Unit 4 Immunology and Immunohematology
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
99 Terms
anamnestic/booster/ secondary response
rapid inc. in blood Ig following second exposure to an Ag
Ab
antibody/immunoglobin; protein induced by and reacts with Ag
Ag
antigen/immunogen; foreign substance that induces an immune response but in order to do so must contain a protein/CHO
causes production of Ab and/or sensitized lymphocytes
B lymphocyte (B cell)
type of lymphocyte primarily responsible for the humoral (bodily fluids) immune response; developed in bone marrow
produce Ab that reacts specificaly react with the antigen
What stimulates humoral immunity?
vaccines
cell-medicated immunity
immunity provided by T cells and cytokines
compliment
group of plasma portions that can be activated in immune reactions
help cause cell lysis and initiate inflammatory response
cytokines/lymphokines
any various non-antibody proteins secreted by cells of the immune system that help regulate the immune response
dendritic cells
cells in lymphoid tissue that network to trap foreign Ag
enzyme immunoassay (EIA)
an assay that uses an enzyme-labeled antibody as a reactant
epitope/ antigenic determinant
portion of Ag that reacts with specifically with an Ab
humoral immunity
immunity provided by B cells and Ab
immunocompetent
capable of producing a normal immune response
immunocompromised
having reduced ability/ inability to produce normal immune response
immunoflorence
Ab are labeled with florescent dye to detect Ag (direct, mores sensitive due to the fact that more than one molecule of florescent labeled Ab can bind to first Ab) or Ab (indirect); often used to detect autoantibodies
dyes emit particular wave length when hit with a UV light
immunoglobins (Ig)
Ab make up 10~15% of serum protein
named by placing anti- in from of the Ag name
macrophages
long-lived phagocytic tissue cells that are derived from blood monocytes
function in destruction of foreign antigens; serve as antigen-presenting cells
plasma cell
differentiated B cell that produces Ab
precipitation
formation of an insoluble Ag-Ab complex
primary lymphoid organs
organs in which B and t cells acquire their special characteristics (bone marrow and thymus)
secondary lymphoid tissue
tissues in which lymphocytes are concentrated (spleen, lymph nodes, tonsils)
seroconversion
appearance of Ab in the serum or plasma of an individual following exposure to an antigen
serology
study of Ab and Ag in serum or plamsa using immunological methods
T lymphocyte (T cell)
lymphocyte responsible for the cell-mediated immune response developed in thymus
secrete cytokines
thymus
gland located in the upper chest that is the primary lymphoid tissue in which lymphocytes mature and acquire T cell characteristics
titer
reciprocal of the highest dilution that gives the desired reaction
determined by titration
specific immunity
immune response that recognizes and remembers different antigens and is able to direct a response to a specific antigen
What does Ig molecule look like after in action of the papain enzyme?
Fab fragment because it contains antigen binding sites (ab)
Fc fragment because it is easily crystalized (c)
How do the Ig classes differ?
The chemical structure of the 2 H chains are different for all five classes.
What are the Ig classes and their functions?
IgG: gamma globin/ immune globin long lasting
IgA: plasma or serum IgA is a monomer and secretory IgA is a dimer
IgE: inc. in many parasitic infections
IgM: largest Ig (5x bigger than IgG)
primary and secondary Ab response
pg 440
Describe how you can acquire immune deficiencies:
acquired: drugs; corticosteroids and chemotherapy agents are immunosuppressants
inherited and congenital (presented at birth)
serology (serum) tests include:
HIV, flu, hepatitis, and rubella tests
What are monoclonal and polyclonal Ab used for?
reagents in immunology kits
sensitivity
lowest concentration capable of being detected by a test method; if not done can result in false negetives
how is Ab concentration estimated?
make serial dilutions to determine maximum dilution
Ag-Ab reaction tests include:
Agglutination
Agar precipitation
Nephelometric assays
Immunofluorescent (IF)
Enzyme immunoassays (EIA)
Chromatographic immunoassay
Chemiluminescence immunoassay
Flow cytometry techniques
*pink ones are all labeled antibody assays
what tests are based of agglutination?
