Fischer Esterification
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
What is the general reaction for Fischer Esterification (include catalyst)?
Carboxylic acid + Alcohol ⇌ Ester + Water (catalyzed by concentrated H₂SO₄).
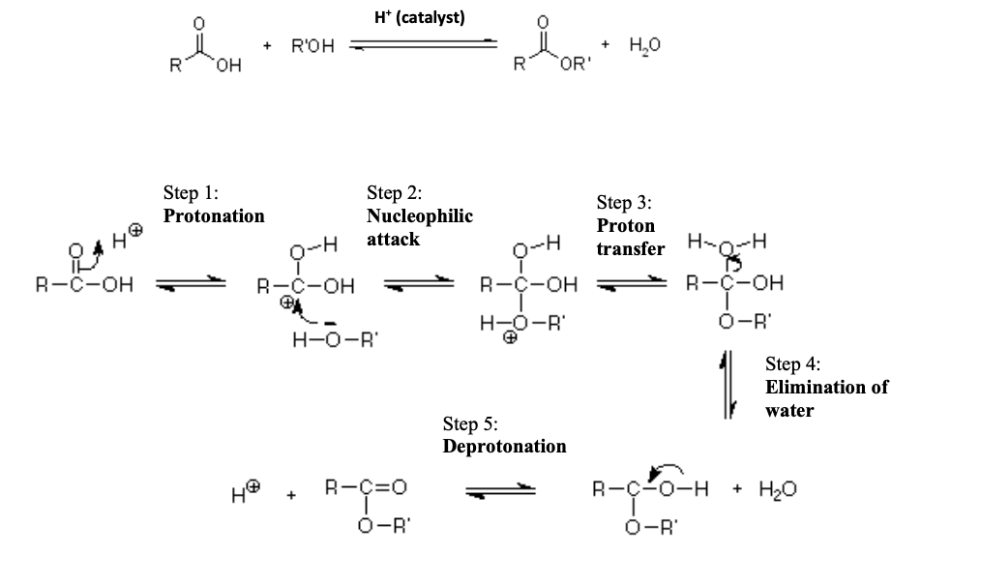
How can you shift the Fischer esterification equilibrium toward product formation?
Use excess alcohol or acid.
Remove water as it forms.
Why is the reaction mixture refluxed in Fischer esterification?
Maintain constant, elevated temperature (around boiling point).
Prevent loss of volatile reactants/products.
Speed up the reaction.
Drive reaction closer to completion.
What is the approximate temperature during reflux?
Around 100–110°C (slightly below boiling point of acetic acid, ~118°C).
What is the purpose of transferring the reaction mixture to a separatory funnel and adding water?
To dilute and remove sulfuric acid and water-soluble impurities.This process helps to separate the ester from the reaction mixture and facilitates the purification of the product.
What reaction happens when adding water after reflux?
Sulfuric acid dissociates:
H₂SO₄ → H₃O⁺ + HSO₄⁻
Why is sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO₃) added during work-up?
To neutralize any remaining acetic acid and sulfuric acid.
What is the reaction between acetic acid and sodium bicarbonate?
CH₃COOH + NaHCO₃ → CH₃COONa + CO₂ (gas) + H₂O
Why is saturated sodium chloride (NaCl) added during the work-up?
"Salts out" the organic layer.
Aids better separation by breaking emulsions.
No chemical reaction, just separation aid.
What is the purpose of drying the organic layer with sodium sulfate (Na₂SO₄)?
Removes any residual water from the organic layer.
What happens when sodium sulfate reacts with water?
Na₂SO₄ + H₂O → Na₂SO₄·10H₂O (hydrated sodium sulfate)
What is the purpose of decanting into a clean vial after drying?
To isolate the pure ester product from the drying agent.
How do you determine the limiting reagent (LR) in Fischer esterification?
The alcohol (e.g., isoamyl alcohol) is usually the limiting reagent.
How can you recognize an ester in an IR spectrum?
Strong C=O (carbonyl) stretch around 1735–1750 cm⁻¹.
C–O stretch around 1000–1300 cm⁻¹.
Why does reflux help drive Fischer esterification to completion?
Keeps temperature high and constant.
Helps remove water (if using a drying agent).