B2.2 Organelles in Animal and Plant Cells
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
What is the first main idea of the Cell Theory?
All living things are made of cells, The cell is the basic unit of life, Cells come from other cells
What is the basic unit of life that all living things are made up of?
Cells
What are the two types of organisms based on the number of cells?
Multicellular (many cells) and Unicellular (one cell)
What are examples of unicellular organisms?
Paramecium, amoeba, and euglena
What does the cell theory state about cells and life?
Cells are the basic structure of life and perform all life processes.
What are organelles in single-celled organisms?
Organelles are tiny parts inside the cell that help the organism survive and function, like organs in the body.
How do cells reproduce?
Cells reproduce by copying their DNA and splitting into two new cells.
How do new cells help living organisms?
New cells help living organisms grow by replacing old cells and adding more cells.
Do animal and plant cells have the same structures?
Yes, both animal and plant cells have organelles that help them function and perform life processes.
What is the term for the genetic information in cells?
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid)
Why is cell division important for multicellular organisms?
Cell division helps multicellular organisms grow and repair tissues.
What is the function of the cell membrane?
The cell membrane surrounds the cell and controls what materials flow in and out of the cell.
What is the function of the cytoplasm?
The cytoplasm is a jelly-like substance that suspends all organelles in the cell.
What do lysosomes do in a cell?
Lysosomes are the digestive centers of the cell, breaking down food, old cell parts, and invaders like bacteria and viruses
What is the role of mitochondria in a cell?
Mitochondria generate energy for the cell through respiration, similar to a power plant.
What is the function of the nucleus in a cell?
The nucleus controls all activities of the cell and contains the cell’s DNA (genetic information).
What do vacuoles do in a cell?
Vacuoles store nutrients, water, and waste products. Animal cells have many small vacuoles, while plant cells have one large central vacuole.
What is the function of the cell wall in plant cells?
The cell wall provides structural support and protection to the plant cell.
What do chloroplasts do in plant cells?
Chloroplasts contain chlorophyll and are involved in photosynthesis, where plants make their own food.
What is the term for a specialized structure in a cell?
Organelle
What is the outer covering of a cell?
Cell Membrane
What is the powerhouse of the cell?
Mitochondria
What is the control center of the cell where its DNA is kept?
Nucleus
Why is the cell membrane considered to be selectively permeable?
The cell membrane is selectively permeable because it controls what substances can pass in and out of the cell, allowing some molecules to enter or exit while blocking others.
What does "permeable" mean in terms of a membrane?
Permeable means that all materials can cross the membrane freely.
What does "impermeable" mean in terms of a membrane?
Impermeable means that no materials can cross the membrane.
What does "semi/selectively permeable" mean in terms of a membrane?
Semi/selectively permeable means that only certain materials can cross the membrane, while others cannot.
What is osmosis?
Osmosis is the diffusion of water particles through a selectively permeable membrane
What happens in an isotonic solution?
In an isotonic solution, the water concentration is the same inside and outside the cell, which is a balanced situation and ideal for carrying out life processes.
What happens in a hypotonic solution?
In a hypotonic solution, water concentration is lower inside the cell than outside, so water moves into the cell. This can cause animal cells to swell and burst, while plant cells appear swollen. (Think "HYPO = Hippo" because it’s big!)
What happens in a hypertonic solution?
In a hypertonic solution, water concentration is higher inside the cell than outside, so water moves out of the cell. This causes animal cells to shrivel up and plant cells to become limp.
How are animal cells different from plant cells?
Animal cells are typically smaller and round in shape.
Animal cells do not have a cell wall or chloroplasts.
Animal cells have multiple smaller vacuoles.
How are plant cells different from animal cells?
Plant cells are typically boxy and more rigid.
Plant cells have a cell wall and chloroplasts.
Plant cells have a large central vacuole.
What does Xylem do in plants?
Xylem carries water and minerals from the roots to the rest of the plant.
What does Phloem do in plants?
