Test Review 3 ( antibiotics/antifungals-TB/anativiral/antparasistic
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
91 Terms
what is Narrow specturm
Drugs that are only active againsta few species
safter and better since they target things more specifically
what does broad spectrum mean
drugs that are active agsinst a wide variety of microbes
what are the two kinds of defense/resistance principles
Innate(natural)
Acquired over time
may become less ensteiv to a drug or lose sensitivity
antibitotic resistance can develop to sevreal drugs
ass. w/ extended hospitalizations( morbitity and mortality)
what is antimicrobial stewardship
a multifaceted approach aimed at optimizing the use of antimicrobials (antibiotics, antifungals, and antivirals) to ensure their effectiveness and safety for patients while minimizing the risk of antimicrobial resistance
What is the process for selecting antibiotics
identify the infecting organism
think about drug sensivity of the infecting organsim
infestin site and status of host defenses
consider any allergies. inability of the drug to penetrate infection site and suscepibility of pt to have risk of frisrt choice drug toxicity
How do we idenifty the infectiing organsim
a gram-stained preperation of blood, urine, exudate, sputum, etc.
Polymerase chain rxns(PCR): detect low bacteria/virus titers
genertates thousands of DNA?RNA copies of the infecting microbe
more specific than a gram stain
what are gram-posative bacteria
its cell wall contains a thick layer of peptidoglycan and stains blue or purple after a Gram stain
what are gram negative bacteria
are bacteria that have a thin peptidoglycan layer and an outer membrane containing lipopolysaccharides.
more harmful and harder to kill because of the extra outer membrane
what are the 3 kinds of selective toxicty
bacterial cell wall disruption
inhibits bacterial enzymes
disrupts protein synthesis
what are the misuses of antibacterial therapy(5)
attempted treatment of viral inf
treatment of fever of unkown origin
improper dosing
treatment in the absense of adequate bacteriologic info.
omission of surgical darinage
what assessments are needed proir and during therapy
Prior:
Assess inf. ( vital , wound appearance, sputum, urine, & stool)
Obtain history to determine allergies or previous reactions
C & S PRIOR to therapy
During:
WBC mointored
Observe pt for s/s of anaphylaxis- d'c drug IMMEDIATELY and call rapid response (if in-pt) or 911 (outpt). Will likely need epinephrine & antihistamine
Monitor bowel function. Report diarrhea, abd cramping, fever, bloody stools, and s/s of clostridioides difficile associated diarrhea (CDAD
what kind of pt education is important during antibiotic treatment
Instruct to take medications around the clock and finish medications as directed (even if feeling better)
Advise to report about super infections (black, furry tongue overgrowth; vaginal itching or discharge; loose/foul smelling stools) and allergies
Advise not to treat diarrhea w/o consulting provider
Most antibiotics DO NOT affect contraceptive drug therapy except the rifampicin family
what are the diff types antibiotic drug rxns
what drugs can pateint be allergic too if they are allergic to penicillin
Cephalosporins have cross sensitvity
what drugs weakned the bacterial cell wall
B-lactams
penicillins
cephalosporins
carbapenems
Vancomyocin
what are the 5 generations cephalosprins
There are five generations of cephalosporins34 .
