antimicrobial drugs and resistance
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
what are antimicrobial drugs
compounds that inhibit or kill the growth of microorganisms
What is selective toxicity
Damage to pathogen without harming the host
What are the two types of antimicrobial drug effects
-cidal and -static
What does the spectrum of activity refer to in antimicrobial drugs
Rang of microbes affected by the drug
What is a narrow spec. antiobiotic
Affects only microbes within a limited group
What is an example of a narrow spec. antibiotic
Penicillin G - works against Gram positive bacteria
What is a very narrow spec antibiotic
Affects only a very specific group
What is an example of a very narrow spec. antibiotic
Isonazid - works against mycobacteria
What is a broad spec. antibiotic
works against a wide range of microbes
What is an example of a brad spec. antibiotic
Tetracycline - works against both gram negative and gram positive
What does an antibiotic that inhibits synthesis of LPS affect
It affects Gram negative bacteria
What does an antibiotic that inhibits endosposre formation affect?
It affects Gram positive bacteria
What are growth factor analogues
Structurally similar to growth factors, interfere with metabolism
how do sulfa drugs inhibit bacterial growth
They interfere with folic acid synthesis
structurally similar to PABA
What is a characteristic of quinalones
They interfere with DNA replication in bacteria
what enzyme do quinalones target
DNA gyrase
what is an example of a quinalone
ciproflaxcin
how does resistance to ciproflaxcin occur
Mutation of DNA gyrase binding site
what is an antibiotic
antimicrobial agent produced by other microorganisms
why are most antibiotics semi-synthetic
natural antibiotics are modified to change properties
What is the active structural component of β-lactam antibiotics?
β-lactam ring
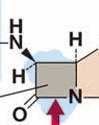
How do β-lactam antibiotics work?
They inhibit bacterial cell wall synthesis
bind to penicillin binding proteins
what enzyme do some bacteria produce to resist β-lactam antibiotics
β-lactamase
what do semi - synthetic penicilins’s do?
alter the activity through changes to side chains
What is methicillin designed to do?
fight multiple antibiotic resistant S.aureus
What is MRSA
methicillin resistant S. aurues
cephalosporins
structurally different from penicillins, but include β-lactam ring
Broad spec
more resistant to β-lactamase
treat infections by penicillin resistant Gram negative bacteria
what is ceftriaxone
A third generation cephalosporin antibiotic
How does ceftriaxone differ from penicillins?
It has a broader spectrum and more resistance
what is vancomycin used for
first line treatment against MRSA
Very narrow spec.
what is the modes of action of vancomycin
Blocks cross-linking of peptidoglycan
what are aminoglycosides
Protein synthesis inhibitors targeting the ribosome
what do aminoglycosides target
target 30S subunit
what is an example of aminoglycosides
streptomycin
macrolides
structure based on lactone rings
what is an example of macrolides
erythromycin
What do macrolides target
50S subunit
narrow spec.
what produces tetracycline
Streptomyces aureofaciens
what does tetracycline inhibit
30S subunit
what is the spectrum of tetracycline
Broad spec, heavily used antibiotics
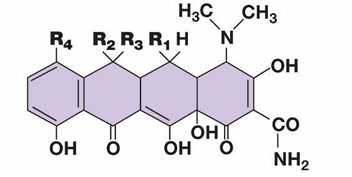
what is daptomycin
a cyclic lipopeptide antibiotic
how does daptomycin work
forms pores in the cell membrane
Narrow spec.
last resort AB against MRSA
what is platensimycin
A novel antibiotic inhibiting fatty acid biosynthesis
what is platensimycin not clinically useful
Humans clear the drug too fast
what microorganism produces paltensimycin
streptomyces platensis
what is intrinsic resistance
Natural resistance to one or more antibiotics
What is acquired resistance
ability to resist effects of normally sensitive agents
how can resistance genes be transferred
Through horizontal genes transfer
what is one mechanism of antibiotic resistance
inactivation of the drug by enzymes
e.g beta lactamases
what is metabolic by pass in antibiotic resistance
acquiring systems that reduce dependence on antibiotics
how do some bacteria decrease drug uptake ?
by modifying porin proteins
how do bacteria modify drug targets
by altering ribosomal proteins
what are efflux pumps
transporters that expel antibiotics from the cell
how does antibiotic overuse contribute to resistance?
it selects for antibiotic resistance strains
what is the consequence of antibiotic resistance in pathogens
infections become difficult to treat
what is the role of infection prevention in combating resistance
it reduces the spread of resistant strains
why is rapid diagnosis important in preventing resistance
it ensures appropriate use of antibiotics
What is prudent use of antibiotics
using antibiotics only when necessary
how can transmission of resistant bacteria be prevented
through proper hygiene and sanitation practices