L2 - Epithelium I
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
What are common components of tissues and organs?
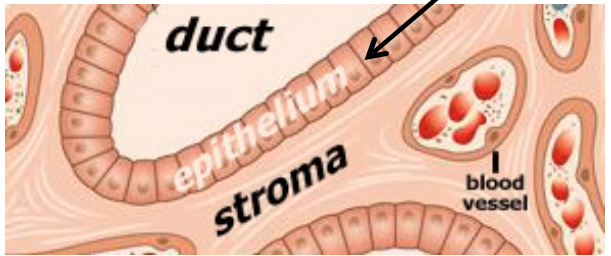
Parenchyma - includes cells responsible for tissue’s function
Stroma - consists of supporting tissue (usually connective tissue, except in the CNS)
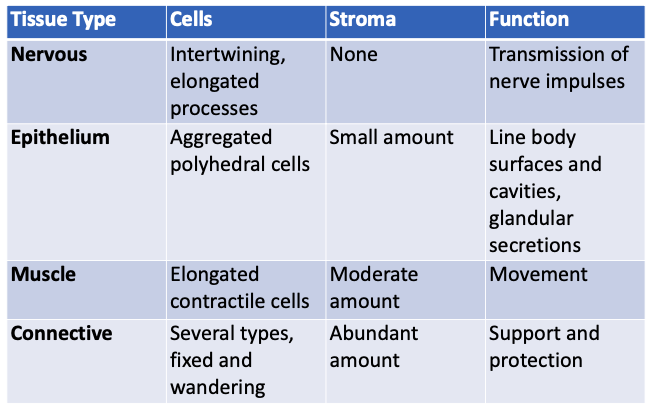
Comparison of the 4 basic tissue types:
What are the 3 primary germ layers?
Ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm
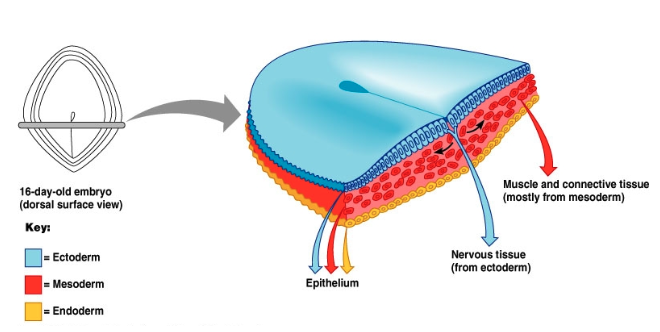
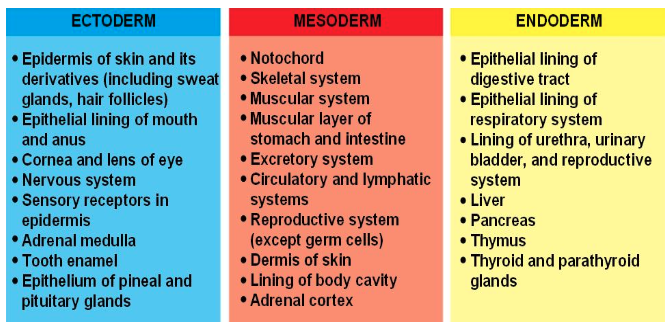
Major derivatives of the primary germ layers:
Are organs composed of one tissue type?
No, they can be composed of many tissue types
What are some key characteristics of epithelium?
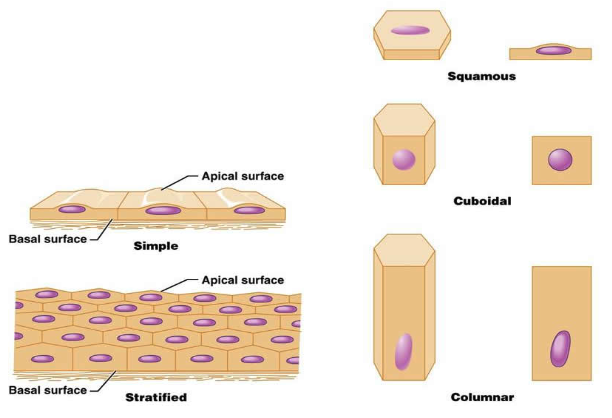
Classified according to cell shape and number of cell layers
Little extracellular space between adjacent cells
Polar orientation - apical end (faces lumen) and basal end (attaches to other tissue type)
Can have well-developed apical modifications
Forms basement membrane
What are the main functions of epithelium?
Similar to cell membranes: separates self from non-self
Divides body into functional compartments
Forms barriers to control and modify substance movement
Key roles:
Covering, lining, protecting (e.g. skin, membranes)
Secretion (e.g. glands)
Absorption (e.g. intestines, kidney tubules)
Contractility (e.g. mammary & salivary glands)
Why is epithelium essential for body exchange?
