Molecular Pathology Techniques
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
108 Terms
One of the problems of amplification and analysis of DNA from formalin-fixed tissue is:
Cross-linking of nucleic acid to protein with subsequent NUCLEIC ACID FRAGMENTATION
Amplification and analysis of DNA from formalin fixed tissue is best limited to _____ base pairs
<300 (short sequences)
T or F
Heparin has been shown to inhibit the polymerase chain reaction
TRUE
T or F
Bouin and Zenker fixatives can be used with common nucleic extraction protocols
FALSE
They should be avoided as they introduce chemicals
For solid phase extraction of DNA, the nucleic acid binds to ______ under high ionic strength (______ astringency) conditions and can be washed and eluted with a ____ ionic strength eluant.
For solid phase extraction of DNA, the nucleic acid binds to SILICA under high ionic strength ( LOW astringency) conditions and can be washed and eluted with a LOW ionic strength eluant.
RNA is ____ stable than DNA
RNA is LESS stable than DNA (due to the presence of RNases)
The quality of nucleic acid can be verified through spectrophotometric absorption at:
260nm
Nucleic acid absorbs light at 260nm wavelength, so 1 unit of absorbance equals _____ of DNA or ____ of RNA
Nucleic acid absorbs light at 260nm wavelength, so 1 unit of absorbance equals 50ug/mL of DNA or 40ug/mL of RNA
Purity of DNA can be assessed with a ratio of absorbance at ___ to ___ (protein absorbs light at ___)
A ratio of ___ is considered to be relatively pure and free of contaminating protein
Purity of DNA can be assessed with a ratio of absorbance at 260nm to 280nm (protein absorbs light at 280nm)
A ratio of <1.8 is considered to be relatively pure and free of contaminating protein
What is the amount of DNA present per cell?
5-10pg
When studying molecular techniques, there are general considerations to keep in mind to choose the most appropriate method, mention some of those:
• What type of template is used?
• What type of probe is used for detection?
• What type of enzyme is used?
• If amplification occurs, how is it mediated?
• How is the template detected?
• For what applications is this platform best suited?
• What are pitfalls associated with this particular method?
Some applications of PCR in molecular diagnostics are:
1) To test if specific template is present (e.g. pathogen DNA)
2) To discriminate between wild type or mutant sequence at
a particular position in genomic DNA (e.g. JAK2 V617F)
• Allele specific primers
3) To determine size of DNA region (e.g. # CAG repeats)
4) To provide template for downstream applications:
a) RFLP analysis
b) Sequencing
Polymerasa used in PCR reactions:
Taq polymerase (Thermus aquaticus)
It is stable at high temperature and allow the reaction to be started and finished in a closed, temperature cycling system
Starting ingredients for PCR
1. DNA template
2. Set of complementary primers
3. dNTPs
4. Taq
5. Magnesium
6. Buffers/ denaturing agents
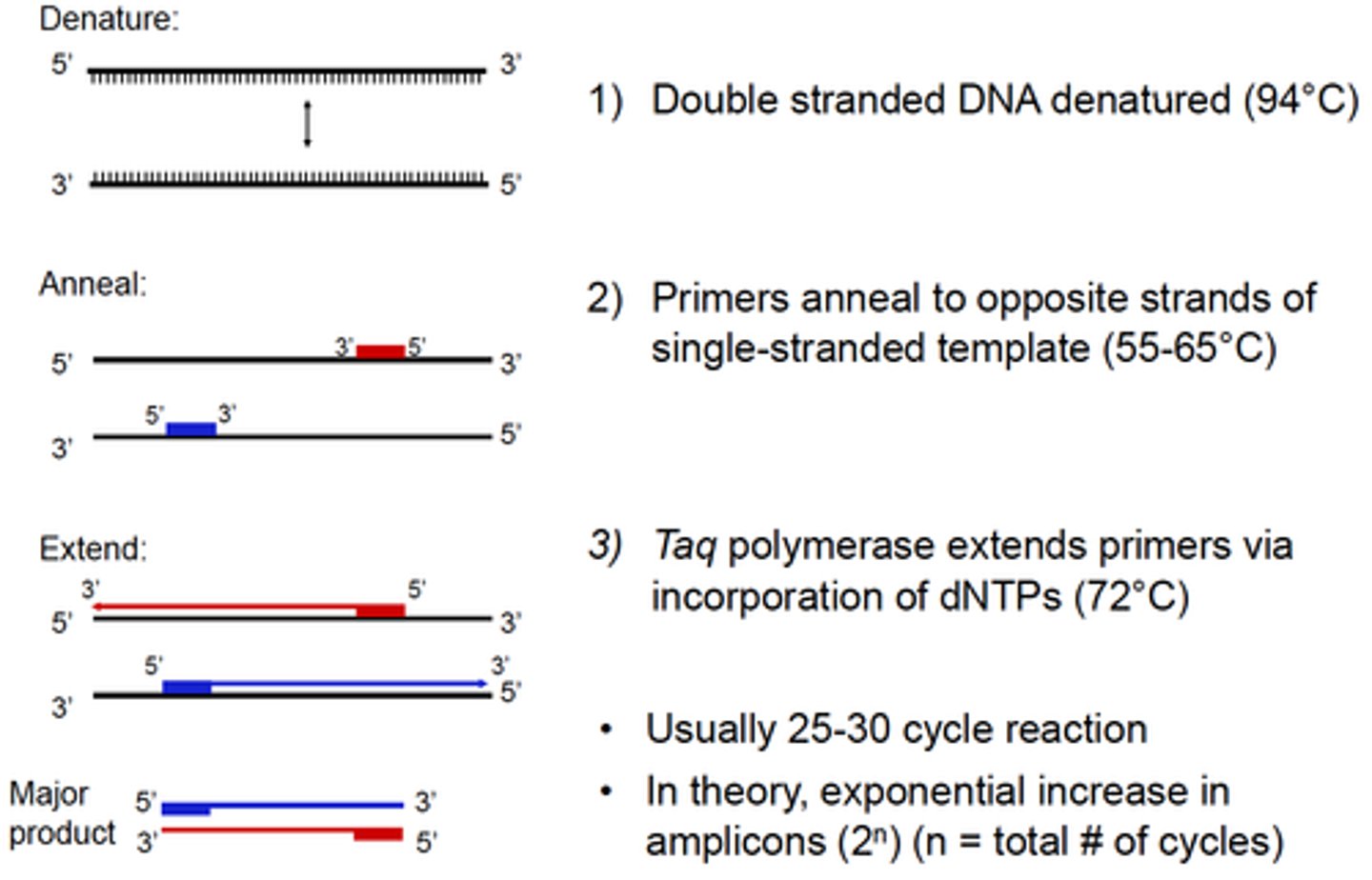
The steps for PCR include:
1. Denaturation (95°C)
2. Annealing (65°C)
3. Extension (72°C)
Describe the PCR technique:
1) Template:
• Isolated genomic DNA or cDNA, or a cell lysate
2) Pair of oligonucleotide primers (~18-24 nucleotides long)
• Anneal to complementary sequences on opposite template strands flanking region of interest
3) Deoxynucleotide triphophates (dATP, dCTP, dGTP, dTTP)
4) Taq DNA Polymerase:
• Thermostable enzyme isolated from Thermus aquaticus
• 5'→3' DNA polymerase activity & 5'→3' exonuclease activity
• Requires Mg2+ cations for activity (provided by a buffer)
Primers should be chosen carefully, what are few of the requirements are:
1. Melting temperatures of each are similar
2. No sequence similarities between the pairs -> can lead to PRIMER-DIMER formation
What is the amount of DNA produced from a PCR reaction?
DNA= 2ⁿ, where n: number of cycles
Every 3.3 PCR cycles, there is __ fold amplification of nucleic acid
Every 3.3 PCR cycles, there is 10 fold amplification of nucleic acid
(2³=10) If there are 100 copies in cycle 7, then there will be 1000 copies in cycle 10!? cycle 3
Methylation of genes is associated with ________ of gene expression
Methylation of genes is associated with REPRESSION of gene expression
What is used for pretreatment of nucleic acid in the Methylation specific PCR technique?
Sodium Metabisulfite
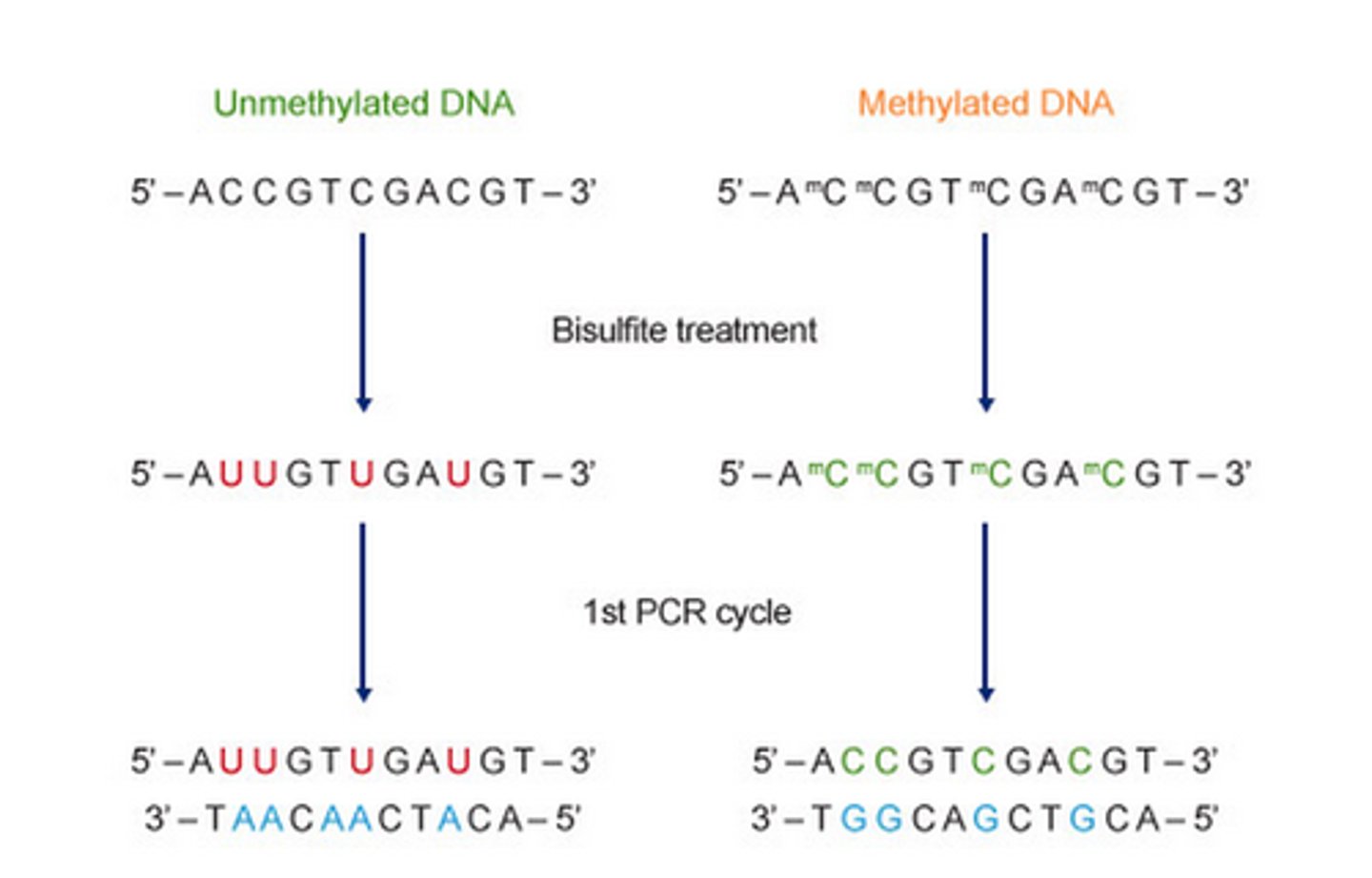
Methylation-specific PCR method is based on treating DNA with ______ in order to determine its methylation pattern.
This leads to the deamination of _____ residues and converts them to ______, while 5-mC residues remain the same. The treatment generates specific changes in the DNA sequence, potentially providing single-nucleotide resolution information about the methylation status of a DNA region.
Methylation-specific PCR method is based on treating DNA with SODIUM BISULFITE in order to determine its methylation pattern.
This leads to the deamination of CYTOSINE residues and converts them to URACIL, while 5-mC residues remain the same. The treatment generates specific changes in the DNA sequence, potentially providing single-nucleotide resolution information about the methylation status of a DNA region.
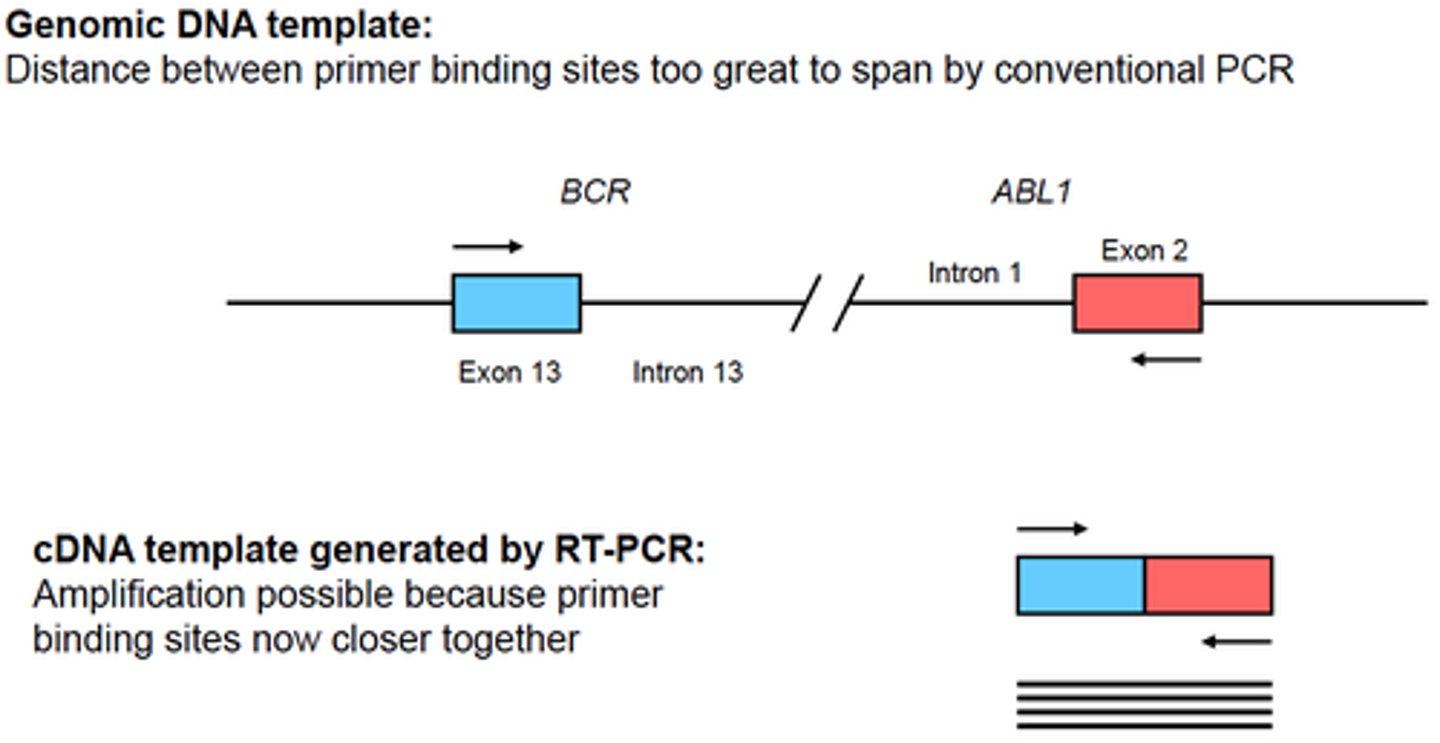
RNA cannot be directly amplified in a PCR reaction. What technique allows the production of a DNA copy from an RNA template?