Phloem carries sugars from the leaves to the rest of the plant (up and down)
How does water get into plants?
Water enters the root hairs through osmosis.
The water travels through the Xylem and is pushed to the rest of the plant.
Transpiration happens when water vapor is lost through tiny openings in the leaves called stomata.
This loss of water pulls more water from the roots up to the leaves (like a straw).
How do plants get sugars?
Plants make sugars in the leaves through photosynthesis.
What else do plants make during photosynthesis besides sugars?
Plants also make oxygen during photosynthesis.
Where do plants store their sugars?
Plants store sugars in the leaves, stems, and/or roots.
How do sugars move throughout the plant?
Phloem transports sugars to other parts of the plant.
What are specialized cells in multicellular organisms?
Specialized cells have specific shapes and functions that allow them to perform certain roles in the body. These cells are different from each other and work together to form tissues, organs, and organ systems.
What is biological organization?
Biological organization refers to how cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems are organized to form a complete organism. Specialized cells form tissues, tissues form organs, organs form organ systems, and systems work together to create an organism.
How do specialized cells contribute to plant structure?
In plants, specialized cells like fluid conduction cells form the xylem, which transports water. Xylem combines with phloem and epidermal tissue to form the stem, and the stem, leaves, and flowers together make up the shoot system.
What are the 4 types of human body tissue?
Nervous: Detects & controls (found in brain, nerves, spinal cord)
Muscle: Movement (found in cardiac, smooth & skeletal muscles)
Epithelial: Lines & protects organs (found in skin, GI organs)
Connective: Pads & supports (found in fat, bones, tendons)
What is a Red Blood Cell?
A red blood cell is a disk-like, flexible cell that carries nutrients and waste. It delivers oxygen to organs and removes waste, and is enucleated when mature.
What is a Bone Cell?
Bone cells form a rigid matrix and are responsible for building and repairing bone tissue.
What does a Root Hair Cell do?
Root hair cells increase surface area to absorb more water through osmosis, helping the plant take in water and nutrients.
What is a Smooth Muscle Cell?
Smooth muscle cells are elongated and can contract and relax automatically. They are part of the muscles that move the body or organs, like the heart and digestive organs.
What is the function of Skin Cells?
Skin cells form a protective barrier on the surface of the body, protecting it from outside elements.
What is a Cancer Cell?
Cancer cells are mutated cells that divide rapidly and can form tumors, destroying healthy surrounding cells.
What does a Fluid Conduction Cell do in plants?
Fluid conduction cells join together to form the xylem, which transports water throughout the plant.
What is a Nerve Cell?
Nerve cells are long cells with connections at both ends. They receive sensory information and send signals to the brain and body to control actions.
What do Guard Cells do in plants?
Guard cells surround stomata on plant leaves and control their opening and closing, regulating transpiration (water loss).
What does an Inner Ear Hair Cell do?
Inner ear hair cells have tiny hairs that amplify and transmit sound waves to the nervous system, which processes them in the brain.
What is a Cone Cell?
Cone cells in the eye allow organisms to see colors by receiving light input and enabling color vision.
What is the role of White Blood Cells?
White blood cells are part of the immune system. They defend the body by surrounding and digesting harmful substances, viruses, and bacteria.
How are animal cells and plant cells different?
Animal Cells: Typically smaller, round, do not have a cell wall, chloroplasts, or a large central vacuole.
Plant Cells: Typically boxy, have a cell wall for structure, contain chloroplasts for photosynthesis, and have a large central vacuole for storing water and nutrients.
How are diffusion and osmosis similar and different?
Similarities: Both diffusion and osmosis move particles from an area where there are lots of them to an area where there are few. Both do this without using energy.
Differences:
Diffusion: This is when any kind of particle (like gases or liquids) moves from a place with a lot of particles to a place with fewer.
Osmosis: This is a special type of diffusion, but it only happens with water molecules moving through a special membrane (like in cells).