Everything that enters or exits the body must pass through at least one layer of epithelium
Shapes of epithelial cells:
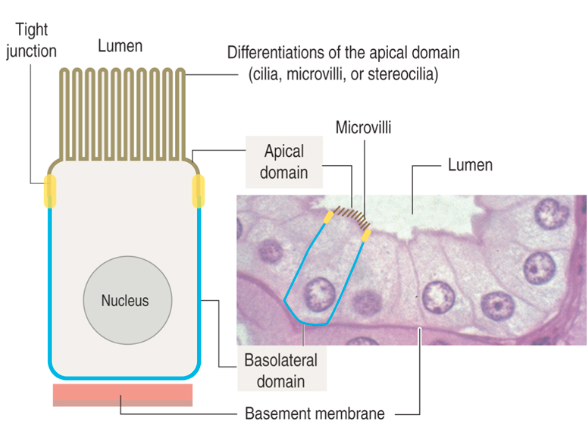
What is the basal surface of epithelial cells?
Faces the underlying connective tissue
Attached to the basement membrane
Contains adhesion molecules and cell junctions
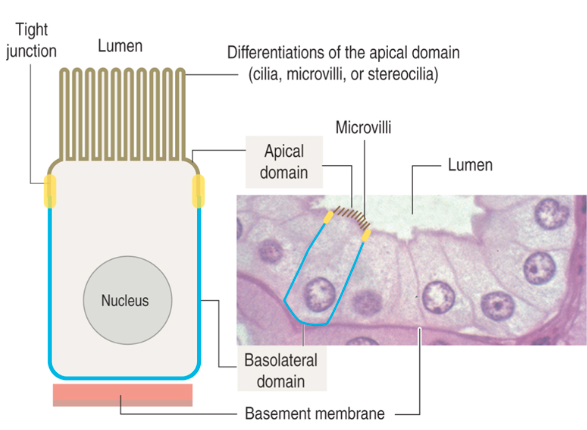
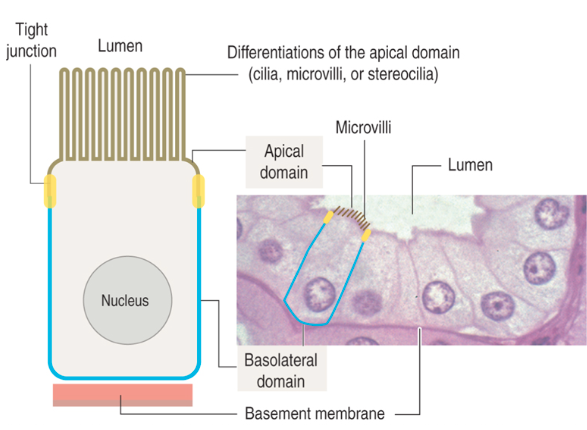
What is the apical surface of epithelial cells and its features?
Faces a cavity, lumen, or external surface
May have microvilli or cilia
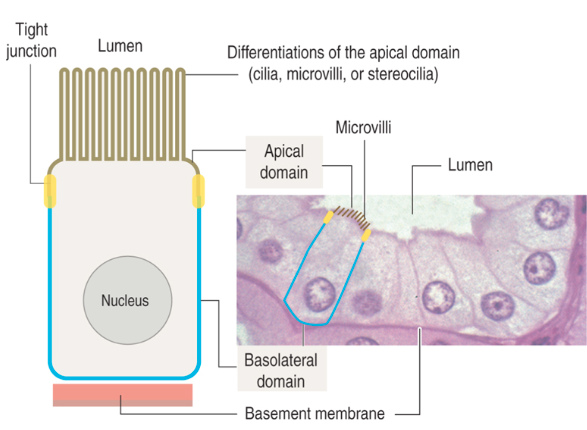
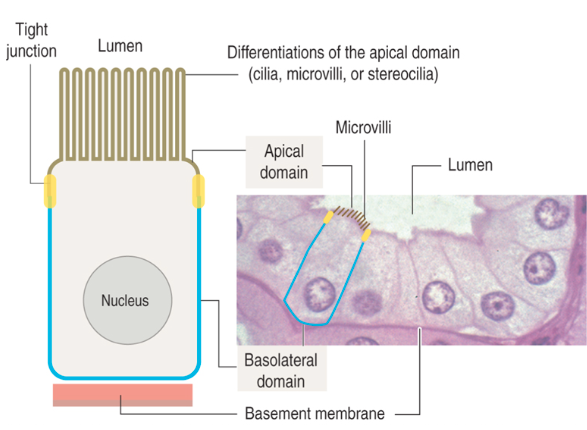
What are the lateral surfaces of epithelial cells?
Sides in contact with adjacent cells
Contain cell junctions
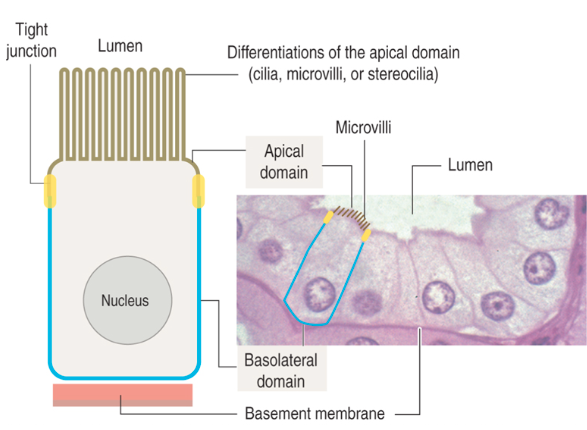
Epithelial cell polarity and specialized structures:
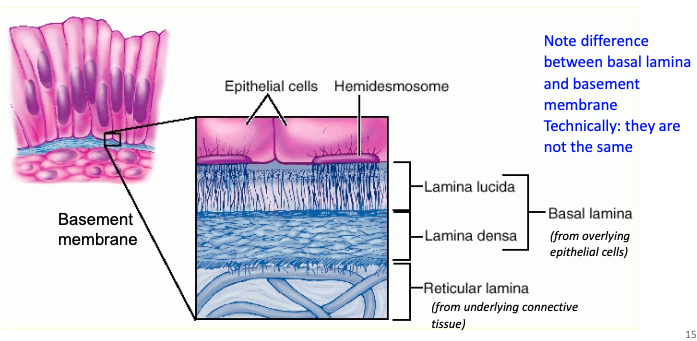
What is the basement membrane?