Reverse transcriptase PCR
In the reverse transcriptase PCR reaction, a second DNA strand is synthesized from the first ____ strand and a double stranded DNA representation of the RNA is produced. This dsDNA can be used as a template for PCR.
In the reverse transcriptase PCR reaction, a second DNA strand is synthesized from the first cDNA strand and a double stranded DNA representation of the RNA is produced. This dsDNA can be used as a template for PCR.

Some applications of RT-PCR are:
- Detection of an organism with an RNA genome (eg. certain viruses)
- Detect of a fusion transcript generated by a translocation
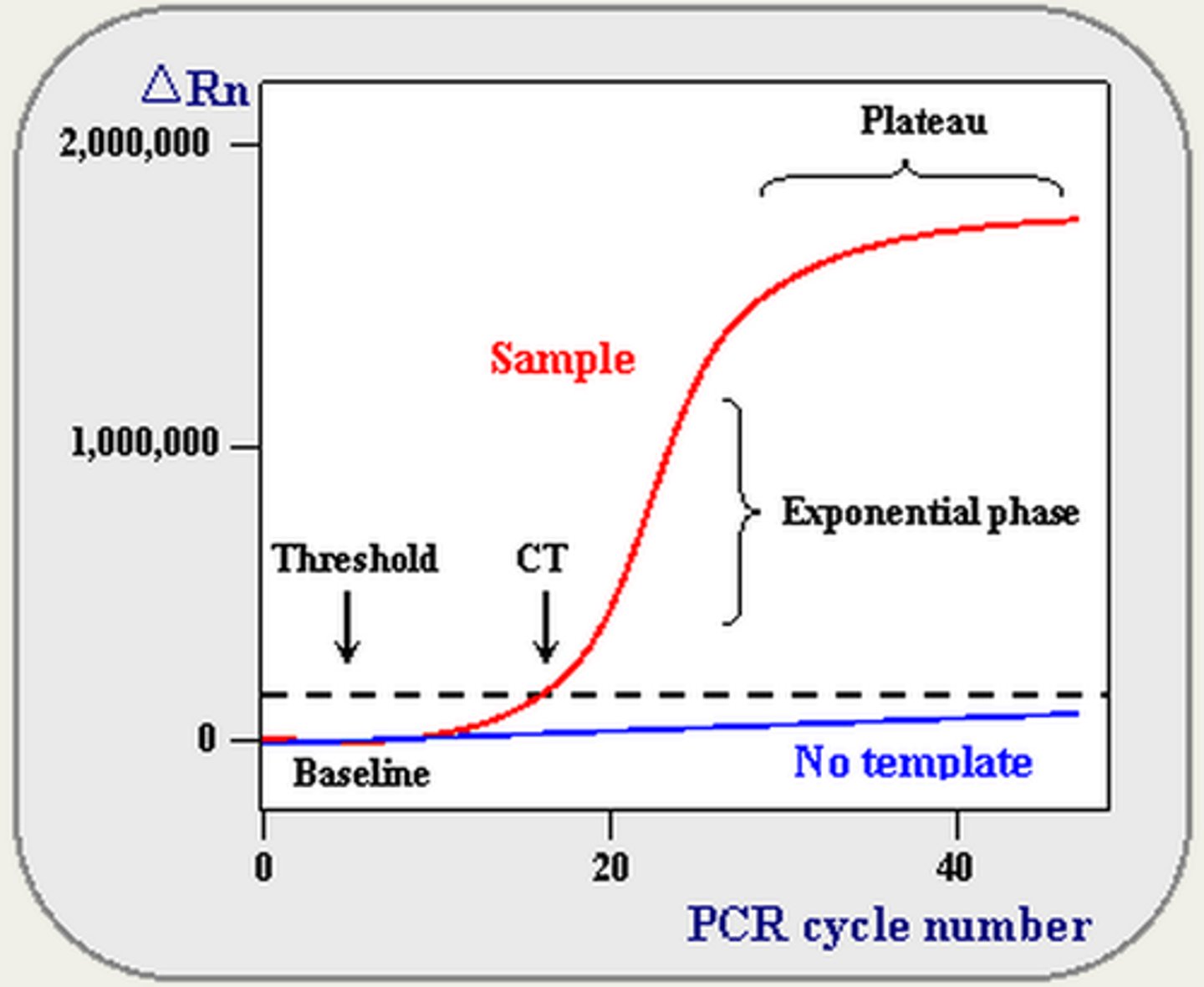
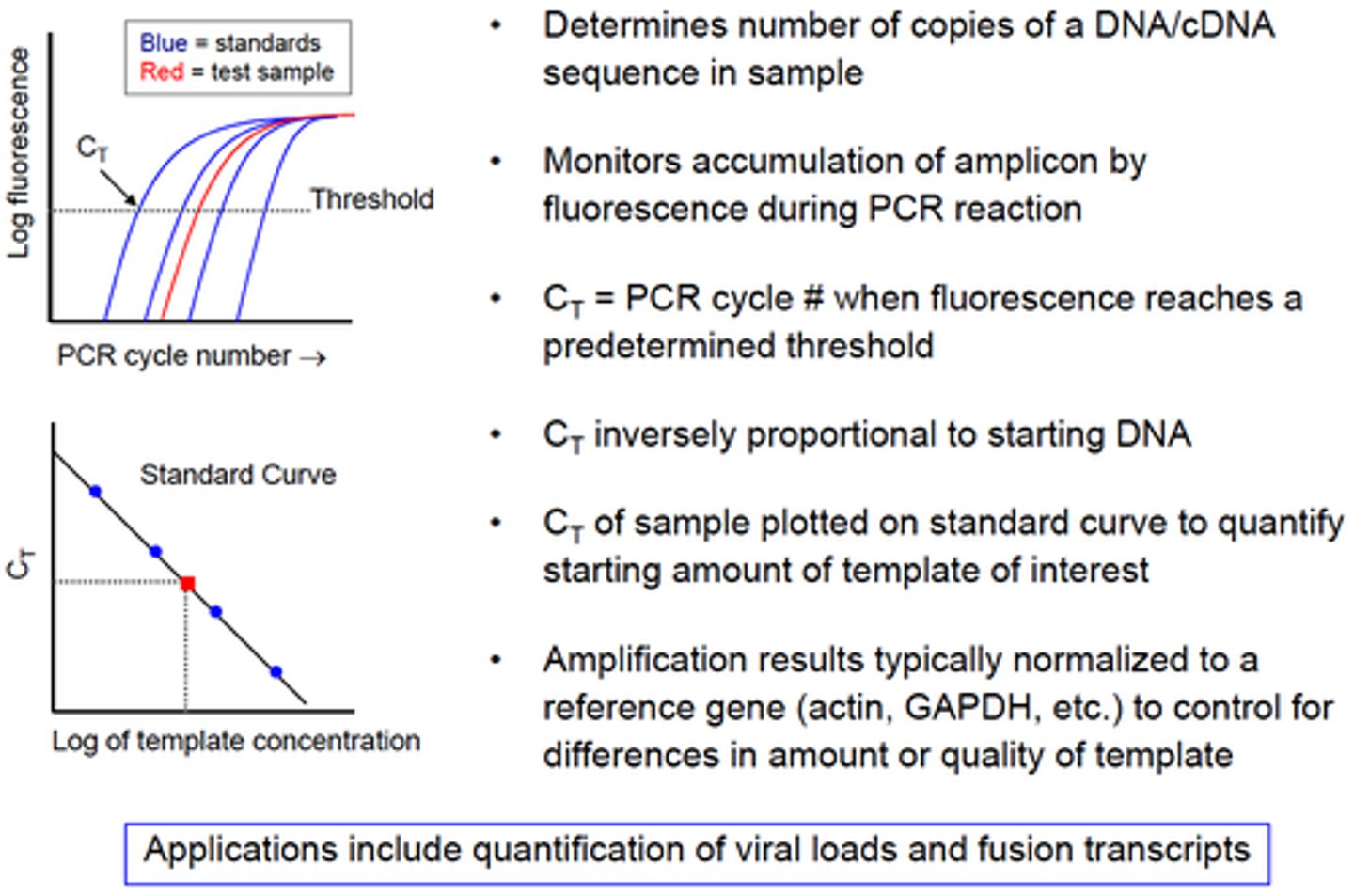
Technique that enables detection of synthesized DNA as it is being produced:
Real Time PCR
By monitoring amplification during the logarithmic stage, one can directly compare different samples.
In Real Time PCR, the cycle at which amplification enters the logarithmic phase (which is also directly dependent on the amount of starting template) is called:
Crossing threshold (Ct)
The more starting material the sooner the reaction will enter the logarithmic phase of amplification.
- Baseline is defined as PCR cycles in which a reporter fluorescent signal is accumulating but is beneath the limits of detection of the instrument.
- ΔRn is an increment of fluorescent signal at each time point.
- Threshold is an arbitrary level of fluorescence chosen on the basis of the baseline variability.
- A signal that is detected above the threshold is considered a real signal that can be used to define the threshold cycle (Ct) for a sample. Ct is defined as the fractional PCR cycle number at which the reporter fluorescence is greater than the threshold.
List the principles of Real-Time (Quantitative) PCR:
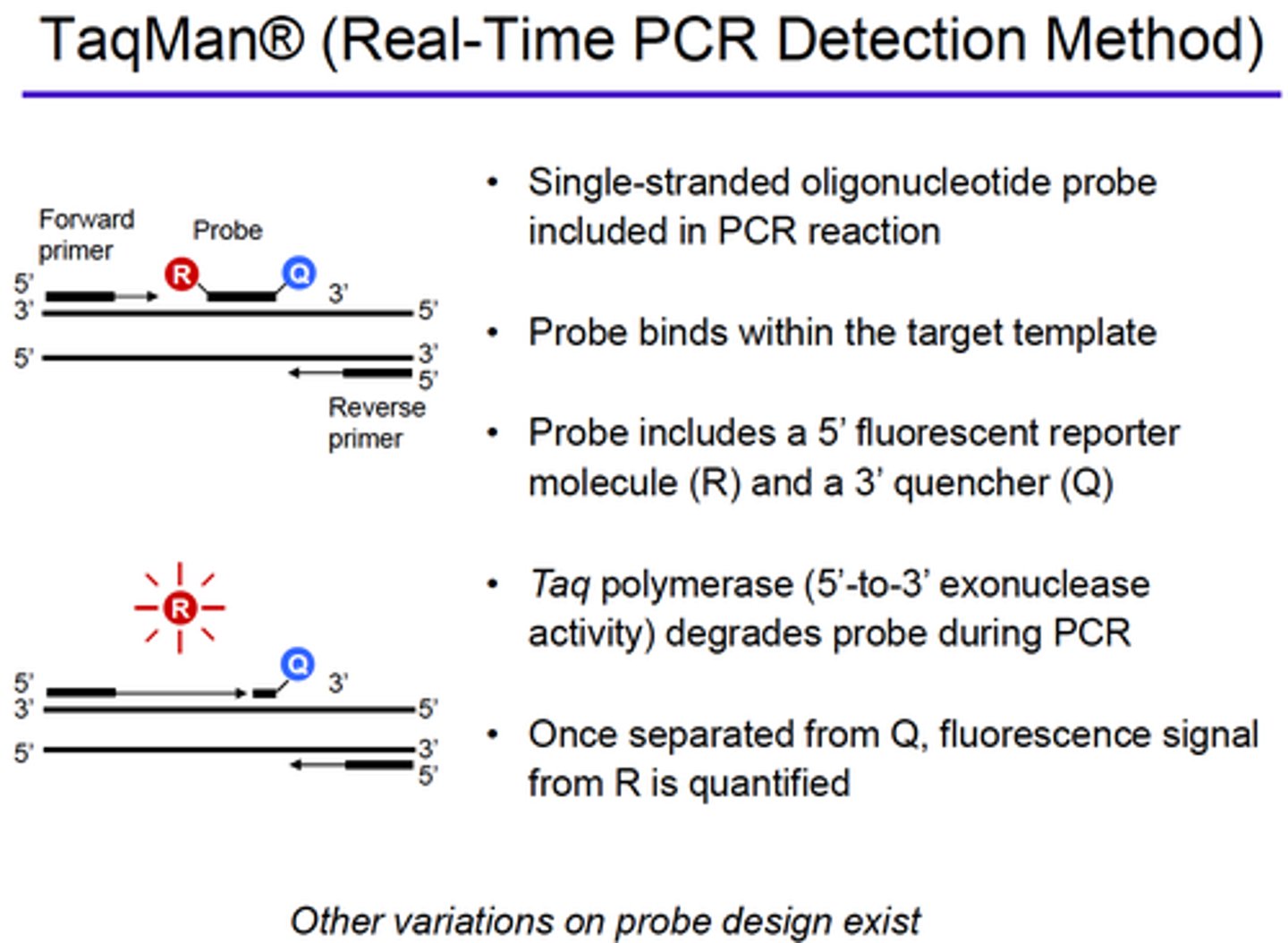
Explain how fluorescence is generated when using TaqMan in Real-Time PCR method:
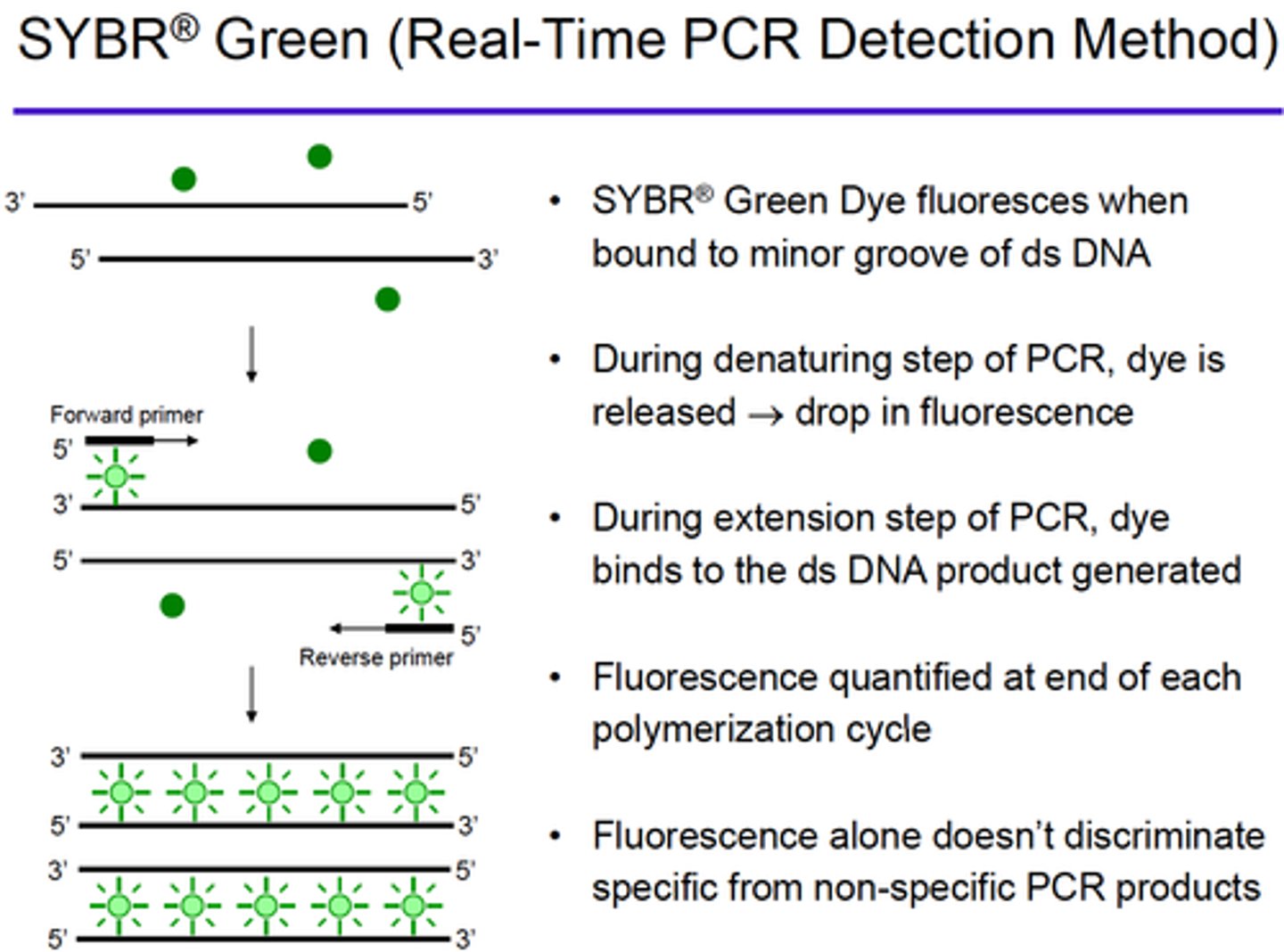
Explain how fluorescence is generated when using SYBR Green in Real-Time PCR method:
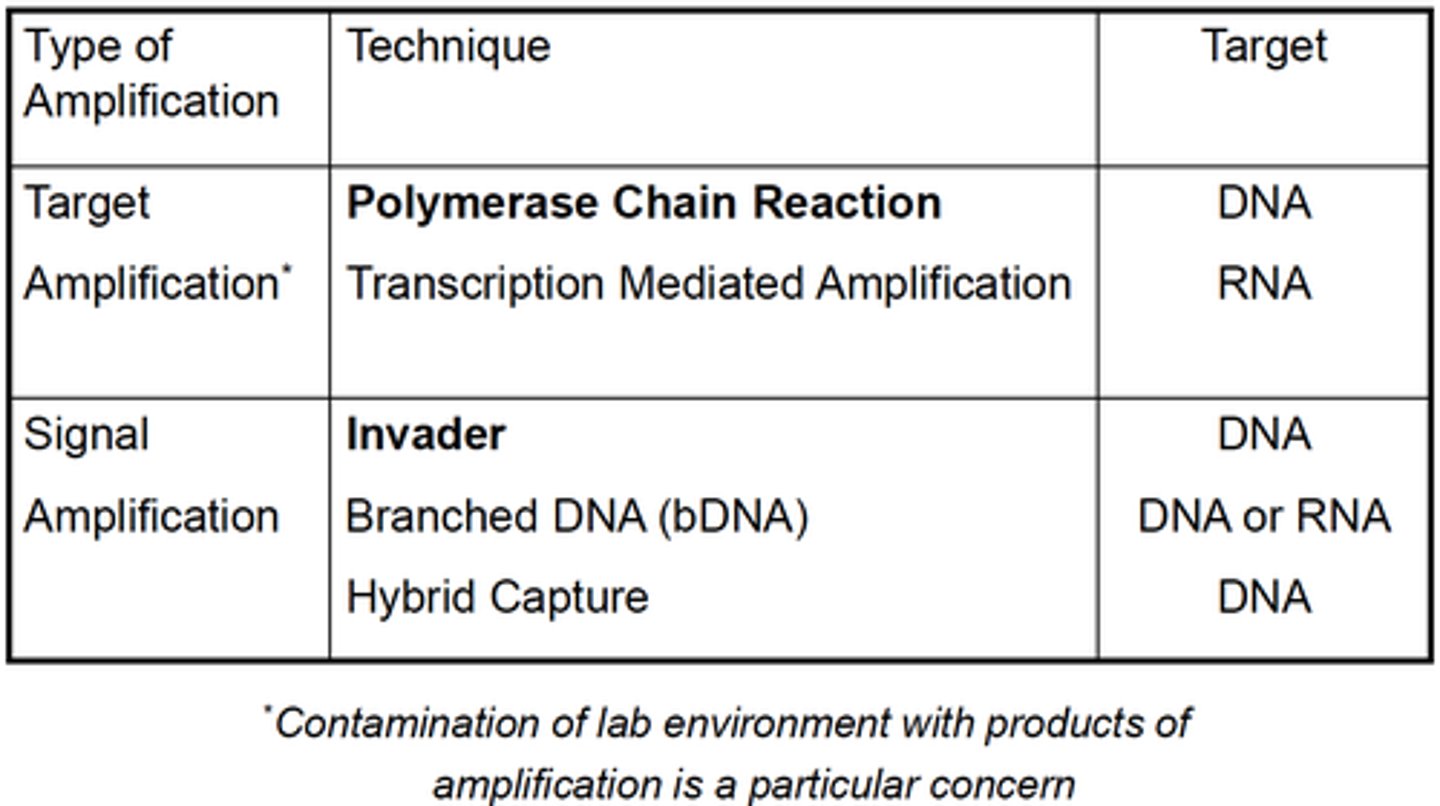
Types of nucleic acid amplification:
Target
Signal
Give examples of amplification techniques used for Nucleic Acid Detection:
Mention one problem of
- Target amplification
