The Tissue Level of Organization
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Anatomy I: by Larry Hernandez
Your Welcome :3
Tissue
Collections of specialized cells and cell products that performs a limited number of functions
Histology
The study of tissues
Epithelial (Covering)
Covers exposed surface
Lines internal passageways
Forms glands
Connective (Support)
Fills internal spaces
Provides structure and strength to support other tissues
Transport material
Stores Energy
Muscle (Movement)
Specialized for contraction
Skeletal muscle, heart muscle, and walls of hollow organs
Neural (Control)
Carries electrical signals from 1 part of the body to another
Primary Germ Layer
Embryonic give rise to all four tissue types in adults
Ectoderm:
Nervous, epithelial (Epidermis)
Mesoderm:
Muscle, connective, epithelial (Endothelium + Mesothelium)
Endoderm:
Epithelial (Mucosa)
Epithelial Tissues
2 Categories:
Epithelia:
Layers of cells covering internal or external surfaces
Glands:
Structures that produce fluid secretions
Key Concept
Tissues are: Collections of cells and cell products that preform specific, limited functions
4 Tissue types form all the structures of the human body
Special Structures and Functions Of Epithelial Tissues
Topic
Characteristics of Epithelia (Title)
Structures of Epithelia
Cellularity:
Little extracellular matrix, mostly cells
Contacts:
cells linked by tight junctions
Polarity:
Apical (apex) + Basal surfaces, separate functions
Attachment:
attached to Connective tissue (CT) via basal lamina
Avascularity:
No blood vessels, diffusion of connective tissues
Regeneration:
High turnover, stem cells at basal surface. (Once every day)
Functions of Epithelia:
Provide physical protection:
abrasion, dehydration, infection
Control Permeability:
semi-permeability covers all surfaces
Digestion: small intestine (absorbs) and digestive system lining
Provide Sensation:
Sensory Neurons
Produce specialized secretion (Glandular Epithelium)
Protection, chemical messages
Free Surface and Attached Surface
Apical Surface: Exposed to the environment may have:
-Microvilli: absorption or secretion
-Cilla: fluid movement
Basolateral Surface: attachment to neighboring cells via intercellular connections
Intercellular Connections
General Adhesion: Large Connections
CAMs (Cell Adhesion Molecules):
Connect adjacent membranes or binds extracellular materials (e.g. basal lamina)
Intercellular cement:
Thin layer of hyaluronan
(Proteoglycan):
Attach adjacent membranes
Specific Adhesion = Cell Junctions
Tight Junctions
Gap Junctions
Desmosomes
Cell Junctions
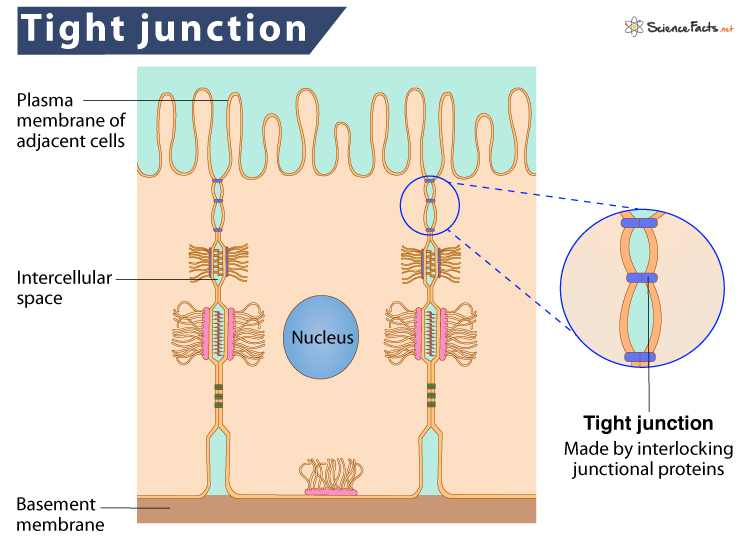
Tight Junction:
Interlocking proteins, bind lipid portion of membrane, water tight seal.