A thin layer of specialized extracellular material between the basal surface of epithelial cells and the underlying connective tissue
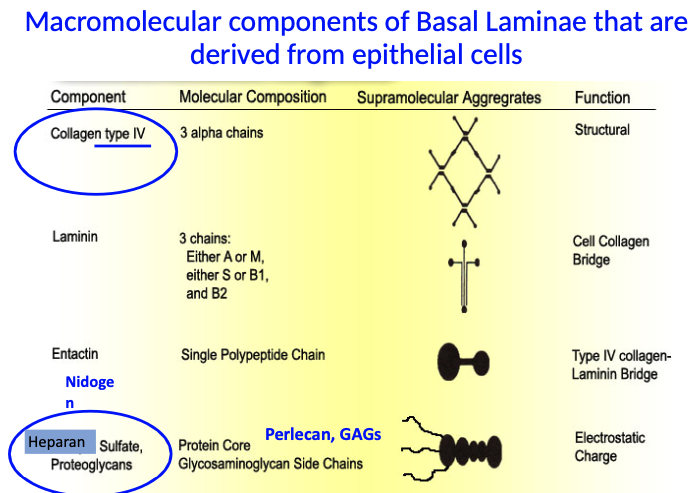
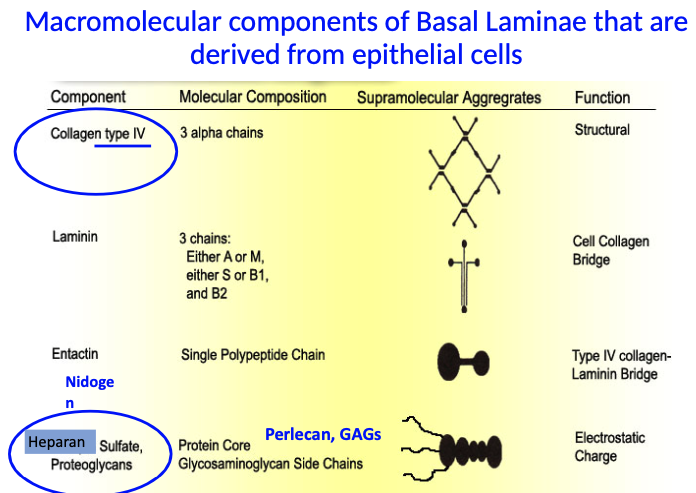
What are the key components of the basal lamina made by epithelial cells, and what do they do?
Collagen type IV: provides structural support (associate w/ basal lamina)
Nidogen: links collagen IV and heparan sulfate proteoglycans
Heparan sulfate proteoglycans (e.g., Perlecan, GAGs): provide electrostatic charge and filtering ability
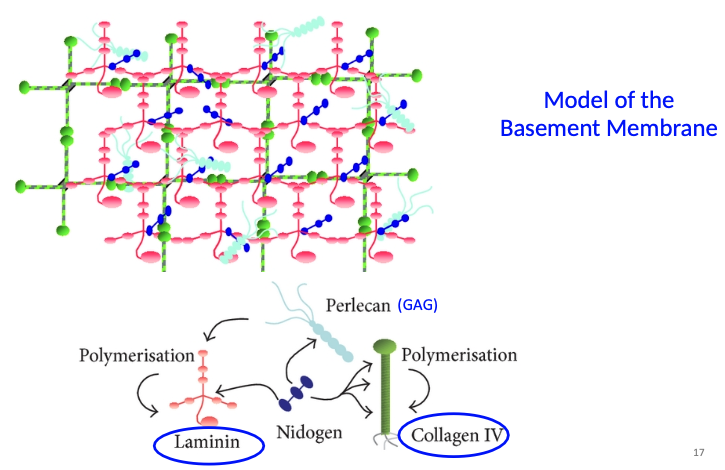
Model of basement membrane:
What are some functions of the basement membrane?
Structural base and attachment site for epithelial cells
Semipermeable barrier, assists in filtration of fluid/substances from underlying capillaries (blood vessels don’t penetrate epithelium)
Influences cell proliferation, differentiation, signal transduction, and cell metabolism
Pathway for cell migration
Helps establish cell polarity
How are basement membranes visualized?