As we progress from 1st to 5th generation, there is increasing activity against gram-negative bacteria and anaerobes, increasing resistance to destruction of β-lactamases, and increasing ability to reach the CSF
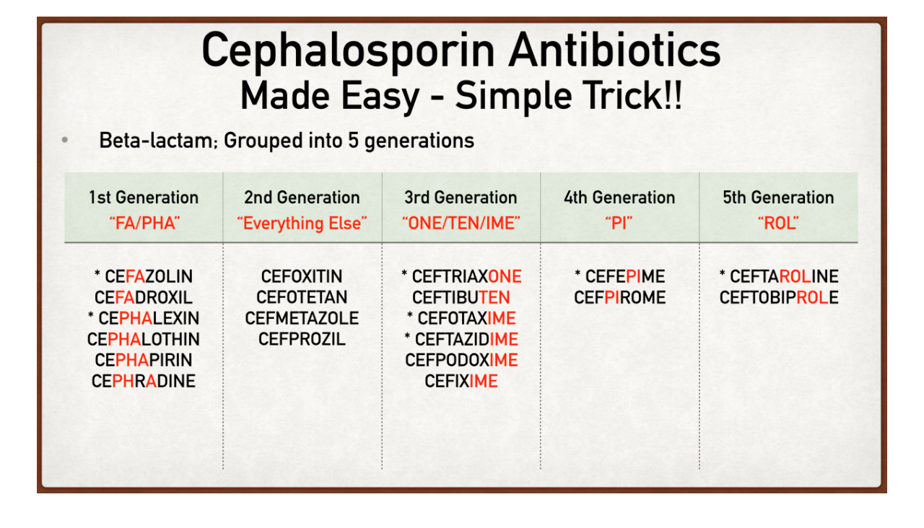
what drugs are in the 1st generations of cephalosprins(6)
cefazolin
cefadroxil
cephalexin
cephalothin
cephaprin
cephradine
what drugs are in the 2nd generations of cephalosprins(4)
cefoxitin
cefotetan
cermetazole
cefprozil
what drugs are in the 3nd generations of cephalosprins(6)
ceftraixone
ceftibuten
cefotaximie
ceftazidime
cedpodoxime
cefixime
what are the 4 generation cephalosprins(2)
Cefepime
Cefpirome
what are the 5th generation cephalosproins(2)
ceftaroline
ceftobiprole
what drugs inhibits protein synthesis
tetracylines
macrolides
aminoglycosides
what are 3 beta-Lactams
penicillins
cephalosporins
Crabapenems
what is the action of penicillins
target penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) when bacteria are growing, disrupting cell wall synthesis
all PCNs have a β-lactam ring joined to a second ring which is essential for antibacterial actions
what is the actions for cephalosproins
Disrupt cell wall synthesis & activate autolysins causing bacterial cell death
what is the action for carbpenems
what are the side effects for penicillin
Lots of GI upset like nausea, vomiting and dirrhea
rash
Urticaria
what are the side effects for fluroquinolone
Aortic aneurysm
photosensitivity,
rash
hepatotoxicity
C-diff
abd pain (n/d)
increased liver enzymes
arthralgia
myalgia tendonitis
tendon rupture
CNS- agitation( confusion, dizziness, drowsiness, ha, insomnia, paranoia)
Black Box Warning Tendon Rupture: Disrupts extracellular matrix of cartilage in immature animals increasing r/f tendon rupture (young/older age, solid organ tx, and taking glucocorticoids)
Black Box Warning Myasthenia Gravis: can exacerbate muscle weakness and should not receive this drug.
what are the side effects for cephalosporin
C. Diff
diarrhea
pain with IM site
phlebitis at IV site
Rarely- neutropenia, agranulocytosis, eosinophilia, lymphocytosis, thrombocytopenia, thrombocytosis
what are the side effects of amphotecicin B
Cerebral palsey
hypotension
n/v/d
hyperbilirubinemia
increase liver enzymes
nephrotoxicity
chills/fever
phlebitis (these are all common!)
what are the side effects for Fluconazole
QT interval prolongation
SJS
hepatoxicity
n/v/d
Vancomycin
inhibits cell wall synthesis, promoting bacterial lysis and death
only for gram posative organism
used for MRSA, C-Diff, seroius inf.
what are some side effects of vancomyocin
renal impairment(esp w/ other renal toxic meds), ototoxicty, and phlebitis
what is the therapeutic level for vancomyocin
10-20mg/L
what are some important things to note about vancomyocin
assess the 8th cranial nerve by audiometry
watch vanc levels for toxicty( under 10= subtherapeutic, and over 15-20= toxicty)
monitor Iv sites cosley for any tissue ncrosiis or severe pain w/ extravastion
educate pt on reporting any tinnitus, vertigo and hearing loss
what are tetracylines
broadspectrum drugs, that suppress bacterial growth by inhibiting protein synthesis by binding to 30S ribosomal subunit and inhibit the RNA transfer to the messenger RNA ribosome complex. This prevents additional amino acids to the growing peptide chain.
