BMS 2401 Final Review
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Quiz 7, 8, 9, 10
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Define Agglutination formation
Agglutination forms with the presence of specific antibodies as a response to particulate antigens
Define Precipitin formation
Preciptin forms with the presence of specific antibodies as a response to insoluble, non-particulate host cells
Innate immunity includes which two types of Mechanical barriers
Mucous
Skin
What is immunity or resistance?
A natural or acquired state that protects an organism from certain diseases or infection. The ability to resist disease may be innate (nonspecific) or it may be adaptive (also called aquired, or secific), which the disease state is stimulated in the host.
What is ELISA
The procedure is predicated on the use of an enzyme-linked (labeled) specific antibody to demonstrate the agglutination reaction for the interpretation of the test result.
(T/F) PCR is a laboratory technique for rapidly producing (amplifying) millions to billions of copies of a speciic DNA which can be studied in greater detail
True
(T/F) Molecular techniques can be grouped into three categories: polymerase chase reaction (PCR), hybridization and next-generation sequencing
True
Applications of the PCR technique includes:
DNA cloning for sequencing
Construction of DNA-based phylogenies
DIagnosis and monitoring of genetic disorders
Amplification of ancient DNA
Analysis of genetc fingerprints of DNA profiling
What are the steps involved in PCR
Initation
Denaturation
Annealing
Elongation/Extension
PCR is determined by:
Gel Electrophoresis
What are the distinguishing characteristics of protozoa
Absence of a cell wall
Locomotion
Heterotrophic nutrition
Mostly asexual reproduction
Which protozoa class is parasitic?
Sporozoa
Protozoa of which class possesses long, whip-like flagella used as a means of locomotion?
Mastigophora
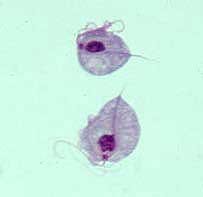
Which type of disease does this parasite (Trichomonas vaginalis) cause?
Trichomoniasis, which is a sexually transmitted disease
Give an example of a parasite that has a simple lifecycle
Entamoeba histolytica
Balantidium coli
Giardia intestinalis
What are the advantages of the API20E strip?
Minimal storage space
Use of less media
Rapid results
Use of a computerized system for identification of organisms
What are the disadvantages of the API20E strip?
High error rate
Limited scope (only identifies Enterobacterieae
One-time use
Which bacteria is gram negative, rod-shaped, mesophillic, non-fastidious, and non-spore formers
Enterobacteriaceae
Which bacteria is not a member of the Enterobacteriaceae family?
Pseudomonas
Which bacteria are a member of the Enterobacteriaceae family?
Enterobacter
Shigella
Klebisella
Name an organism of unknown that was used in lab 10 (API 20E strip)
Salmonella enterica