Basement membranes show up best with PAS stain (due to GAGs)
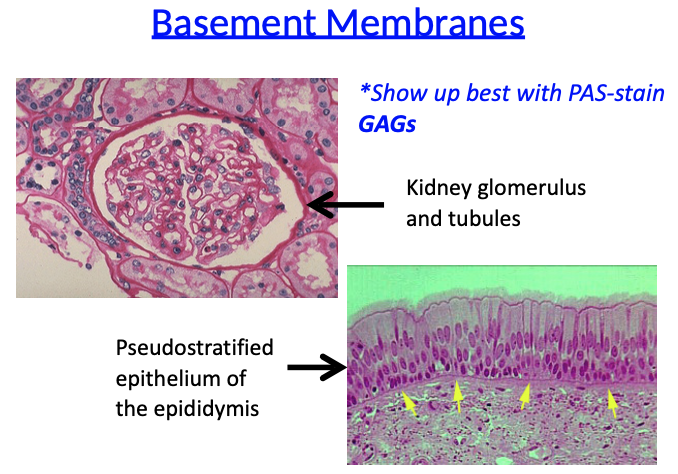
PAS stain basement membrane:
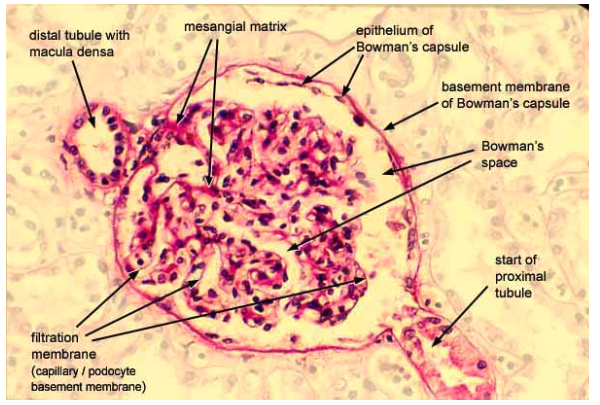
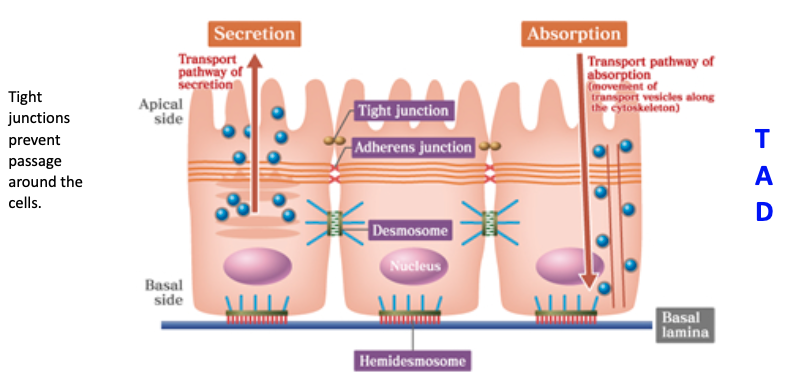
What is the function of cell junctions?
Form seals between cells (occluding junctions)
Sites of adhesion (adhesive or anchoring junctions)
Channels for communication (gap junctions)
What is the order of junctions that you’ll find from the apical to basal side of epithelial cells?
Tight → Adherens → Desmosome
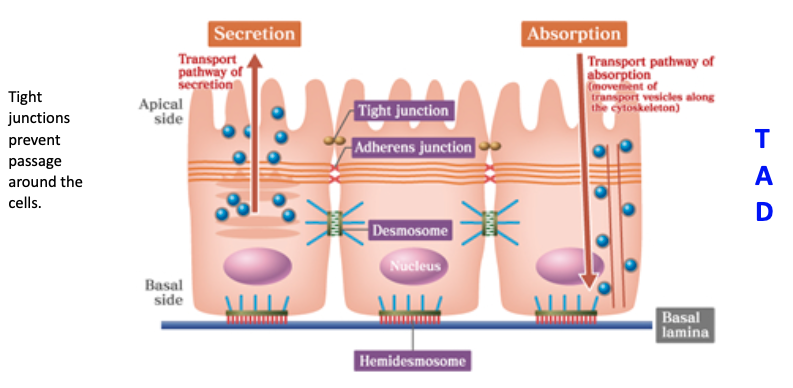
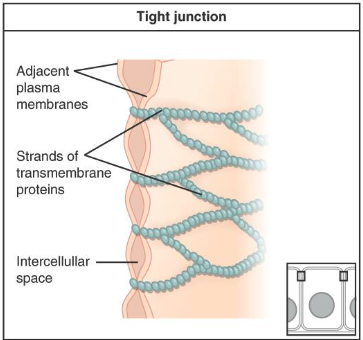
What are tight junctions (zonula occludens) and their structure?
Involve the transmembrane protein claudin
Form a band completely encircling each cell, sealing the space between cells
Located at the most apical part of epithelial cells
What are the functions of tight junctions?