what are the side effects of tetracyclines
GI (n/v/d, esophagitis, hepatotoxicity), nephrotoxicity, photosensitivity
what are some important things to note about tetracyclines
avoid bedtime dosing
avoid w/ calcium/dairy, antacids, mag-containing meds, sodium bicarb, iron supplements w/i 1-3 hrs of tetracyclines (chelates-decreases absorption)
Educate pts on reporting any superinfection, use sunscreen & protective clothing, discard outdated prescriptions- toxic
what is Uncomplicated Acute cystitis (UTI)
Mostly women of childbearing age
E.coli is principle organism (80%), then S. saprophyticus, and enterococcus faecalis
S/S: dysuria, urinary urgency, urinary frequency, suprapubic discomfort, pyuria, & bacteriuria (>100,000 urine bacteria)
what are the 1st and 2nd line of defense for treating UTI’s
First line tx: trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole and nitrofurantoin
Second line tx: fluroquinolones and Fosfomycin
what is sulfonamide( actiona nd side effects)
a medication used to treat UTI’s, Inhibit synthesis of tetrahydrofolate (folate derivative). Bacteria will be unable to synthesize DNA, RNA, & proteins
S/E:
hypersensitivity
drug fever
rash [Stevens-Johnson syndrome]
photosensitivity
blood dyscrasias
agranulocytosis
leukopenia
aplastic anemia
thrombocytopenia)
kernicterus (newborns)
renal damage
what is Trimethoprim(action and S/E)
a medication used to treat UTI’s, Inhibit dihydrofolate reductase (enzyme that converts dihydrofolate to its active form: tetrahydrofolate (folate derivative). Bacteria will be unable to synthesize DNA, RNA, & proteins
active aginst most gram neg bacilli and some gram-pos.
S/E:
altered taste, epigastric discomfort, glossitis, n/v, pruritis, rash
Sulfamethoxazole (SMZ) and Trimethoprim (TMP)( pt education)
used togtheor to treat UTI’s, broad spectrum, less microbial resistance
need to assess for infection, IV site for phlebitis, allergies to sulfonamides, renal function, increase fluid intake (1-1.5 L/day), rash (SJS), may cause hypoglycemia, monitor CBC, potassium bilirubin, renal labs, alk phos
Use sunscreen/protective clothing, notify HCP for skin rash, fever, mouth sores, bleeding/bruising. May cause fetal harm (use multiple BC methods)
what are Sulfamethoxazole (SMZ) and Trimethoprim (TMP) contraindicated
Severe hepatic or renal impairment
hypersensitivity to sulfonamides or trimethoprim
drug-induced thrombocytopenia from SMZ or TMP
children < 2 (kernicterus)
What is Nitrofurantoin(action and S/E)
the first drug of choice, a broad spectrum bacteriostatic at low concentrations and bactericidal at high concentrations. Injures bacteria by damaging DNA. Becomes concentrated in the urine
S/E: GI (anorexia, n/v/d, hepatoxicity, c-diff), rust/brown urine discoloration, photosensitive, blood dyscrasias, hypersensitivity, pulmonary fibrosis
what are some contraindications for Nitrofuratonin
Oliguria, anuria, signif renal impairment, pregnancy near term and infants < 1 month.
what are some important points for nitrofuratoin
assess for S/S UTI, I/O, bowl function (c-diff), pulmonary reactions (cough, fever, chills, dyspnea). Monitor LFTs, renal function, CBC periodically
administer w food to decrease GI irritation. DO NOT CRUSH tablets or open capsules. Urine discoloration is not significant, watch for adverse effects
what are some TB drug principles
it needs twio phase active TB treatment
initial is to eliminate dividing bacilli
2 months of 4 daily drugs( rifampin, isoniazid, pyrazinamide, ethambutol)
Continuation phase
4 months w/ 2 daily drugs( Isoiazid, Rifampin)
what kinds of drugs are used to treat TB
rifampin
isoniazid
pyrazinamide
ethambutol
Rifampin action
Inhibits RNA synthesis by blocking RNA transcription in susceptible organisms
Rifampin side effects and considerations
S/E:
HEPATOTOXICITY,
STEVEN JOHNSON SYNDROME
red discoloration of tears & urine
abd pain
n/v/d
flatulence
Nursing Considerations:
Assess liver function
Educate: S/S hepatitis or thrombocytopeni
may decrease oral contraceptive effectiveness;
saliva, sputum, teeth, sweat, tears, urine feces may become red-orange-brown (soft contact lenses may become permanently stained)\
Avoid alcohol!
Do not confuse w/ rifaximin or rifamate
what is the action for Isoniazid
Action-inhibits mycobacterial cell wall synthesis & interferes w/ metabolism.
what are the side effects and considerations for isoniazid
S/E:
HEPATOTOXICITY, Pancreatitis, peripheral neuropathy
Nursing considerations:
Assess liver function
Educate: S/S hepatitis
Avoid alcohol!
what are some actions for Pyrazinamide
converted to pyrazinoic acid in suspectable strains of Mycobacterium which lowers the environmental pH
what are the side effects and nursing considerations for Pyrazinamide
S/E:
HEPATOTOXICITY, hyperuricemia
Nursing Considerations:
Assess liver function & uric acid
Educate: S/S hepatitis, may precipitate acute gout
Avoid alcohol!