Blood typing, bacterial infection, latex test for rheumatoid arthritis.
What is the following picture? (pg 442)
the one on the left is a positive agglutination test and the one on the right is a negative agglutination test.
What antibody class reacts the best to agglutination?
IgM
What Ab class reacts the best to percipitaion?
IgG
What does a positive precipitation test look like and when do they happen?
formation of a white precipitate on Agar or agarose
only happens when Ag and Ab are in the correct proportions
radial immunodiffusion is used for what?
to estimate the concentration of IgG, IgM, and IgA in a pts serum
How does RID work?
1) agar diffused with anti-IgG (or IgM or IgA) has wells in it that are filled with, pts serum or known amount of IgG (standard).
2) as IgG in serum or standard diffuse out of wells that react with the anti-IgG and form immune complexes leaving a white ring of precipitation round the well
3) The diameter of the ring is proportional to the concentration of IgG
pg443.
CFS
chronic fatiuge syndrome
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)
virus that affects lymphocytes and is the cause of infectious mononucleosis
carry virus in throat and saliva
heterophile Ab
group of multi specific antibodies (IgM class) that are increases in infectious mononucleosis and react w/ heterogeneous Ag not responsible for their production
incubation period
time elapsed between exposure to infectious agent and appearance of symptoms (4-6 weeks)
infectious mononucleosis (IM, mono)
contagious viral disease cause by infection of B cells w/ EBV
symptoms:
fatigue
fever
lymphadenopathy
headache
occurring primarily in 15-25 y/o age group
lymphadenopathy
condition in which lymph glands/nodes are enlarged or swollen
What are hematological findings of IM?
lymphocytosis with 10-20% of WBC being atypical under microscoped blood smear
immunological findings of IM?
inc. heterophile Ab
peak 3-4 weeks of after symptoms begin and decline to low lvs. after 3 months
describe specimen collection for rapid IM testing:
whole blood from capillary puncture or venous puncture with heparin or EDTA anticoagulant.
or with serum, heparinized plasm, or EDTA-anticoagulated plasma
what does failure of internal control indicate?
test was not preformed correctly and/or reagents were not working properly
How do you know internal/external control failed in a rapid IM test?
test complete window does not have a vertical blue line in it after 10 mins.
RHEUMETOIDS FACTORS
autoAb (typically IgM class) directed against Fc fragment of the human IgG; seen in serum of pts who have RA and Sjogren’s
elevated in the blood and synovial fluid
scleroderma
systematic/localized autoimmune connective tissue disease
chronic hardening (sclero) of skin (derma) and connective tissue
Sjogren’s syndrome
systematic autoimmune disease affecting moisture producing glands (tears, sweat, and saliva) but also organs
synovial
of or relating to lubricating fluid of the joints
agglutination test for RF:
latex particles are coated in IgG and pts serum are mixed
RFs bind to the latex particles and cause agglutination
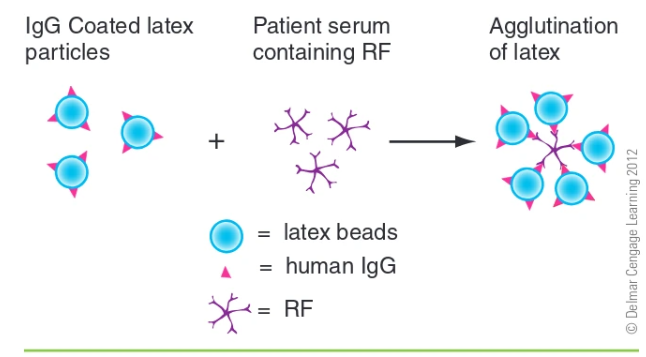
What is the usual specimen for latex agglutination tests?
serum, but venipuncture blood (red/gray topped) is okay as well, blood is allowed to clot and serum is removed by centrifuge
what is the dilution for serum before testing for agglutination?