Seal to prevent flow of materials between cells (paracellular pathway)
Maintain cell polarity by keeping apical and basolateral membrane proteins in their respective regions
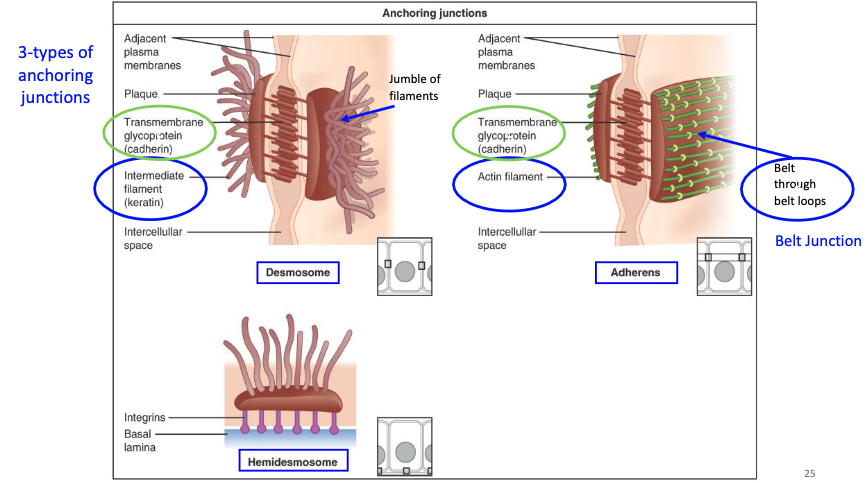
What are the 3 types of anchoring junctions, and what cytoskeletal elements do they connect to?
Adherens junction – connects to actin filaments (belt-like)
Desmosome – connects to intermediate filaments (spot-like, strong)
Hemidesmosome – connects cells to the basal lamina via intermediate filaments
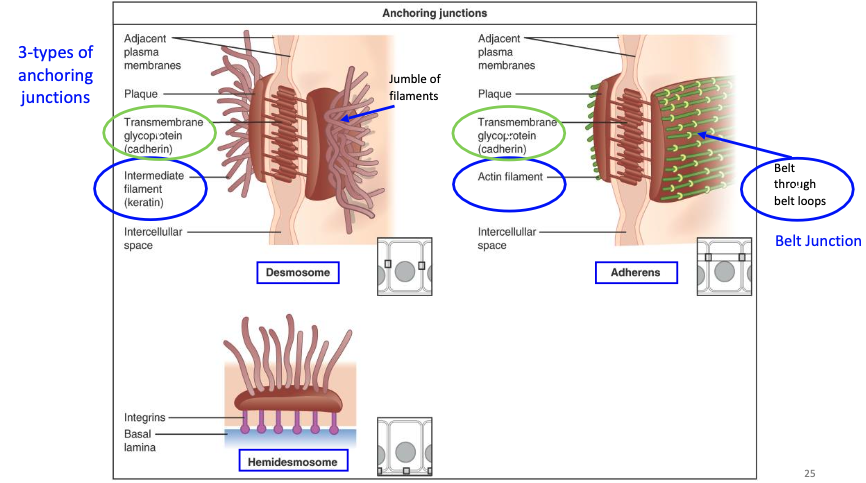
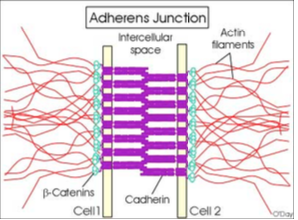
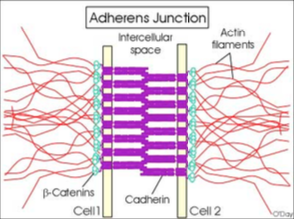
What are adherens junctions (zonula adherens) and how do they work?
Located just below tight junctions
Form a belt-like adhesion between cells
Use cadherin (needs Ca²⁺) to connect to catenin and actin filaments inside the cell
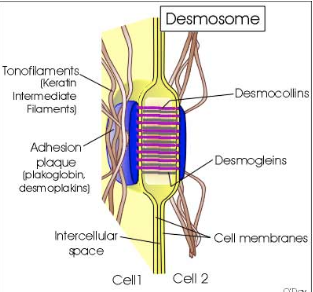
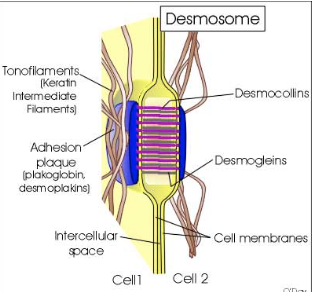
What are desmosomes (macula adherens) and how do they function?
Provide a firm spot of adhesion between cells
Use cadherin-like proteins (desmogleins, desmocollins)
Have an adhesion plaque that anchors to intermediate filaments (keratin)
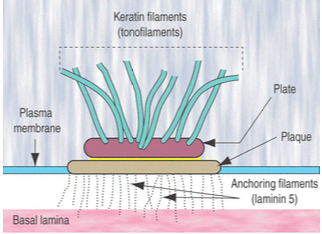
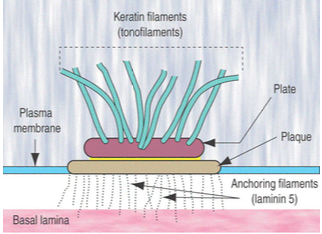
What are hemidesmosomes and what do they connect?
