Diversity - Exam Review
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
Taxonomic Categories
Domain (least specific)
Kingdom
Phylum
Class
Order
Family
Genus
Species (most specific)
Species
a set of animals or plants, members of which have similar characteristics to each other and which can breed with each other
Taxonomy
the branch of biology that identifies, names, and classifies species
Binomial Nomenclature
two part name called the 'species/scientific name
Genus name species name (Castor canadensis)
Prokaryotic
an organisms whose cells lack a membrane-bound nucleus and other organelles (Bateria and Archaea)
Eukaryotic
an organism whose cells contain a membrane-bound nucleus (Protista, Plantae, Fungi, Animalia)
3 Domains
Bateria (Prokaryotic)
Archaea (Prokaryotic)
Eukarya (Eukaryotic)
Characteristics of Kingdoms
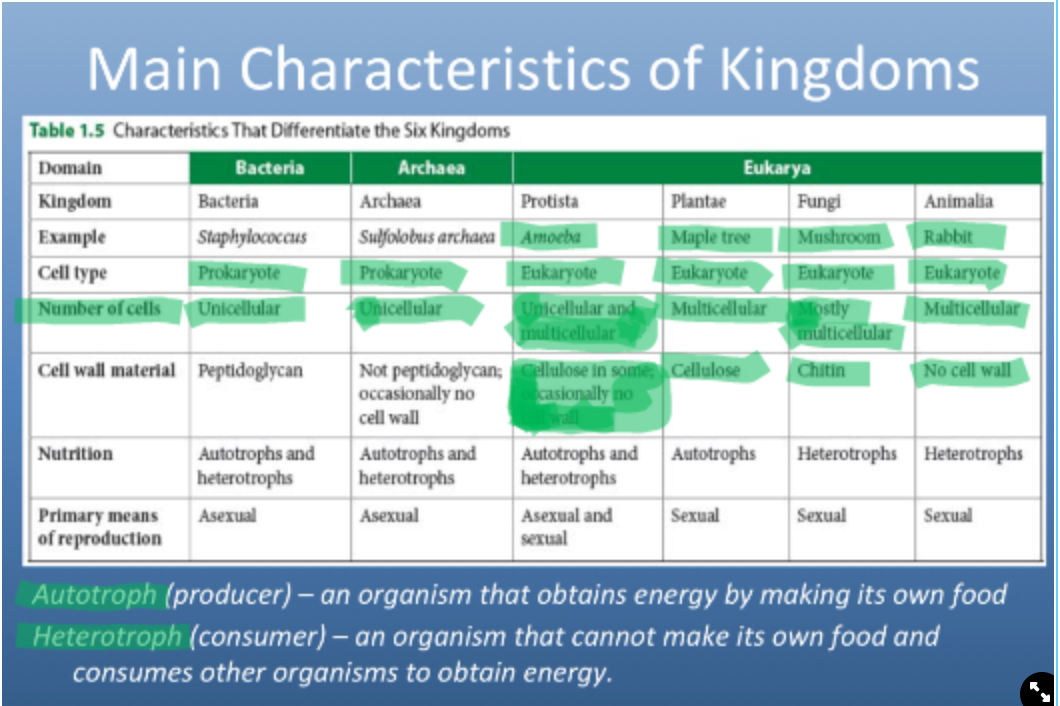
Dichotomous key
A system for narrowing down the identification of a specimen, one step at a time
Sexual
organism combines the genetic information from each of its parents and is genetically unique
Asexual
one parent copies itself to form a genetically identical offspring
Autotroph
an organism that obtains energy by making its own food
Heterotrophs
an organism that cannot make its own food and consumes other organisms to obtain energy
Genetic diversity
the range of different inherited traits within a species
Ecosystem diversity
all the different habitats that exist.
Species diversity
the variety of different species.
Virus
A virus is a pathogen that can cause an individual to develop an illness.
Capsid
the protein shell of a virus, enclosing its genetic material
lytic cycle
-cycle where viruses inject their DNA or RNA into a host cell
-host cell mistakes virus for food particles
-the cell makes copies of the virus and causes the cell membrane to burst
-kills host cells within minutes of infection)
lysogenic cycle
-longer cycle that viruses inject their DNA or RNA into a host cell
-genetic material stays hidden
-when the host cell makes new cells, it copies the viruses genetic material
DNA
the molecule that carries genetic information for the development and functioning of an organism
RNA
70% of viruses - covid 19
molecules that are present in the majority of living organisms and viruses. It is made up of nucleotides, which are ribose sugars attached to nitrogenous bases and phosphate groups.
provirus
a form of a virus that is integrated into the genetic material of a host cell and by replicating with it can be transmitted from one cell generation to the next without causing lysis.
retrovirus
type of virus that inserts a DNA copy of its RNA genome into the DNA of a host cell that it invades
reverse transcriptase:
a DNA polymerase enzyme that transcribes single-stranded RNA into DNA
host chromosome
living thing that is capable of getting infected by a virus
Coccus
a bacterium with a rounded or spherical shape
Bacillus
a bacterium with a rod-like shape
Binary Fission
the cell divides itself into two, equal, identical parts with the same DNA
Conjugation
the process by which one bacterium transfers genetic material to another through direct contact
Endosymbiosis
one organism (endosymbiont) living inside of cell of another organism (host) for their mutual benefit
Host cell
a cell that engulfs another cell
Endosymbiont
a cell that is engulfed by another cell in endosymbiosis
Parasite
an organism that lives on or in a host organism and gets its food from or at the expense of its host
Pseudopod
a temporary growth on a cell that allows it to be mobile, almost like a little foot
Cilium
a hairlike projection from the surface of a cell
Flagellum
an organ that develops in the uterus during pregnancy that provides oxygen and nutrients to a growing baby
Gametophyte
the individual or generation of plants or fungi with alternating sexual and asexual generations that produces gametes
Sporophyte
the diploid multicellular stage in the life cycle of a plant or algae which produces asexual spores
Cone
contains the reproductive organs of certain nonflowering plants. the cone has distinguishing features of pines and other conifers
Flower
reproduction structure designed to encourage pollination (sperm (pollen) and eggs meet, once they meet they can make the seeds that can turn into fruits later on) - angiosperms
Fruit
Fertilization of sperm and egg creates fruit that contain seeds. - gymnosperms
Mono/Dicot
two major types of flowering plants
mono: 1 cotyledons
dicot: 2 cotyledons
Hypha
a long, branching, filamentous structure of a fungus
Mycelium
the main body of the fungus
Lichen
any of numerous plant like living things made up of an alga and a fungus growing together on a solid surface (as a rock or a tree)
Invertebrate/Vertebrates
Invertebrates: animals without a backbone
Vertebrates: animals with backbone
Radial/Bilateral Symmetry
Radial: plant and animal symmetry in which similar parts are arranged in a balanced way around the center of the body
Bilateral: a form of symmetry in which the opposite sides of the body are similar.
Segmentation
the division of some animal and plant body plans into a series of repetitive segments
Polyp:
a projecting growth of tissue from a surface in the body, usually a mucous membrane.
Medusa:
one of two principal body types occurring in members of the invertebrate animal phylum Cnidaria. It is the typical form of the jellyfish.
Exoskeleton
a hard, protective covering located on the exterior of an animal
Tetrapod
a four legged vertebrate
Ecto/Endothermy
Ectotherm: cold blooded animal
Endotherm: warm blooded animal
Mammary Gland
the gland that produces milk in mammals