Intro To Psychology Exam 2
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
8 Steps to Scientific Method
ask a question
do background research
form a hypothesis
design study/test hypothesis
analyze data
draw conclusion
communicate results
refine/replicate
2 innate fears
loud noises
falling
Instinct vs Reflex
Instinct - behaviors triggered by broader range of events (aging or change of seasons) — bigger — spider spinning web
Reflex - motor/neural reactions to a specific stimulus (knee-jerk or pupils contracting) — smaller
perception vs sensation
Perception : way that sensory information is interpreted and consciously experienced — interpreting visual information
Sensation : what happens when sensory information is detected by a sensory receptor — just visual
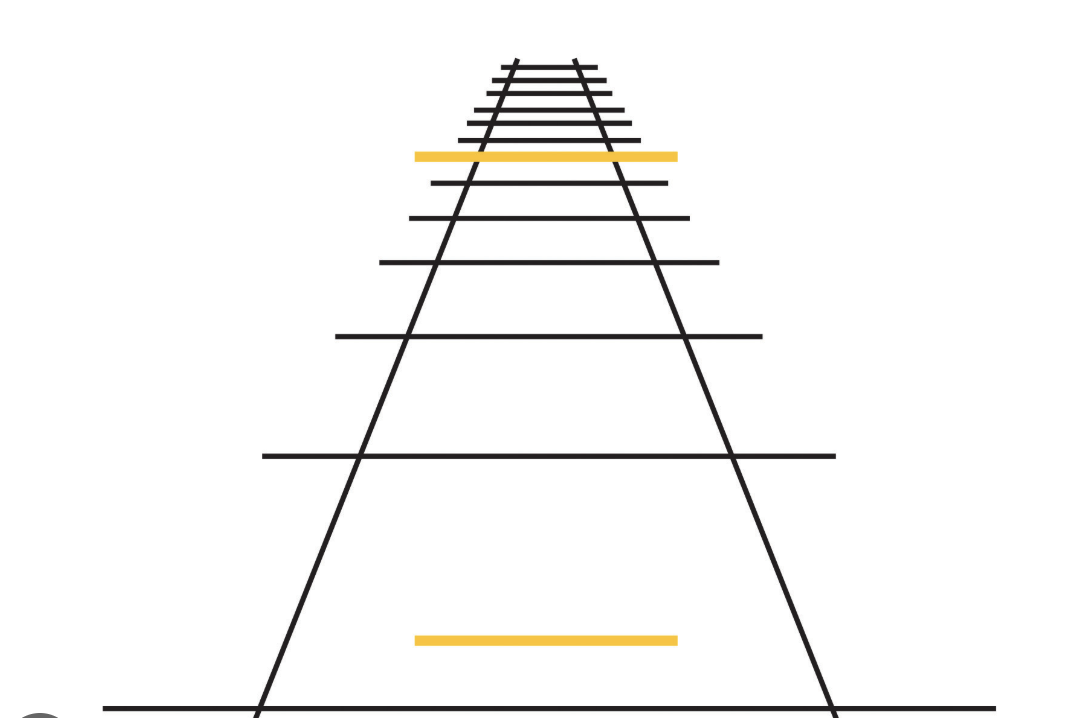
Gestalts Image
perception and sensation?
