Chemistry Alphonse HS Test Family/Group Names and Electron Configuration
1/28
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
low melting and boiling points, brittle, not good conductors
nonmetals
high melting and boiling points, malleable, conduct electricity and heat well
metals
elements that have properties in between metals and nonmetals
metalloids
react violently with water
alkali metals, alkaline earth metals
3 alkali metals
Li, Na, K
3 alkaline earth metals
Be, Ca, Mg
3 transition metals
Fe, Cu, Au
3 post transition metals
Al, Sn, Pb
3 metalloids
As, Bi, Si
3 halogens
F, Cl, Br
3 noble gasses
He, Ne, Ar
why are copper and aluminum used for wires
conduct electricity well as transition metals
why are rubber and nonmetals used for oven mitts to remove hot things
they transfer heat slow to prevent a burn
4 building block elements of life
C, H, O, N
how many electron in s orbital
2
how many electron in p orbital
6
how many electron in d orbital
10
as principal quantum number increases, how does size and energy change
orbital is larger and increases in energy
aufbau principle
electron occupies lowest energy orbital first
pauli exclusion principle
maximum of 2 electrons occupy a single orbital, only if the electrons have opposite spins
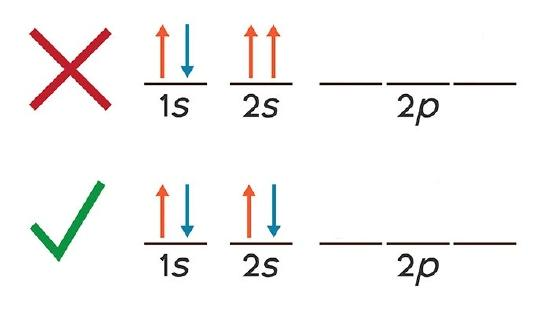
what is an orbital diagram
orbital diagram uses boxes to show electron spin and orbital occupation
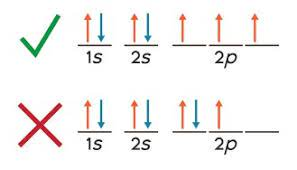
