MKTG 371 SDSU Sharma Final
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
what is a need?
a discrepancy between someones actual state and their ideal or desired state
What are the 5 properties of needs?
1. dynamic
2. exist in hierarchy
3. can conflict
4. can be internally or externally aroused
5. can be influenced
What do marketers care about needs?
1. that they can be identified or discovered
2. that they can be influenced and triggered
What factors affect need awareness?
1. internal influences
2. external influences
3. social influences
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
-physiological
-safety
-love/belonging
-esteem
-self-actualization
Motivation Definition:
inner state of arousal directed toward achieving a goal; may vary in strength
What do motives affect?
- attention, information search, perception
- attitudes
- behaviors
Core Social Motives (BUCKET)
B: belonging
U: understanding
C: control
K: -
E: self-enhancement
T: trust
What is the fundamental motive that drives behavior?
The need to belong
Values Definition
enduring beliefs that guide what behavior or outcomes are desirable or good
What is the main tool we use for values?
VALS - psychographic tool that measures demographics, values, attitudes, and lifestyle variables
-used to identify potential target markets and learn to communicate with them more effectively
- based on customers resources and self orientations
techniques to gather info about needs, motives, and values
- observational research
- laddering
- surveys
- experiments
- many others
What are the key dimensions in the VALS framework?
1. tendency to consumer primary motivation
2. ideals, achievement, self-expression
What phase are interviews good for?
exploratory research phase
What phase are surveys good for?
Descriptive Data
How can marketers "create" or "trigger" needs?
moving up perceived desired state or moving down perceived actual state
Influencing perceived needs: Pain vs. Pleasure
- gain pleasure: link product/brand with desired end result
- avoid pain: your product/brand as the weapon to prevent undesirable states
Qualitative work:
provides rich thought and feelings
Quantitative work:
allows for testable hypothesis and percriptions
T or F: Qualitative comes BEFORE quantitative
True
How do marketers create triggers?
by focusing on benefits or pain aversion
How do people evaluate options?
1. Rational Agent neo-classical economics
2. Bounded rationality behavioral decision theory
what is the rational Agent model of neo-classical economics? (Thorstein Veblen)
- know what they want
- time consistent
- NO capacity restraints
- They MAXIMIZE
- choose product that best matches their (stable) preferences
What is the Behavioral Decision theory? (Herbert Simon)
- capacity restraints
- not always consistent
- operating within bounds
- these people SATISFICE
- inconsistent, ineffective, and often require help to make decisions
Rational agent model- Neoclassical
People will maximize—always choose the product that best matches their (stable) preferences
bounded rationality - behavioral decision theory
people will satisfice - they are inconsistent, ineffective, and often require help making choices
(evaluation of options stage) "evoked set" or "considered set"
AKA consideration set (top of mind) small relative to the total number of options available
(evaluation of options stage) "extended problem solving"
- higher involvement
- generally used when getting infrequently purchased, expensive, high risk or new goods or services
"routine problem solving"
- low involvement
- inexpensive and has limited risk if purchased
We search and evaluate based on:
- internal searches (memory, knowledge, personal experiences)
- social/external searches: word of mouth, public sources
Homo economics:
- infinitely sensitive, incredibly smart
- maximizes across all decisions
asocial and greedy, pursues wealth
homo sapiens:
- limited processing capacity: memory, attention, will
- satisfices: aims for "acceptable" performance
- has social concerns, positive and negative
Reflective System (system 2)
- slow, effortful
- rule-governed
- serial, needs to be learned
- deliberately controlled
- easy to modify

Reflexive System (system 1)
- fast
- automatic
- effortless
- associative
- difficult to modify
How do the two brain systems interact ?
there is a part of the mind or brain that takes the quick, instinctive thoughts generated by System 1 and processes or edits them before they become fully formed actions or decisions.
Heuristics:
Rules of Thumb (short cuts) to simplify judgements and decisions
Biases:
when judgements deviate systematically from what is considered optimal or appropriate
representativeness hieristic:
When we judge the probability that an object or event A belongs to class B by looking at the degree to which A resembles B (CORRELATION DOESN'T EQUAL CAUSATION)
availability heuristic
top of mind or things that come to mind first from past experiences
form level:
exact substitute for the product
ex: Apple iPhone, android smartphone
category level:
same category of product
ex: dominos pizza - to any fast food or other pizza place
need level:
satisfies basic need
ex: car - need of transportation
Market Analysis 3Cs
- customer
- company
- competition
strategic: STP
- segmentation
- targeting
- positioning
Tactical decisions (action plan ) 4Ps
- product
- promotion
- price
- place
WISE framework for consumer behavior
internal, social and external factors at the decision making stage
information processing includes
cognitive vs. emotions
product categories are
higher vs. lower involvement
decision strategy includes
optimizing vs. satisfying
Decision strategy 2
compensatory vs. non compensatory
compensatory
think tradeoffs - okay fine ill pay more for better quality
non compensatory
not willing to make any tradeoffs or substitutes
secondary data
- lower cost, available immediately
- hidden assumptions/agendas
- may answer slightly different questions
- no competitive advantage
primary data
1. exploratory research
2. descriptive research
3. experiments
what order should you conduct primary research?
