SOC 100 (Exam 2)
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
105 Terms
Lower-income
households with income less than two-thirds the median household income, after adjusting for household size
ex: if median income is $100k, then lower-income is <$66k
Middle-income
households with income two-thirds to double the median household income, after adjusting for household size
ex: if median income is $100k, then middle-income is $66k-$200k
Higher-income
households with income double the median household income, after adjusting for household size
ex: if median income is $100k, then higher-income is >$200k
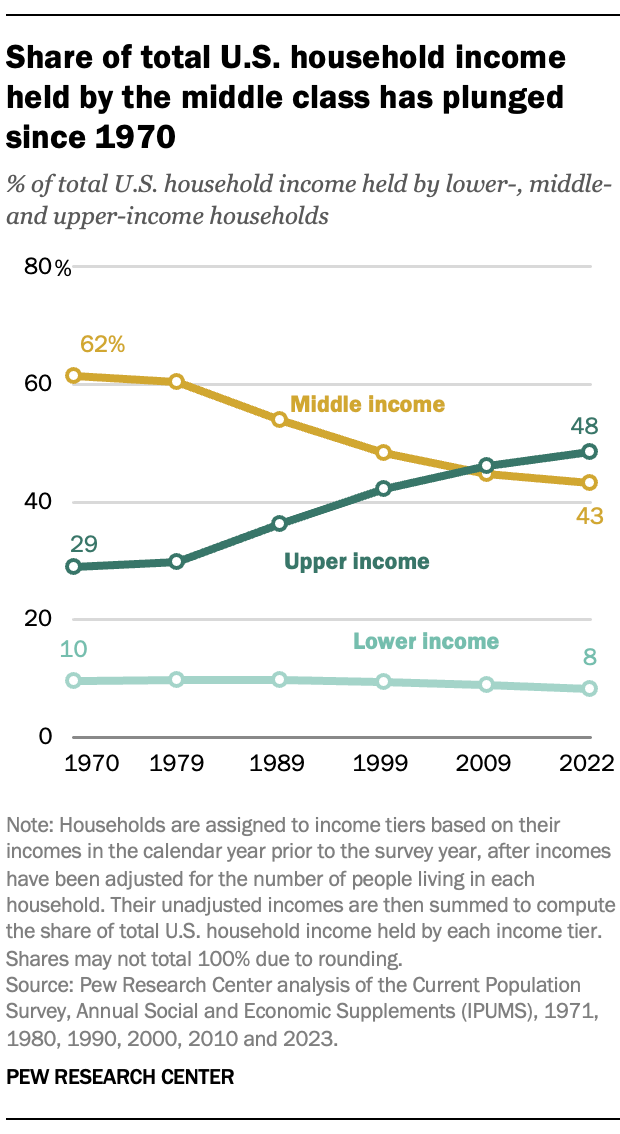
Shrinking middle class
since the 1970’s, there are less Americans in the middle-income bracket; meanwhile, the upper class is growing
Income
money received by a person for work, from transfers (gifts, inheritances, government assistance), or from returns on investments
Wealth
family or individual’s net worth (i.e. total assets - total debts)
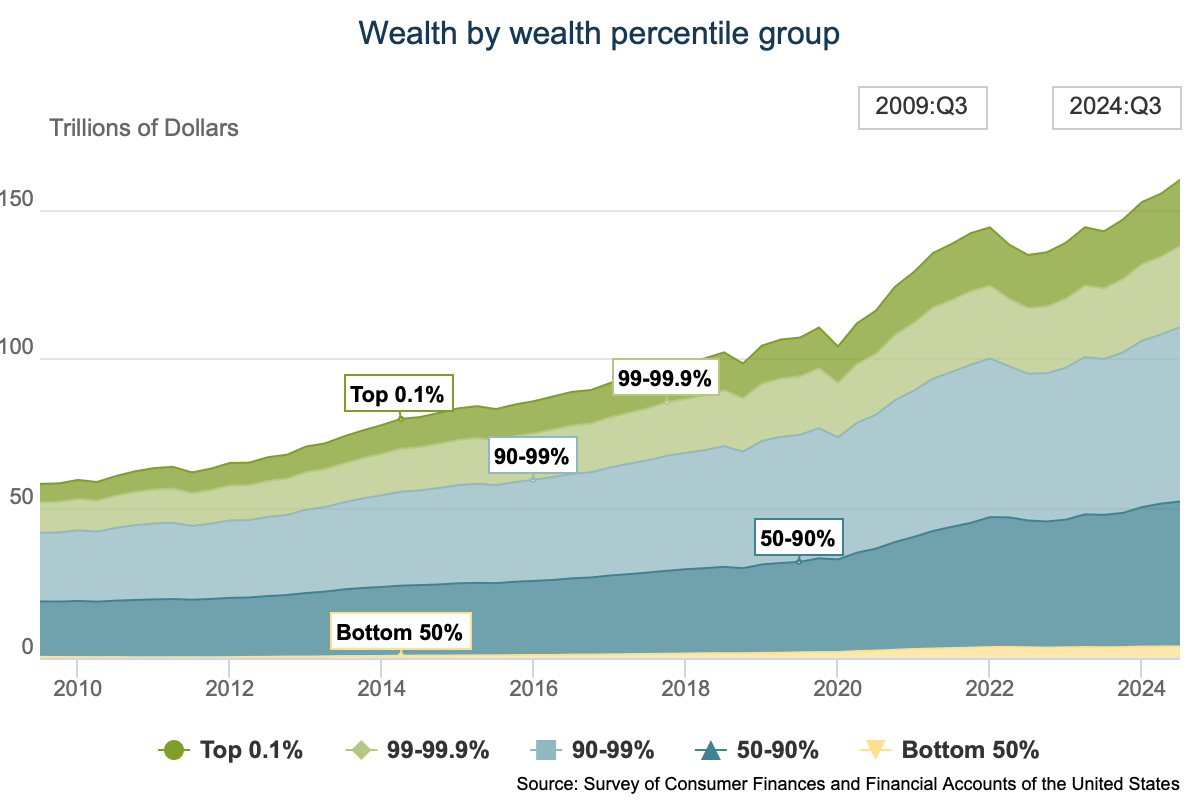
Wealth inequality
the richest 10% of Americans control about half the nation’s wealth
ex: Elon Musk (FUCK YOU), Mark Zuckerberg (FUCK YOU), Jeff Bezos (FUCK YOU)
Equality of opportunity
everyone has an equal chance to achieve wealth, social prestige, power