- Signal amplification
- Target amplification: Contamination
- Signal amplification: greater failures than target amplification
Both PCR and TMA (Transcription mediated amplification) are TARGET amplification techniques, what are the targets they amplify?
PCR: DNA
TMA: RNA
List SIGNAL amplification techniques with their corresponding target:
Invader: DNA
Branched DNA (bDNA): DNA or RNA
Hybrid Capture: DNA
Transcription mediated amplification (TMA) and Nucleic acid sequence-based amplification (NABSA) are related techniques, what do they have in common?
Isothermal amplification
RNA targets
Primarily used for infectious disease applications
Principle is similar: Utilize specific sequences that are recognized by bacteriophage RNA polymerase in order to make more RNA copies
Transcription mediated amplification (TMA) and Nucleic acid sequence-based amplification (NABSA) are related techniques, where do they differ?
TMA uses a reverse transcriptase
NABSA uses a separate RNase H enzyme to degrade the RNA in an RNA:DNA hybrid
What is the principle of SIGNAL amplification and list advantages/disadvantages .
Signal amplification techniques aim to detect nucleic acid by amplification of the signal rather than amplification of the starting material.
They are less susceptible to spurious results due to contamination.
They are usually not as sensitive.
What can you amplify using SIGNAL amplification techniques?
One can amplify the PROBE (the cleavase reaction (Invader assay), or ligation amplification reaction)
One can amplify the SIGNAL itself (the branched DNA or hybrid capture techniques)
Explain the principle of the CLEAVASE (Invader assay) technique (type of PROBE amplification)
It is capable of multiplexing and very sensitive.
The principle is:
- A specific probe is bound to a sequence of interest
- A second specific probe hybridizes the already bound probe
- This creates a unique triplex structure that is recognized by a CLEAVASE (an endonucleasa)
- Upon cleavage, a specific probe sequence is released
- The probe can be detected via release of a quencher from a fluorophore-labeled fragment by cleavase or with an additional probe-specific secondary probe
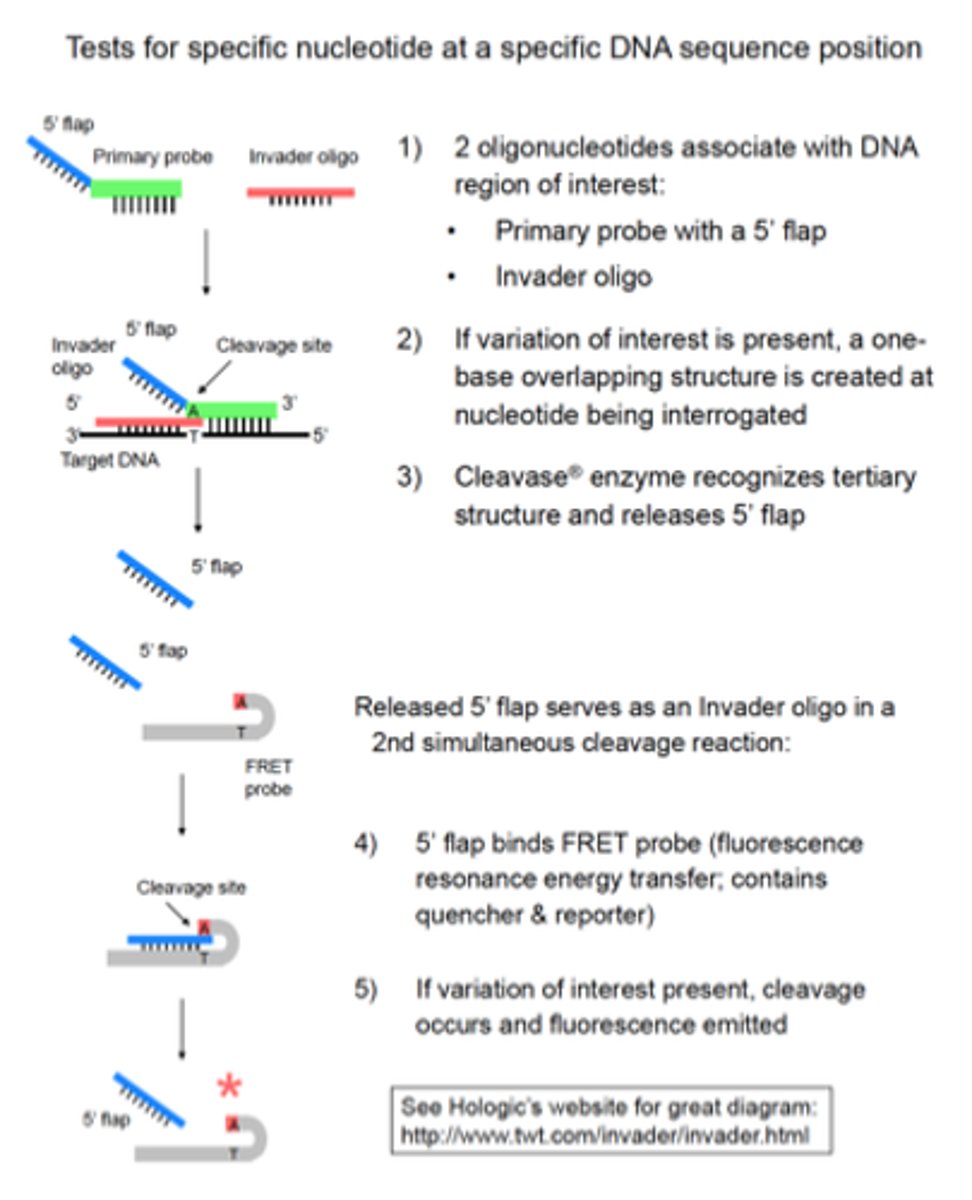
What do you need for the Cleavase (Invader assay)?