hunds rule
single electrons with the same spin must occupy each equal energy orbital before electrons of opposite spins can occupy the same orbitals
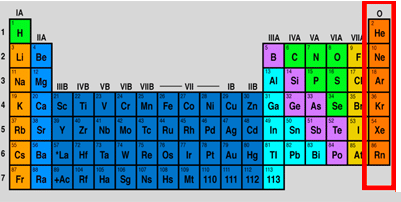
which family/group name is this
noble gasses
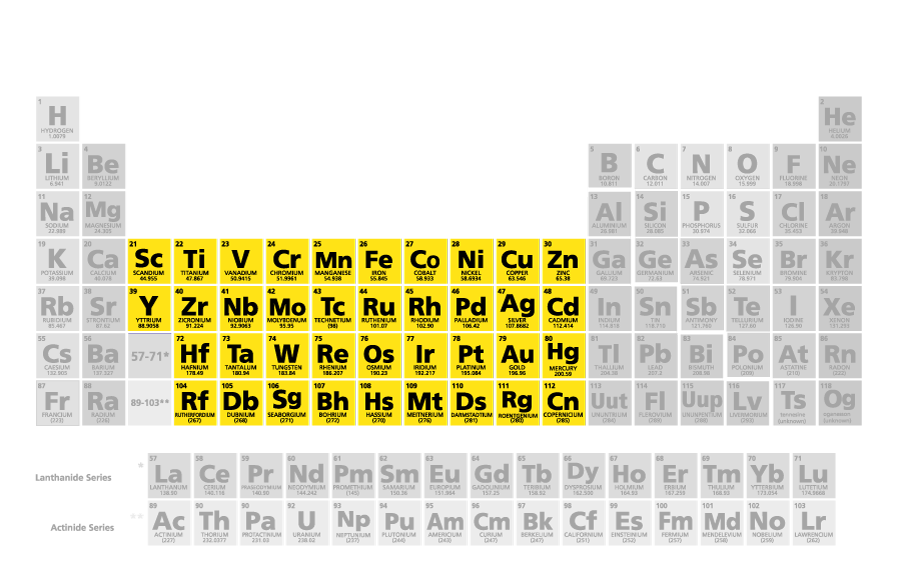
which family/group name is this
transition metals

what family/group name is this
alkali metals
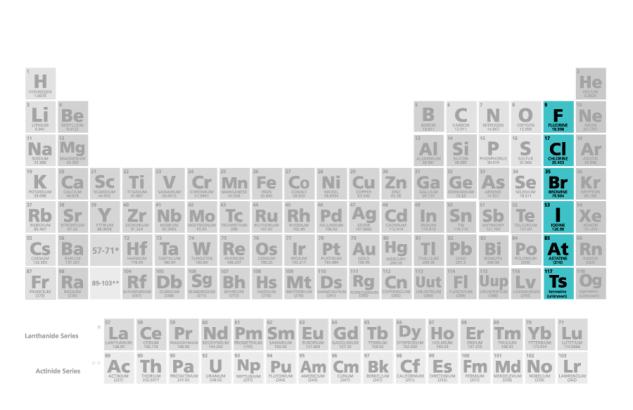
what family/group name is this
halogens
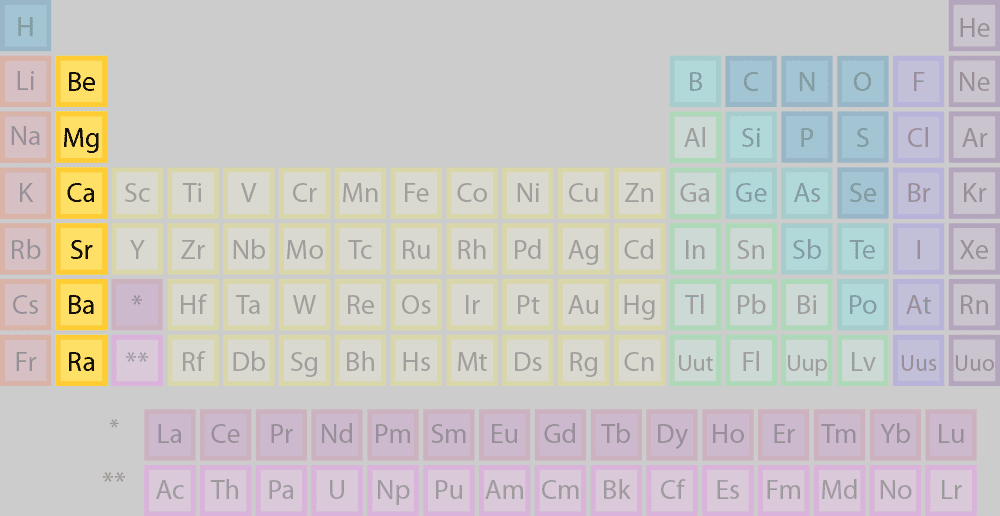
what family/group is this
alkaline earth metals
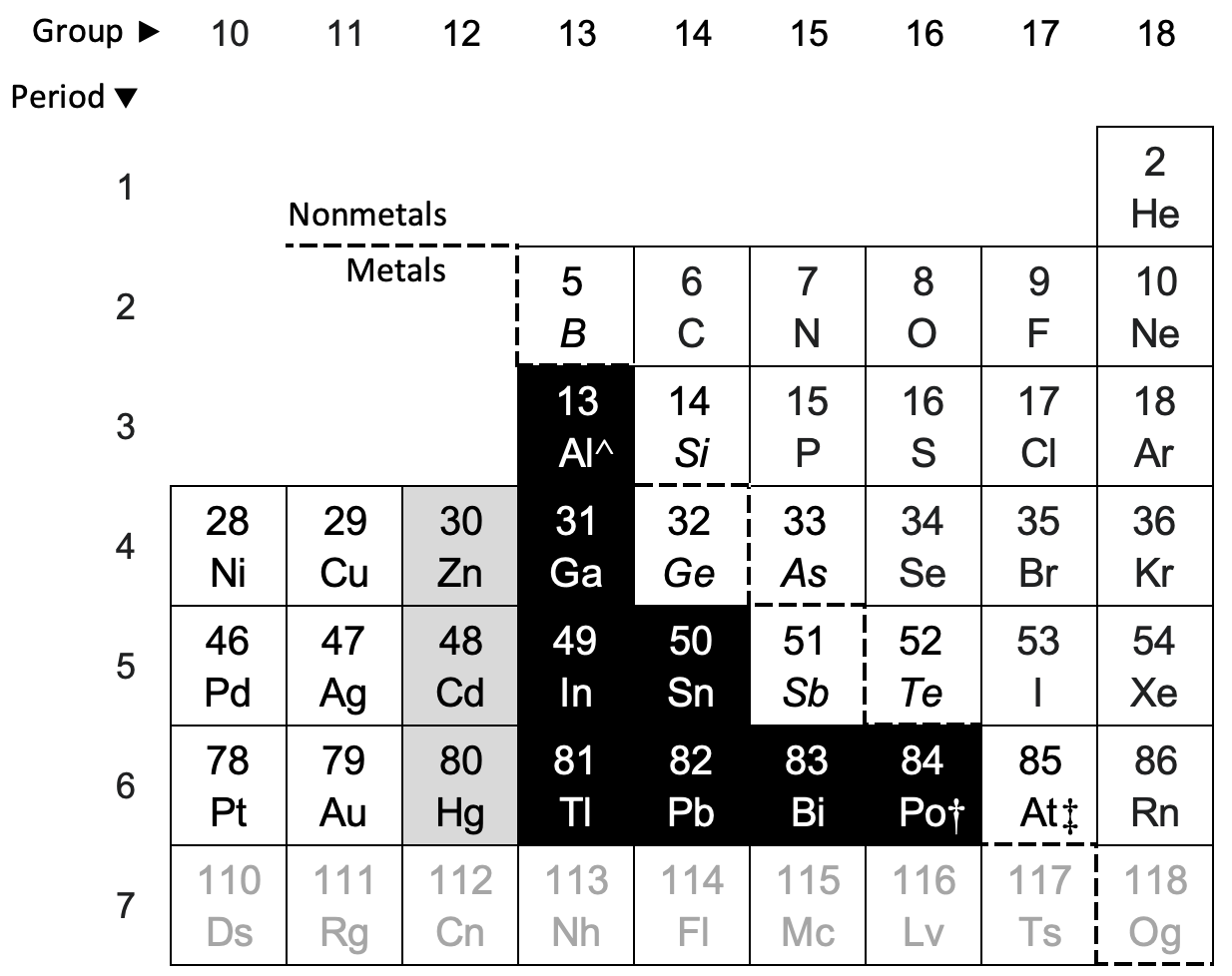
what family/group is this
post-transition metals
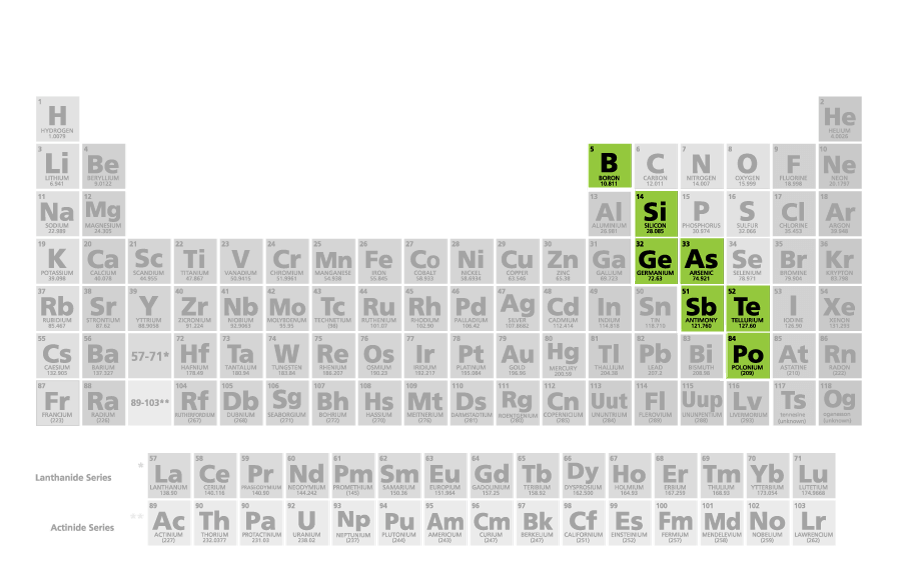
what family/group is this
metalloids