The Nervous System
1/67
Earn XP
Description and Tags
AB Highschool bio30 Nervous system (unit 1)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
Soma
Houses important cell bits like the mitochondria
Nucleus
The brain of the neuron Holds genetic data for protein synthesis Houses and builds DNA
Dendrites
Receivers of the neurotransmitters’ electrical signals from other neuron (axon terminals)
Myelin Sheath
Protects and insulates the axon Allows for efficient and quick transport impermeable to Na+ (sodium)
Node of Ranvier
Spots where Na+ (sodium) can enter and cause a nerve impulse (action potential)
Axon
Part that carries electrical signals away from the soma and towards other neurons
Axon Terminal & Bulb
Place where the electrical signals depart from on the neuron (via neurotransmitters)
Neurons
Cells specialized in conducting nerve/electrical signals over long distances
Central Nervous System
Home of the brain and spinal cord. Where your body processes sensory information and turns it into decisions. Also the only place that conscious thought happens. Houses interneurons
Peripheral nervous system
Everything around the central nervous system. Sensory and motor neurons are housed here. Where you sense everything.
Grey matter
Unmyelinated neurons. Surround the brain, covered with fissures (folds)
White matter
Myelinated neurons, inside the brain. Faster transport.
Forebrain
Cerebrum, thalamus, hypothalamus
Midbrain
Tectum, tegmentum
Hindbrain
Pons, cerebellum, medulla oblongata
Frontal lobe
Conscious thought, memory, intelligence, personality, Broca's area, voluntary muscle movements
Parietal lobe