• Wild type and variant nucleotide distinguished by:
- 2 different primary probes (with unique 5' flap sequences)
- 2 different FRET probes (with different emission spectra)
• Isothermal process
• Single tube
• Signal amplification occurs because:
1) Multiple primary probes can repeatedly bind target and be
cleaved
2) Each 5' flap released can bind multiple FRET probes
Applications: Detection of Factor V Leiden, Prothrombin G20210A, others
Explain the principle of the LIGATION AMPLIFICATION technique (type of PROBE amplification)
- Employs a thermostable LIGASE
- Allows the discrimination of DNA sequences differing in only a single base pair
- The principle is based on the ligation of 2 adjacent oligonucleotide primers, which have been designed to hybridize with the target DNA
- The 3' target sits immediately adjacent to the 5' end of the next
- The point where they meet is the location of a known potential single base pair difference in the targeted sequence
- The two primers will be joined by DNA ligase
- 4 separate probes are utilized for each dsDNA
- If there is any mismatch at the 3' end of one of the probes adjacent to the 5' end of the second probe, the ligation cannot occur
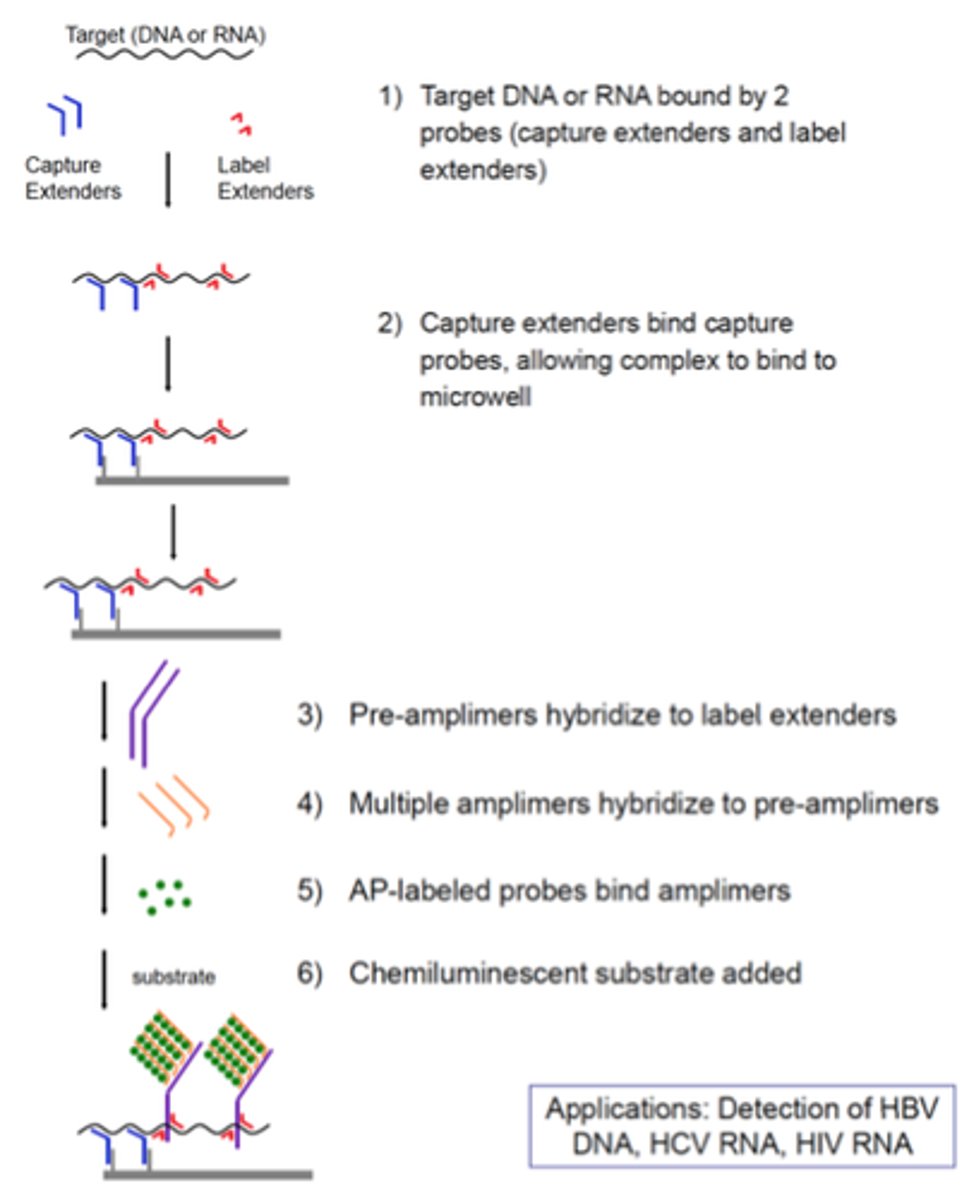
Explain the principle of the Branched DNA technique (type of signal amplification)
- Amplifies the signal from a nucleic acid molecule
- A capture probe is bound to a solid support, usually either beads or the wells of a plate
- A hybrid probe called an extender, is designed to hybridize to a nucleic acid of interest as well as the capture probe
- As a result: target nucleic acid is immobilized on the solid support
-To the immobilized complex, a second hybrid probe called a label extender is bound
- The label extender recognizes both the target nucleic acid and the molecule called a preamplifier
- Once the preamplifier is bound to the label extender the preamplifier molecule acts as the trunk of a tree on which an amplifier molecule forms the branches
- The amplifier molecule in addition to recognizing the preamplifier also is studded with numerous biotin molecules
- The biotin molecules are each recognized by a streptavidin-fluorophore conjugate with when excited fluoresces like the lights on a tree
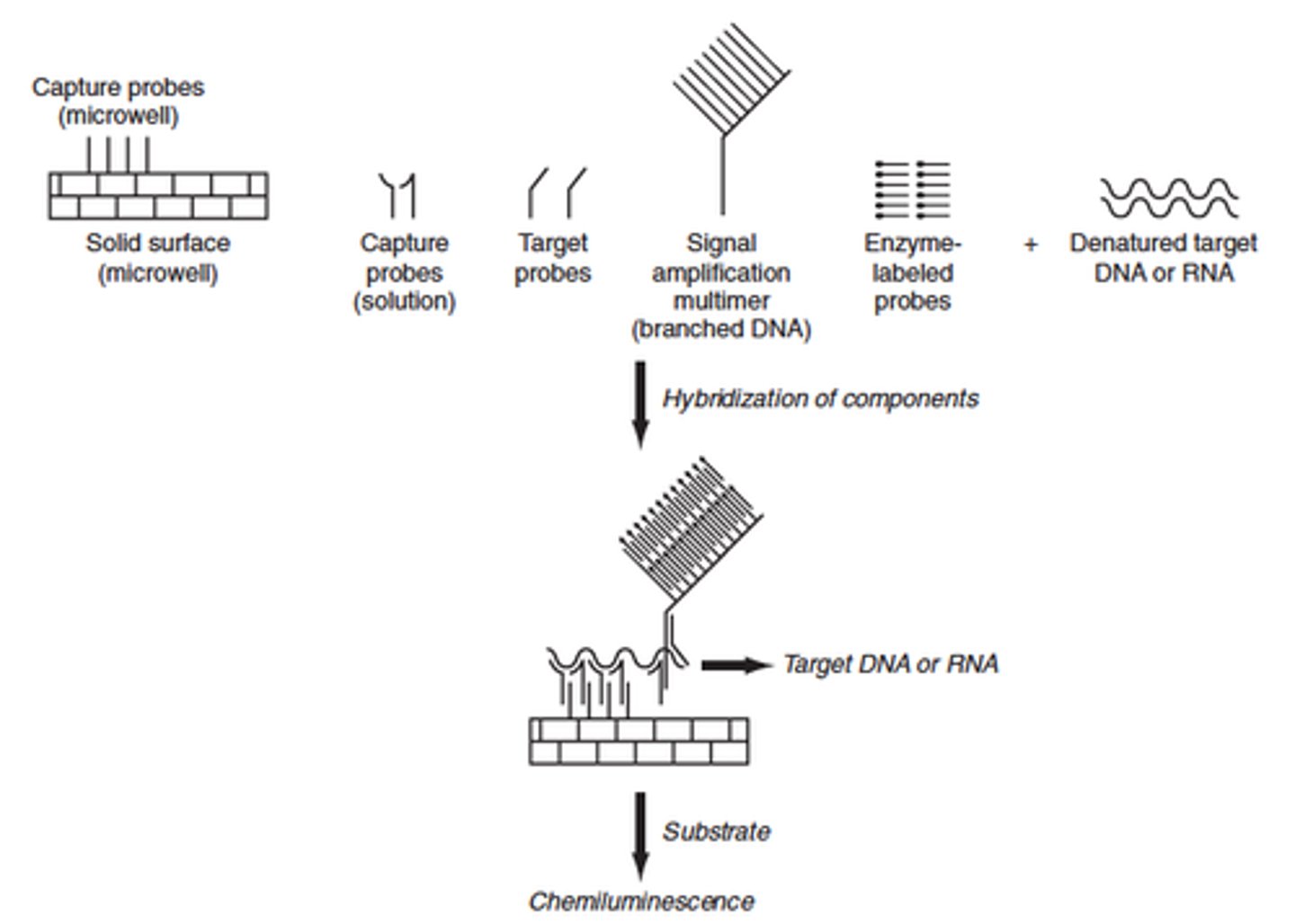
Explain the principle of the Branched DNA technique (type of signal amplification)
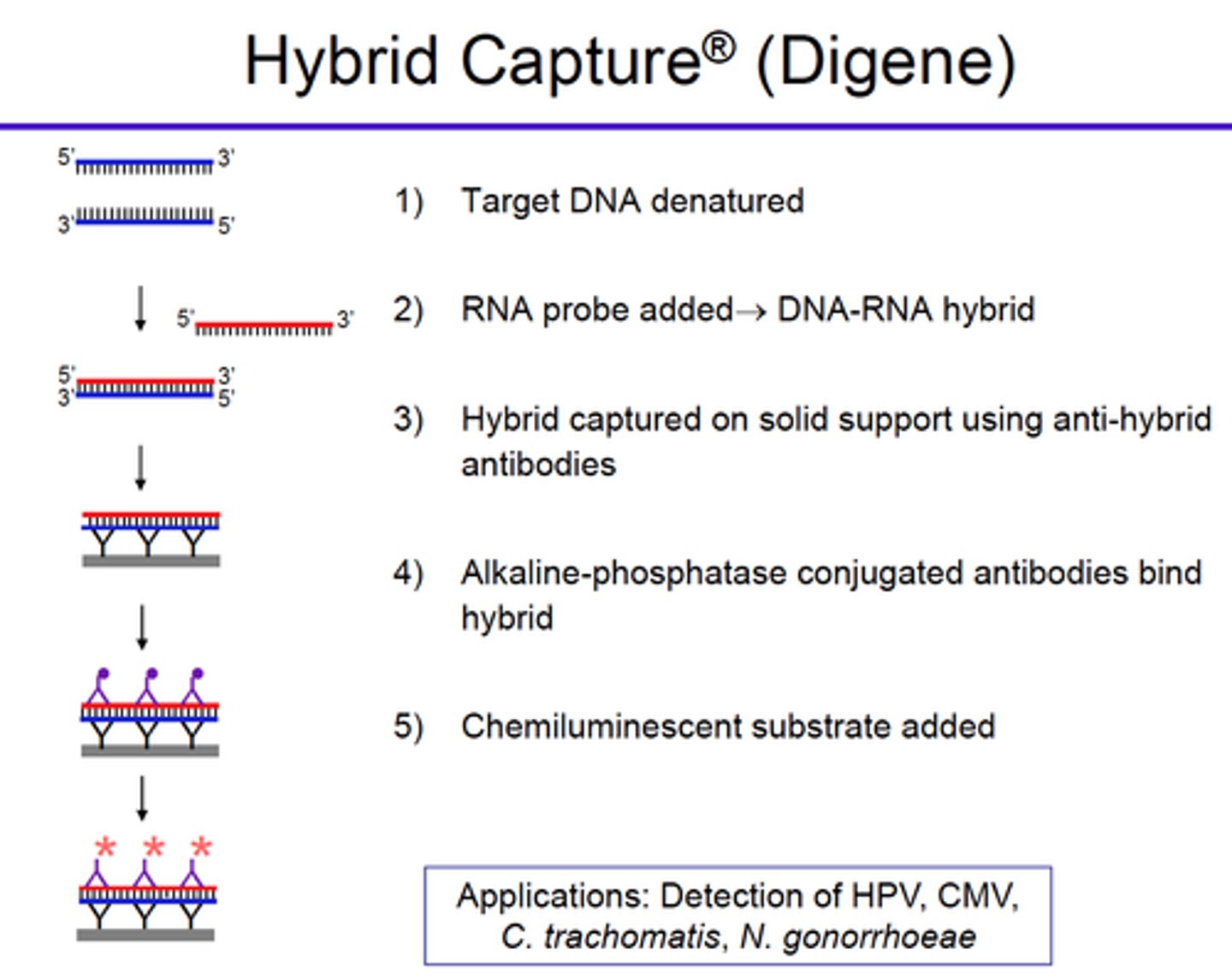
Explain the principle of the Hybrid capture technique (type of signal amplification)
- A series of RNA probes directed against specific DNA sequences is incubated with specific antibodies that recognize RNA:DNA hybrid molecules
- A sandwich approach is employed: immobilize these antibodies to the wells of a plate, bind hybrid DNA/RNA molecules, then recognize with a conjugate antihybrid antibody
One of the advantages of Melting curve analysis is:
Describe the principle of the Melting curve analysis method:
Increased specificity of PCR product identification
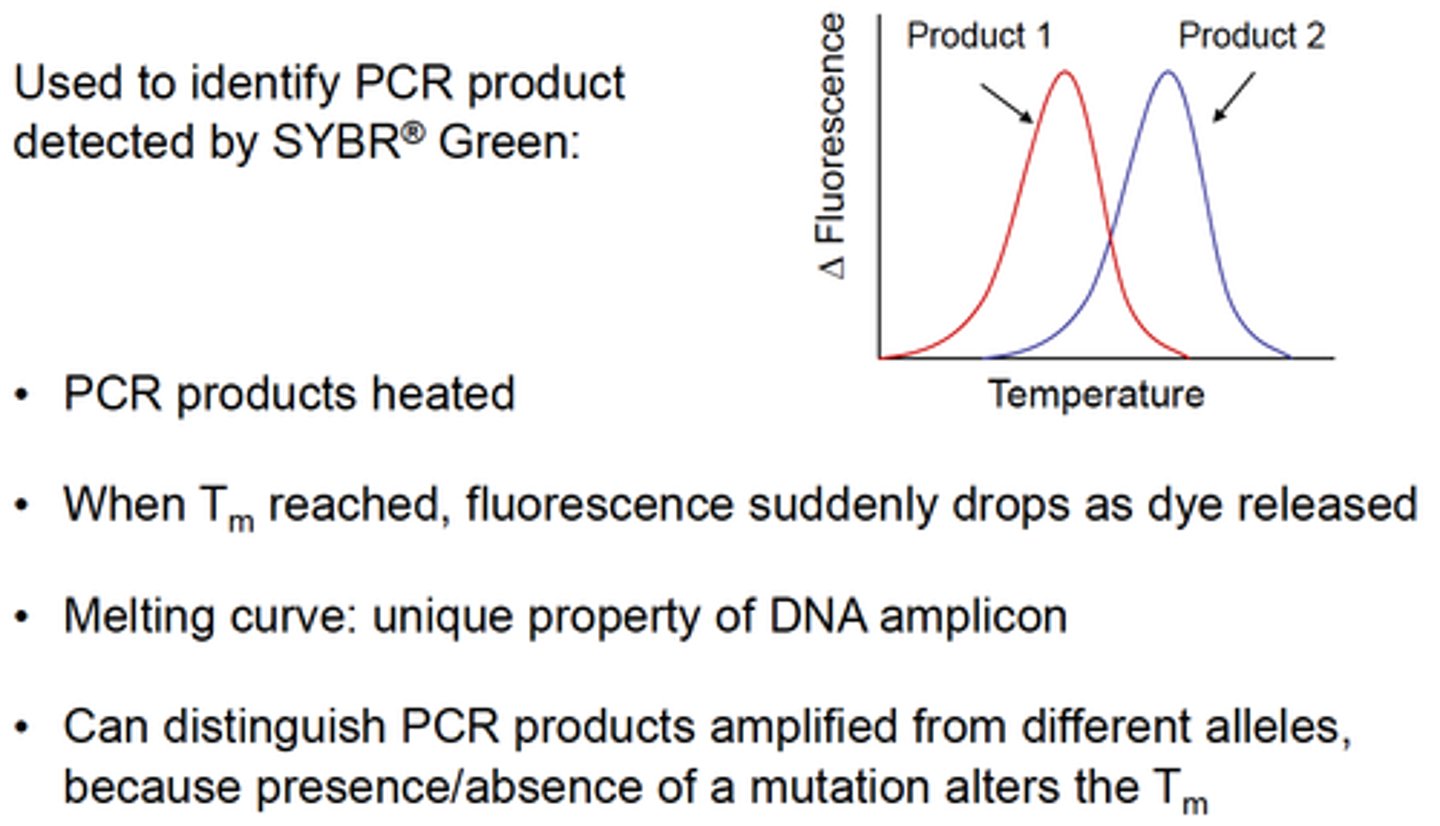
What do you measure during the Melting curve Analysis procedure?