Q: How does your body use 3 types of specialized cells to function?
Red Blood Cells: These cells are disk-shaped and carry oxygen and nutrients to organs, while also carrying waste away. Their flexibility allows them to squeeze through tiny blood vessels and help the body get the energy it needs.
Muscle Cells: These cells are long and can contract or relax to make the body move. They help your body move by making muscles shorter or longer, like when you walk or run.
Nerve Cells: These cells have long extensions and help send signals to and from your brain. They help you feel things and control movements by sending electrical messages throughout your body.
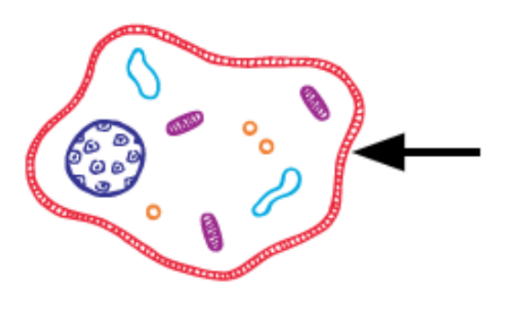
What is this?
Cell Membrane
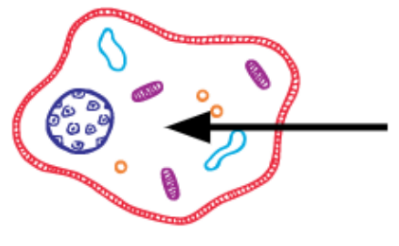
What is this?
Cytoplasm
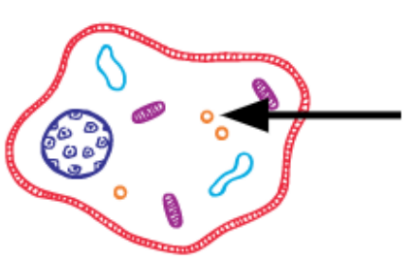
What is this?
Lysosome
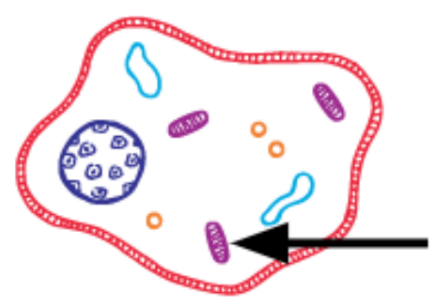
What is this?
Mitochondria
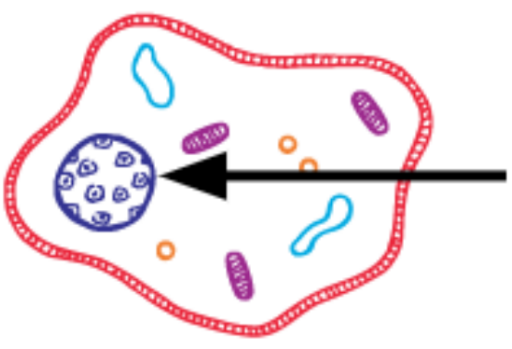
What is this?
Nucleus
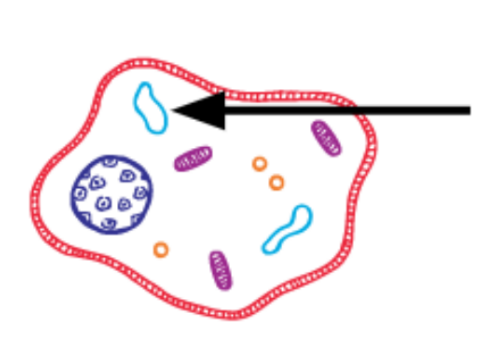
What is this?
