micro exam 3
1/159
Earn XP
Description and Tags
i am cry
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
160 Terms
temperature, pH, water, oxygen
What 4 factors affect microbial growth
cardinal temperatures
maximum, minimum, and optimum temp for microbes
Psychrophiles
cold loving, 0-20*C
Fragillaria
optimum 7*C
Chlamydomonas (algae)
pink snow
Facultative psychrophile
aka psychrotolerant, usually grow 25-30*C, but can grow lower
Thermophiles
optimum temps 45*C or higher
hyperthermophiles
greater than 80*C, mainly archae, desert soils, hotsprings, hydrothermal vents
higher temps than eukaryotes
Prokaryotes grow at ___ temps than eukaryotes
65*c
eukaryotes max temp
higher temps than photosynthetic
nonphotosynthetic organisms are able to grow at ___ temps than photosynthetic organisms
higher temps than more complex
structurally less complex organisms grow at ___ temps than more complex organisms
Thermus aquaticus
taq polymerase,
higher concentrations of unsaturated fats
psychrophiles have ___ concentrations of unsaturated fats
thermophiles have ___ concentrations of saturated fats
higher concentrations of saturated fats
Mesophiles
optimum temp is 15-45*C
pH 5-9
most natural environments have a ph of what?
thermoacidophiles
hot springs
halophiles
salt loving
barophiles
organisms that thrive under high pressure
obligate aerovbe
requires oxygen
microaerophile
requires oxygen but at less concentrations
anaerobe
does not require oxygen
obligate anaerobe
harmed by oxygen
facultative anaerobe
survives with oxygen, but can exist without it
aerotolerant anaerobe
tolerates oxygen but does not need it for growth, fermenters
oxygen toxicity
oxidizing agent, small amounts formed during cellular respirations
superoxide ion
O2 + e- —> O2- accumulates in anaerobes exposed to O2 inactivates cell components
superoxide dismutase
O2- + O2- + 2H+ -—> H2O2 + O2
Catalase
2H2O2 —> O2 + 2H2O
peroxidase
NADH + 2H+ + H2O2 —> 2H2O + NAD+
aerobes have what enzymes
superoxide dismutate, catalase, peroxidase
facultative anaerobes have what enzymes
catalase sometimes absent
aerotolerant have what enzymes
superoxide dismutase, lack catalase
obligate anaerobes have what enzymes
lack all 3
agar
slime of red algae, metabolically inert, solidifies at 42*C
Synthetic media
chemically defined, exact composition and ingredient weight
complex media
natural, exact compostions not known, beef extract, yeast extract, nutrient, TSA, corn meal agar, potato dextrose agar
selective medium
suppresses growth of unwanted bacteria, select for desired bacteria, mannitol salts agar MSA, selects for S. aureus
Differential medium
makes growth of one bacterial species look different from another, blood agar, some bacteria cause hemolysis, MSA low pH, phenol red from red to yellow
anaerobic medium
removes oxygen, sodium thioglycolate combines with oxygen, special growth chambers
enrichment medium
broth, selective medium, increase low numbers of desired bacterium from mixed environmental of clinical sample
binary fission
divide to 2 cells
DNA replication
is bidirectional
MreB protein and shape
spiral inside periphery of cell in rods, directs cell wall synthesis to contract, cocci lack MreB protein
Crescentin, caulobacter crescentus
vibrio, long concave curvature, inhibits growth
N = N02n
N= end count, N0= beginning count, n= # of generations
how to find n
n= 3.3(logN-logN0)
g=t/n
how to find generation time g
biofilm
slime encases aggregation of microbiota
intracellular cyclic di-guanosine monophosphate
triggers connection and attachment
matrix
made of polysaccharide proteins, glycoproteins, glycolipids, DNA, extracellular polymeric substances
what do biofilms offer?
UV light, antibiotics, antimicrobial, resist phagocytosis
Vibrio cholerae
cholera, oceans, low densities, teeth, pipes, oil pipes, used in sewage treatment
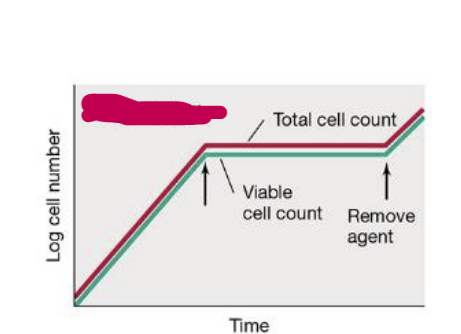
bacteriostatic
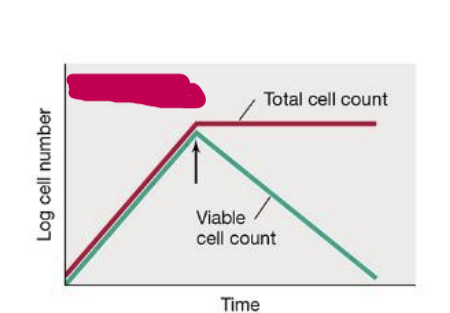
bacteriocidal
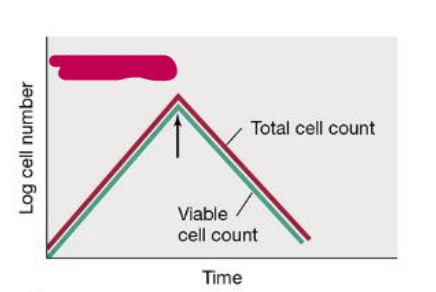
bacteriolytic
decimal reduction time
food industry, time for ten-fold reduction in living cells, 10% remain
pasteurization
62.8*C for 30 min, 72*C for 15 seconds, milkd
dry heat
hot air, 160*C, 2 hrs, needed to kill endospores, flaming
lowering temps
preservation, depress metabolic rates, bacteriostasis, refrigeration to 4*C, freezing, eukaryotic cells destroyed, spores survive
dessication
preservation of drying, jerky, dried grains
osmotic pressure
salt, sugar
radiation
ionizing radiation to form hydroxyl radicals to damage cell DNA, gamma rays, x rats, penetrating, spices, meats, veggies, milk, heat sensitive surgical materials
nonionizing radiation
ultra violet, damages DNA, not penetrating, germicidal lamps, surface sterilization
filtration
filters with 0.2 micrometer pores, HEPA filter
disinfectant
chemical applied to object to kill
sanitizer
reduce, may not eliminate microbial numbers
antiseptic
applied to tissue, kills or inhibit, bacteriostatis, bactericidal
minimum inhibitory concentration
smallest amount of an agent needed to inhibit growth of a test organism
stromatoliites
fossilized microbrial mats
hydrogen hypothesis
hypothesis suggesting that life originated from hydrogen-producing microorganisms, emphasizing the role of hydrogen in early cellular metabolism.
oligodynamic action
the mechanism by which small amounts of heavy metals inhibit microbial growth.
surfactants
compounds that reduce surface tension, allowing easier mixing and interaction of liquids, often used in detergents and emulsifiers.
diplomonads
protist, 2 nuclei of unequal size, mitosomes reduced mitochondria, lack ETC, CAC, genes, flagellated
Giardia intestinalis
lamblia, diplomonad, gastroenteritis, 30,000 cases, form cysts: resistant structures
Parabasalids
parabasal body, connects flagellum to golgi app. lack mitochondria, have hydrogenosomes, anaerobic,
euglenozoans
chloroplasts present or absent, autotrophs/heterotrophs, no pathogens
euglenids
Euglena, pellicle, stigma, two flagella, one emergent, or inside, paramylon for storage of B-1,3
kinetoplastids
mass of circular DNA in the single mitochondria, kDNA, lack chloroplasts
Trypanosoma brucci
african sleeping sickness, tse-tse fly, subsaharan
T. cruz
Chagas, kissing bugs in latin america
Leishmania
skin, sandflies
Alveolates
sacs under cytoplasmic membrane
ciliates
paramecium, macro, micronucleus, conjugation for sexual repro
Balantidium coli
gastroenteritis
Apicomplexans
non-motile, Plasmodium: malaria, P. falciparum most lethal, P. vivax most common
sickle cell anemia
heterozygous, resistant to malaria in area where common
Toxoplasma gondii
cat feces, undercooked meat, gasterenteritis
Dinoflagellates
photoautotrophs, 2 flagella, dino-whirled, armored from cellulase plates, pigment: carotenoids red to brown, endosymbiosis with corals, bioluminescence, red tide, accumulates in shellfish and passes toxins to humans
Pfiesteria piscidia
dinoflagellate accumulates in fish and leads to death
Amoebozoa
pseudopodia, amoeba
Entamoeba histolytica
amoebic dysentery, amebiasis
Naegleria fowler
primary amoebic: meningoencephalitis (PAM) swimming, nose to brain, cyst, trophozoite, flagellate
chlorophyta
green algae, chlorophyll a and b, starch, cellulose walls, rise to land plants
Rhudophyta
red algae, chlorophyll a and d, phycoerythrin: red, macroscopic, nori, carrageenan reacts with milk protein to form gel
Gelidium
source of agar
Stramenophiles
photosynthetic or not, flagellate
Phaeophyta
brown algae, kelps, macroscopic, fucoxanthin golden brown, laminarin storage, algin slime from surface used as thickening agent
Diatoms
Bacillariophyta, fucoxanthin carotenoid, golden brown, walls have SiO2 glass, radial bilateral, fats, oils, chrysolaminarin for reserve, free floating,