Human Health
1/42
Earn XP
Description and Tags
APES
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
LD50
refers to the dose or concentration of the chemical that kills 50% of the population being studied
LD50 measurement in (units)
mass (g. mg)/body unit mass (kg)
ppm - parts per million (in air)
Response Studies
studies that expose an organism to different doses of concentrations of a chemical in order to measure the response (effect) of the organism
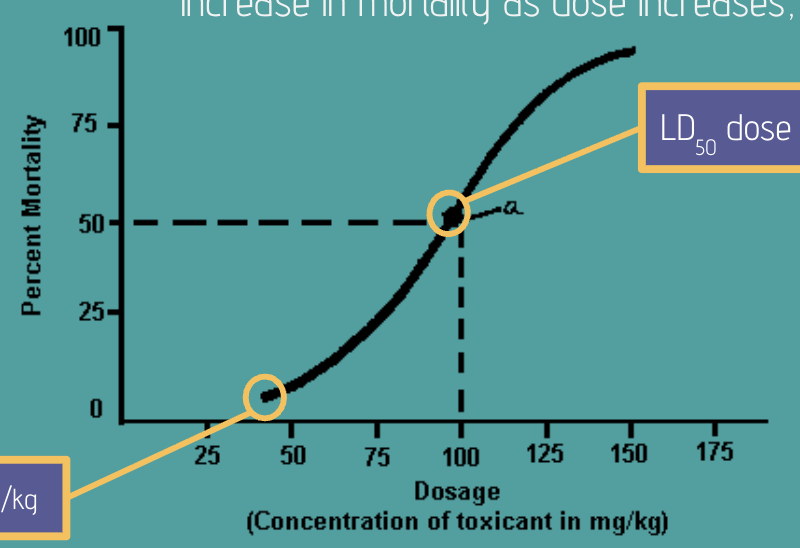
Dose Response Curve
data from a dose response study, graphed with percent mortality or other effect on the y-axis and dose concentration of chemical on x-axis
Threshold or toxicity threshold
lowest dose where an effect (death, paralysis, cancer) starts to occur
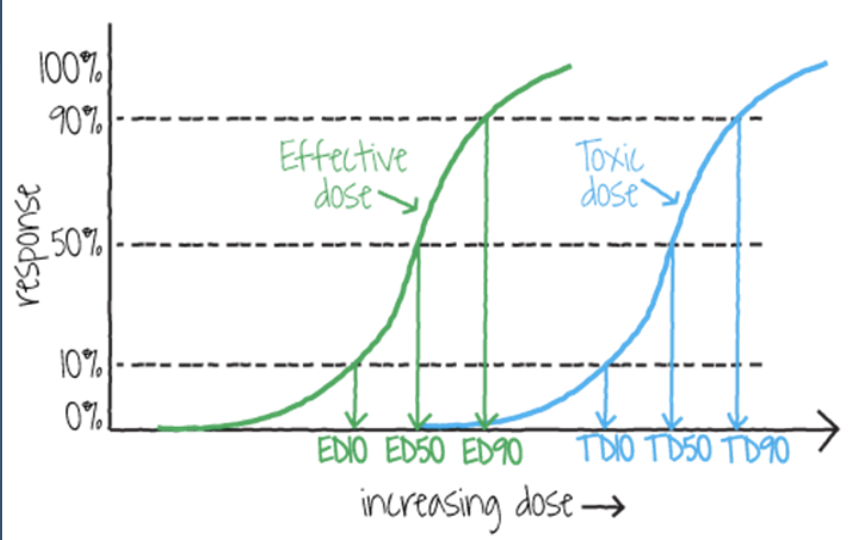
ED50
the dose of concentration of a toxin or chemical that causes a non-lethal effect (infertility, cancer, paralysis, etc) in 50% of the population being tested
What are dose response data done on?
