Mains electricity
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
What are the risks of electrical devices?
- electric shocks from contact with exposed live wires
- fires & burns from overloaded circuits & current that it is too high
- tripping hazards from trailing cables
- shocks & malfunctions from damaged equipment & when water comes into contact with electricity
How can the device & user be protected from potential risks?
- insulation & double insulation
- earthing
- fuses
- circuit breakers
How does insulation & double insulation protect the device & user?
- insulation (e.g. plastic) covers exposed wires & absorbs any heat that is produced from the circuit
- this protects the user from electric shocks & burns
How does earthing protect the device & user?
the earth wire is connected to the casing of the appliance
so if the live wire touches the appliance casing, the earth wire provides an alternative path for electricity to flow
this ensures that people don’t get electric shocks when in contact with the live appliance casing
How do fuses protect the device & user?
- fuses stop the flow of current if it gets to high by melting
- this protects the device from fires caused by components functioning at a too high temperature as well as protecting the user from burns
- fuses are easy & cheap to replace
How do circuit breakers protect the device & user?
- circuit breakers stop the flow of electricity if a fault is detected or the current is too high
- this prevents the device from overloading & short circuiting which could lead to a fire
- circuit breakers act faster than fuses & can be reset, rather than needing replacement
What happens when current flows through a resistor?
- the resistance causes some the electrical energy to transfer to heat energy
- some components are designed to make sure sure this happens (e.g. electrical heaters have a lot of resistors to ensure that a lot of heat is produced due to the high resistance)
What is the formula linking power, current & voltage?
power = current × voltage
P = I × V
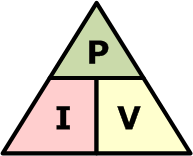
What is the formula linking energy transferred, current, voltage & time?
Energy transferred = current × voltage × time
E = I × V × t
What is the difference between alternating current & direct current?
- alternating current (a.c.) is constantly changing magnitude & direction whereas direct current (d.c.) only flows in 1 direction
- alternating voltage produces alternating current
- direct voltage produces direct current
What is mains electricity?
- the electricity that is delivered to homes & businesses through an electric grid
- it is an alternating current supply
- in the UK, mains electricity has a frequency of 50Hz & 230V