Ethambutol action
inhibits mycobacteria growth
what are the side effects and nursing considerations for Ethambutol
S/E:
HEPATITIS, optic neuritis
Nursing considerations:
Assess renal & liver function & uric acid
Educate: S/S hepatitis, may precipitate acute gout
Monitor color discrimination monthly
what are the 3 types of helmonthic infestations
nemotoda
trematoda
cestoda
what is a intestinal nemotoda dn what is used to treat it
a roundworm that infects the intestines
treated w/ albendazole and mebendazole
what is the actions for albendazole
inhibits tubulin polymerization=loss of cytoplasmic microtubules
causes death ot affcected larvae
what are the side effects(3) and considerations for Albendazole
S/E:
Increased LFTs
PANCYTOPENIA
headache
Nursing considerations:
Verify neg pregnancy
Monitor LFTs, WBC
Administer w/ food (high fat)
Use contraception during & at least 3 days after therapy
What is acylovir
An anti-herpes medication that doesn’t cure it but can help reduce signs/symptoms
action: Intereferes w/ DNA Chain replication
what are the side effects and nursing consideration for Acyclovir
S/E:
NEPHROTOXICITY (especially w IV), SEIZURES, STEVEN-JOHNSON SYNDROME, N/V/D, dizziness, headache, pain with IV-phlebitis
Nusring considerations:
MEDICATION COMPLANCE lessens episodes. Start tx ASAP
Avoid sexual contact with lesions present. Condoms to be used with sexual contact
May feel fatigued when starting to take the medication
Assess lesions and monitor renal function (BUN, serum creatinine, & CCr) before/during therapy
USE GLOVES-assess lesions
Disseminated VZV airborne and contact precautions
Women w/ genital herpes-yearly Papanicolaou smears-increased r/f cervical cancer
what is malaria
a parasitic disease that is found mostly in the tropics and transmitted thru a mosquito bite
treated w/ Artemisinin
artemisninin side effects
dizziness
fatigue
HA
weakness
abd pain
anorexia
n/v
muscle pain
what is the antiviral treatment used for COVID-19
Nirmatrelvir and ritonavir = Paxovid
what is Paxlovid
Nirmatrelvir- Inhibits viral replication.
Ritonavir is a pharmacokinetic enhancer with no activity against SARS-CoV-2 but inhibits CYP3A-mediated metabolism of nirmatrelvir resulting in increased nirmatrelvir plasma concentrations.
Recommened to give w/in 5 days of symptoms
can cause GI problesm like dirrhea or dysgesusia
what is dysgeusia
a taste disorder characterized by a distorted or altered sense of taste, where food or drinks may taste metallic, bitter, sour, or otherwise unpleasant, even when they should taste normal.
influenza antivral treatment
Oseltamivir( tamiflu)
what is Oseltamivir( tamiflu)
It is an anti-flu prevention and treatment for flu A and B
inhibits neuraminidase , a viral enzyme required for replication to preevnt the release f virus from the infected cells
can cause a headache
what are some nursing consideratiosn for Oseltamivir( tamiflu)
Flu last 5-10 days, with days 3-5 being the worst w/ symptoms
Not curable, but speeds up viral shedding
Helps lessen the symptoms up to 3 days (if given within 12 hrs of onset)
Only can be given within the first 48 hours of symptoms
what drugs are known to be nerphrotoxic
Acyclovir (especially IV)
aminoglycosides
tetracyclines
vancomycin (especially with other renal toxic medications)
amphotericin B
tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF)
Concurrent use of NSAIDs and other nephrotoxic drugs with TDF may increase the risk of acute renal failure1
what is HIV
a retrovirus (lack self-replication) targeting CD4 cells mainly T lymphocytes (also macrophages and microglia- but these are generally resistant to HIV destruction)
Replicates rapidly during ALL infection stages & mutates rapidly
Spread through infected body fluids: blood, breast milk, semen, vaginal fluids (NOT through urine, feces, saliva, tears)
has 3 phases ( rapid replication, latency, AIDS)
what ae the two actions for drugs to treat HIV
durgs that inhibit HIV enzymes
Drugs that block HIV entry to cells
what are the 4 kinds of drugs that inhibit HIV enzymes
Nucleoside/Nucleotide Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors (NRTIs)
Nonnucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors (NNRTIs)
Protease Inhibitors
Integrase Strand Transfer Inhibitors (INSTIs)
what kinds of drugs block HIV entry into cells
Attachment Inhibitors
Fusion Inhibitors
CCR5 Antagonists
what are the side effects for and main drug of Nucleoside/Nucleotide Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors (NRTIs)
Tenofovir
SE-rash, depression, HA (TDF only)
what are the side effects for and main drug of Nonnucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors (NNRTIs)
Efavirenz
rash and psychiatric/neurological complains (decreased concentration, strange dreams, delusions, mania, increased suicide rates (HR 2.6)
what are the side effects for and main drug of Protease Inhibitors
ritonavir
Lipodystrophy (but also seen with HIV who have never been treated w/ this med), nausea, fatigue, paresthesia, dyslipidemia
what are the side effects for and main drug of CCr 5 Antagonists
Maraviroc
Generally, WELL tolerated. Some have cough, fever, rash, MS problems, abdominal pain, dizziness
Limited impact on lipid levels
what does Hepatitis B treatment look like
The therapy goal for Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is HBV DNA suppression and loss of HBeAG and HBsAG24.
