Phylum Platyhelminthes: Flukes (Cram)
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
What are the two classes of flatworms
Class Trematoda
Class Cestoda
What is the common name for class Trematoda? Remember: It was a fluke I survived the tremor
Flukes
What is the common name for class Cestoda?
Tapeworms
Term that describes how most Platyhelminths have both male and female reproductive organs
Hermaphroditic
Do Platyhelminths move around to feed?
No
What two structures can Platyhelminths have to attach themselves to the host?
Ventral sucker
Oral sucker
What type of lifestyle do Platyhelminths have?
Indirect
How are flukes flattened, what do they resemble?
Dorso–ventrally, leaf
Why are the cecal contents of flukes known as "fluke puke"
Becaused they lack an anus, cecal contents are regurgitated
How do you test for the presence of fluke eggs in feces?
Sedimentation, too heavy to float
Where do fluke eggs usually need to land in order to hatch?
Water
Fluke larva in egg hatches
Miracidium
What does a miracidium have to do in its first 24 hours in order to survive?
Find an intermediate host (IH)
Miracidium penetrates the IH, becomes sac–like, containing many germinal cells
Sporocyst
Each germinal cell in a sporocyst turns in 5–8 of these
Redia (rediae plural)
Tadpole–like form after redia
Cercaria
What are the three things a cercaria can do?
Go into another IH, become metacercaria
Encyst on vegetation as a metacercaria
Go directly into DH, metacercaria stage skipped
What is the genus species known as the common liver fluke?
Fasciola hepatica
What are the two most important definitive hosts of Fasciola hepatica?
Sheep and cattle
What is the intermediate host for Fasciola hepatica?
Water snails
What is the site of adult Fasciola hepatica in the DH?
Bile ducts
What is the site of immature Fasciola hepatica in the DH?
Liver parenchyma
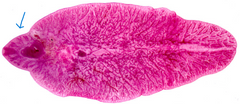
What is a major anatomical feature of Fasciola hepatica?
Anterior projecting cone
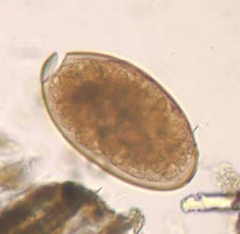
Cap on the end of fluke eggs
Operculum
How long is the prepatent period for Fasciola hepatica?
10–12 weeks
Disease developed due to the migration of Fasciola hepatica
Black disease (Clostridum novyi B)
True or false: Fasciola hepatica cause anemia
True. They are avid bloodsuckers
What should you NOT treat flukes with?
Ivermectin
What should you use to treat flukes?
Anthelmintics
What genus species is commonly known as the giant liver fluke?
Fascioloides magna
What are the four domesticated definitive host species of Fascioloides magna?
Cattle, sheep, llama, pig
What is the intermediate host of Fascioloides magna?
Water snail
Which is the largest fluke of any domesticated species?
Fascioloides magna
What is the prepatent period for Fascioloides magna in cattle?
30–32 weeks
How are Fascioloides magna encapsulated in deer?
Thin, fibrous capsules connected to bile ducts, this allows the passage of eggs into the feces
How are Fascioloides magna encapsulated in cattle?
Thick walled, fibrous capsule that occludes bile ducts. Eggs can't pass into the environment
How are Fascioloides magna encapsulated in sheep?
They aren't. Flukes can migrate freely, causing extensive liver damage
What can farmers do to their feilds in spring to decrease the larval stages of Fascioloides magna?
Controlled burning
What genus species is commonly known as the lancet fluke?
Dicrocoelium dendriticum
What are the three domestic definitive host species of Dicrocoelium dendriticum?
Sheep, goats, cattle
What are the two intermediate hosts of Dicrocoelium dendriticum?
Land snails\n2. Brown ants
What are the two sites for adult Dicrocoelium dendriticum in the definitive host?
Bile ducts\n2. Gallbladder
What is the prepatent period for Dicrocoelium dendriticum?
10–12 weeks
True or false: Dicrocoelium dendriticum are highly pathogenic, it usually takes very few flukes to cause symptoms
False. It is not uncommon for 14,000 adult flukes to infect a host at one time
What species is common in sled dogs or dogs that eat raw fish?
Metorchis conjunctis
What are the two domestic definitive host species for Metorchis conjunctis?
Dogs, cats
What are the two intermediate hosts of Metorchis conjunctis?
Water snails\n2. Wide variety of fish species
What is the site of adult Metorchis conjunctis flukes in the definitive host?
Bile ducts
What is the prepatent period for Metorchis conjunctis?
16 days
What genus species is known as the salmon poisoning fluke?
Nanophyetus salmincola
What are the two domestic definitive host species for Nanophyetus salmincola?
Dogs, cats
What are the two intermediate hosts for Nanophyetus salmincola?
Water snails\n2. Salmon or trout
What is the site of adult Nanophyetus salmincola flukes in the definitive host?
Small intestine
Which is the smallest fluke of domesticated species?
Nanophyetus salmincola
What is the prepatent period for Nanophyetus salmincola in dogs?
5–8 days
True or false: Nanophyetus salmincola are highly pathogenic, they cause fever, lack of appetite, vomiting, and diarrhea which can be fatal
False. The fluke itself is relatively harmless, the pathogenic effects are due to them being vectors of a Rickettsia bacteria
What is the genus species commonly known as the lung fluke?
Paragonimus kellicotti
What are the two domestic definitive host species for Paragonimus kellicotti?
Dogs, cats
What are the two intermediate hosts for Paragonimus kellicotti?
Water snails \n2. Crustaceans (crabs, crayfish, etc.)
What do Paragonimus kellicotti flukes cause in the lung parenchyma?
Cysts
What is the genus of fluke known as the intestinal fluke?
Alaria species
What are the two domestic definitive host species for Alaria spp?
Dogs, cats
What are the two intermediate hosts for Alaria spp?
Water snails \n2. Tadpoles (these may be eaten by frogs, snakes, etc. But no futher development takes place)
What is the site of adult Alaria spp flukes in the definitive host?
Small intestine
Are Alaria spp. generally very pathogenic?
No
What are two anthelmintics commonly used for the treatment of flukes?
Albendazole2. Fenbendazole