ex: the American Dream, Monopoly game
Equality of condition
everyone should have an equal starting point
ex: Affirmative Action, DEIA
Equality of outcome
everyone should end up in the same position
ex: state massively redistributes so everyone has the same income and kind of house
Stratification
hierarchical organization of society into groups with differing levels of power, social prestige, status, economic resources
Estate system
politically-based system of stratification characterized by limited social mobility
ex: feudal Europe
Caste system
religion-based system of stratification characterized by NO social mobility
Slavery
form of social stratification where some people own others as their property
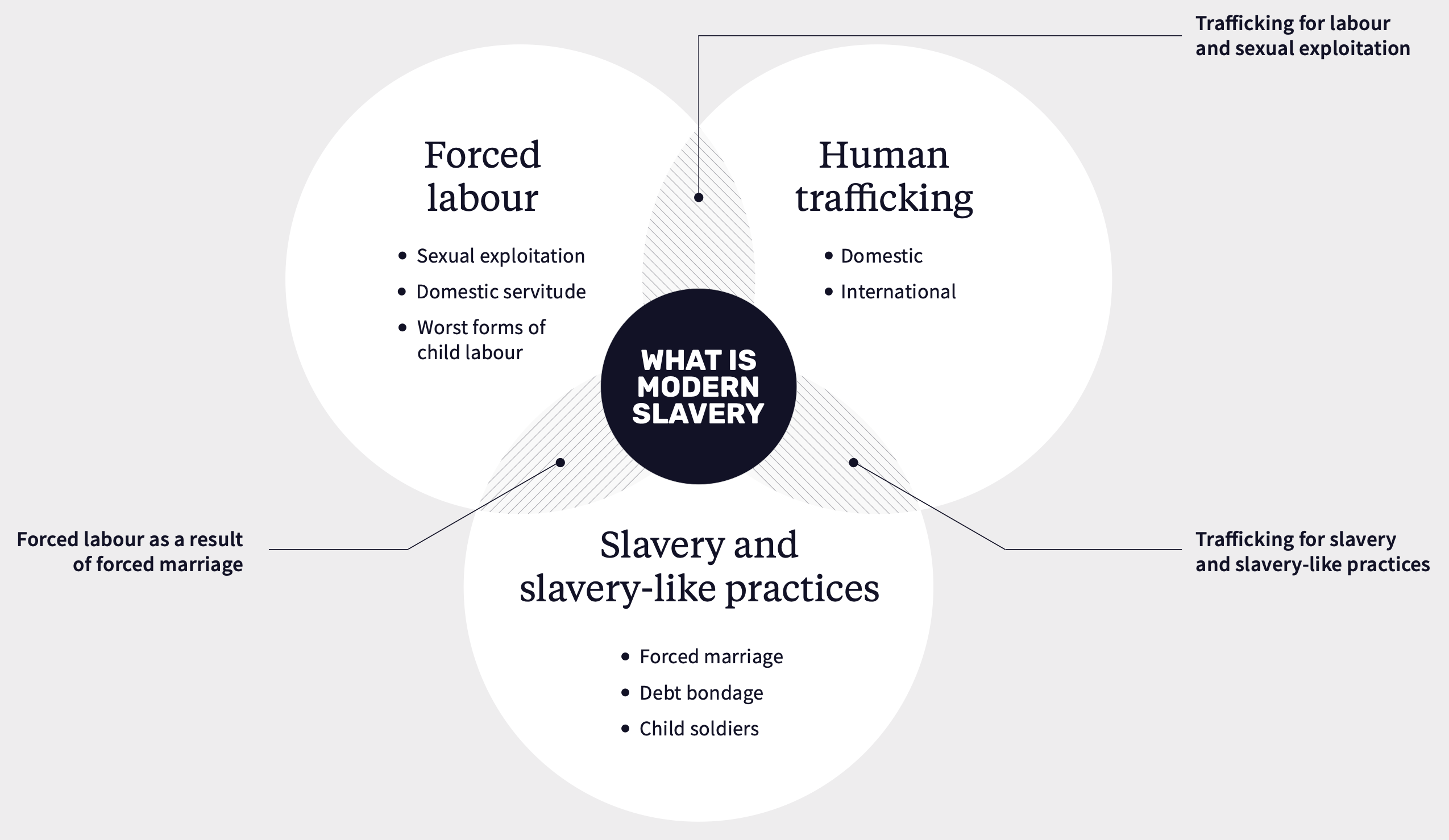
Modern slavery
situations of exploitation a person can’t refuse or leave due to threats, violence, coercion, deception, or abuses of power
ex: forced labor, forced marriage, debt bondage, sexual exploitation, human trafficking
New slavery
people use slaves to get rich, then toss them aside
focused on big profits and cheap lives
not about owning people, but controlling them completely
people are disposable tools for making money
Old slavery vs. New slavery
legal ownership asserted vs. avoided
high purchase cost vs. low purchase cost
low profits vs. high profits
shortage of potential slaves vs. surplus
long-term relationship/maintained vs. short-term/disposed
ethnic differences important vs. unimportant
Status hierarchy system
system of stratification based on social prestige
ex: prestige of a surgeon is much higher than that of a dishwasher
Class system
economically-based hierarchical system characterized by cohesive oppositional groups and somewhat loose social mobility
Differing views of class
Karl Marx: bourgeoisie (capitalist class) and proletariat (working class)
Erik Olin Wright: people can fall between bourgeoisie and proletariat class (manager of a company isn’t the owner but is still controlling other people)
Max Weber: people have property/skills to leverage in the marketplace, class can move up or down (rather than two opposing sides)
Education
key mechanism of social stratification
pathway to upward mobility
but also system to reinforce existing class, racial, gender inequalities through unequal access to resources, opportunities, credentials
Social mobility
movement between different positions within a system of social stratification in a society
more stagnant and lower in the U.S. than other developed countries
high geographic variation within the U.S.
