module 4
1/25
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Memory in Embedded Systems
Read-Only Memory (ROM)
Random Access Memory (RAM)
Memory According to the Type of Interface
Memory Shadowing
Memory Selection for Embedded Systems
ROM
Read-Only Memory
Read-Only Memory (ROM)
a non-volatile type of memory commonly used in embedded systems.
data stored in ROM cannot be modified or erased once it is programmed during manufacturing.
is a type of memory that retains its contents even when the power is turned off
used to store firmware, boot loaders, and system configuration data that are essential for the functioning of an embedded system
is often referred to as "non-volatile" because it retains data without the need for a continuous power supply.
The data stored in ___ is non-erasable and non-modifiable, making it ideal for storing critical system information
Types of ROM
Mask ROM
PROM (Programmable Read-Only Memory)
EPROM (Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory)
EEPROM (Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory)
Flash Memory
Mask ROM
This type of ROM is manufactured with a fixed pattern during the chip fabrication process. The data is permanently embedded in the ROM, and it cannot be changed or updated
PROM (Programmable ROM)
allows users to program the memory once by using special programming equipment. Once programmed, the data becomes permanent and cannot be altered
EPROM (Erasable Programmable ROM)
is similar to PROM but can be erased and reprogrammed using ultraviolet light exposure. It requires a special erasing device to remove the existing data before reprogramming.
EEPROM (Electrically Erasable Programmable ROM)
can be electrically erased and reprogrammed using specific voltage levels. Unlike EPROM, it does not require UV light for erasing and is more convenient for in circuit updates.
Flash Memory
is a type of EEPROM that allows multiple-byte erasure. Widely used in embedded systems due to its high density, fast erasure, and reprogramming capabilities
Most embedded systems, such as microcontrollers (e.g., Arduino), use _____________ to store sketches.
retains its contents without power and can be electrically erased and reprogrammed.

Applications of ROM
Firmware Storage
Boot Loaders
System Configuration Data
Limitations
it cannot be modified or updated once programmed
higher manufacturing costs
require upfront design decisions
RAM
Random Access Memory
Random Access Memory (RAM) Definition and Characteristics
Volatile memory
Allows read and write operations
Examples: Static RAM (SRAM), Dynamic RAM (DRAM)
Random Access Memory (RAM) Applications and Limitations
Storing program code, data, and variables during runtime
Faster access but larger in size compared to ROM
Random Access Memory (RAM)
is a type of volatile memory commonly used in embedded systems. It is called "random access" because it allows for both read and write operations, and data can be accessed in any order, unlike sequential access memory.
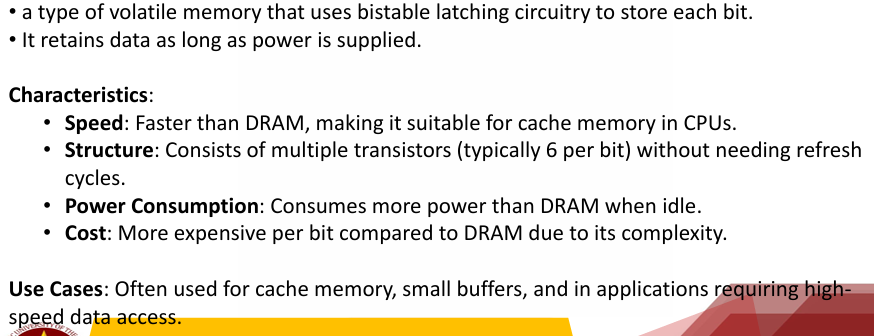
Static RAM (SRAM)
Fast, more expensive, used for small, high-speed applications.
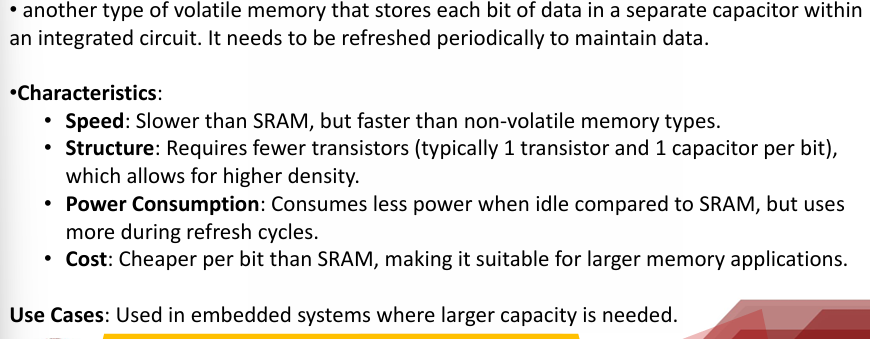
Dynamic RAM (DRAM)
Slower, cheaper, used for larger memory needs.
Parallel Memory Interfaces
_______________ allow multiple bits of data to be transmitted simultaneously. This type of memory is typically faster due to the simultaneous transfer of data bits.