1. Exploratory research
2. Descriptive research
3. Experimental research
Primary data: exploratory
explore broad, early stage objective and questions (uses small sample size)
Primary data: descriptive
investigate more precise better defined questions
Primary data: experiments
establish cause and effect relationships
leading question: why do you like Wendy's fresh meat better than those of competitors
what's wrong: customer is led to make statements already favoring Wendy's burgers
ambiguous question: do you eat fast food restaurants regularly? Yes? No?
what's wrong: what is meant by the word regularly? once a day, month, year?
unanswerable question: what was the occasion for you eating your first hamburger?
what's wrong: who can remember the answer? assume that they have even tried a burger before
two questions in one example: do you eat Wendy's hamburgers and chili? Yes? No?
how do you answer you eat their burgers but not their chili
non exhaustive question example: where do you live? Dorm? at home?
what's wrong: what do you check if you live in an apartment or other type of living?
non mutually exclusive answers example: what is your age? Under 20? 20-40? 40 and over?
what's wrong: what answer does a 40 year old check?
WISE FRAMEWORK
- watch
- internal
- social
- external
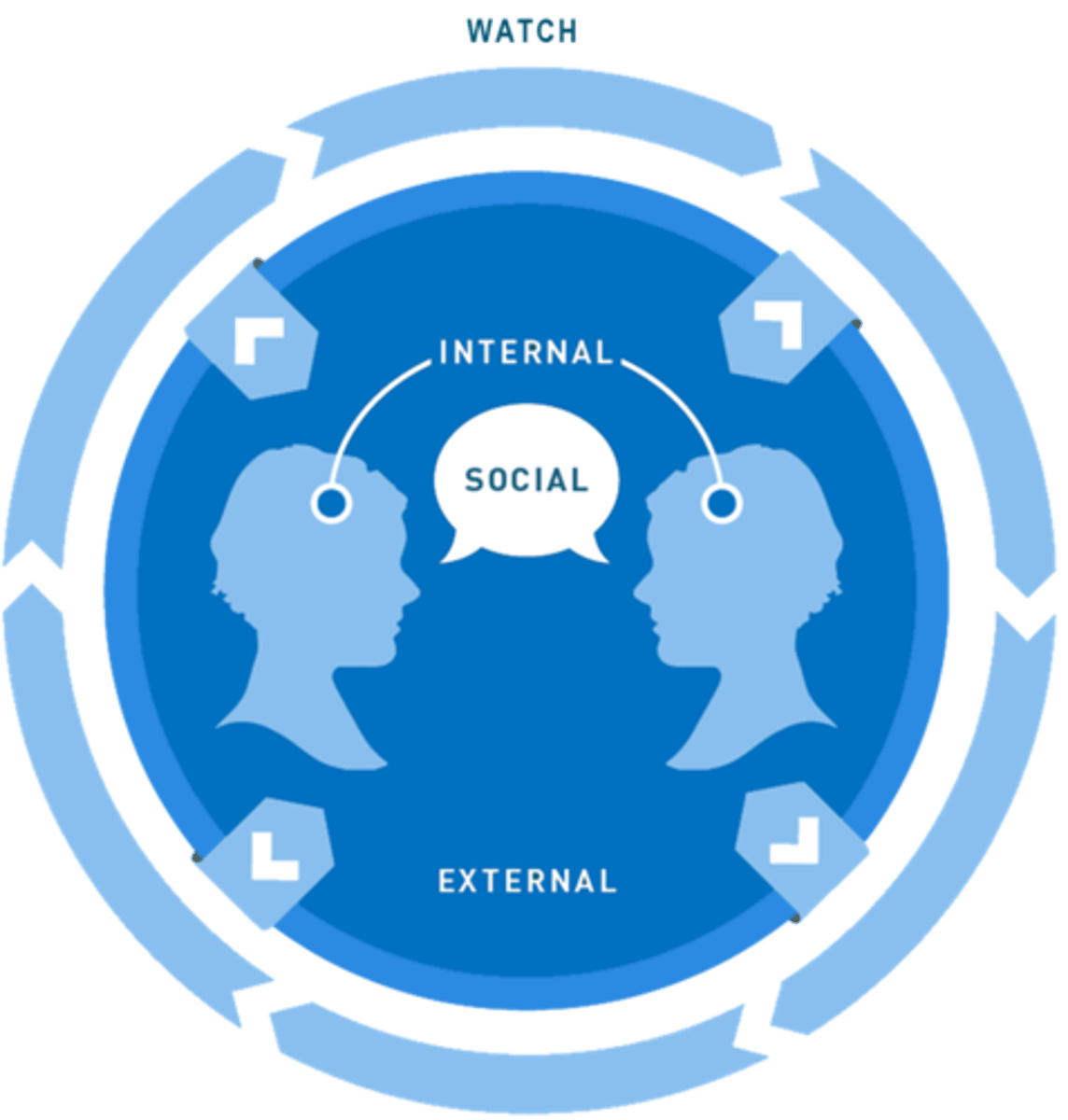
What do we need to do to understand consumer need recognition?
- understand consumer motives
- understand consumer values
- then you may "create needs"
T or F: humans are social beings; all motives are social motives
True
Is this true of values?: values can change, but tend to be more stable than motives
True
what ways can we measure Values?
- laddering
- interviews
- social groups
- VALS obvi
tips to increase contagiousness
- controversy
- social currency
- triggers
- emotions
- social proof
- stories
Paradox of pricing:
there is a pain of paying, but consumers who use pai for products tend to buy again
(post consumption stage) economic value:
when a product offers tangible monetary savings ate point of purchase or over the long term use
(post consumption stage) functional value:
(most common when consumers think of value) when a product offers useful features
(post consumption stage) psychological value
when a product offers "intangible" or perceived benefits
- Experiential value
- Social value
descriptive norm:
The perception of what most people do in a given situation.
injunctive norm:
a norm that defines what behaviors are typically approved or disapproved