Factors for social mobility
Segregation
Income inequality
Quality of public schools
Strength of social networks
Family structures
Intergenerational mobility
movement up or down a social stratification hierarchy from one generation to another
ex: parents work on a farm while child graduates college and works for a big company
Intragenerational mobility
movement up or down a social stratification hierarchy within the course of one’s personal career
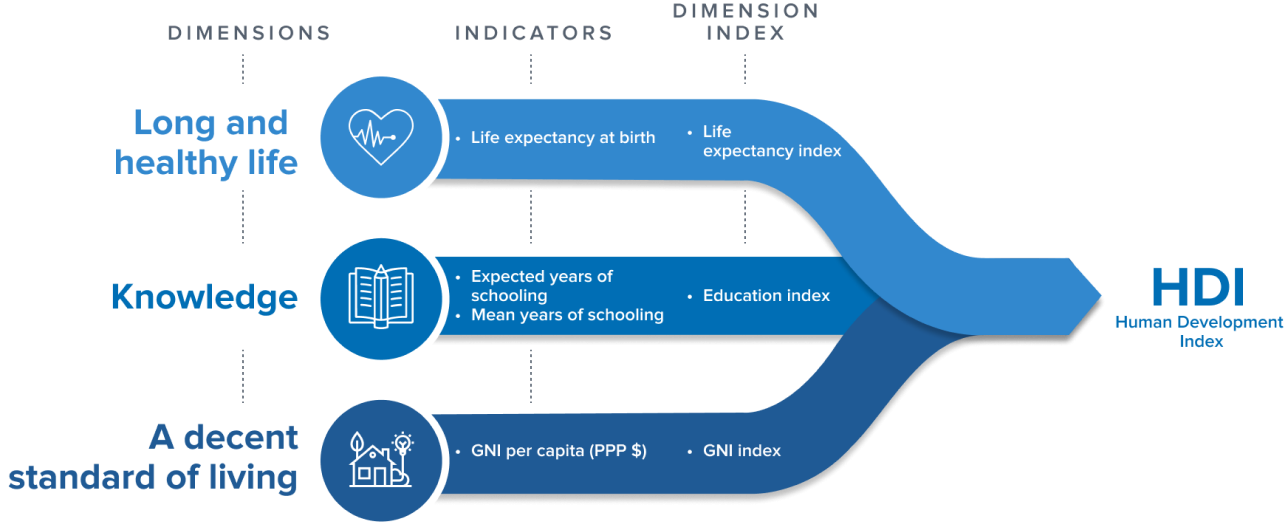
Human development index
estimate of a nation’s well-being by measuring its life expectancy, education, and gross national income per capita (size of economy)
Unweighted international inequality
measure of income/wealth for a country
Population weighted international inequality
measure of income/wealth for every person in a country
True world income distribution
measure of income/wealth for the entire population of the world
Modernization theory
emphasizes internal factors
all countries follow a uniform evolutionary route
country must develop the necessary beliefs, values, and norms for trade, industrialization, and rapid economic growth
ex: Jared Diamond’s Guns, Germs, and Steel
Dependency theory
emphasizes external factors
disadvantaged position in world economy (bananas vs. iPhones)
relationships with developed countries are barriers to development
Neoliberalism
free-market forces, achieved by minimizing government restrictions on business, will provide the greatest economic benefit to the widest range of people
liberalization, privatization, austerity
Geography and global inequality
high transportation costs
prevalence of disease
low agricultural productivity
Development traps
barriers that hinder a country’s growth
conflict
natural resources
landlocked with bad neighbors
bad governance
Institutions
rules influencing how the economy works and the incentives that motivate people
Inclusive institution
democratic
result of low colonial settler mortality
willingness to share country’s wealth
Extractive institutions
exploitative
result of high colonial settler mortality
power concentrated in the hands of elite
Sex
perceived biological differences society uses to distinguish males from females
a continuum, not a binary
Intersex
people who are born with sex characteristics that don’t fit the male/female binary
Gender
a social position; behaviors and a set of attributes associated with sex identities
Cisgender
people whose gender identity aligns with their assigned sex at birth
Transgender
people whose gender does not align with their assigned sex at birth
Gender identity
how someone internally understands their gender, regardless of their physical body
Gender expression
how someone outwardly shows their gender identity which may or may not align with society’s expectations for their gender/assigned sex at birth
Gender dysphoria