Bind cells to the basal lamina (not to other cells)
Use integrins that attach to laminin and type IV collagen
Anchored to the cell's intermediate filaments (keratin)
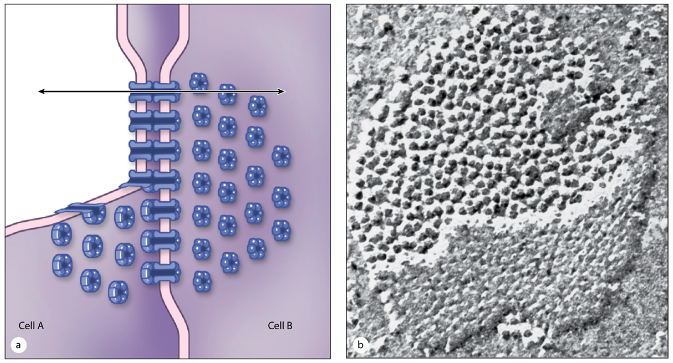
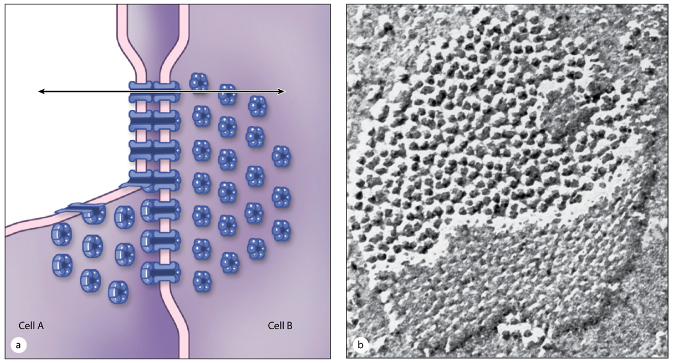
What are gap (communicating) junctions and what do they do?
Made of connexin proteins forming connexons (pores)
Allow rapid exchange of molecules between adjacent cells
Crucial in cardiac muscle for coordinating heartbeats
Comparison of cell junctions:
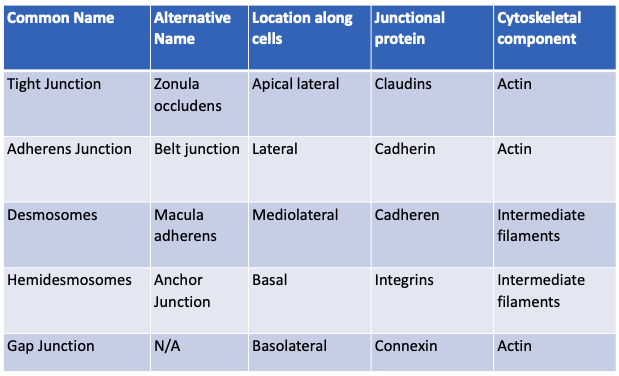
TEM of cellular junctions:
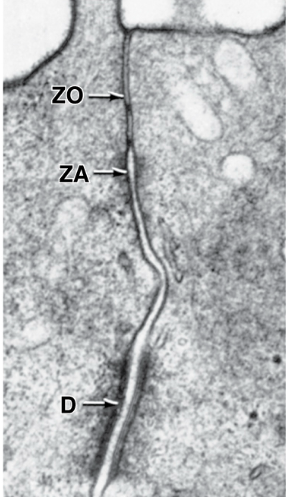
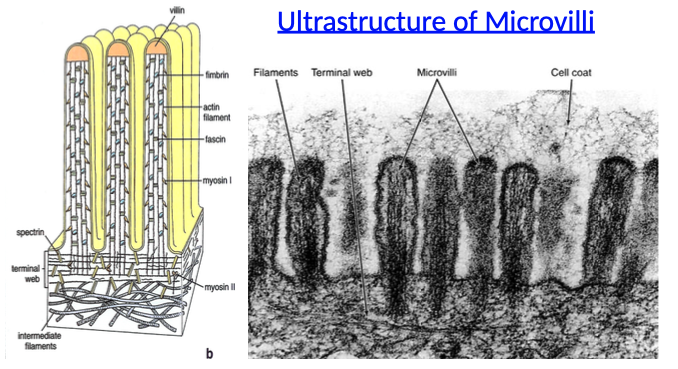
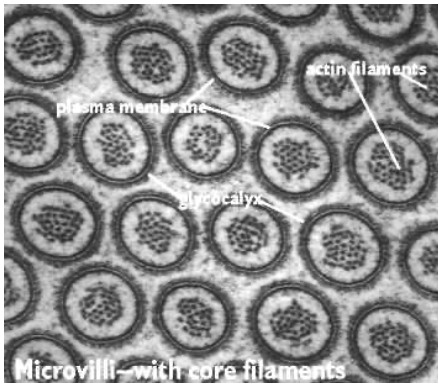
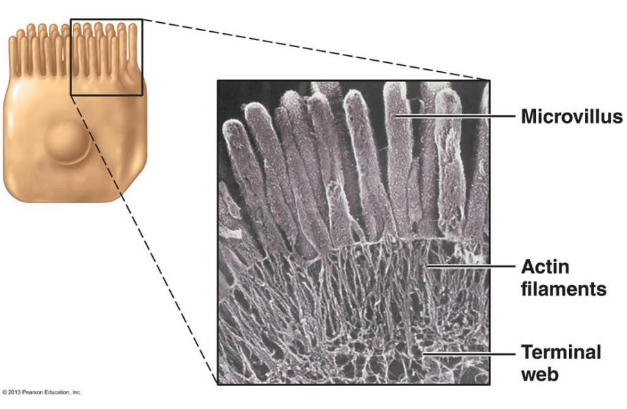
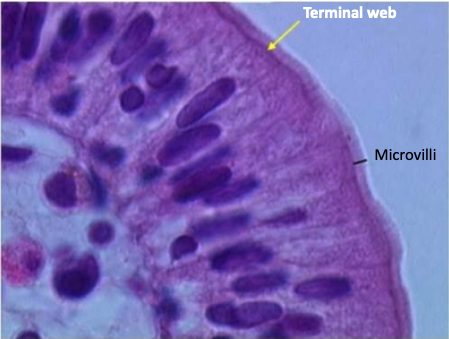
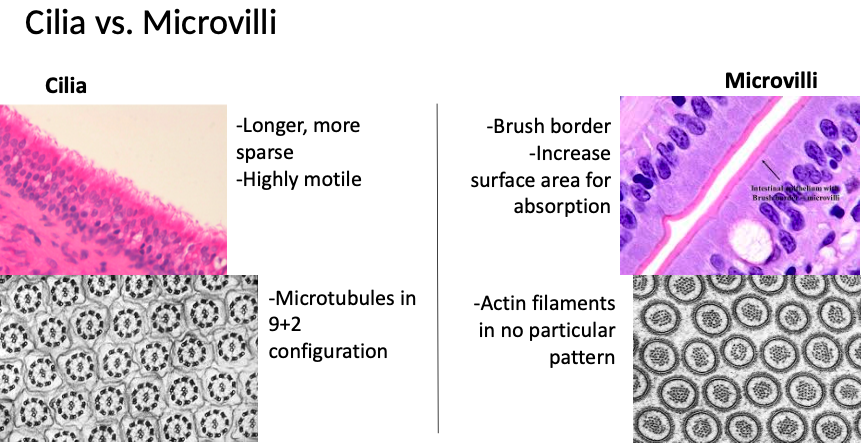
What are microvilli and what is their function?
Microvilli are extensions/foldings of the plasma membrane
They increase surface area for ABSORPTION, especially in intestinal epithelium
What is the glycocalyx and what does it form with microvilli?
Glycocalyx is a thick layer of glycoproteins covering microvilli