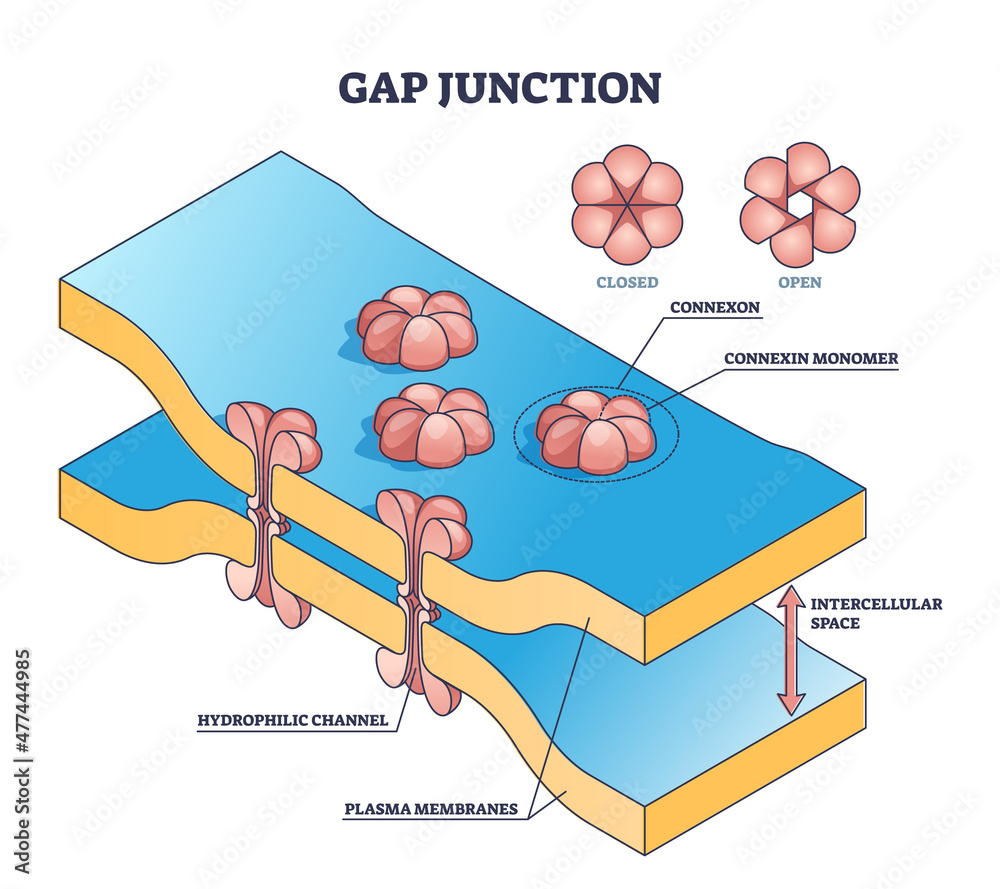
Gap Junction:
Connexons form channel, allow molecules to pass for communications
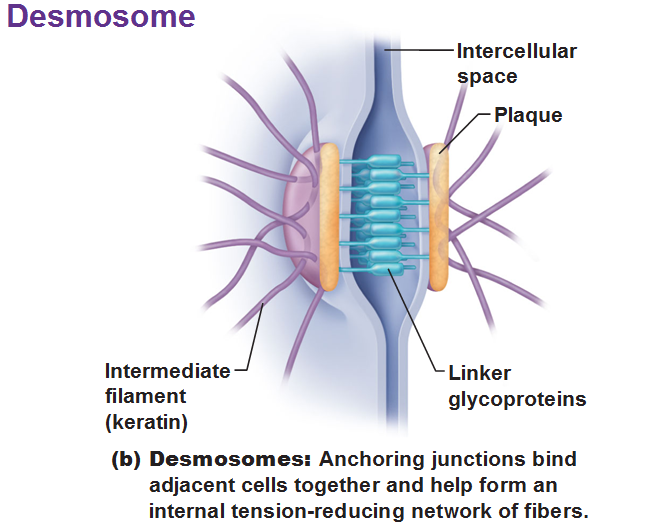
Desmosomes:
CAMs + intercellular cement on dense area to cytoskeleton, resist streching and twisting
Cell Junctions: Gap Junction
Connexons form protein channels allow molecules to pass for communication
Rapid Communications
Allow ions to pass
Coordinated contractions
Cell Junction: Tight Junction
Between 2 cell membranes
Interlocking proteins, binds lipids portion of membrane
Prevents passage of water and solutes
Cell Junction: Desmosomes
Cell Adhesion Molecules + intercellular cement on dense area are attached to the cytoskeleton
Resist streching and twisting
Belt Desmosomes:
Continous band in apical region, attached to microfilaments
Button Desmosomes:
“Spot Weld”, attachment to intermediate filaments
Hemidesmosomes
Half button desmosomes at basal surface, attaches to basal lamina
Classes of Epithelia
Based on shape and layers
Shape: (All are hexagonal from the top)
Squamos: Flat, disc shaped nucleus
Cuboidal: Cube or sqaure, center round nucleus
Columnar: Tall, Basal oval nucleus
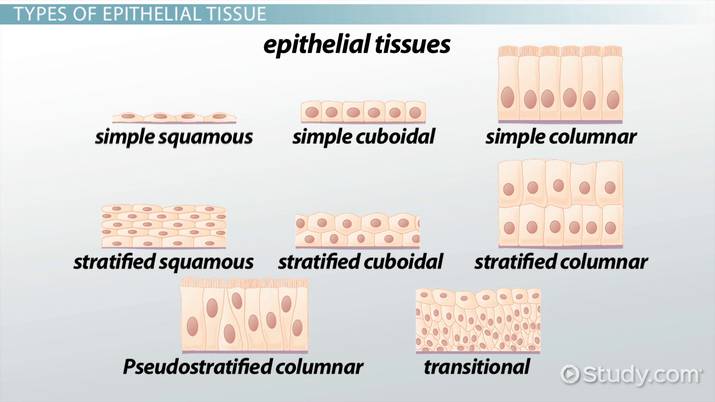
Layers
Simple Epithelium:
Single layer of cells
Function: absorption, secretion, filtration
Stratified Epithelium:
Two or more layer of cells
Function: protecton
Eight Types of Epithelial Tissue
Simple Squamos Epithelium
Stratified Squamos Epithelium
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium
Transitional Epithelium
Simple Columnar Epithelium
Pseudostratified Coulmnar Epithelium
Stratified Columnar Epithelium
Simple Squamos Epithelium
Thin Delicate
Locations: found in protected regions
Mesothelium (serosa), endothelium (blood vessels, heart), kidney tubules, cornea, and alveoli of lungs
Functions: absorption, diffusion, filitration or secretion
Stratified Squamos Epithelium
Basal Cells:
Look cuboidal, apical cell squamos
Found on exposed surfaces
Functions:
Provide protection from absorption, pathogens, and chemicals
Two Types:
A.) Nonkeratinized = Muscosa
Kept Moist
All Cells nucleated
Location: mouth, esophagus, anus, and vagina
B.) Keratinixed = Epidermis
Dry, apical cells dead
Cells contain keratin protein to resist dehydration and add strength
Simple Cuboidal Epithelia
Location:
Kidney Tubules
Pancreas
Salivary Glands
Thyroid
Functions:
Secretion
Absorption
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium
Rare
Typically Two Layers
Location:
Some sweat glands
some mammary glands
Function:
protection
excretion, and secretion