Fluorescence, while incrementally increasing the reaction temperature
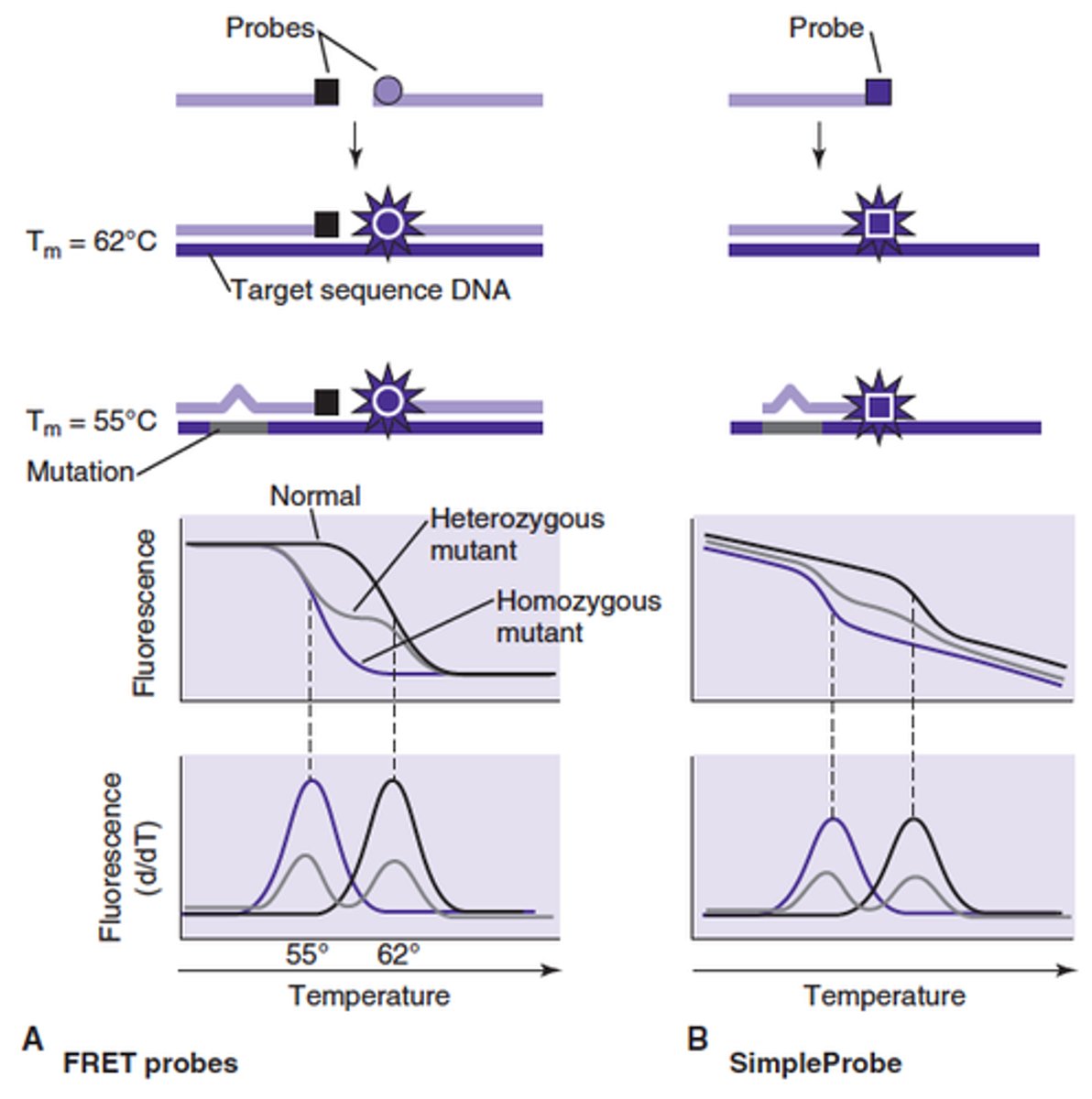
T or F
Hydrolyzable probes can be used during the Melting curve analysis procedure
False
How is MELTING POINT defined?
As the point at which 50% of the product is single stranded
On a plot of fluorescence vs temperature the melting point is the point of maximal change in rate of melting
Name few characteristics of a product that could influence the melting point
Length
G:C content
Amount of mismatch
How does Multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification (MLPA) work?
For each possible mutation there is a specific probe and an adjacent anchor probe separated by a single base.
Only when the 2 probes anneal adjacent to each other are they able to be subsequently ligated and then amplified with probe-specific primers.
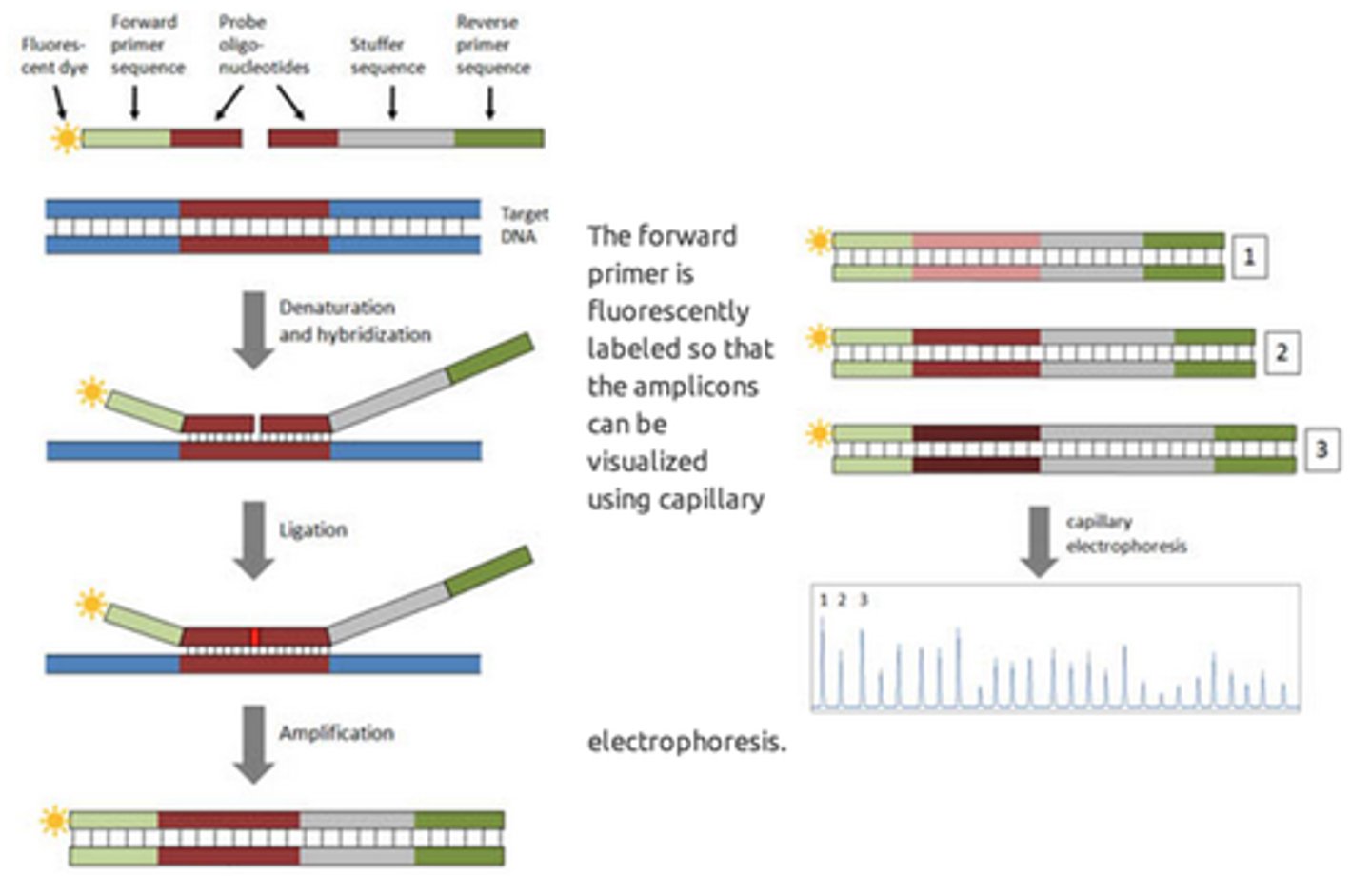
What is one advantage of the Multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification (MLPA)?
It can interrogate multiple (sometimes several hundred) mutations at the same time.
It uses numerous specific probes, each containing gene-specific sequence and sequence shared with all the other probes for PCR.
The Multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification (MLPA) technique and variations are useful for?
Determination of single nucleotide polymorphisms/ mutations
Dosage and copy number
Methylation status
What is the principle of mass spectrometry?
It can separate particles based on their individual mass to charge ratios
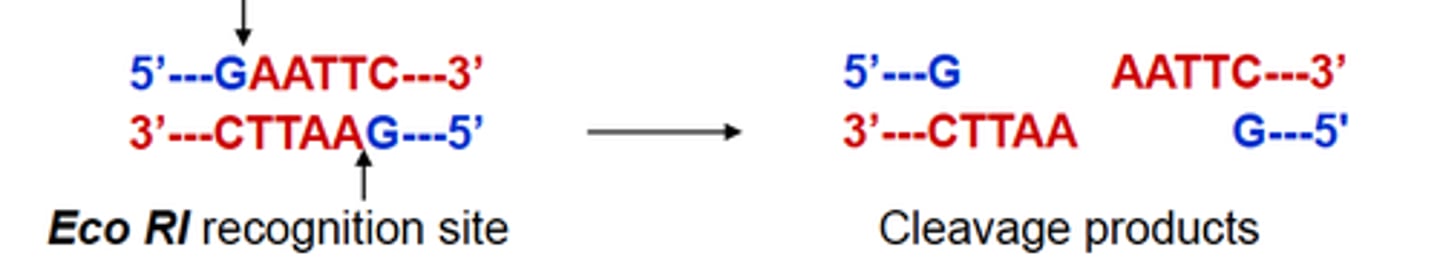
What are the restriction enzymes and what do they do?
- They are bacterial endonucleases
- They recognize and cleave specific DNA sequences (4-12 nt long)
- They leave either a 5' overhand blunt end, or a 3' overhang
- Mutations in sequence sites can result in either loss of gain of a recognition sequence
- Used in Southern blot or the restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) assay (mutations with loss or gain of a cleavage recognition site)
What is blotting?
Tranferring nucleic acid or protein to a solid support
- The molecules of interest are first separated from other molecules through gel electrophoresis
- The gel is then blotted to a solid support membrane through either capillary or electrophoretic action
- Once transferred, the molecules on the membrane can be probed
- The presence of a signal and its location on the membrane when hybridized to the probe characterize the molecule of interest
What is blotted with Southern blot technique?
DNA
Describe the steps for Southern Blot Analysis and its main application:
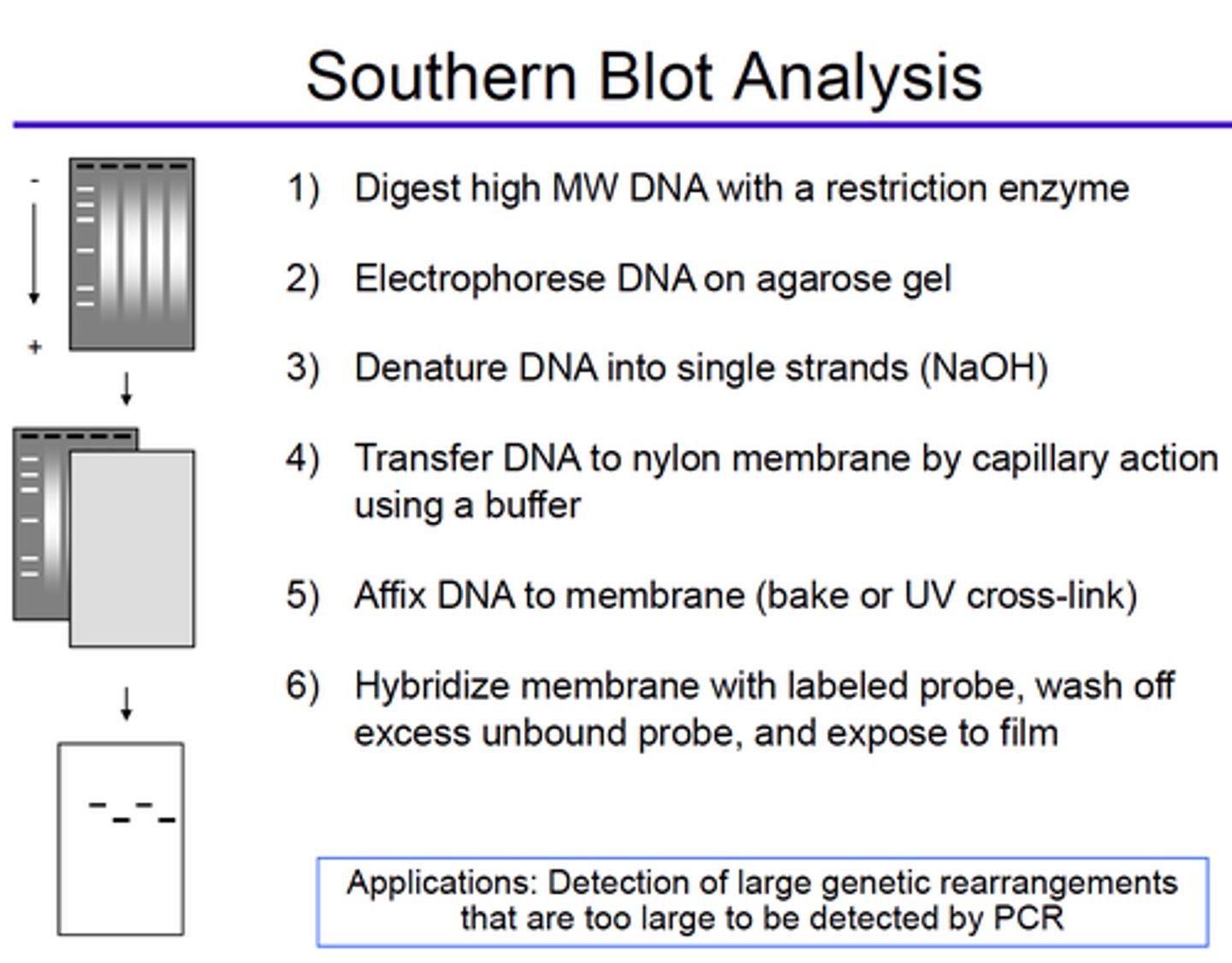
What is blotted with Northern blot technique?
RNA
What is blotted with Western blot technique?
Protein
Explain the principle of Sanger sequencing:
To perform in vitro DNA replication with a radiolabeled primer, but to terminate replication selectively at each different base.
- Initially, 4 different reactions were performed, one for each of the bases
- In each reaction deoxynucleotides and dideoxynucleoties were added
- Dideoxynucleotide lacks the 3' hydroxyl needed to perfom the phosphodiester bond, so replication ceases
- The mix undergoes electrophoresis through polyacrylamide gel → Would separate the strands of DNA by length and provide a ladder, each rung representing an aborted replication due to incorporation of a chain terminating dideoxynucleotide
- When each of the 4 reactions was run next to one another the sequence of the target could be read from the bottom (SHORTEST fragments) to the top (LONGEST fragments).
- The technique has been simplified through the use of dideoxynucleotides conjugated to different fluorophores
Explain the principle of Sanger sequencing method:
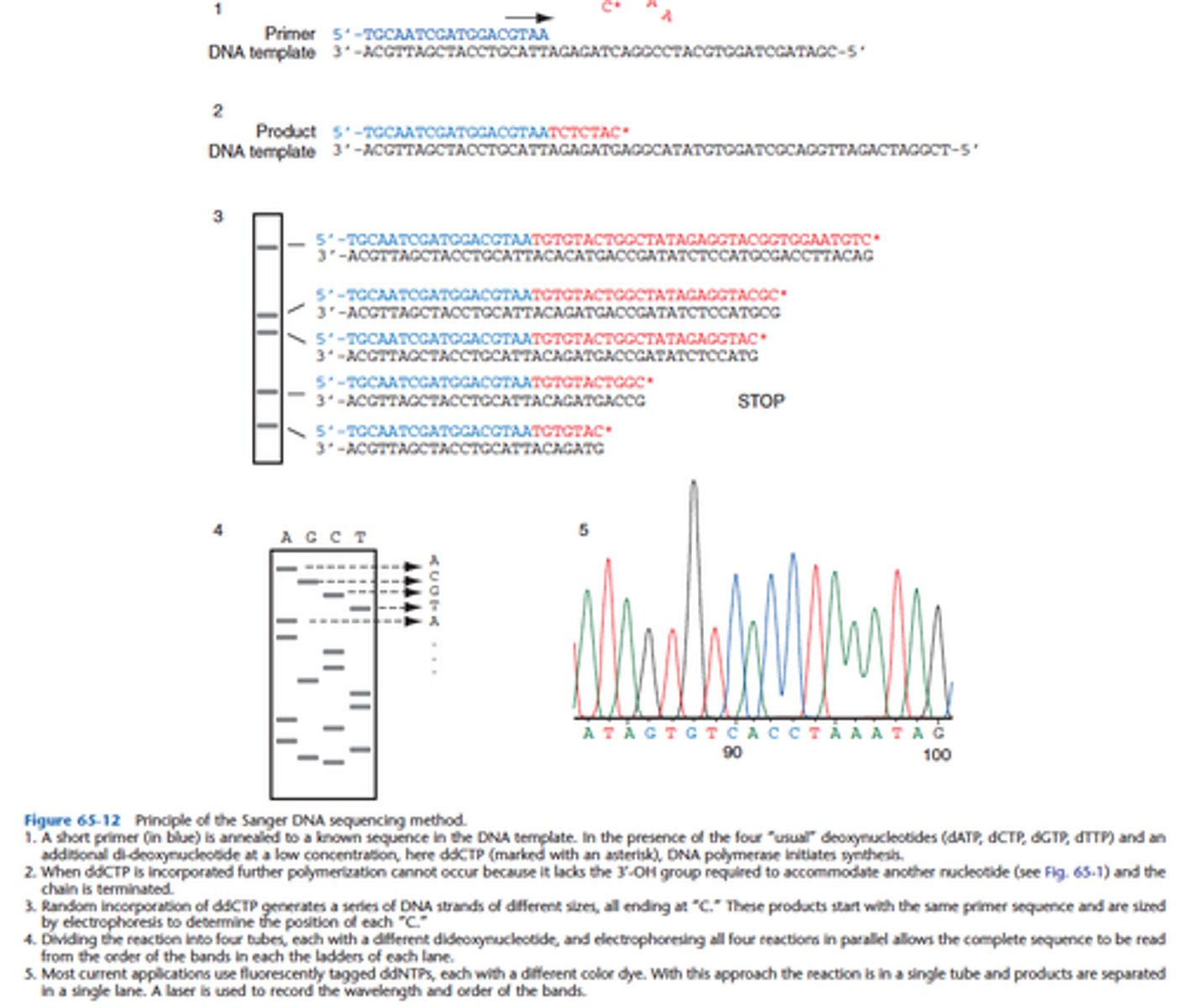
In the Sanger Method, what is radiolabeled for detection?
Either the primer or one of the dNTPs
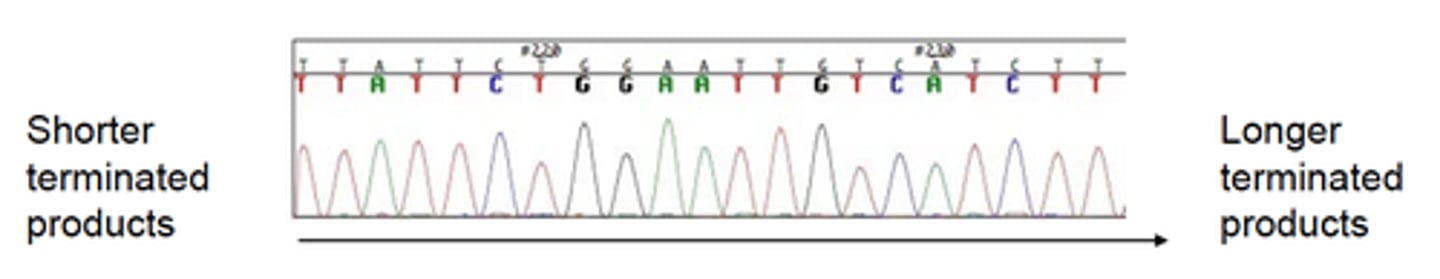
What is the principle of the Dye-terminator Method used for DNA sequencing (which is a modification of the Sanger method)?
• Performed in a single tube
• Includes all 4 ddNTPs (each labeled with a different fluor)
• Products fractionated by size via electrophoresis through polymer filled capillary
• Products detected as sequentially pass by laser
• Chromatogram: each peak = PCR products of specific size
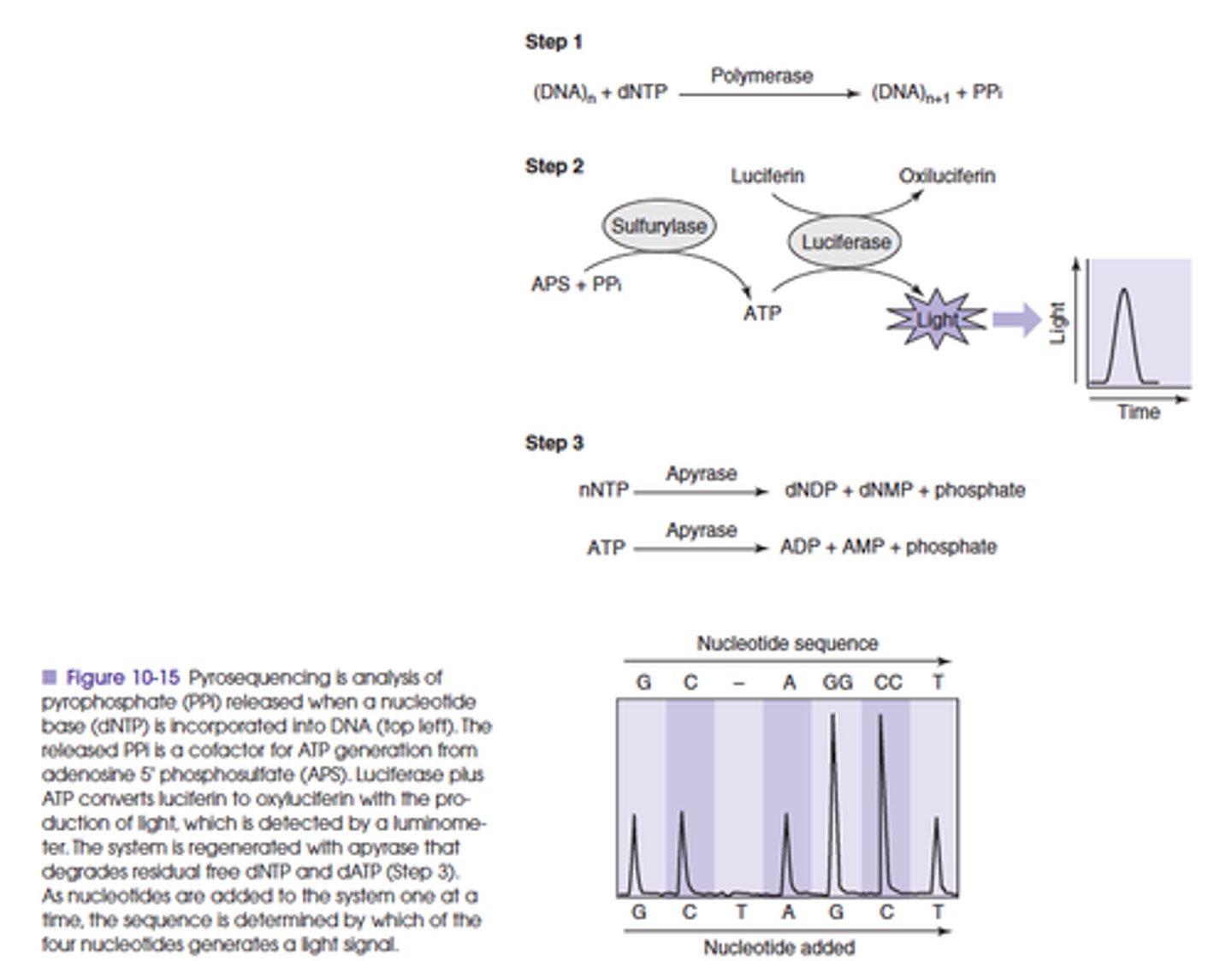
Explain the principle of Pyrosequencing (single base extension)
Quantitative measurement of the pyrophosphate that is released whenever a trinucleotide phosphate is incorporated into a phosphodiester bond
- By sequentially adding each base, a single base extension reaction will occur whenever the appropriate complementary base is added
- When a single base is incorporated, phryrophosphate is released
- The released pyrophosphate (due to secondary light production) is related to the number of bases incorporated, then the sequence of target DNA can be inferred
If a string of identical bases is encountered in a sequence, then there will be stoichiometrically more pyrophosphate released than if there was a single base
What are the advantages of pyrosequencing? What type of alterations is this good for?
It is rapid, inexpensive and sensitive
Best utilized to analyze sequences close to the primer. For this reason it is often used for POINT MUTATIONS or SINGLE NUCLEOTIDES POLYMORPHISMS
What is one of the advantages of Next Generation Sequencing?
Next generation sequencing is designed to sequence large numbers of templates simultaneously, yielding not just one, but hundreds of thousands of sequences in a run that takes a few hours.
Most of the techniques are founded on: massive parallel in vitro sequencing, sensitive detection and separation of individual signals, and subsequent computerized assembly of all the contiguous sequences (contigs).
What is one of the goals of Next Generation Sequencing?
The goal of next generation sequencing is to achieve the sequence of the human genome for a minimal cost ($1,000), making genomic studies a routine component of both research and clinical analysis.
What type of technologies include Next Generation Sequencing?
Next generation sequencing includes technologies such as the 454 FLX pyrosequencer (Roche), the Illumina Cluster bead array system (Luminex), the HeliScope single-molecule sequencing system (Helicos Bioscience), and SOLiD sequencing by ligation (Applied Biosystems).
Next generation sequencing requires novel methods of template preparation, such as emulsion PCR and bridge PCR or single-molecule capabilities.
Powerful computer data assembly systems are required to organize the massive amounts of sequence information that is generated. These technologies can be used not only to sequence multiple whole genomes but also to investigate populations of small genomes such as microbial diversity.
Some of the challenges of Next Generation Sequencing include:
Ongoing challenges with massive sequencing
include:
- the integration of technologies and
- the compromising of accuracy for throughput
When is the restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) analysis used?
If a mutation changes the structure of a restriction enzyme target site or changes the size of a fragment generated by a restriction enzyme (RFLP) analysis can be used to detect the sequence alteration (by Southern blot).
How is RFLP performed?
To perform PCR-RFLP, the region surrounding the mutation is amplified, and the mutation is detected by cutting the amplicon with the appropriate restriction enzyme. Mutations may inactivate a naturally occurring restriction site or generate a new restriction site so that digestion of the PCR product results in cutting of the mutant amplicon but not the normal control amplicon or vice versa.
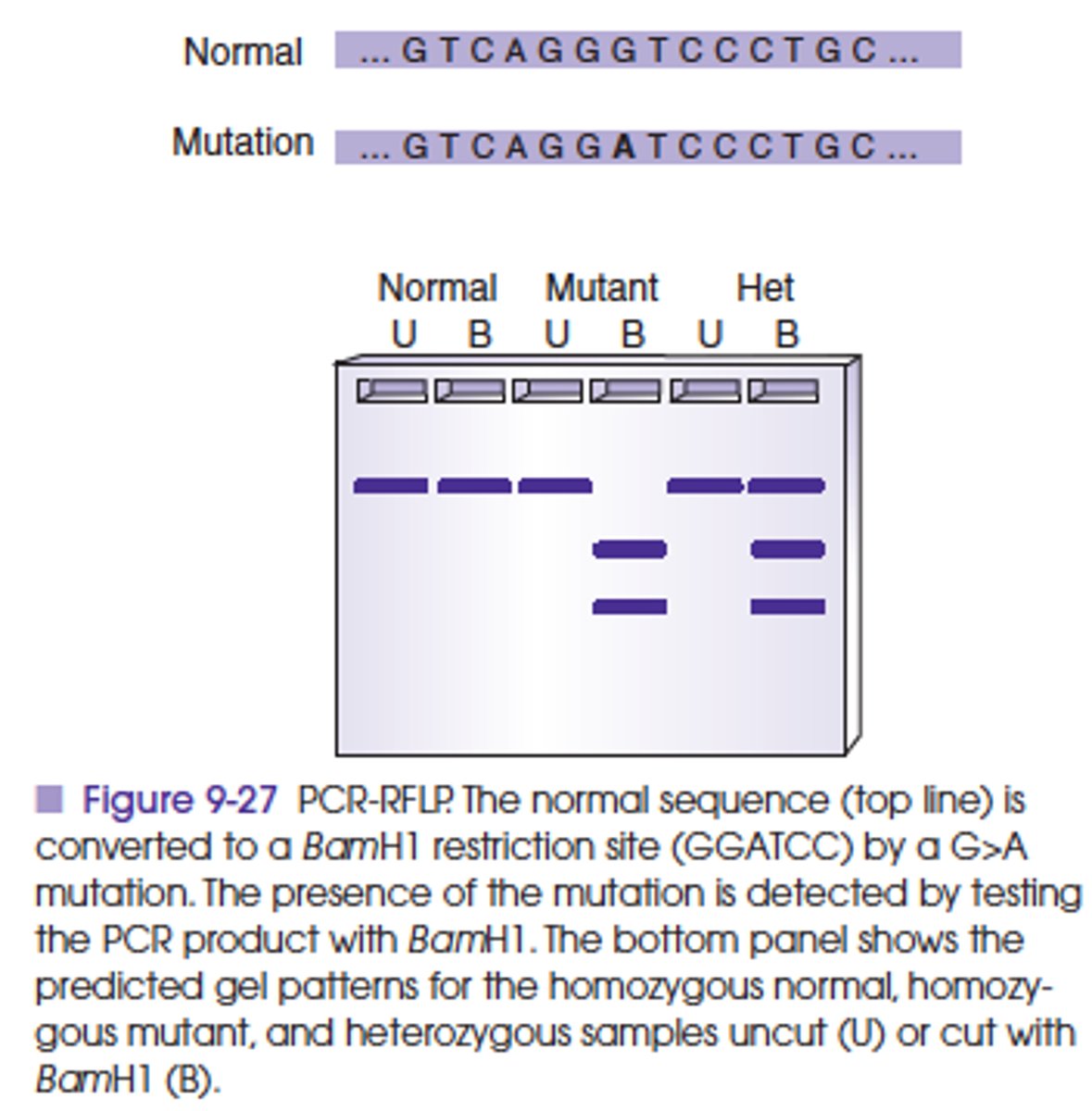
T or F
Can PCR-RFLP be multiplexed to detect more than one gene simultaneously?