conflict between a person’s gender identity and their assigned sex, causing significant distress
Gender roles
sets of behavioral norms associated with masculinity, femininity, or other
Gender in the workplace
gender plays a powerful role in shaping workplace experiences (e.g. jobs, wages, treatment)
Causes of gender pay gap
gender segregation in workplace
socialization
employer hiring practices
Gender typing in the workplace
women holding occupations of lower status and pay (i.e. secretary or retail) and men holding jobs of higher status and pay (i.e. manager or professional)
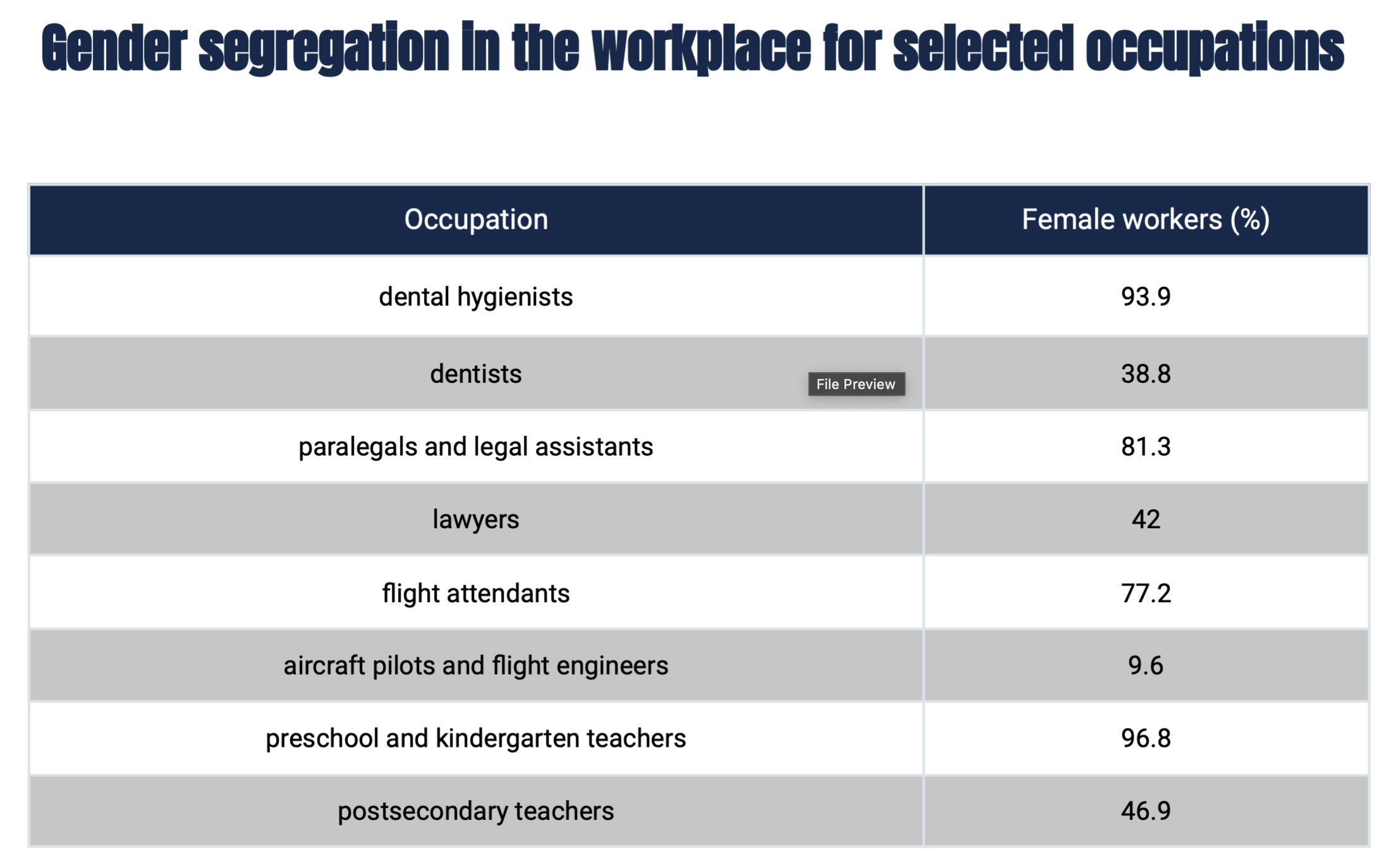
Glass ceiling
invisible limit on women’s climb up the occupational ladder
Glass escalator
accelerated promotion of men to the top of a work organization, especially in feminized jobs
ex: a male kindergarten teacher who becomes the principal
Gender at home
men and women specialize in different chores
women spend more time doing unpaid housework/care work
women spend more time on child-rearing responsibilities
Second shift
unpaid work of housekeeping and childcare that faces family members, disproportionately women, when they go home after their paid jobs
Functionalist view of gender inequality
view of gender inequality; gender differences, specifically specialization in different tasks, contribute to social stability and integration
reinforces status quo, inhibits change
Conflict view of gender inequality
view of gender inequality; uneven distribution of power in society; men have had more access to resources (wealth, education, political influence) which they have used to maintain dominance over women
Interactionist view of gender inequality
view of gender inequality; we constantly perform masculinity and femininity; there is potential for change but we tend to reaffirm and reproduce gender norms
Intersectionality
social identities like race, class, gender, ability status, and sexual orientation intersect/interact, shaping unique experiences of advantage and disadvantage
recognition that our lives are shaped by multiple interacting identities
Graying
increasing proportion of a society’s population is older
Practical difficulties of aging
difficulty of aging; physical changes associated with growing older
Symbolic difficulties of aging
difficulty of aging; social and psychological implications that arise from the aging process
Biological aging
changes in reproductive capacity, immune system response, cardiovascular functioning
varies by genes, lifestyles, luck
age-linked, not age-caused
Psychological aging
how old one feels, acts, behaves
not necessarily equal to chronological age
most personality traits, self-concept, self-esteem remain fairly stable from midlife onward
Social aging
society shapes the meanings and experiences of aging
expectations/assumptions of behavior and capabilities at different ages