Together, microvilli and glycocalyx form the brush border
How is celiac disease related to microvilli?
In celiac disease, immune reaction to gluten causes loss of the microvilli brush border
Leads to malabsorption in the intestines
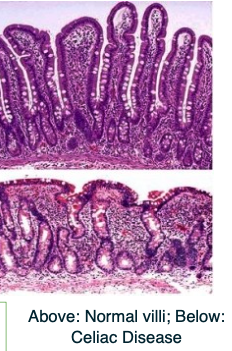
What is the internal structure of microvilli made of?
Core contains bundles of actin filaments
Cross-linked by anchoring proteins like fimbrin and myosin
How are microvilli anchored in the cell?
Actin filaments in microvilli connect to intermediate filaments
This connection is made via the terminal web at the base of the microvilli
Microvilli in cross-section:
Electron microscope image of microvilli:
Microvilli in light microscopy:
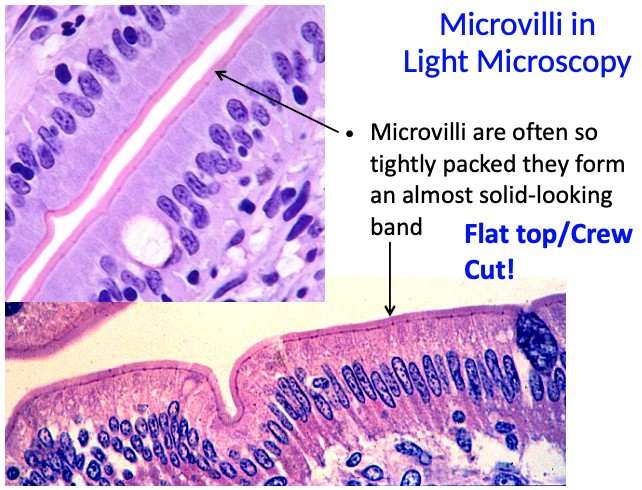
What is the terminal web and how can it be seen in relation to microvilli?
The terminal web is a dense region beneath the microvilli at the apical boundary of the cell
It can appear as a darker-staining band under the microscope
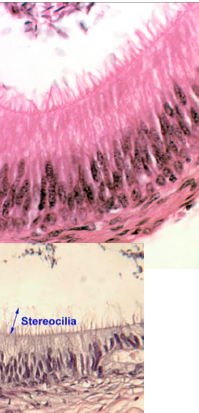
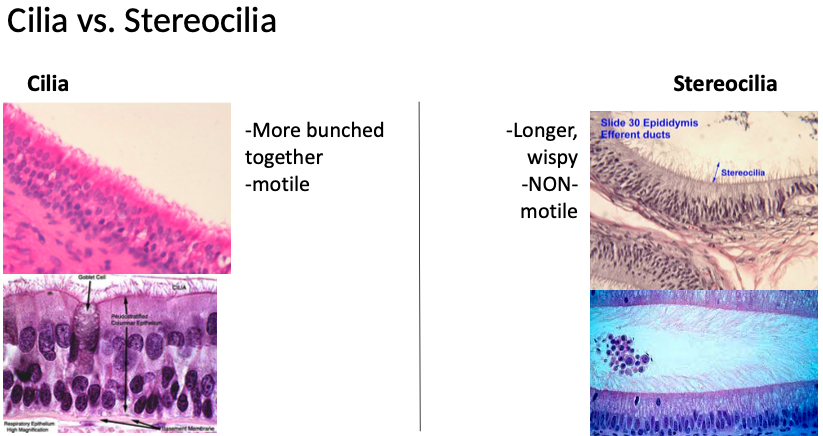
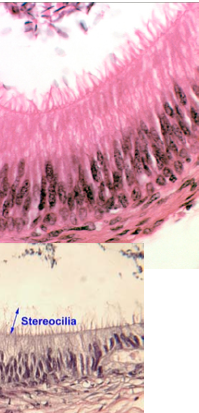
What are stereocilia and where are they found?