Somatosensory functions (touch, taste), processes info about body position
Occipital lobe
Processes visual information
Temporal lobe
Auditory reception (hearing) & memory, Wernicke s area (language comprehension)
Cerebellum
Limb movements, balance, muscle tone
Pons
Relay station between cerebrum and cerebellum
Medulla oblongata
Autonomic nervous system, connection between PNS & CNS
Hypothalamus
Regulates the pituitary gland, keeps body in homeostasis with autonomic system & hormones
Corpus collosum
Communication between hemispheres, a bundle of nerves
Cerebrum
Complex thought, hemispheres are connected by a bundle of nerves
Paraplegia
Injury below the first thoracic vertebrae, paralysis generally @legs
Quadriplegia
Injury of spinal cord close to neck, paralysis to most of body
Myelinated neurons
White matter of brain, conducts nerve impulses, can regenerate after injury
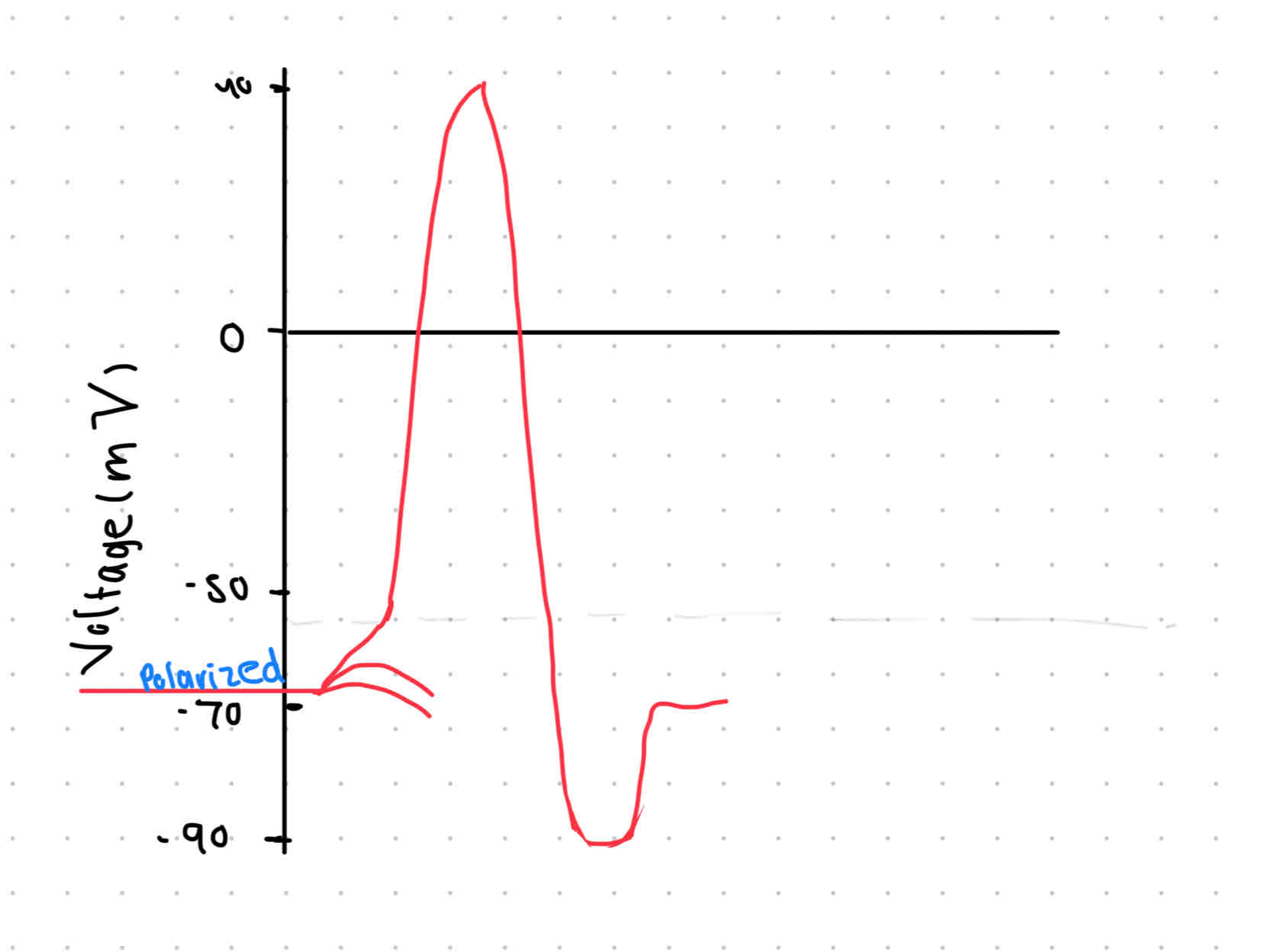
Polarized/resting state
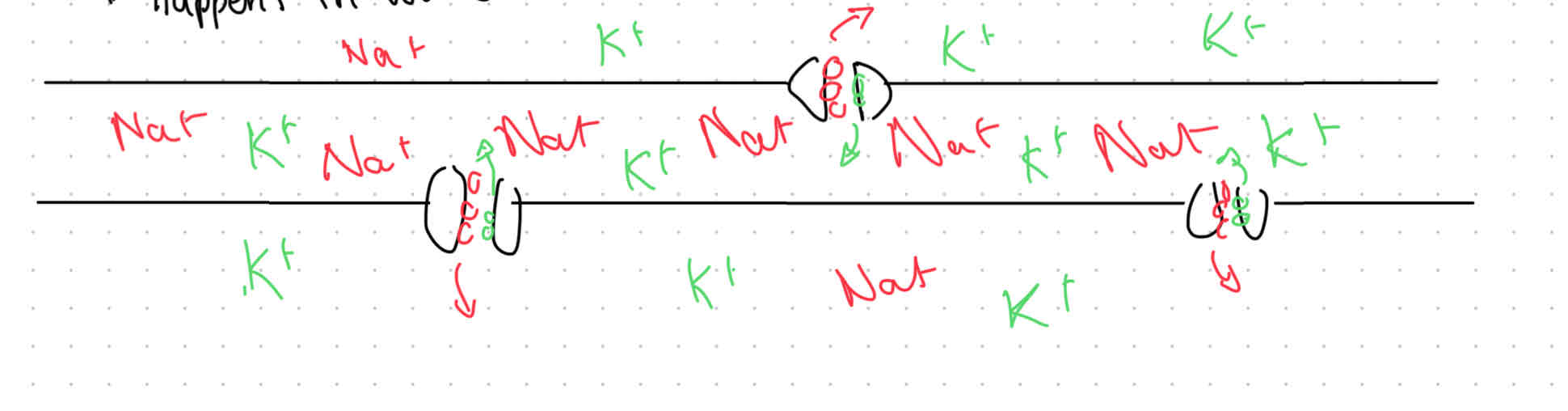
Inside cell voltage → - 70 mV RMP, inside cell ↑ [K+] outside cell ↑[ Na+] (like a salty banana!) 🍌
Sodium-Potassium pumps move 3 Na+ inside and 2 K+ outside to maintain -70mV (K+ leaks out through channels 😓)
![<p>Inside cell voltage → - 70 mV RMP, inside cell ↑ [K+] outside cell ↑[ Na+] (like a salty banana!) <span data-name="banana" data-type="emoji">🍌</span></p><p>Sodium-Potassium pumps move 3 Na+ inside and 2 K+ outside to maintain -70mV (K+ leaks out through channels <span data-name="downcast_face" data-type="emoji">😓</span>)</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/ab58ab6f-a018-4edc-accb-e99df3865f75.jpg)