TRUE
This has been practical for detection of separate gene mutations that affect the same phenotype, for example, factor V Leiden and prothrombin. Alternatively, a combination of SSP-PCR and PCR-RFLP is also applied to simultaneous detection of mutations in more than one locus.
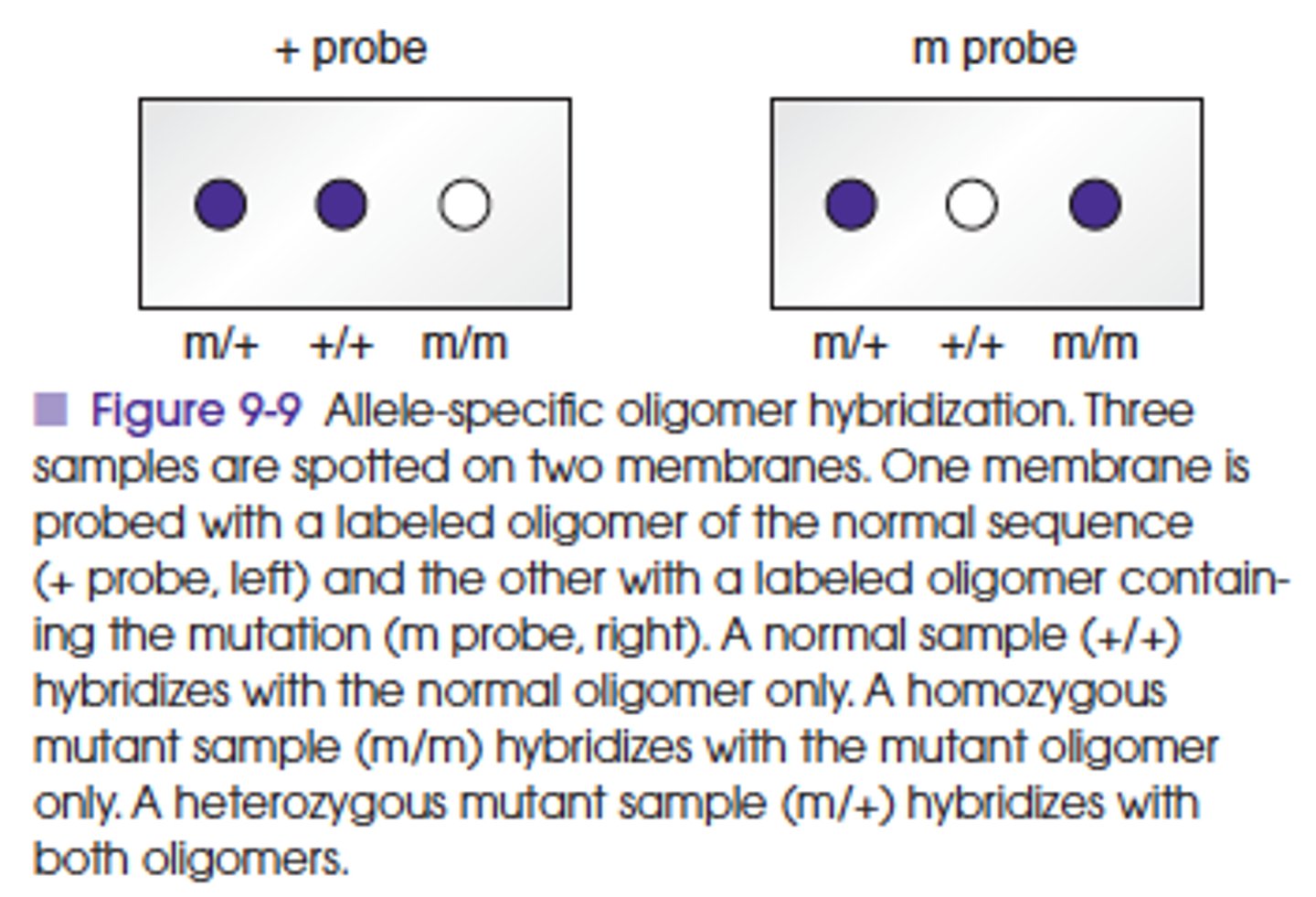
What is the principle of Allele-specific hybridization, or allele-specific oligometer hybridization (ASO) method?
Utilizes the differences in melting temperatures of short sequences of about 20 bases with one or two mismatches and those with no mismatches.
Synthetic single-stranded probes with the normal or mutant target DNA sequence are used for this assay.
At specific annealing temperatures and conditions (stringency), a probe will not bind to a near complementary target sequence with one or two mismatched bases, whereas a probe with a perfect complementary sequence will bind.
ASO is a dot blot method, similar to the Southern blot method that uses an immobilized target and a labeled probe in a solution.
This method has been used in clinical testing for detection of specific mutations and polymorphisms and for typing of organisms.
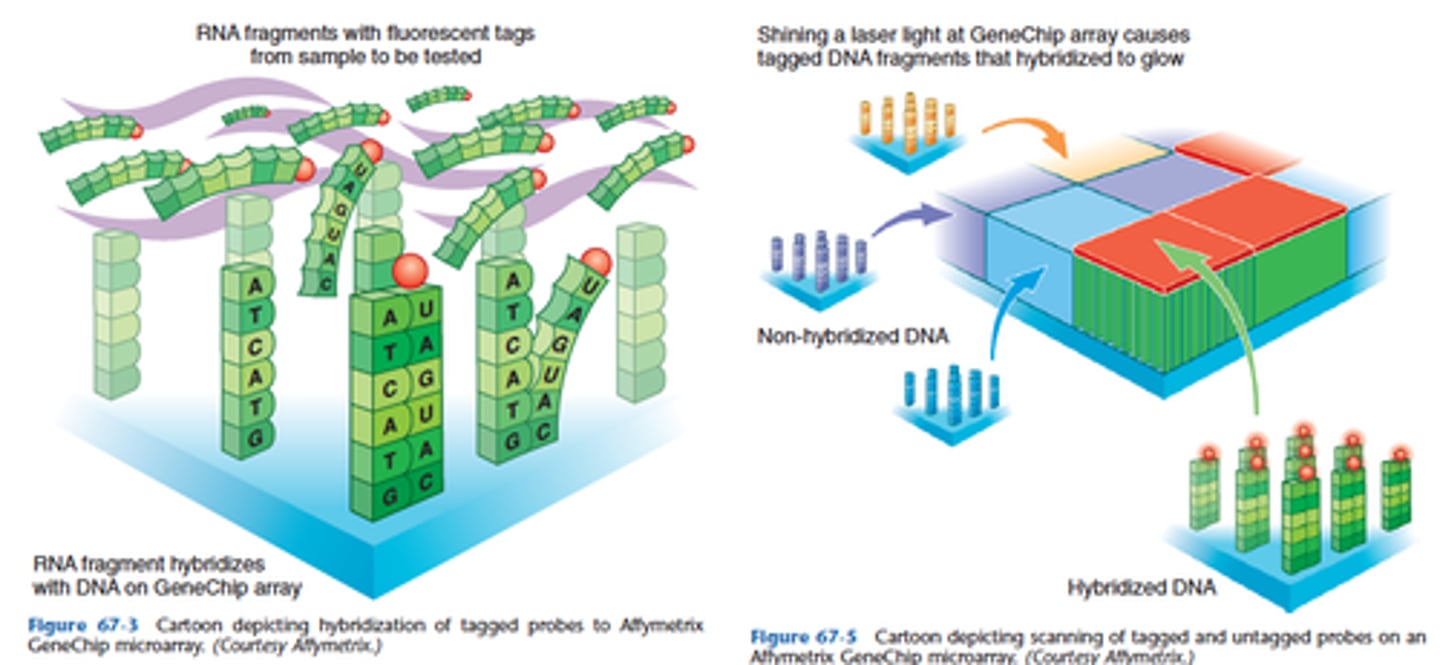
What is one advantage of the ARRAY (microarray) technology?
Focus on a SINGLE gene with higher resolution (as in ASO procedures).
The advantage of array methods is the large number of potential sequence mutations or SNPs than can be tested simultaneously!!!!
Array is also designed to test multiple genes for sequence mutations.
Array technology provides a unique and powerful approach to screen a sample for dozens to thousands of genes.
• Positive signals are generated when a tagged nucleic acid moiety hybridizes with its complementary probe localized on a solid support (i.e., "chip").
• Numerous applications of array technology have been proposed in the past few years, ranging from molecular staging of tumors to the identification and characterization of microbial agents.
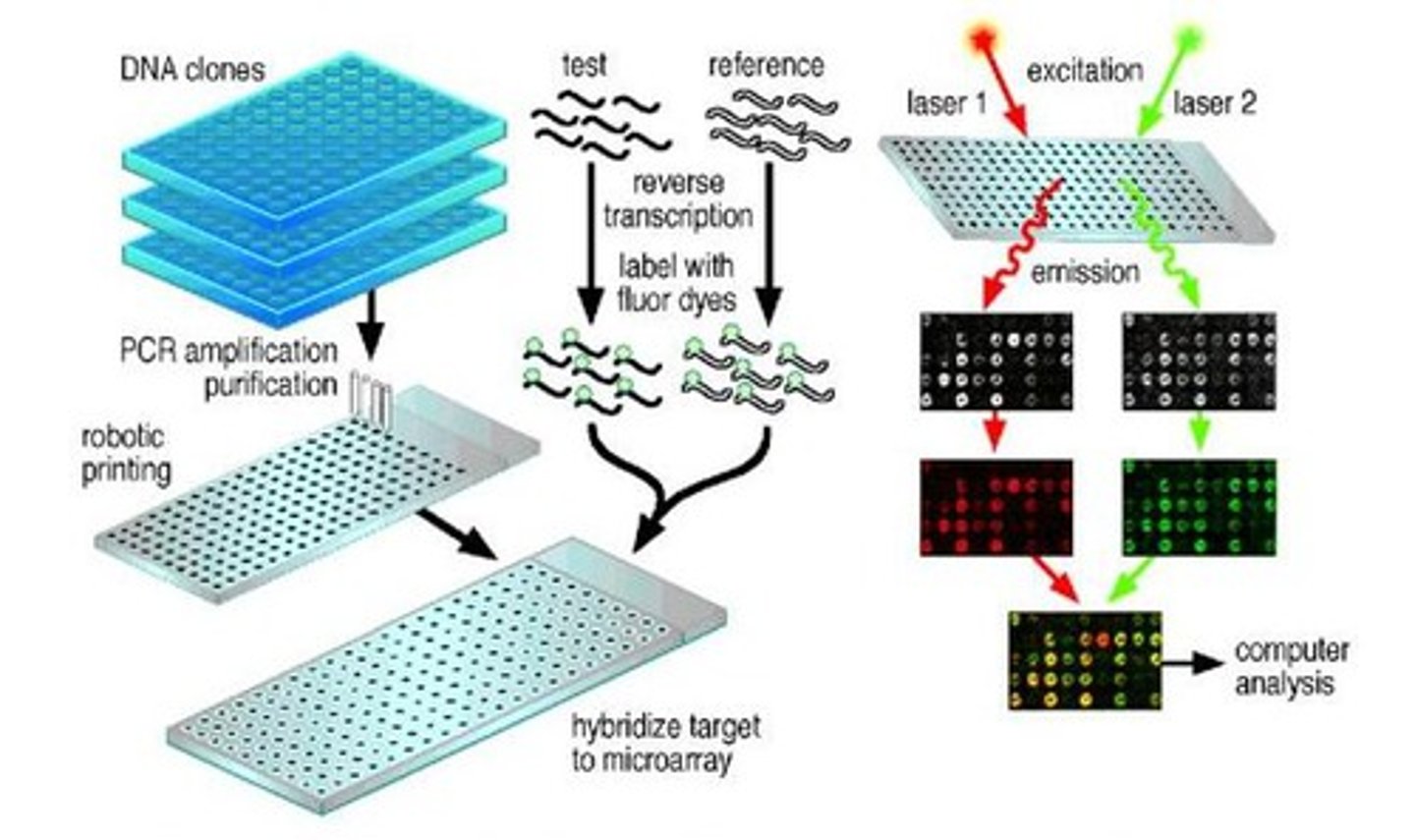
What is the difference between a macroarray and a microarray?
List some applications of microarray technology.
In general, arrays are described as macroarrays or microarrays, the difference being the size of the sample spots. Macroarrays contain sample spot sizes of about 300 microns or larger and can be easily imaged by existing gel and blot scanners. The sample spot sizes in microarray are typically less than 200 microns in diameter and these arrays usually contains thousands of spots.
Microarrays require specialized robotics and imaging equipment that generally are not commercially available as a complete system.
There are two major application forms for the DNA microarray technology:
1. Identification of sequence (gene / gene mutation): example hereditary diseases.
2. Determination of expression level (abundance) of genes: During the viral infection, the viral genome would up-regulate the protein expression in the host level so that it would help to produce the DNA polymerase for viral DNA synthesis. As the virus start to duplicate the virus particle, the viral genome would show significant abnormal expression. By using the DNA array, it could also be detect while the infection is in the early stage.
Some of the advantages of Fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) include:
Ability to use numerous different samples (such as interphase cells)
Ability to interrogate individual cells in a background of other cells
Ability to separate signals in space
Ability to quantitate signals
Ability to detect multiple signals in a single specimen
Mention the 3 major types of probes used in conventional FISH analysis
1. Chromosome enumeration probes
2. Locus-specific probes
3. Probes that cover the entire chromosome used for chromosome painting
What do chromosome enumeration probes target?
They target repeat regions present in the centromeric region of the chromosome.
They are often used in combination with locus-specific probes to determine identity and copy number of individual chromosomes.