data from other mammals (mice, rats)
used to simulate human toxicity
to determine maximum allowable levels for humans, divide LD50 or ED50 dose concentration by 1,000 (for extreme caution)
Acute Studies
only measure effects over a short period of time
lab isolated
don’t measure ecological effects of organisms dying
most dose response studies are acute
Chronic Studies
longer-term and follows developmental impacts
Endocrine Distruptors Def.
chemicals that interfere with the endocrine (hormonal) systems of animals
bind to cellular receptors ment for hormones, blocking the hormone from being received
What is a common source of endocrine disruptors in the environment?
human medication flushed down the toilet
Endocrine Disruptors
Atrazine
DDT
Phthalates
Lead, arsenic, mercury
Human medications
Mercury
naturally occurring in coal, released by anthropogenic activities
coal combustion, trash incineration, burning medical waste, heating limestone for cement
attaches to PM released by burning & deposits in soil.water wherever PM settles
can be released if coal ash stored in ponds overflow & runoff
endocrine disruptor - inhibits estrogen & insulin
Teratogen - chemical harmful to developing, can accumulate in fetus brain
Arsenic
naturally occurring element in rocks underground that can dissolve into drinking water; natural release into groundwater can be worsening by mining
Anthro sources - formerly in pesticides applied to ag fields, lingers in soil, wood treatment, coal combustion
Carcinogenic - (lungs, bladder, kidneys) & endocrine disruptor
Endocrine disruptor - specifically glucocorticoid system (can be removed with water filters)
Lead
found in old paint (in homes), old water pipes, and soil contaminated by PM from vehicle exhaust (in 70s)
released in fly ash (PM) of coal combustion
neurotoxicant (Damages central nervous system, esp. in children)
endocrine disruptor
Can be removed with water filters
Coal Ash
source of mercury, lead, and arsenic
attaches to fly ash (PM) from smokestack and be carried by wind, deposited in ecosystems far away
both fly and bottom coal ash are often stored on site. in ponds, dug into soil & lined with plastic
ponds can leach into groundwater, contaminating it with arsenic, lead, mercury
ponds can overflow & runoff into nearby surface waters & agricultural fields
can be converted to methylmercury by bacteria
Routes of Exposure
ways that a pollutant enters the human body
lead —> water pipes & paint drops
mercury —> seafood (tuna)
CO —> indoor biomass
PM —> pollen, dust, etc
Arsenic —> rice, groundwater
Synergism
interaction of two or more substances to cause an effect greater than each of them individually
ex. asthma caused by PM from coal PPs and COVID-19 damaging lungs
Dysentery
bacterial infection caused by food or water being contaminated with feces (often from sewage release into rivers & streams used for drinking water)
causes very severe dehydration due to diarrhea
poor sanitation & unfiltered waters
Mesothelioma (Asbestos)
a type of cancerous tumor caused by exposure to asbestos, primarily affecting the lining of the respiratory tract, heart or abdominal cavity
exposure comes primarily from old insulation materials used in attics, ceiling, and flooring boards. when the insulation becomes physically disturbed, asbestos particles are released into the air & inhaled
must be professional removed
Tropospheric Ozone (O3)
worsens respiratory conditions like asthma
limits overall lung function
irritates muscles or resp. tract causing constriction of airways & shortness of breath
worsens the respiratory conditions like asthma, bronchitis, and emphysema
only harmful in troposphere (beneficial in stratosphere)
Pathogens
living organism (virus, bacteria, fungus, protist, worm) that causes an infectious disease
capable of being spread of transmitted
noninfectious diseases are not transmissible
pathogens adapt and evolve to take advantage of humans as hosts for their reproduction and spread
Vectors
a living organism (rats, mosquitos) that carry and transmit infection pathogens to other organisms
climate change is shifting equatorial climate zoners north and south away from the equator, this brings warmer temps to subtropical and temp regions —> allows pathogens and their vectors to spread north & south to parts of the world previously too close
Infectious Disease & Development