Transitional Epithelium
Relaxed:
Looks like stratified cuboidal
Stretched:
Looks Squamos
Location:
Urinary Bladder
Ureters
Function:
Tolerate Excessive stretching
Simple Columnar Epithelium
Nuclei line up near the basal lamina
Apical surface of cells often has microvilli = “brush border’ (In intestine)
Goblet cells often present:
Secrete mucus
Locations:
Stomach, intestine, gallbladder, uterine tubes and collecting ducts of kidney
Functions:
Absorption or secretion
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium
Several cells contact basal lamina
Some too short to reach apical surface
Nuclei scattered so it appears stratified
Tall cells have cilia on apical surface
Goblet cells (muscus) often present
Location:
Nasal Cavity, trachea, bronchi, male reproductive tract, female uterine tubes
Functions:
Move material across surface
Stratified Columnar Epithelium
Rare
2 layers or mutiple layers with only apical layer columnar
Location:
(Tiny parts of): pharynx, epiglottis, anus,mammary glands, salivary glands, urethra
Function:
Minor protection
Cell Biology
Topic
Cell Biology: Listing
Cell Membrane (1)
Osmosis, Diffusion
Cell Wall
Cytoplasm (2)
Nutrient Water
Nucleus (3)
Chromosomes/ Alleles
DNA/RNA
Mitochondria and Golgi Apparatus (4)
Ribosomes (5)
Proteins make things go
Protein synthesis
Mitosis and Meiosis
Glandular Epithelia
Endocrine Glands: “Internally Secreting”
Secrete into intersitial fluid —> Blood
Secretions = hormones
Regulate and coordinate activities
e.g. pancreas, thyroid, pituitary
Exocrine Glands: “Externaly Secreting”
Secreting duct —> Epithelial Surface
e.g. dogestive enzymes, perspiration, tears, milk and mucus
Classified three ways:
1.) Mode of Secretion
2.) Type of secretion
3.) Structure
A.) MODE OF SECRETION
Merocrine Secretion:
Product released form secretory vesicles by exocytosis
e.g. Mucus, Sweat
Apocrine Secretion:
Product accumulates in vesicles
Apical region of cell which vesicles is shed to release product
e.g. milk
Holocrine Secretion:
Product accumulates in vesicles
Whole cell is lysed to release product
Cells dies, must be replaced by stem cells
e.g. Sebum
B.) TYPES OF SECRETION
Serous Glands: Water + Enzymes
e.g. parotid salivary glands
Mucus Glands: Mucin
(+Water= Mucus)
e.g. goblet cells
Mixed Endocrine Glands:
(Serous + Mucus secretion)
e.g. submandibular salivary glands
C.) Gland Structure
The exocrine gland can be classified
unicellular glands: 1 cell
e.g. Goblet cells which are scattered among epithelia
found in the intestinal lining
Multicellular Glands:
group of cells named for shape and structure