Serial Memory Interfaces
_____________________ transmit data one bit at a time, which can lead to lower complexity and reduced pin count.

Memory-Mapped Interfaces
In embedded systems, certain memory types can be accessed as part of the system's address space
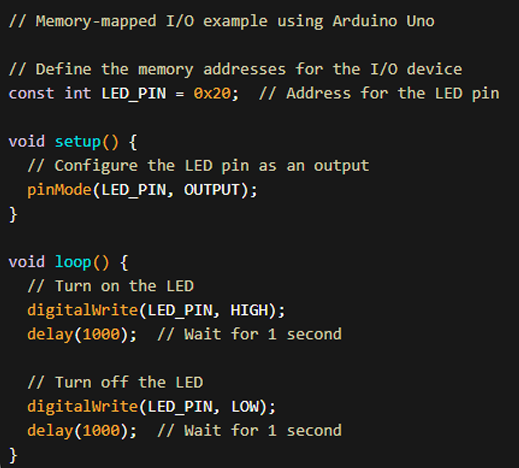
a method of interfacing hardware devices with a microcontroller through memory addresses.
Specific memory addresses in the system’s address space are allocated for hardware devices, allowing them to be accessed like regular memory locations. Hardware devices (like sensors) are assigned specific addresses within the main memory range.
This means that the CPU can read from or write to these devices using standard memory operations.

Direct Memory Access (DMA)
_______ allows peripherals to access memory without CPU intervention, optimizing data transfer rates:
Characteristics: Reduces CPU load and improves system performance. Commonly used in applications requiring high-speed data transfer, like audio and video processing.
Memory-Mapped I/O
Memory Shadowing
is a technique used to improve performance and reliability by creating a duplicate or "shadow" copy of a section of memory.
- Duplicating critical data or program code in a secondary memory space.
- Purpose is to ensure that the system can continue to operate correctly even in the event of a fault or error in the primary memory.

Key Characteristics of Memory Shadowing
Redundancy
Performance Improvement
Error Detection and Recovery
Common Factors for Selecting Memory in Embedded Systems
Type of Memory
Performance Requirements
Capacity Needs
Power Consumption
Cost
Reliability and Durability
Interface Compatibility
Data Retention
Size and Form Factor
Availability and Support
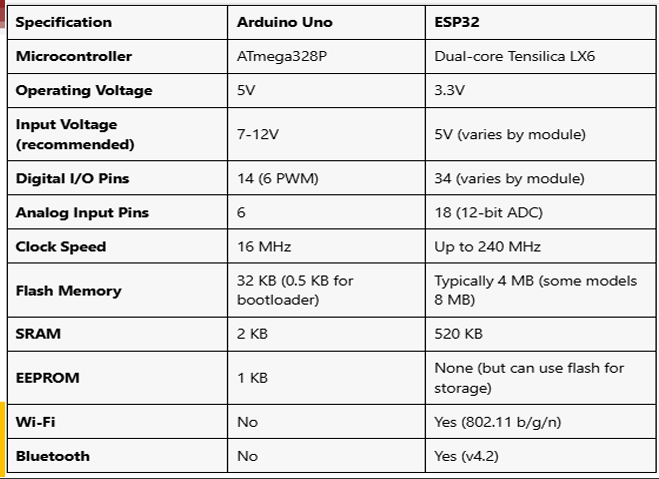
Comparison of ESP32 and Arduino Uno