1:20
Test results for agglutination on RF:
absence of agglutination in pts serum indicates RF are WNL and are reported as negative, no agglutination
presence of agglutination indicated that the pt had elevated RFs
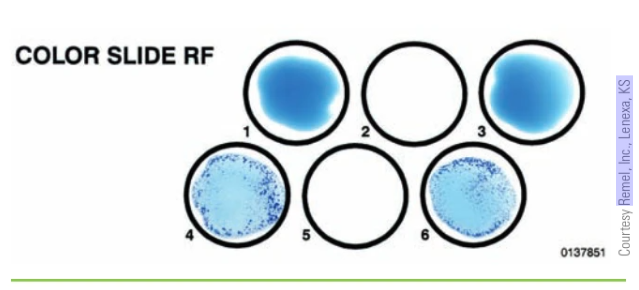
Can RA be ruled out is a pt has a negative Rf test?
No
hemagglutination
agglutination of RBC
human chronic gonadotropin (hCG)
human/uterine hormone produced by placenta (h/uGC); typically reached detectable levels in urine after one week of implantation and rise durring first trimester of pregnancy
implantation
attachment of the early embryo to the uterus
teratogenic
relating to a substance or agent capable of leading to birth defects by causing change or harm to a fetus or embryo
trophoblastic
relating to embryotic nutritive tissue
What are pregnancy test based off of?
detection of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) hormone
how does autoagglutination work for pregnancy tests
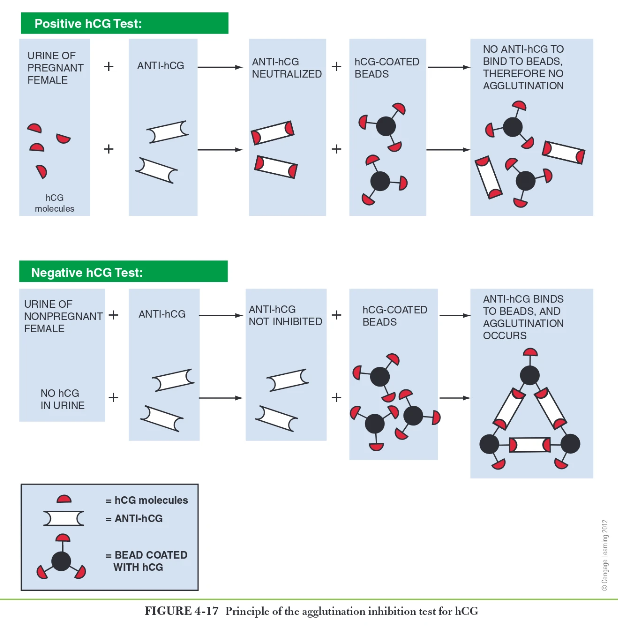
What urine has the highest specific gravity?
first morning specimen (1.020 or higher) if SG is high then so are the hCG hormones
apheresis
process of removing specific component such as platelets from a donners blood and returning remaining blood components to donors circulation.
immunohematology
study of human blood groups; often called blood banking or transfusion services
Why are blood transfusions considered transplants?
because they are administered intravenously
what diseases are transmittable through blood?
What is a common anticoagulant used in blood donations?
citrate-phosphate-dextrose-adenine (CPDA)
antiserum
serum that contains Ab
blood group Ab
protein (Ig) that reacts specifically with a blood group Ag
blood group Ag
substance/structure on the RBC membrane that stimulates Ab formation and reacts w/ Ab
forward grouping/ typing or direct grouping
use of a known antisera (Ab) to detect unknown antigens on pts cells
direct so the antiserum it agglutinates with is the blood type (ex. unknow blood type react w/ anti-A serum = blood type A)
histocompatibility testing
assay to determine if a donor and recipient tissue are compatible
human leukocyte Ag (HLA)
one or several antigens present on leukocytes and other body cells that are important to transplant rejection
major histocompatibility complex (MHC)
group of genes responsible for producing antigens such as HLA that are important in organ tissue transplants
reverse grouping
use of known cells (Ag) to identify unknown Ab in the pts serum or plasma
not reliable until about 6 months of age as Ab are not well developed.
