Food service costs
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
sole proprietorship
owner has total decision making authority
least costly
avoid double taxation of owner and business
unlimited personal liability
partnership
increases sources of knowledge
easiest to initiate
avoids double taxation of owner and business
unlimited liability
C corporation
limited liability of ownership
easier to attract capital
ease in transferring ownership
costly and time consuming to create
doublet taxation
S corporation
limited liability of owners
avoids double taxation
ease in transferring ownership
high tax rate than c corp
limited to 75 stockholders or less
limited liability company
limited liability of owners
can have multiple owners
avoids double taxation of owner and business
costly and time consuming to create
aspects of accounting
auditing
cost accounting
financial accounting
managerial accounting
cost accounting
determination and control of cost
financial accounting
reporting of transactions for an organization and the periodic prep of various reports
managerial accounting
uses historical and estimated financial data to assist management in daily operations
basics of accounting
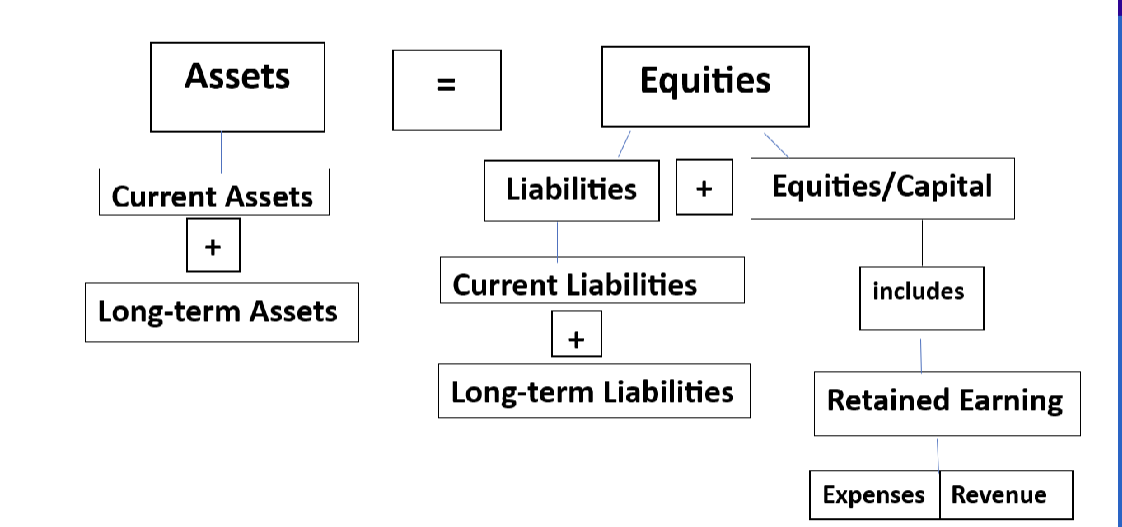
assets, equities, liability, capital
assets
things that have value
equities
ownership or claims against the assets
liabilities
claims against the company
debts
capital
interest of the owners in the company
food service assets
cats, money, inventory, accounts receivable, equipment, stocks and bonds
balance sheet
statement which shows the financial condition of a business at a given point in time
income statement
statement which shows the results of operating a business over a period of time
also called profit and loss statement
operating statements
often used interchangeably with profit and loss statements
frequently completed on a monthly basis and will have more specifics to better analyze how your business is doing
financial statements
balance sheets
income statement - revenue and expenses
major expenses
labor, food, operating expenses
accounting methods
recording transactions
cash
accrual - record transitions when revenue is earned not necessarily received and when expenses are incurred regardless of when cash goes out
importance of cash handling
separation of duties
who has access to cash
security background checks on employees
reconciliation
unaccounted audits
cash drawers
surveillance cameras
major expenses
labor - salaries
food - cost of goods sold
operating expenses
2 times of recording transactions
cash - record transactions at the time the cash actually goes in or out of the business
accrual - used most frequently record transactions when revenue is earned not necessarily received and when expenses are incurred regardless of when cash goes out
assets = equities
fixed costs
do not vary with volume or service rendered, even if volume increases or decreases, these costs do not vary
considered non-controllable
may vary but not because of volume
variable costs
costs vary directly and proportionately with the volume of business
controllable
semi variable costs
vary in the same direction but less than proportionately with changes in volume
usually controllable
Full cost
direct + indirect costs
direct costs
items of cost which are specifically traceable to an item, food, labor
indirect costs
elements of cost that are associated with an item but are not directly traceable to an item, utilities, supervisor’s salary
sunk costs
already incurred and cannot be recouped by a new decision or alternative
differential cost
amount of increase or decrease in cost when you compare alternative choices
straight line depreciation
original cost - less salvage value
double declining balance
if 20%
$10,000 × 20%
$2000 depreciation year 1
$1600 depreciation year 2
$1200 depreciation year 3
sum of the years digits
add #’s 1-n (estimate life)
food cost %
cost of food/food sales
labor cost %
cost of labor/food sales
primal foodservice costs
food cost
labor cost
food cost
most readily controlled items and is subject to the greatest fluctuations
consider:
menu planning
type of service
purchasing method
receiving control
purchases method
purchases for period of time/food sales
frequently look at total purchases/# meals served
inventory method
[beginning inventory (1st day of month) + food purchases (for that month] - [closing inventory (last day of month)] / cost of food
pre-cost an item
purchase price, amount purchases, cooking process (shrinkage + EP)
EP cost/# portions
selling price methods
factor mark up method
prime cost method
actual cost method
demand oriented pricing
competitive pricing
factor-pricing/conventional method
based on raw food cost and a mark up factor
prime cost method
food % + labor cost % = prime cost %
mark up factor = 100%/prime cost %
actual cost method
menu price = food costs + labor cost + variable costs + fixed cost + profit
demand-oriented pricing
whatever the market will bear
often time based pricing (lunch, early bird specials)
competitive pricing
compare to the competition
not a calculation
dynamic pricing
not necessarily planned but when low inventory, very high demand
odd cents pricing
ends in odd number
number other than zero
just below zero
pricing by the ounce
$ per ounce
two tier food service
offering upscale items at a different price
table d’hote
fixed priced menus
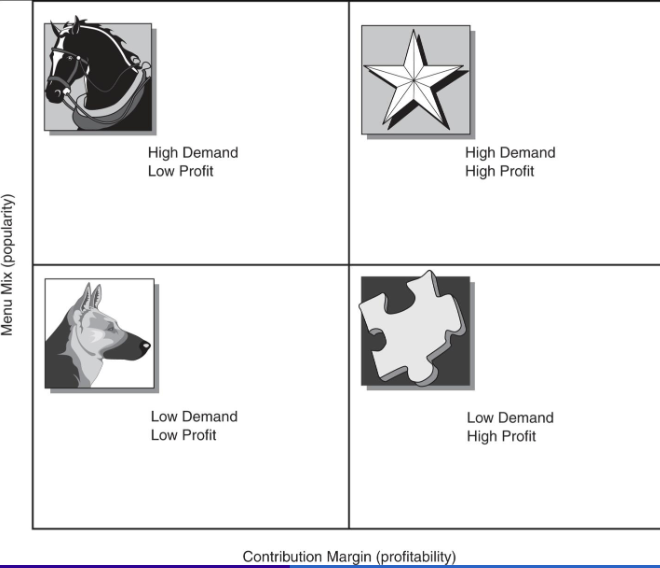
menu engineering
computerized menu analysis
focus on looking at which menu items make money
CM contribution margin
MM menu mix
popularity and profitability