sensation - seeing the lines
perception - seeing a railroad
absolute threshold
the minimum amount of stimulus energy that must be present for the stimulus to be detected 50% of the time
the eye can detect a candle flame from 30 miles away half the time
difference threshold
difference in stimuli required to detect a difference between the stimuli
seeing a phone light up in a dark room vs a lighten room — the difference in how bright the phone screen appears
sensory adaption
not receiving stimuli thats remained relatively constant over prolonged periods of time
stop noticing a beeping sound over time
perceptual hypothesis
educated guess used to interpret sensory information
airport security spotting weapons based off training
operant conditioning schedules
fixed interval
variable interval
fixed ratio
variable ratio
fixed interval
reinforcement is delivered at predictable time periods (5,10,15,20 minutes)
variable interval
reinforcement is delivered at unpredictable time intervals (5, 7, 10 20 minutes)
fixed ratio
reinforcement is delivered after predictable number of responses (after 2, 4, 6, 8 responses)
variable ratio
reinforcements are delivered after unpredictable number of responses (after 1, 4, 5, 9 responses)
thinking vs cognition vs intelligence
cognition is acquiring and using knowledge (learning a friend’s phone number)
thinking is manipulating the information and forming concepts from it (problem solving, language, memory)
intelligence is the overall capacity to learn / dependent on persons potential (adjusting to new technology quickly easy for some harder for others)
operant conditioning vs classical condition vs observational learning
operant conditioning - organisms learn to associate behavior to its consequence (being spanked after cursing) (stimulus soon after)
classical conditioning - learning to associate stimuli and consequently anticipate events (dogs salivating to sound of bell, rang bell and fed dog (can’t control its own salivation it is a reflex)) (stimulus before)
observational learning - learn by watching others and the imitating or modeling what they do or say
stimulus discrimination
when an organism learns to respond differently to various stimuli that are similar
(cat running when they hear the can manually opened, but not recognizing electric can opener)
stimulus generalization
when an organism demonstrates the conditioned responded to stimuli that are similar to the conditioned stimulus
(cat running to both the electric can opener and the manual can sound because they are similar enough to one another)
spontaneous recovery
the return of a previously extinguished conditioned response following a rest period (manual food opener — electric — manual — the cat will re-learn the manual food opener sound much quicker the second time around)
Extinction
the decrease in the conditioned response when the unconditioned stimulus is no longer presented with the conditioned stimulus (when the pairing of cat food to opener is haulted the cat stops coming in for cat food when they hear the noise)
schema
mental construct consisting of a cluster or collection of related concepts
role schema
makes assumptions of how individuals in certain roles will behave
firefighters as brave
event schema
set of behaviors that can feel like a routine
walking into elevator, click button, wait, doors open, walk out
What impacts perception?
1. sensory adaption (not perceiving stimuli that remains relatively constant over time)