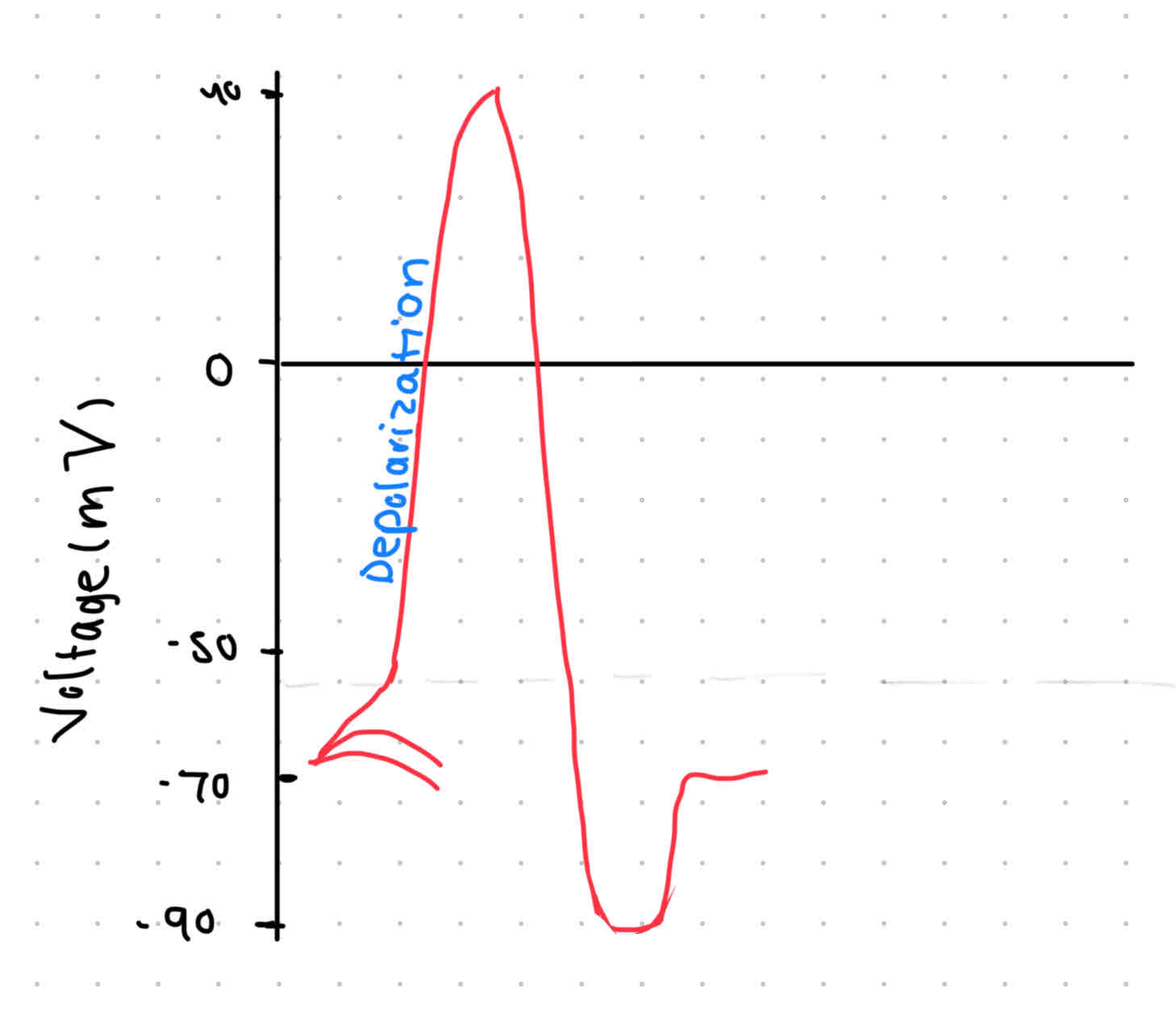
Depolarization
Stimulus arrives!
Impulse causes sodium gates to open
Sodium (Na+) floods in
Membrane potential goes -70mV → +40mV
All or nothing (has to reach -55mV)
Na+ gates close @ equilibrium
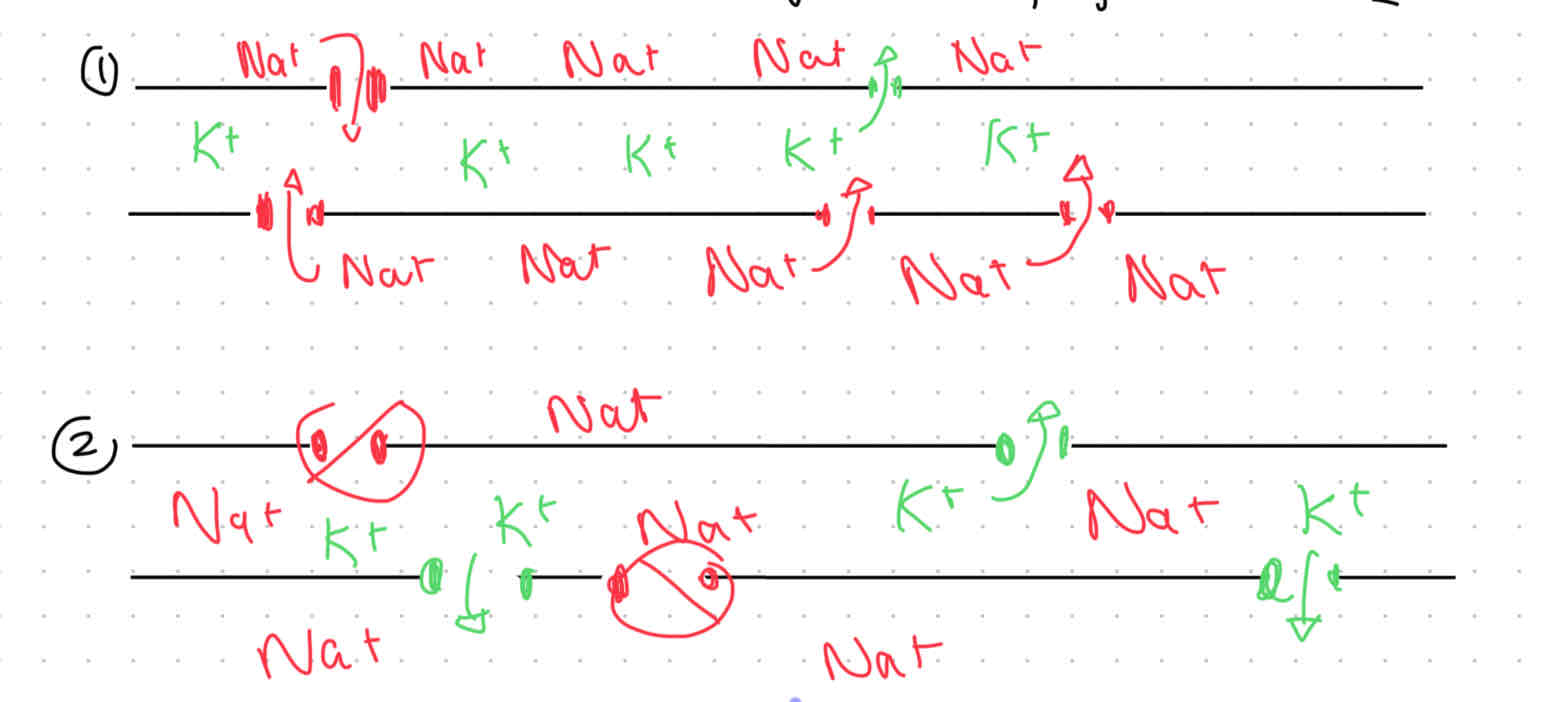
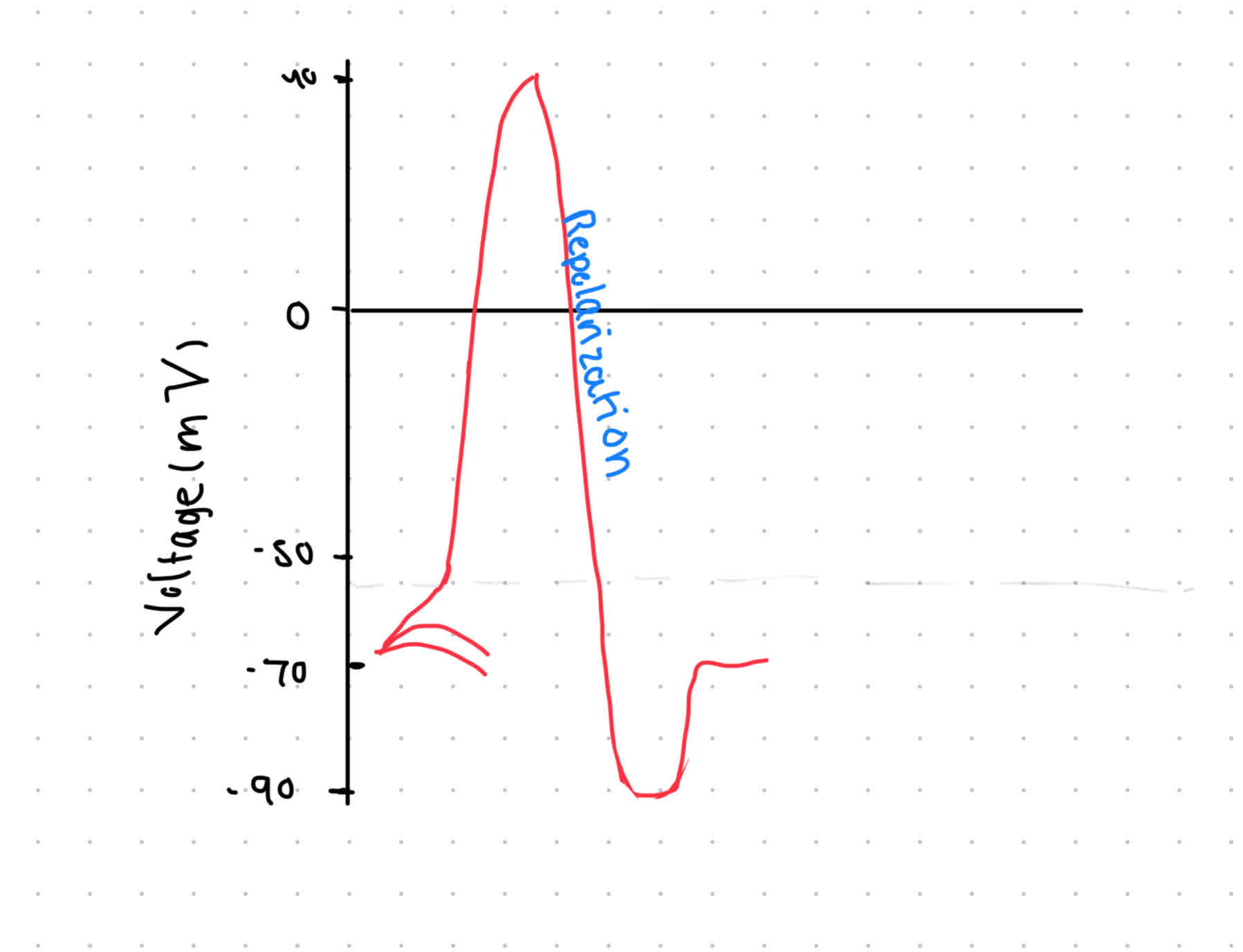
Repolarization
Trying to get back to normal
K+ gates (@ protein channels) open
Na+ and K+ concentrations have switched
Sodium-potassium pumps kick in to switch the Na+ and K+ back to original spots
trying to re-establish -70mV
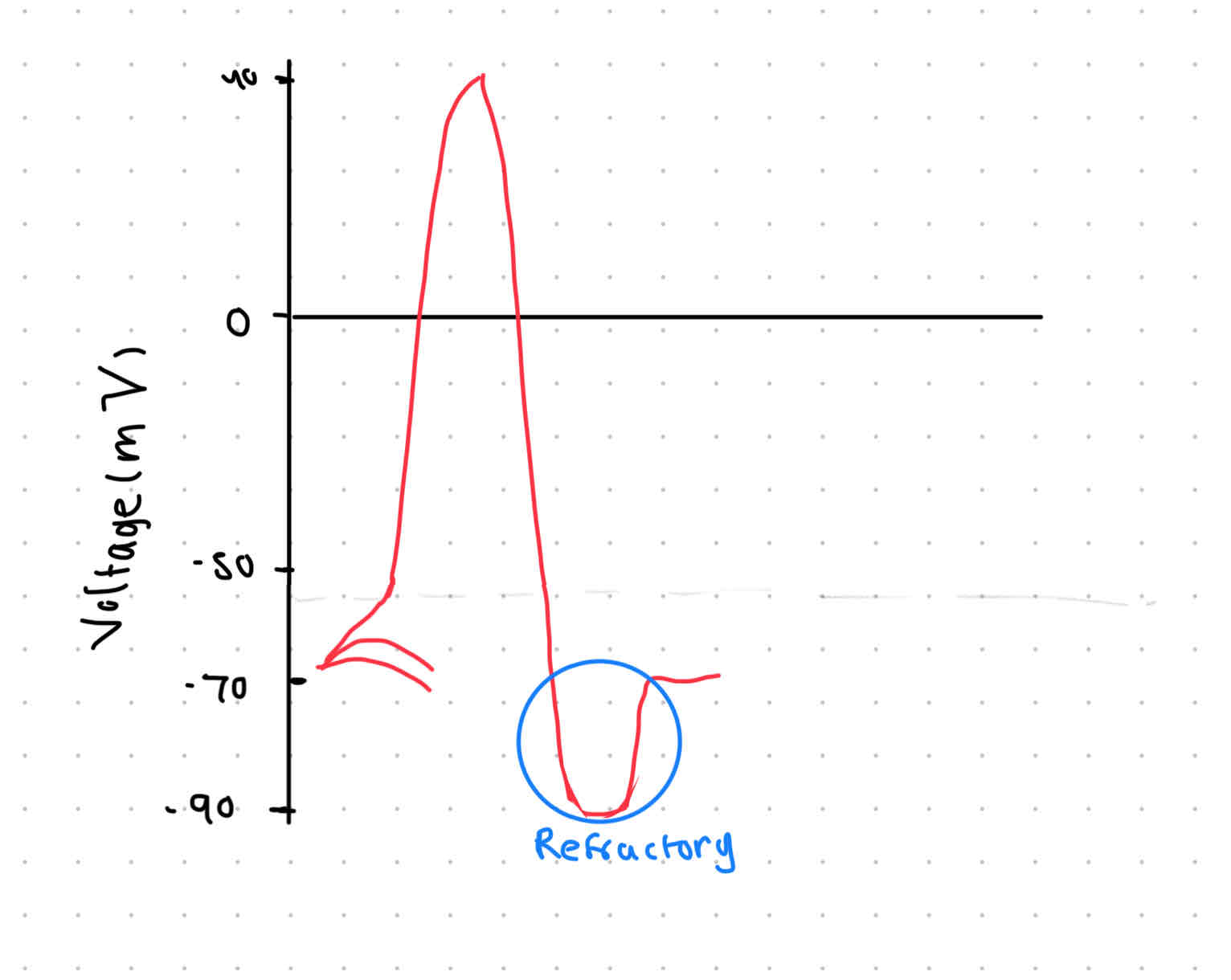
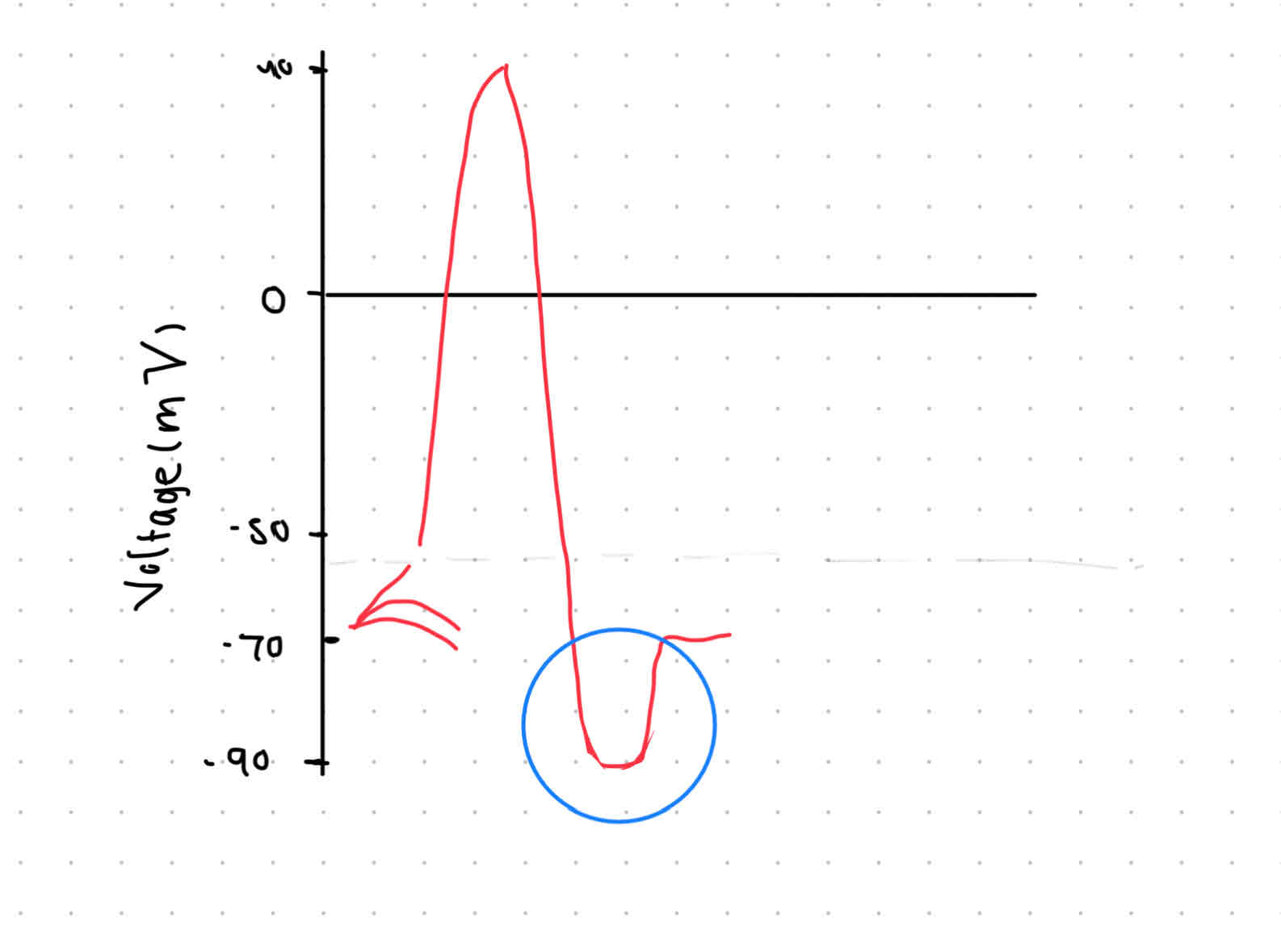
Refractory period
SUPER rest
Time to get ready again
Sodium-potassium pump overshoots → -90mV
Recovery → gives it a chance to rest
pumps slow down
Na+ and K+ diffuse
Thermoreceptors
