mcb small things to remember
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Nirenberg and Leder
genetic code and codons
pol 1 transcribles
rRNA
pol 2 transcribles
mRNA
pol 3 transcribes
tRN
eukaryote initiation of transcription
no sigma factor in RNAP, transcription factors
bacteria initiation of transcription
sigma factor binds to promoter on DNA directly
-10 consensus sequence
TATAAT
-35 consensus sequence
TTGACA
how many subunits in RNAP II/holoenzyme
6
which subunit in holoenzyme is special
σ
one gene/one enzyme modifications
info to make all proteins is in genes, and many proteins are not enzymes
some proteins = 2 or more polypeptides
some mRNA can make 2+ polypeptides
some genes produce non-coding RNA
Beadle and Tatum
bread mold and mutations, discovered one gene/one enzyme
Archibald Garrod
inheriting a mutated gene is correlated with defect in metabolism
R Kornberg
chromatin in the nucleus looks like beads on a string
a cell has lots of chromatin and no nucleolous, it is in __
m-phase
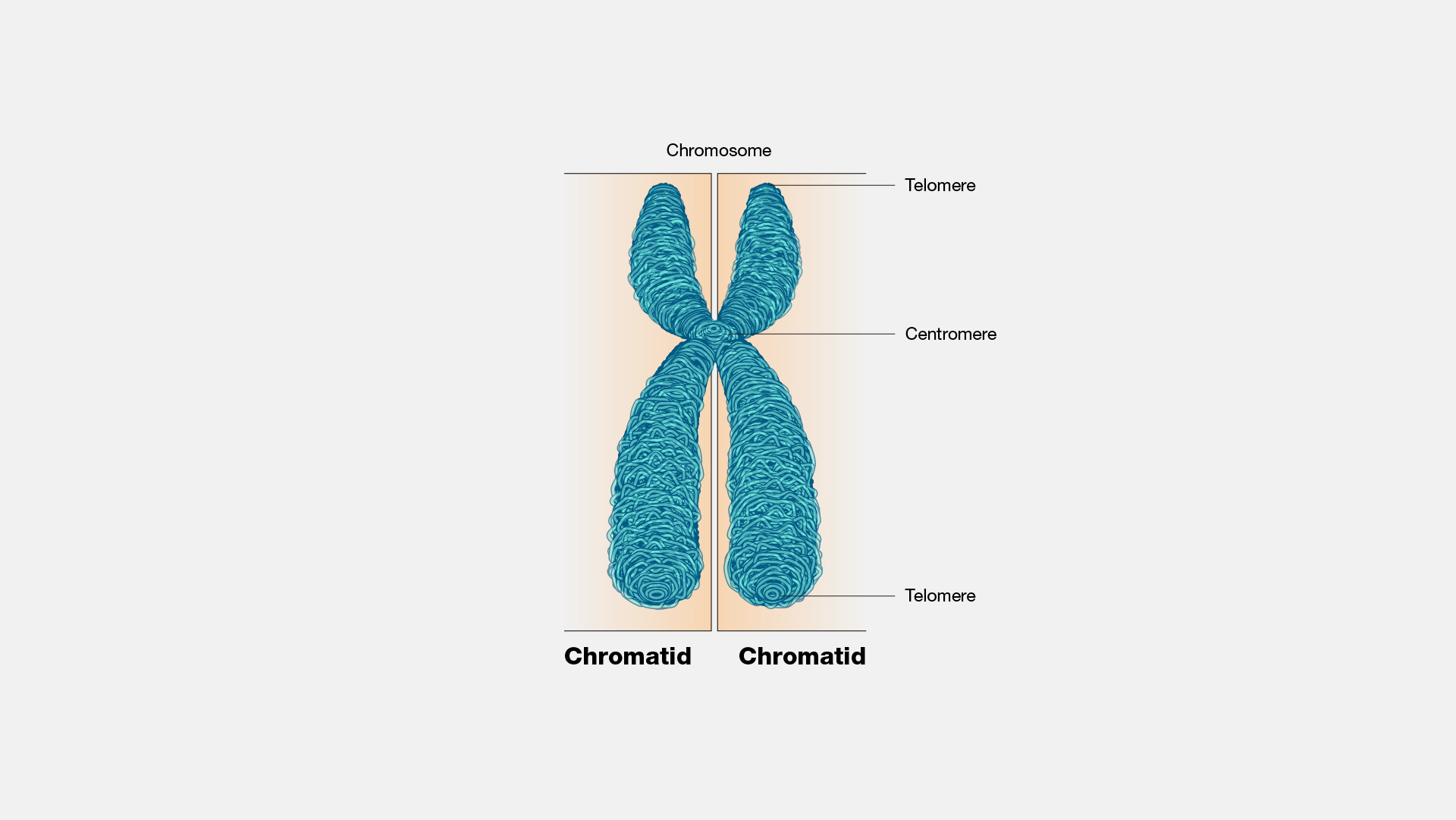
what phase is this chromosome
m phase
m phase chromatin
heterochromatin, tight
interphase chromatin
euchromatin, loose (30-nm)
telomerase
extends DNA strand, solves end replication problem
DNA ligase
seals nicks
DNA pol 1
removes primer and fills in RNA primer gap
RNA primer
creates RNA start of Okazaki fragment
nucleosome
8 histones, 146 base pairs (doesn’t have H1)
num of histone proteins
5
__ dont have histones
bacteria
nucleosome + H1
chromatosome (has 166 base pairs)
solenoid
chromatin model that is see through
zig zag
chromatin model that is not see through
what does supercoiling in bacteria?
topoisomerases
fix end replication with
telomerase (RNA dependent, DNA synthesizing)
steps of end replication
telomerase extends, primase makes RNA tail, polymerase puts down new DNA and nothing is cut off
Horowitz and Woodcock
zigzag model of nucleosomes
proofreading
3’ to 5’ exonuclease activity
why is DNA replication so accurate
A-T and G-C bonding is strong
DNA pol unlikely to catalyze mismatched bases
can proofread
Glycolysis (input of 1 glucose and 2 ATP)
2 Pyruvate + 2 NADH + 2 net ATP
Pyruvate oxidation (2 pyruvate)
2 Acetyl-CoA + 2 NADH + 2 CO₂
Citric acid cycle (2 acetyl-coA)
4 CO₂ + 6 NADH + 2 FADH₂ + 2 ATP
oxidative phosphorylation/ETC (uses NADH and FADH2)
H₂O + 32 ATP, regenerated NAD⁺ and FAD
MCB number of ATP produced from 1 glucose
36
transcription reads
3’ to 5’