Longer and sometimes branched structures, similar to microvilli
Increase surface area for ABSORPTION
Found in epididymis and ductus deferens, and also in ear hair cells for mechanosensory function
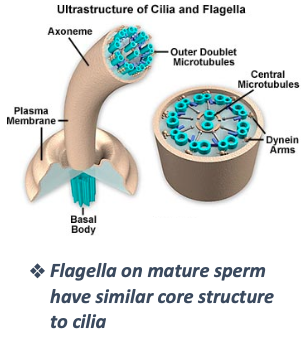
What are cilia and what is their structure?
Highly MOTILE, elongated structures
Contain a core axoneme with a 9+2 microtubule arrangement (9 peripheral pairs + 2 central)
Insert into basal bodies (like centrioles)
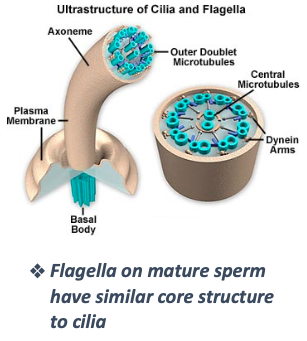
How do cilia move and what is their function?
Move in a metachronal rhythm, creating a one-way current
Help move substances across the cell surface
Flagella (like in sperm) share a similar internal structure
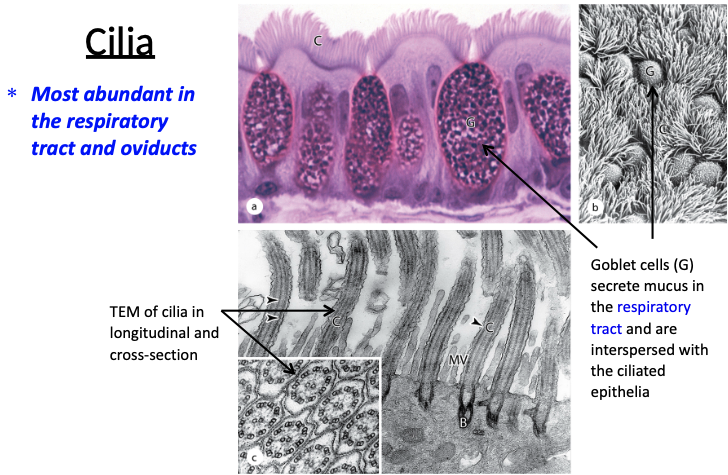
Where are cilia most abundant?
Most abundant in respiratory tract and oviducts.
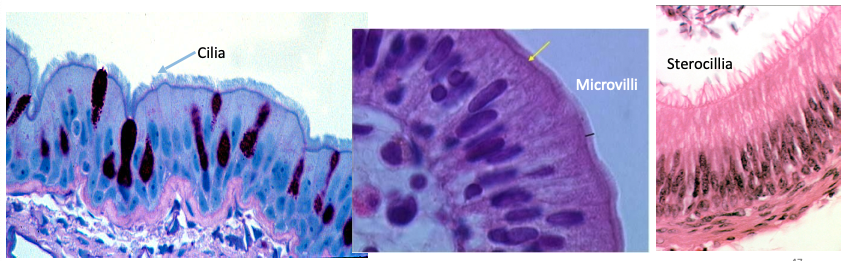
What are some differences between cilia and microvilli?
Cilia are longer and more sparse than microvilli (individual cilia more easily discernible)
Dark line of basal bodies along apical surface of ciliated cells appears similar to terminal web of microvilli
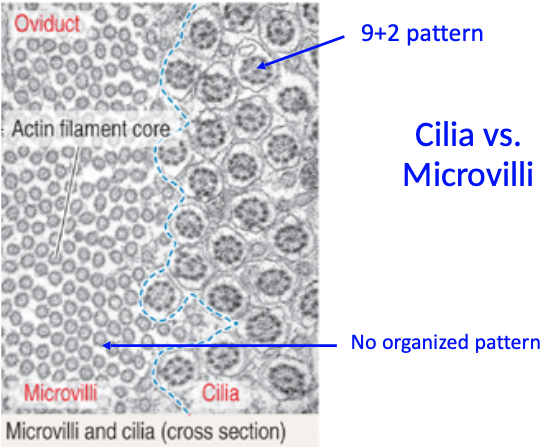
Cilia vs. Microvilli:
Cilia vs. Stereocilia: