Alkene and Alkyne Reactions
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
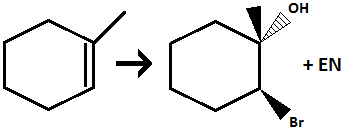
Halohydrin Formation of Alkenes
Reagents: X2, H20
Addition of OH group and halogen atom across alkene
OH goes in most substituted position
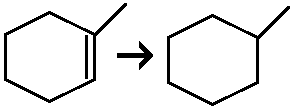
Hydrogenation of an alkene
Reagents: H2, Pt
Syn addition of H
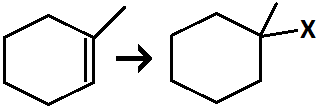
Hydrohalogenation of alkene
Reagents: HBR
(adding ROOR produces antimarkovnikov product)
addition of halogen and H across alkene
forms a carbocation intermediate
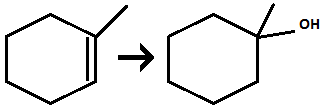
Hydration of alkene
Reagents: H3O+/dilute H2SO4
Markovnikov addition of OH and H across alkene
Hydroboration - Oxidation of alkene
Reagents: 1) BH3, 2) NaOH, 3) H2O2
Antimarkovnikov and sun addition of OH and H across alkene
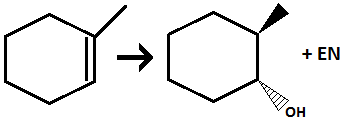
Halogenation of alkene
Addition of 2 Halogen atoms across alkene

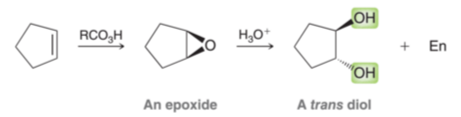
Antidihydroxylation of alkene
Reagents: 1) RCO3H, 2) H3O+
Forms epoxide intermediate
Addition of 2OH across alkene
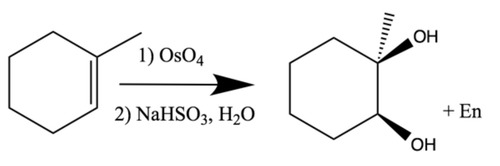
Syn dihydroxylation of alkene
Reagents: KMnO4, and NaOH, H2O
Syn addition of 2OH across alkene
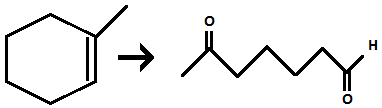
Ozonolysis of alkene
Reagents: 1) O3, 2) DMS
cleaves carbon-carbon bond to form either ketone or aldehyde FG
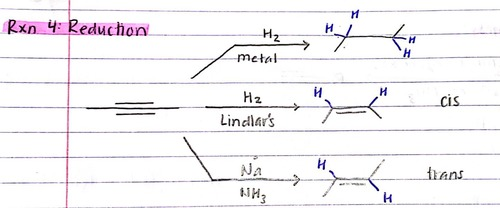
Reduction reactions of alkynes
Reduces alkyne to either cis or trans alkene or all the way to alkane
cis alkene reagents: H2 Lindlar catalyst
trans alkene reagents: Na, NH3 (l)
alkane reagents: H2, Pt
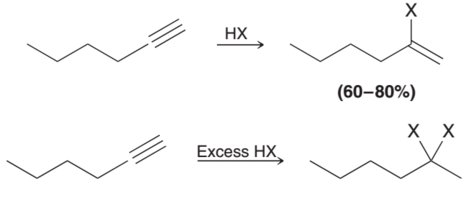
Hydrohalogenation of Alkynes
Reagents: either HX or xs HX (xs goes to alkane)
similar to alkene
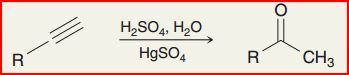
Hydration of alkyne
Reagents: H2SO4, H2O, & HgSO4
Markovnikov addition of OH to create ketone group enol and ketone are tautomers formed under acidic conditions
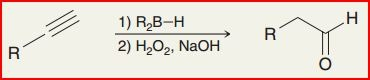
Hydroboration - Oxidation of Alkynes
Reagents: 1) 9-BBN, 2) H2O2, 3) NaOH
Anti-markovnikov addition of OH to create aldehyde group
enol and aldehyde are tautomers formed under basic conditions
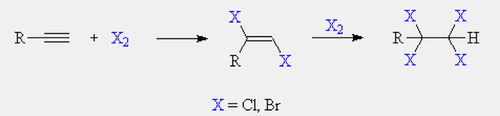
Halogenation of alkyne
Reagents: Br2 or xs Br2
Addition of halogen atoms
Ozonolysis of alkynes
Reagents: 1) O3, 2) H2O
Cleaves alkyne to produce carboxylic acid or Co2
If alkyne is internal, 2 carboxylic FG are made
If alkyne is terminal, a carboxylic FG is made plus CO2