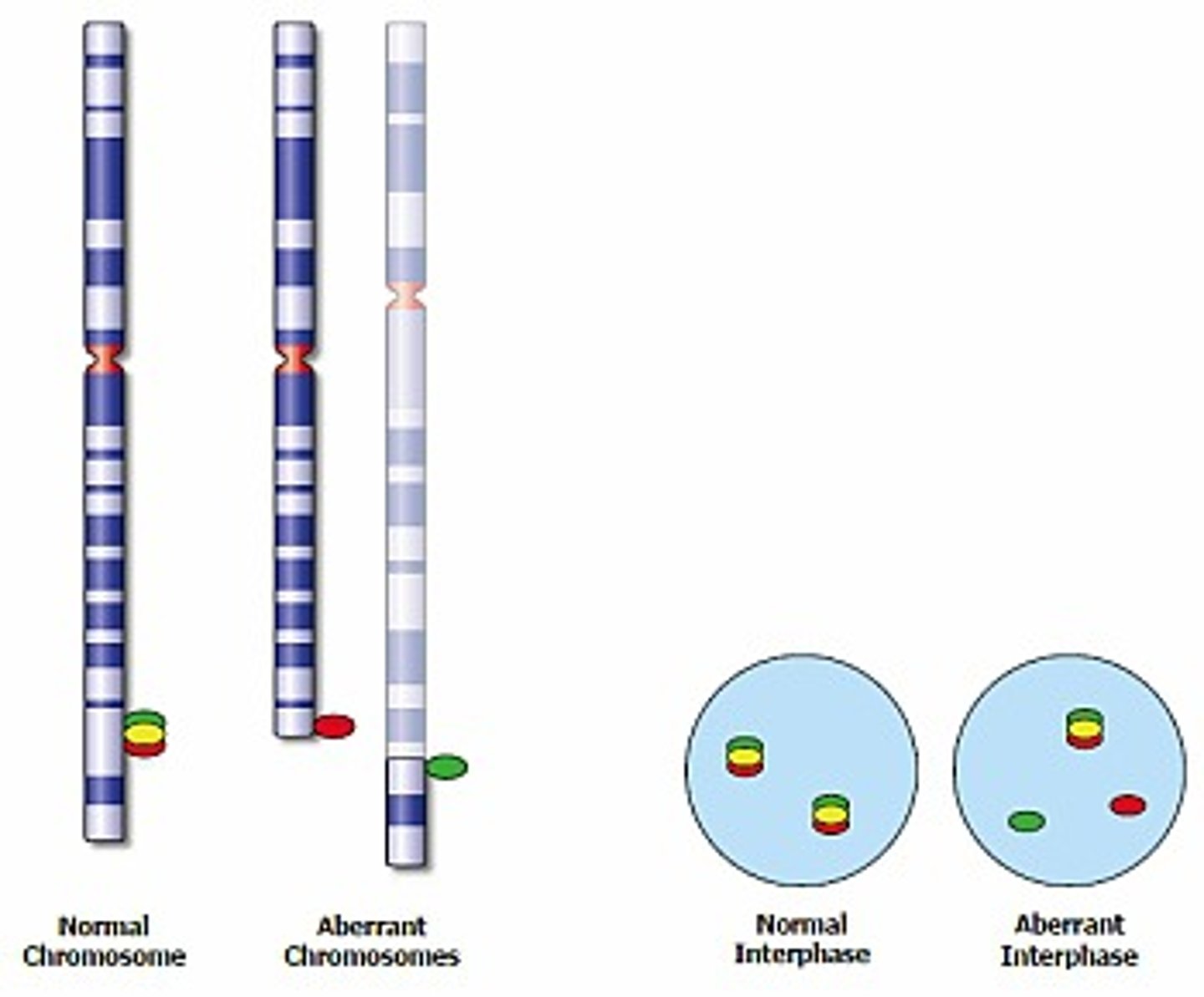
Locus-specific probes are used for translocations, they can be further subdivided according to their goal. What do they try to detect?
1. Fusion genes
2. Break in genes
Fusion probes are useful for:
Well defined translocations with conserved break, fusion probes.
Regarding FISH fusion probes. How would a DUAL COLOR, SINGLE FUSION probe look like?
Dual color, single fusion (2 different colors for the normal genes become a single third color when fused).
Single fusion probes are useful when the translocation is represented in a large number of cells, but is subject to false positives when there are a lower percentage of cells with the defined translocation.
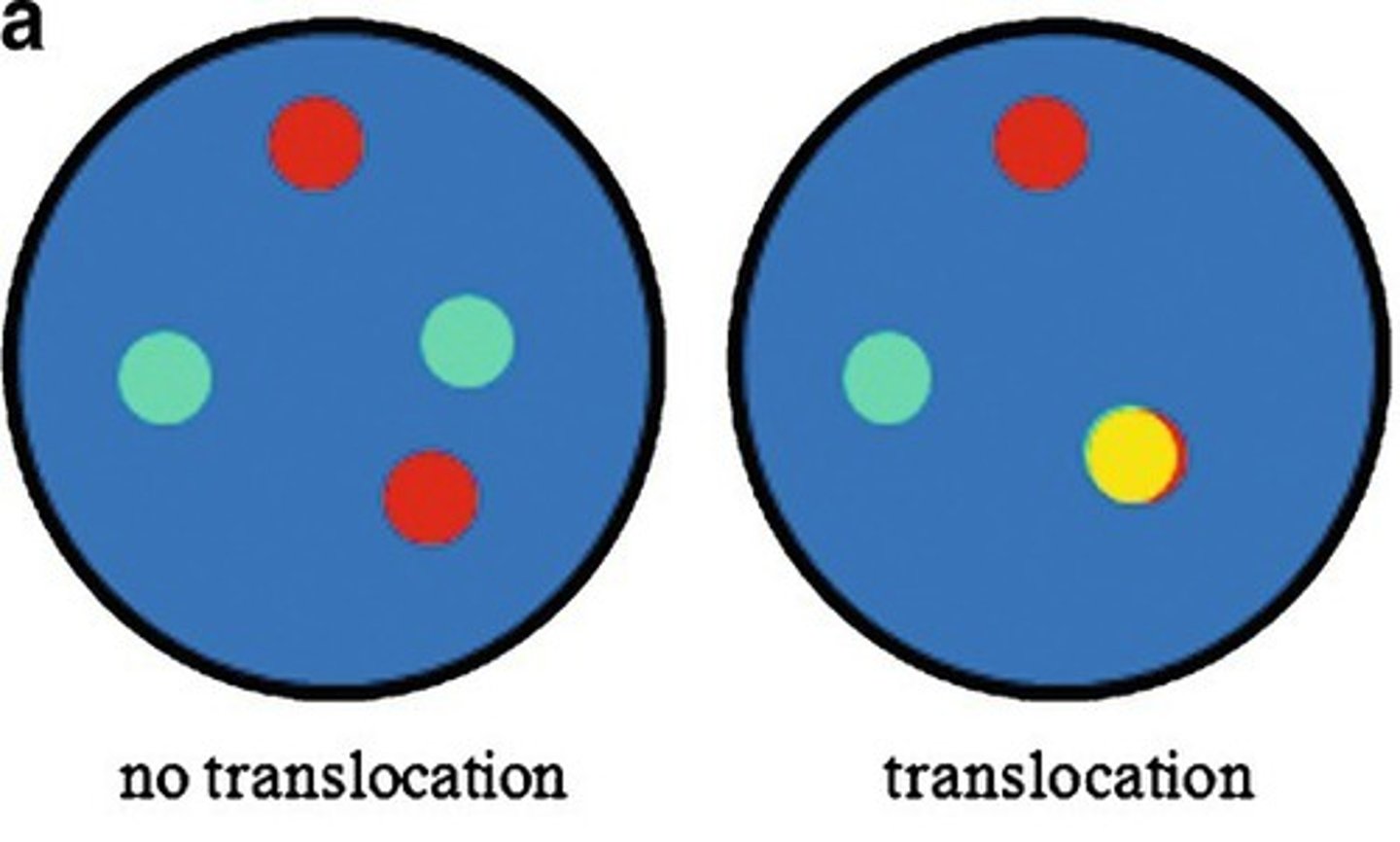
Regarding FISH fusion probes. How would a DUAL COLOR, DUAL FUSION probe look like?
Dual color, dual fusion (2 different colors for the normal genes becomes 2 different colors representing the fusion gene and the derivative gene left behind).
In normal intact cells, two separate red and two separate green individual signals will be visible, whereas a reciprocal translocation will generate two fused red/green signals (often appearing as single yellow signals), accompanied by one red and one green signal (representing the normal chromosomes).
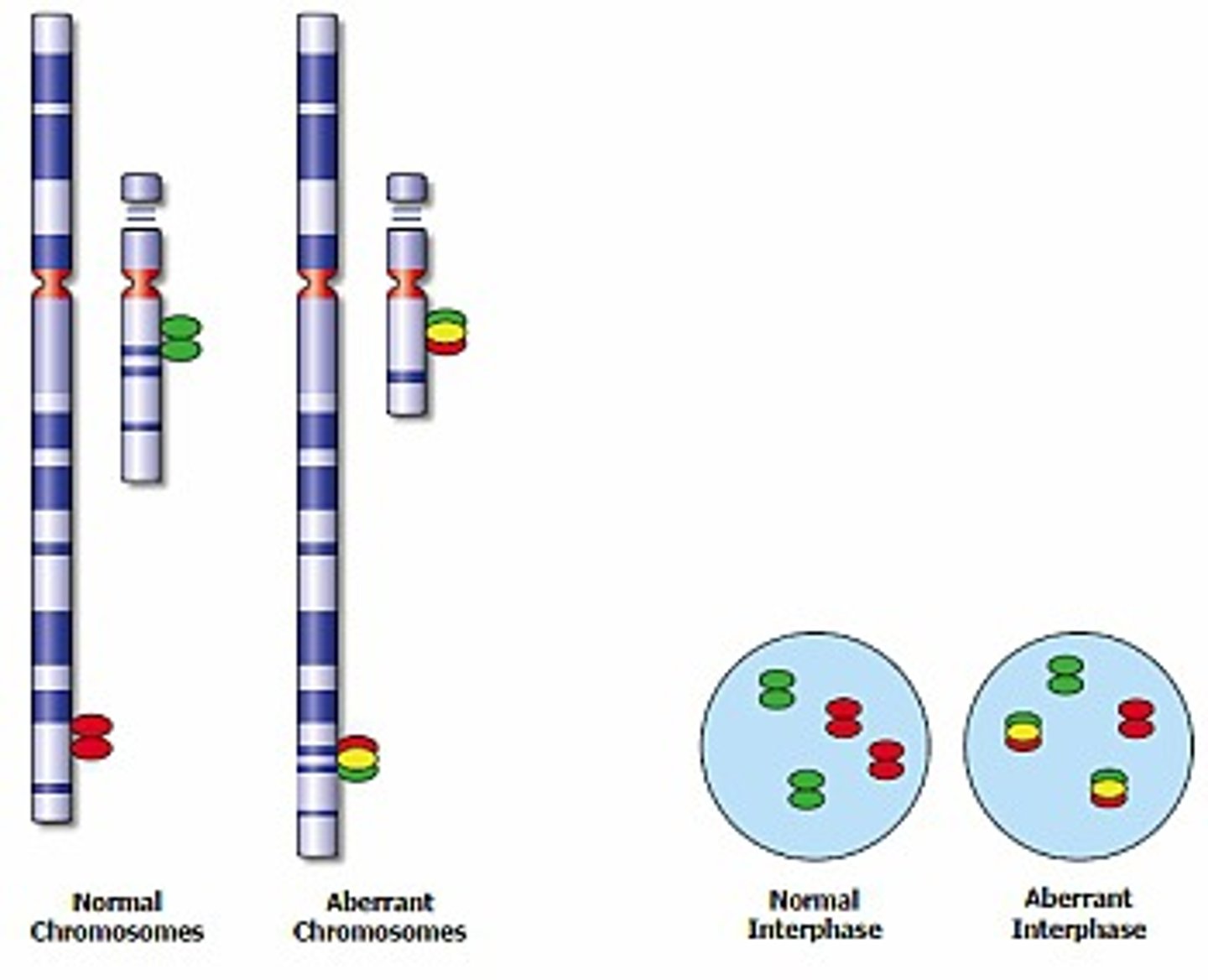
Regarding FISH probes. How would a BREAK APART probe look like?
When would you use it?
With break apart probes a single normal signal is "broken" into 2 separate (separated by space) different colored signals.
It is useful when there is a gene that is more promiscuous and involved in several different translocations.
In normal cells two sets of red/green-fused signals (representing the two alleles) will be visible. In an abnormal diploid cell, in which one allele has been split by a translocation, a separated red and green signal will be visible in addition to the normal fused signal.
What is the principle of Comparative genomic hybridization (CGH)?
CGH is a hybridization technique that provides pan-genomic chromosomal copy number information, providing copy LOSSES and GAINS in chromosomes and subchromosomal regions.
It can determine whether entire chromosome or regions of chromosomes are either amplified or deleted.
What are the most common uses for Comparative genomic hybridization (CGH)?
- Genetic characterization of chromosomal anomalies in developmentally delayed, dysmorphic, or autistic children with no recognized katyotypic abnormalities.
- Characterization of chromosomal gains and losses in cancer cells relative to non cancer cells.
What CANNOT be detected by CGH?
It cannot detect *balanced* *translocations* or any other nonquantitative abnormalities
What does the term ARRAY CGH refers to?
Refers to a similar technique wherein, instead of hybridization to *metaphase* human chromosomes, the differentially labeled probes are hybridized to an array representing the entire human genome or a focal region of interest.
A plot of amplifications and deletions can be precisely mapped to regions of chromosomes
What are SHORT TANDEM REPEATS (STRs)?
Are sequences of DNA that consist of a run of repeat dinucleotides or trinucleotides.
The length (copy number) of these STRs is stably inherited and is normally stable from cell to cell, while different from person to person.
The STR haplotype of an individual is based on _______
The set of chromosomes that they inherit, a copy of one STR allele from each parent.
What is the use of STRs?
- Determine parentage
- For identification of remains for forensic purposes
- For assessment of chimerism in transplant patients
Expansion of STRs within coding sequences is a mechanism of disease in several different conditions, known as ________ such as ________ disease.
Expansion of STRs within coding sequences is a mechanism of disease in several different conditions, known as TRINUCLEOTIDE REPEAT DISORDERS such as Huntington disease.
Different length of STRs in different cells from the same patient is seen in?
Lynch syndrome (anomalies in mismatch repair genes)
What are Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs)?
Are single base pair differences that cause variability in the sequences between individuals.
SNPs are present on average in 1 of every 1000 bases
SNPs usually meet 2 criteria. What are those?
They are present in ≥1% of the population and do not cause disease.
What is referred as the HAPLOTYPE?
The grand total of an individual's SNPs. Certain portions of a haplotype are traceable and useful as a sort of family tree.
T or F
Certain haplotypes are similar within a population
TRUE
They may partially account for the geographic predisposition to certain diseases, traits, or reponses to medications.
What was the goal of the International HapMap project, published in 2009?
Attempt to begin to characterize some of the variation by comparing the haplotypes of certain chromosomes and SNPs between and within widely dispersed populations.
Under CLIA regulations, molecular testing are considered "high complexity". Proficiency testing is available for some of the more common molecular tests. What do molecular laboratories have to do for those tests for which there is no proficiency testing?
Molecular laboratories must implement an alternative plan to verify accuracy at least TWICE annually, in order to be in compliance with CLIA regulations.
One of the limitations of proficiency testing surveys in molecular pathology is:
That the survey material often consists of purified DNA, such that the process of extracting DNA and isolating DNA is not assessed.