too young/to old for certain roles or opportunities
Ageism
discrimination/prejudice against a person based on age
Elder abuse
intentional act/failure to act that causes or creates risk of harm to older adult (60+); often perpetrated by caregiver or someone the elder trusts
Physical abuse of elders
illness, injury, functional impairment, or death of an elder resulting from the intentional use of physical force
Sexual abuse of elders
forced or unwanted sexual interaction inflicted upon an elder
Emotional/psychological abuse of elders
verbal/nonverbal behaviors that inflict anguish, fear, or distress on an elder
Neglect of elders
failure to meet an elder’s basic needs
Financial abuse of elders
illegal, unauthorized, or improper use of an elder’s money, benefits, property, or assets for the benefit of someone else
Prejudice
thoughts and feelings about a social group (age, gender, race, ethnicity, religion, etc), leading to preconceived notions and judgements about the group
Discrimination
harmful/negative actions against individuals based on age, gender, race, ethnicity, religion, etc regardless of their merit
Conflict theory of discrimination
theory of discrimination; those who benefit from systems of inequality want to protect their privileges and exclude members of subordinate groups
Cognitive theory of discrimination
theory of discrimination; automatic, unconscious cognitive processes distort out perceptions and treatment of others; it’s easier to make snap judgements than consciously think
Categorization
ingroups and outgroups
exaggerate similarities and differences
automatically prefer ingroup members to outgroup members
discrimination through ingroup favoritism rather than outgroup antipathy
Stereotyping
attributing traits we associate with a group to individuals of that group; strengthened by confirmation bias
ex: Asians are good at math
Attribution bias
our expectations for others affect the meaning we assign to their behavior
when performance conforms to expectations: attribute to stable, internal traits (ability)
when performance contradicts expectations: attribute to transient, external causes (task difficulty or luck)
we expect ingroup members to succeed
Macro-micro link
categorization, in-group preference, stereotyping at individual level —> in-group members accumulate advantages while out-group members accumulate disadvantages
Disengagement theory
it is functional for society to relieve older people of their traditional roles to free up positions for younger people
ex: forced retirement policies
Activity theory
people who are busy and engaged (aka leading fulfilling and productive lives) are functional for society
ex: remain in work and social roles as long as possible
Continuity theory
elders’ well-being is enhanced when doing activities consistent with their personality, preferences, and activities earlier in life