2. attention
inattention blindness — failure to notice something because you’re inattentive
3. motivation (having a bias)
signal detection theory — change in stimulus detection as a change in mental state
4. beliefs, values, prejudices, and expectations (social media, looking for balance)
5. life/cultural experiences
reflective thinking
recapping on your own thoughts/experiences
critical thinking
the active application of a set of skills to information for the understanding and evaluation of that information.
creative thinking
coming up with unique and novel ideas
divergent thinking
ability to think “outside the box” (all the options) to arrive at novel solutions to a problem
convergent thinking
providing correct or established answer to the problem, one right answer (2+3=5)
connection between language and intelligence
intelligence being the capacity one has for knowledge, we learn how intelligent other are from their communication to us with language. Had they not had the ability to use language, like reading, writing, speaking etc. we would not be able to test the capacity of their intelligence
conditioned stimuli
previously neutral stimulus that after being repeatedly paired with unconditioned stimuli has been triggered to learn a response
sound of bell that makes dog salivate
unconditioned stimulus
stimulus that naturally and automatically triggers a response without any prior learning
dog food
conditioned response
learned response to the previously neutral stimulus
dog salivating after hearing bell
unconditioned response
the natural, unlearned reaction that occurs in response to the unconditioned stimulus
dog salivating seeing food
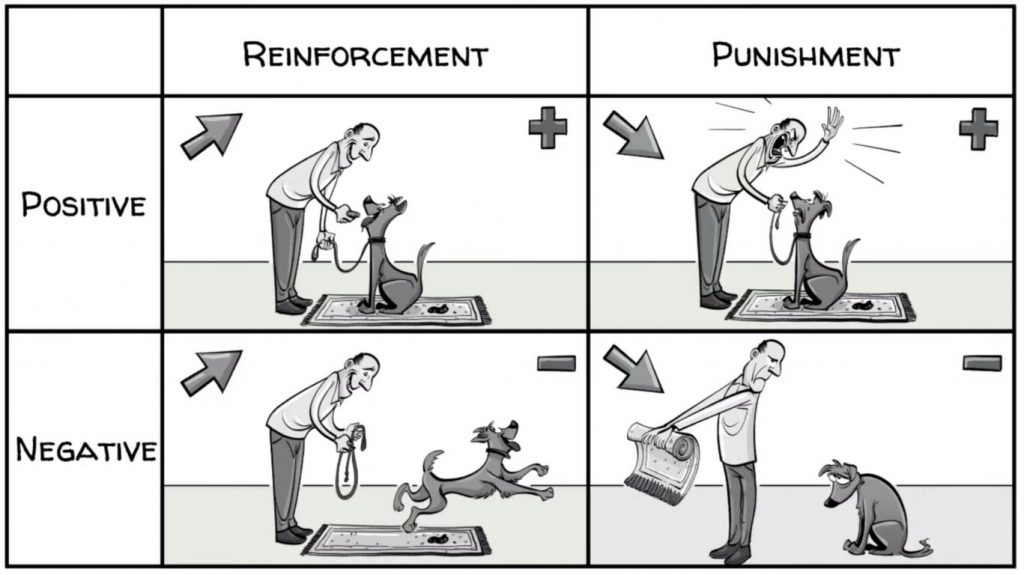
Operant conditioning
organisms learn to associate a behavior with its consequence
shaping
rewarding successive approximations toward target behavior
primary reinforcers
has innate reinforcing qualities (food, sex, water, shelter etc)
secondary reinforcers
has no inherent value, only has quality when paired with something else (money, gold stars, poker chips)
Banderas Four Steps
Pay Attention
Retain/Remember
Repeat
Motivate
How is motivation influenced by punishment or reinforcement?
Social learning theory, if watching the adult be punished for their behavior, the child is less likely to repeat behavior. Though if the adult is rewarded, the child is likely to repeat behavior in hopes for reward.
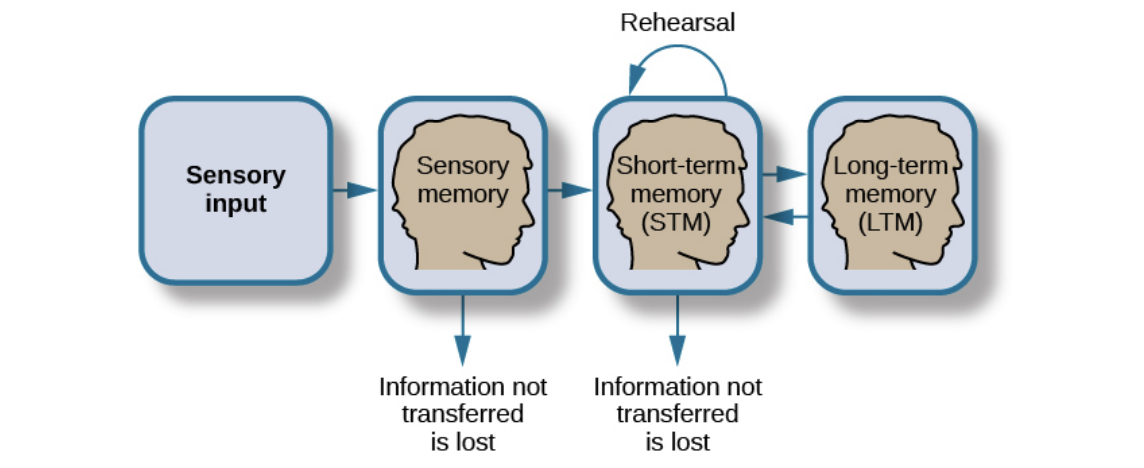
working memory
sensory memory
short-term memory
long-term memory
working memory
“real-time processing” when being given information, not all of it is stored because there is limited information processed to go to short/long term memory files
sensory memory
storage of brief sensory events (including working memories) depends on type of information received
sights, sounds, tastes
short-term memory (STM)
temporary storage system that processes incoming sensory memory
long-term memory (LTM)
how to retrieve long-term memories
recall
recognition
relearning
recall
accessing information without cues (essay test)
recognition
identifying previously learned information after encountering it again, typically after a cue (multiple choice question, choosing the one that looks most recognizable)
relearning
learning information that was previously learned (relearning a language)
heuristics
general problem solving framework “rule of thumb” “my sister went to Saint Mary’s so I will too” choosing the familiar