4 - Ionotropic & Intracellular Receptors
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
What is an ionotropic receptor?
Receptor linked to an ion channel
What type of acetylcholine receptor is
- nicotinic (nAChR)
- muscarinic (mAChR)
ionotrophic
metabotrophic (G protein)
Types of nicotinic receotors (nAChR)
Muscle endplate nicotinic (neuromuscular junction)
Neuronal “ganglionic” nicotinic (ANS)
Which are always reversible: Agonist or antagonist reactions?
Agonist always reversible
antagonists can be both reversible and irreversible
How does the action of toxins work?
example of non-reversible reaction
a-bungarotoxin
Blocks nicotinic ACh receptors at NMJ
Stops muscle contractions
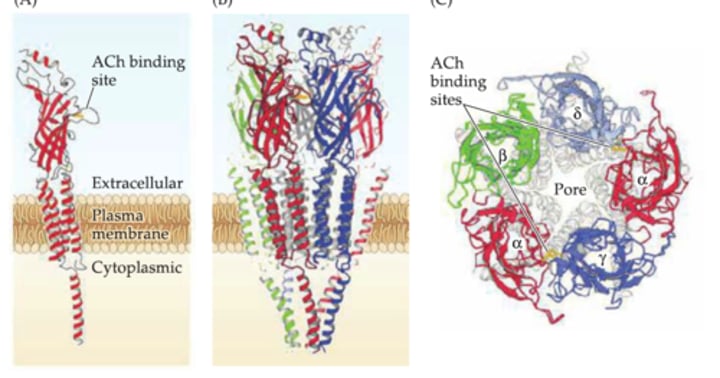
Brief structure of a nAChR
5 subunits
4 Transmembrane domains
ACh binds to alpha subunits
a-bungarotoxin vs d-tubocurarine
a-bungarotoxin —> irreversible
d-tubocurarine —> reversible
How does Curare work?
Example of a reversible reaction
d-tubocurarine
Blocks nAChR (REVERSIBLE)
Stops muscle contractions (used during surgery)
Then can be reversed
allosteric modulators (non-competitive inhibitor)
Substance that binds to cell receptor but binds on the other side
Still causes an effect
E.g. alcohol
Inverse agonist
Binds to the same site as the agonist but causes the opposite effect to the agonist
The GABA receptor is a type of which receptor?
ionotropic
GABA binds, activates receptor, allows chloride to pass through receptor & acts as an inhibitor
What type of hormones commonly activate intracellular receptors?
Steroid hormones
What is the action of an intracellular receptor? Is it a fast or slow acting receptor?
Alters transcription
Slow response
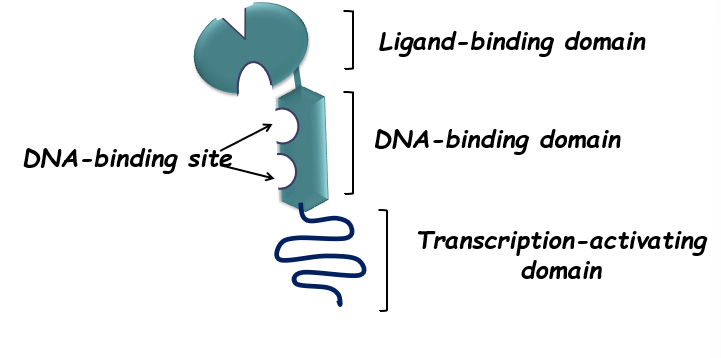
Describe the structure of an intracellular receptor
ligand binding domain
DNA binding domain
Transcription activating domain
How do intracellular receptors work?
Hormones cross plasma membrane & bind to cytoplasmic receptors
Hormone binding alters receptor conformation so it no longer binds inhibitor
Hormone-receptor complex translocates to nucleus
Hormone -receptor complex binds to DNA —> usually turns on transcription but can also turn it off
Cellular response is change in gene expression