ex: former teacher volunteering at a school
Life course theory
people play an active role in determining their physical and mental well-being, but constrained by context
ex: boys and girls may have had similar career aspirations, but men received more structural support than women
Obesity
excessive body weight indicated by a BMI over 30
Causes of obesity epidemic
Biological: genetics and physiology
Economic: food accessibility (i.e. food desert) and SES
Social: cultural norms (i.e. proportions, fast food) and social networks
Technological: food production (i.e. highly processed foods) and lifestyle changes (i.e. that damn phone)
Health
state of complete physical, mental, and social well-being; not merely the absence of disease or infirmity
cultural differences: Hmong girl had severe epilepsy but family believed it was spiritual
Medicalization
when problems/issues become seen as medical conditions in need of treatment
ex: pregnancy and childbirth, alcoholism, mental health, aging, obesity, etc
Sick role theory
functionalist view of health and illness
describes the social rights and obligations of a sick individual
describes behavior a sick person adopts to minimize disrupting others with their illness
conditional: suffers from temporary condition
unconditional: suffers from incurable illness
illegitimate: suffers from stigmatized disease
Lived experience theory
symbolic interactionist view of health and illness
meaning generated from everyday experiences of health
illness work: all tasks directly related to managing medical aspects of chronic condition
everyday life work: routine tasks and duties necessary for maintaining everyday life
biographical work: psychological and emotional adjustments to integrate chronic illness into their life narrative
Stigma
physical/social characteristic labeled as undesirable by society
abominations of the body: anorexia, morbid obesity, etc
tribal stigma of race, nation, religion
blemishes of individual character: alcoholism. depression, etc
Poverty
condition of deprivation due to economic circumstances
diminished capacity to engage in society
inability to live with dignity in one’s society (shame, stigma, etc)
Absolute poverty
not meeting minimal requirements necessary to sustain a healthy existence; defined using universal baseline with no reference to other people’s income or access to goods
Relative poverty
one’s standard of living is below what is generally considered normal or acceptable in society; defined in comparison to other people’s standard of living
one can be poor relatively but not absolutely
Reasons to measure poverty
raise public awareness and address poverty
identify who is affected by poverty
monitor progress and evaluate intervention programs
Official poverty measure (OPM)
measure of pre-tax income that defines poverty in the U.S.