What can ABO grouping check for?
compatible blood and tissue types
paternity
genetic studies
forensic investigations
What are the 4 major blood groups?
A, B, AB, and O
Blood grouping based on antigens:
antigens A and B are found on cell membranes of RBC as well as platelets, leukocytes, and most tissue cells
ABO blood group antigens occur naturally in blood and are in the IgM class.
reverse grouping: If an Ag is missing from an individuals cell the Ab specific to it will be present (ex. group A individuals have anti-B Ab in their blood)
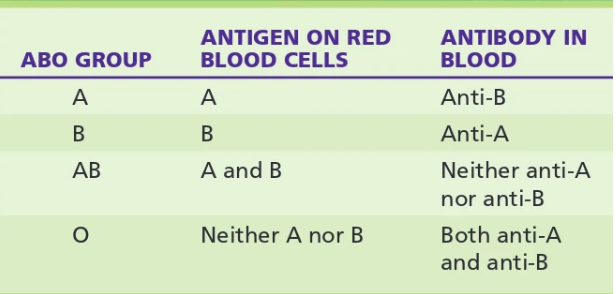
Why are O groups universal donors?
the rule is to not transfuse an Ag a person doesn’t have into their blood and group O doesn’t have any Ag
ABO slide grouping
forward grouping
1) a drop of commercial anti-A serum is placed on one labeled slide and a drop of anti-B serum is placed on another labeled slide.
2)drop of well mixed capillary/venous blood is placed adjacent to each drop if antiserum
3) blood and antiserums are mixed with disposable sticks/stirrers
4) rock slides gently for 2 mins and observe agglutination (agglutination is (+) and no agglutination is (-))

ABO tube grouping
Part 1: forward grouping
create 2-5% RBC suspension by adding 8-19 drops of saline to 1 drop of patients blood for 2 test tubes make sure to label A and B
in A tube put one drop of anti-A and in tube B one drop of anti-B
centrifuge tubes for 15-30 sec. in serological centrifuge
Part 2: reverse grouping to confirm
2 gtts of pts plasma are put into each tube labeled A, B, and control
one drop of group a suspension is put in tube A, one drop of B cell suspension is put in tube B and one drop of 2-5% cell suspension of patients cells is added to control tube.
mix tubes an them put in centrifuge for 15-30 sec.
control tube should always be negative for agglutination
anti-human globulin test (AHG)/Coomb;s test
sensitive test that used commercial anti-human globulin reagent to deduct human globulin coated on RBC
used to test for weak D
feto-maternal hemorrhage (FMH)
occurrence of fetal blood cells entering into the maternal circulation before or durring delivery
hemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN)
condition in which maternity antibody targets fetal RBC for destruction
Rh D immune globulin (RhIG)
a concentrated, purified solution of human anti-D Ab used for injection
What happens to individuals whos blood cells do not have a particular Rh antigen get exposed to it?
an immune response occurs to the Rh antigen
What is the difference between Rh antigens and ABO antigens?
Rh Ag are proteins and only on RBC, no other issues or blood cells.
Antibodies to Rh Ag do not occur naturally
How is Rh D detected?
with forward typing like ABO groups
blood is mixed with Anti-D serum and if cells have D Ag they will agglutinate
describe AHG testing
RBC are incubated w/ anti-D (IgG class) and when showing no signs of agglutination are:
incubated again then rinsed to remove any unbound anti-D.
drop or 2 of AHG reagent is added to cells and anti-IgG will react w/ any anti-D bound durring initial testing.
Centrifuged and observed for agglutination