Vacuole
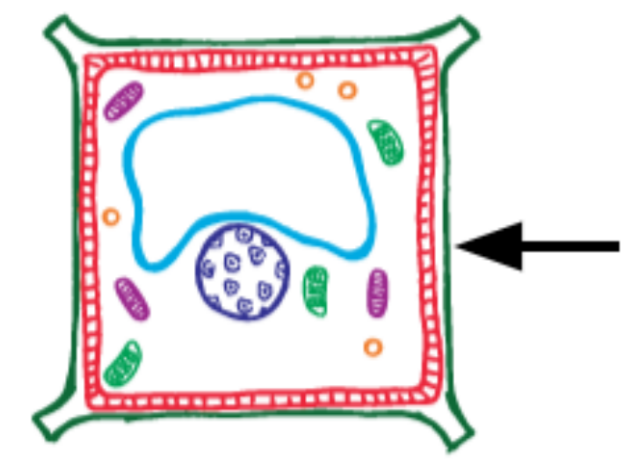
What is this?
Cell Wall
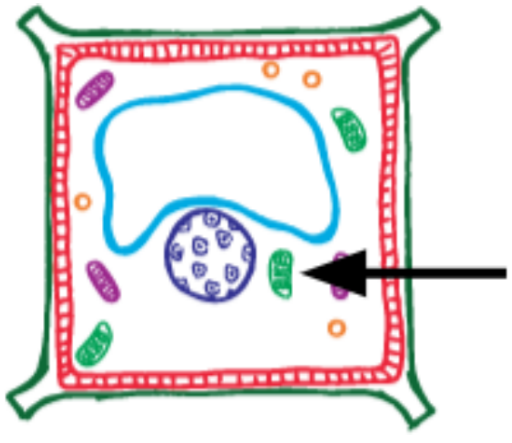
What is this?
Chloroplast
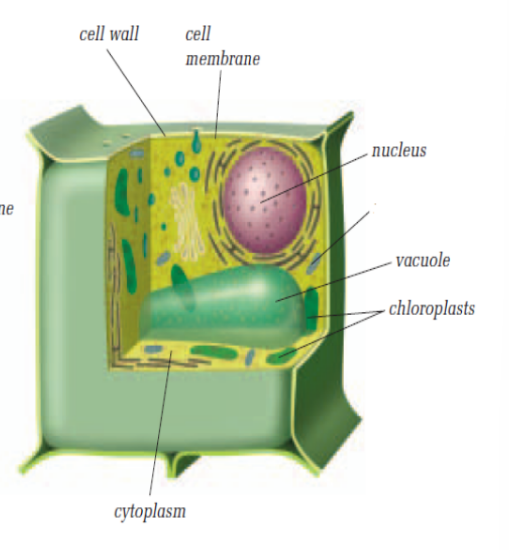
Which cell is this?
Plant Cell
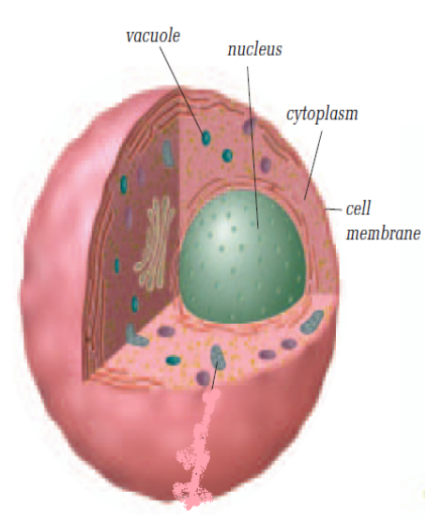
Which cell is this?
Animal Cell
What is the difference between unicellular and multicellular organisms?
Unicellular organisms are made up of one single cell that carries out all the necessary life functions. Examples include bacteria, amoeba, and paramecium.
Multicellular organisms are made up of multiple cells that work together to perform different functions. These cells are specialized for different tasks. Examples include humans, plants, and animals.
Cells to Systems
cells → tissues → organs → systems
What is organelles?
"a small organ" found within a cell that carries out a specific role
What is amoeba?
A type of single-celled organism that can change its shape
What is a cilia?
Tiny hair-like structures that help with movement