3x cost of minimum food diet in 1963
does not vary geographically
adjusted for family size and inflation
no longer relevant to modern expenses (35% of income spent on housing)
Supplemental poverty measure (SPM)
alternative measure of poverty that accounts for non-cash government assistance
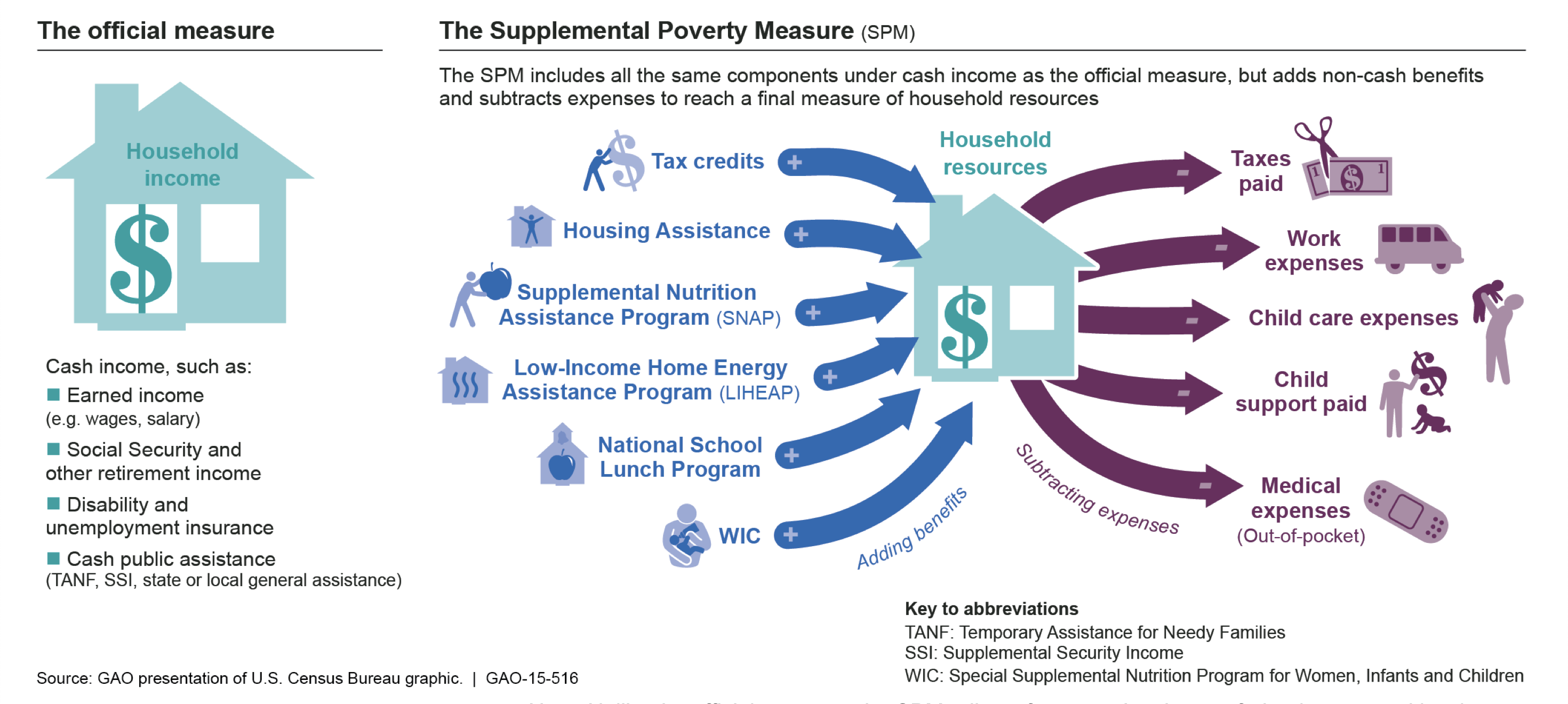
Subjective measure of poverty
people evaluate their own situation with questions such as:
Do you feel poor?
How much is required weekly to keep your household out of poverty?
How far above/below that level is your household?
Deprivation measure of poverty
lack of 4+ socially perceived necessities such as:
eating out once every 2 weeks
replace worn-out furniture
three meals a day
bedroom for every child over 10 of a different sex
Individualistic view of poverty
poverty is a personal problem
results from personal failings and inadequacies
by-product of the poor’s characteristics and behaviors
Structural view of poverty
poverty is a social problem
results from economic and political forces outside a person’s control
limited power to determine whether jobs are available or how much they pay
Cultural theory of poverty
individualistic theory of poverty; poor lack the values and motivation needed to achieve success