Balance of Payments: Current Account
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Macroeconomics
Last updated 3:14 PM on 10/6/24
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
1
New cards
Current Account Balance of Payments
G: Net trade in goods (visible trrade)
S: Net Trade in services (invisible trade)
I: Investment Income (primary income)
T: Net Transfers
2
New cards
How long has the current account deficit been occurring in the UK/
Since 1984
3
New cards
In 2022, how much of the UK economy comprised of the service sector?
79%
4
New cards
Service Sector
Consists of tertiary and quaternary jobs.
5
New cards
MPI
Marginal Propensity to Import
6
New cards
Main reason for a current account deficit (UK)
Trade in goods as the UK has a high MPI. e.g, 50% of all foods imported
7
New cards
Reason for a limited manufacturing capacity:
The UK has shifted from industrial to post-industrial economy. This means the UK mainly relies on high end goods, which require skills and qualifications.
8
New cards
What does the continuous deficit imply about the UK economy?
That it's unbalanced and we have become too over-dependent on capital inflows.
9
New cards
Capital Inflows
Purchases of domestic assets by foreign households and firms
10
New cards
Why has the manufacturing industry fallen?
The UK has become uncompetitive in the trades of goods. We rely on the exportation of services.
11
New cards
What is the reliance of capital inflows based on?
The assumption that the UK will remain an attraction prospect for international investors.
12
New cards
Why is there a possibility for an unsustainable current account deficit?
A fall in demand for high-end services will mean there's no longer a surplus in the financial account which is what is financing the CA deficit.
13
New cards
BofE Governor ____ Carney said that the UK relies on the "________ of strangers".
BofE Governor Mark Carney said that the UK relies on the " kindness of strangers".
14
New cards
Consequences of the UK's over-reliance on the import of goods.
The UK is vulnerable to supply-side shocks which can lead to shortages and a dry-up in supply.
15
New cards
An example of the UK's over-reliance on a certain good.
The UK imports 50% of its natural gas and the invasion of Ukraine by Russia meant lower supply and higher prices.
16
New cards
Explain why higher energy costs will end in decreased standard of living for UK households.
As energy is a necessity, households will have to pay for this good -> leading to a reduction in discretionary spending -> decreased SOL.
17
New cards
Consequences of firms over-reliance on imported energy and raw materials?
- Vulnerable to supply-side shocks which can cause increased production costs and a limited production capacity.
18
New cards
Consequences of an increasingly conflict riven world:
Global market supply could be compromised, resulting in extreme shortages and increased cost push inflation.
19
New cards
Decline in the manufacturing sector has resulted in:
The UK being barred from taking full advantage of export led growth.
20
New cards
Consequences of an increase o=in the demand of UK goods:
- Reduced structural unemployment and income inequality
21
New cards
Where is income inequality experienced in the UK?
In the North of England and South Wales due to major manufacturing companies hubs that were there previously, employing local residents being shut down. As a result, employees struggled to find a job as those secondary jobs require minimal-none qualifications, meaning it was harder to find jobs matched to their skillsets.
22
New cards
Example of Deindustrialisation resulting in unemployment
Port Talbot, Tata Steel in South Wales
23
New cards
How would increased exports have a knock-on effect in demand?
There'd be an increase in demand leading to lower levels of unemployment -> increased tax revenue -> reduction in the UK's sovereign debt.
24
New cards
Increased demand in exports leads to (in terms of the exchange rate):
Upward pressure on the £ pound sterling due to an increased demand in exports -> leading to cheaper imports.
25
New cards
- Lower production costs for domestic firms
26
New cards
- Larger production capacity for domestic firms due to cheaper FOP
27
New cards
Consequences of Cheaper Imports
- Increased standard of living for UK households as they can purchase imports for cheaper.
28
New cards
Why is a deficit on the current account not necessarily harmful?
There's no clear correlation between a CAD or CAS.
29
New cards
Name a strong/weak economy with a substantial deficit/surplus?
Weak: Nepal has a substantial current account surplus but weak economy.
Strong: USA has a significant current account deficit but a strong economy.
30
New cards
What is Brazil doing to reduce the country's reliance on the exportation of primary goods?
Importing capital goods to help with supply-side growth and increase industrialisation.
31
New cards
Why do some countries have a current account surplus but weak economy?
E.g, Botswana has a strong supply of a primary sector good but it doesn't translate well into a high standard of living or MPI hence the surplus.
32
New cards
What HDI does the UK have?
0.93 indicating a high standard of living.
33
New cards
The UK is the _th largest economy.
The UK is the 6th largest economy.
34
New cards
GDP per capita of the UK is in the top ?% of global economies?
GDP per capita of the UK is in the top 10% of global economies?
35
New cards
Why is a deficit on the current account not necessarily harmful? (2)
The severity depends on what has to be done to finance it.
36
New cards
Why has the UK got a financial account surplus?
Due to its attractive destination for global investment and capital, in addition to its mature institutions having low levels of corruption and an established rule of law.
37
New cards
How has the devaluation of the pound sterling been blocked?
Foreign firms are incentivised to buy UK assets, invest in UK equity and purchase UK debt.
38
New cards
Why is there a shortage of UK housing?
Increased demand and inelastic supply, as well as the buying up of UK property by foreign investors due to the asset growth.
39
New cards
Why is the CAD not a priority for politicians?
The UK will continue to attract foreign capital so the financial account surplus will remain to finance the CAD.
40
New cards
Current Account Deficit in the short run:
It seems to be insignificant compared to the many other problems being faced by the UK, e.g, the cost of living crisis/low productivity and cost of debt servicing.
41
New cards
What runs a surplus on the financial account?
Capital Inflows
42
New cards
Current Account Deficit in the long run:
It highlights the unbalanced economy and over-reliance on the financial account surplus as well as the 'kindness of strangers'.
43
New cards
Expenditure Reduction: Name the 2 Ways
Increase in taxes (Contractionary Fiscal Policy)
Increase in interest rates (Contractionary Monetary Policy)
44
New cards
Why may increasing I.R and Taxes not likely be used?
Increasing I.R conflicts with the government objective of having price stability.
45
New cards
Evaluation of Expenditure Reduction:
A left shift in AD may occur making conditions worse... e.g, higher rates of unemployment, reduced profits for domestic firms and increased govt. spending
46
New cards
Expenditure Switching: Name one Policy
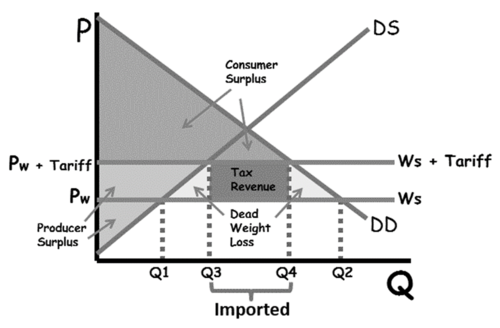
Imposing of Tariffs, as imports are more expensive for firms, who will pass costs onto consumers, decreasing demand for the good. -> as a result, consumers witch to the cheaper domestic alternative, if available
47
New cards
Automatic Stabiliser: What does it rely on?
Marshall Lerner Condition
48
New cards
Automatic Stabiliser
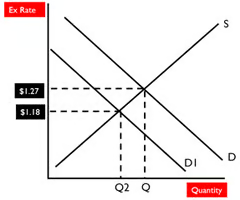
49
New cards
Expenditure Switching: Tariffs Graph