less developed, poor countries typically have higher rates of infectious disease
less sanitation
less access to healthcare
lack of treatment/filtration
tropical climates & more open air living can expose to vectors
Plague
bacterial (pathogen) infection transmitted by fleas (vector) that attach to mice & rats
transmitted by bite, rodent contact or contaminated human fluids
Tuberculosis (TB)
bacterial (pathogen) infection that targets the lungs
transmitted by breathing bacteria from body fluids of an infected person (can linger in air for hours)
causes night sweats, fever, coughing blood ; treatable in developed nations with access to powerful antibiotics
Malaria
parasotic protist (pathogen) infection caused by bite from infected mosquitos
most comm in in sub-Saharan Africa and other tropical regions
West Nile
virus (pathogen) infection caused by bite from infected mosquitos
birds are main host, but the virus can be transmitted to humans by mosquitoes that bite infected bird and then bite humans
Zika Virus
virus (pathogen) infection caused by bite from infected mosquitos & sexual contact
causes babies to be born with abnormally small heads and damaged brains (can be passed down)
SARS (Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome)
coronavirus (pathogen) infection caused by respiratory droplets from infected person
primarily transmitted by touching or inhaling fluids from an infected person
causes form of pneumonia
MERS (Middle East Respiratory System)
Virus (pathogen) respiratory infection transmitted from animals to humans
Cholera
bacterial(pathogen) infection caused by drinking infected water
vomiting, muscle cramps and diarrhea
severe dehydration
Developing Countries
use more subsistence fuels such as wood, manure, charcoal (biomass)
biomass fuels release CO, PM, NO, VOCs
Developed Countries
use more commercial fuels (coal, oil, natural gas) supplied by utilities
typically burned in closed, well ventilated furnaces, stoves
major indoor air pollutants in developed nations come from chemicals in products: adhesive in furniture, cleaning supplies, insulation lead paint
Particulate Matter (PM) Asbestos
PM are a common indoor air pollutant
ex. smoke from indoor biomass and dust and asbestos
absestos is a long, silicate particle previously used in insulation
CO (Carbon Monoxide)
CO is produced by incomplete combustion of basically any fuel
CO is an asphyxiant: causes suffocation due to CO binding to hemoglobin in blood, displacing O2
developed nations: CO released into home by malfunctioning natural gas furnace ventilation
developing nations: CO emitted from indoor biomass combustion for heating/cooking
VOCS (volatile organic compounds)
chemicals used in variety of home products that easily vaporize, enter air, and irritate eyes, lungs, bronchioles
ex. adhesives/sealants, cleaners, plastics and fabrics
(formaldehyde - common adhesive in boards carpets, manufactured things)
Radon Gas
radioactive gas released by decay of uranium naturally found in rocks underground (granite)
usually enters homes through cracks in the foundation & then disperses up from basement/foundation through home
also seeps into groundwater sources
causes lung cancer
Dust & Mold
natural indoor air pollutants that can worsen asthma, bronchitis, COPD, emphysema
Dust: settles in homes naturally, entering air and then respiratory tract
Mold: develops in areas that are dark and damp and not well ventilated
Lead
Found in paint in old homes
lead water pipes also release lead into drinking water sources (as in flint)
damages central nervous system of children due to smaller size and still developing brain
Urban noise pollution
any noise at great enough volume to cause physiological stress (difficulty communicating, headaches, confusion) or hearing loss
ex. construction (jack hammers) transportation (cars), industrial activity (manufacturing plants) , domestic activity (lawn mowing)
Wildlife effects (land)
noise pollution can disrupt animal communication, migration, and damage hearing
physiological stress
hearing: prevent predators from hearing prey and vice versa ; prevent mates from locating each other, decreasing survival chances
Wildlife effects (aquatic)
Aquatic noise pollution comes from the noise of ship engines, military sonar, and seismic air blasts from oil & gas surveying ships
physiological stress: hearing loss, disruption communication
seismic surveying: ships send huge air blasts into water