatids form “chiasmata” (Defined as: Basically two X shaped chromatids literally crossing over and exchanging genetic information, in “alleles”)
What happens after PMAT 1?
After, the 2 cells go the process again, or something quite similar to that, and create 4 cells in total that are unique and different from each other.
What is the Intermediate Filament do?
Provides strength to the cell’s framework (similar to a bone)
What are Ribosomes (/and what do they do)?
Site of protein synthesis (assembly of amino acids, linking them together.)
What does the Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum do?
Produce proteins to the rest of the cell to help it function, flattening sacs with Ribosomes attached to the edges.