No cure
Recommend to start with tenofovir alafenamide 25 mg daily (low drug-resistance & potent)
6 drugs to treat chronic HBV
Alfa-interfreons( interferon alfa-2b & peginterferon alfa-2a)
nuceleoside analogs(lamivudine, adefovir, entecavir, tenofovir)
what are the two formulatiosn for tenofovir
tenofovir disoproxil fumarate & tenofovir alafenamide
Tenofovir alafenamide(TAF)
1st line agent
Can be used as first line therapy in treatment-naïve patients, prior exposure, or drug resistance to other nucleoside analogs
Better option for renal impairment or osteoporosis
Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF)
Disrupts DNA synthesis
No resistance has been identified in clinical trials
what is alfa-interferons(action and S/E)
Action: multiple viral replication cycle effects-binds to host cell membrane receptors- blocks viral cell entry, synthesis of viral messenger RNA & proteins, and viral assembly/release
used to treat Hepatitis B
Side Effects: flu-like s/s, fatigue, neutropenia, depression, alopecia, n,v,d, anorexia
Black Box Warning: May cause or worsen autoimmune, infectious, and ischemic conditions. Serious neuropsychiatric conditions have occurred (suicide and suicidal ideations)
what are the hepatitis C treatment concepts
The treatment goal for Hepatitis C (HCV) is cure, indicated by undetectable HCV-RNA levels22 .
after 12 months of treatment ALT normalizes in up to 50% of pateints
HCV-RBNA levels are undetectable in up to 40% of pateints= cured
combination therapy
Recommended Naïve Patient with or without Cirrhosis Regimens: Glecaprevir 300mg/pibentasivir 120 mg x 8 weeks (PROTOTYPE); or sofobuvir 400mg/velpatasivr 100 mg x 12 weeks - (without cirrhosis)
Obtain HCG test prior to tx
what is Glecaprevir
a protease inhibitor
needs to be used in combinatiopn w/ another anti-HCV drug
need to be taken w/ food to enhance absorption
can cause hepatotoxicty
what is Pibrentasvir
NS5A inhibiotor, used to treat HCV
Pibrentasvir is combined with glecaprevir (NS3/4A protease). Trade name- Mavyret
Treats genotypes 1-6
Contraindicated with moderate to severe hepatic impairment
what are some nursing consideratiosn when treating HCV
HCV one-time screening for US asymptomatic adults w/o liver disease ages 18-79
Record current medications (including OTC/dietary supplements), monitor & educate about drug-drug interactions (especially with HIV co-infection)
Educate about proper medication administration, ADHERENCE, prevention of reinfection
Assess labs (prior and throughout treatment): CBC, INR, hepatic function (albumin, total/direct bilirubin, alanine aminotransferase [ALT], aspartate aminotransferase [AST]), eGFR, HCV RNA (viral load), HIV antigen/antibody, Hep B surface antigen, HCV genotype, serum pregnancy test, HCV genotype
avoid alcohol
what are the s/s for hepatotoxicty
jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
fatigue
nausea/vomiting,
abdominal pain
dark urine, and pale stools
what are the labs for liver toxicty
alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), total and direct bilirubin, alkaline phosphatase (ALP), and liver function tests (LFTs)