Stimulated by heat/cold (skin receptors)
Nocireceptors
Sense pain
Somatic
Voluntary control, carries info from sensory receptors to skeletal muscles, external stimuli
Autonomic
Involuntary control, maintains homestasis (breathing, heart rate, peristalsis), internal stimuli
Sympathetic nervous system
Fight or flight, release of epinephrine/noepinephrine
Parasympathetic
Rest & digest & reproduce, activated when body is at rest, release of acetylcholine
Sclera
Protects eye’s inner layers, maintains eye shape
Cornea
Transparent part that protects the eye, refracts light toward pupil
Choroid layer
Blood vessels that nourish the retina
Iris
Regulates amount of light into eye
Pupil
Opening formed by iris → allows light into eye
Ciliary muscles
Alter shape of lens → adjust focus
Rods
Photoreceptors, detect light in black & white
Dim light
Cones
Photoreceptors, colour, bright light
Fovea centralis
Area where cones are most dense/vision is sharpest
Lens
Focuses light onto retina
Aqueous humor
Maintains shape of cornea
Vitreous humor
Maintains eyeball shape
Optic nerve
Carries impulse (vision-based) to CNS
Ganglion layer
Forms optic nerve that exits back of eye (blind spot)
Astigmatism
Eyeball shape changes the way that the light focuses on retina (improperly refracts the light )
Myopia
Nearsightedness, eyeball is elongated. Focused light falls in front of the retina, can't see stuff far
Hyperopia
Farsightedness (can't see close stuff), eyeball is shortened (focused light falls beyond retina)
Colourblindness
Lack of specific cones ( colour receptors)
Pinna
Direct sound waves to the auditory canal (funnel them)
Auditory canal
Passage for sound waves toward the midear
Tympanic membrane ( tympanum/eardrum )
Pass on vibrations to the ossicles
Ossicles
Malleus, incus, stapes -- amplify the sound waves
Semicircular canals
Sense 3D position & maintain balance. Filled with fluid
Eustachean tube
Allows air pressure to equalize. Tube that connects to throat
Auditory nerve
Sends the action potential (produced by stereocilia in the Organ of Corti)
Cochlea
Where the Organ of Corti is. (i.e, where a nerve impulse/action potential is generated!)
Vestibule
Carry amplified signal from the oval window and sends it to the cochlea
Organ of Corti
Where the stereocillia are housed (where the action potential is actually generated)
Oval window
Turns vibration by ossicles into pressure changes in the inner ear
Olfactory bulb
Processes smells