A+P I Lec Exam 2 Ch 4-6
1/199
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
200 Terms
histology
study of tissues
4 basic tissue types
epithelial tissue
connective tissue
muscle tissue
neural tissue
tight junction (cell junction)
weblike strands of transmembrane proteins that fuse together
tight enough to prevent water and solutes passage bw cells
adherens junction (cell junction)
proteins attach to membrane proteins + cytoskeleton microfilaments
form extensive zones → adhesion belts that circle the cell
epithelial resist separation during contractile activities
transmembrane glycoproteins = cadherins
desmosome (cell junction)
link bw CAMs and proteoglycans
connect to cytoskeleton
very strong!
hemidesmosome (cell junction)
transmembrane glycoproteins = integrins
cell to basement membrane connection
gap junction (cell junction)
membrane channel = connexons
ions and small molecules can pass from cell to cell
epithelial tissue
covers every exposed surface of body + internal linings
many cells tightly packed together
no extracellular matrix
cellularity (characteristics of epithelial tissue)
layers of cells bound tightly together
polarity (characteristics of epithelial tissue)
structural/functional differences within same cell
attachment (characteristics of epithelial tissue)
epithelia are attached to basement membrane
avascularity (characteristics of epithelial tissue)
lack of blood vessels but do have nerve supply
regeneration (characteristics of epithelial tissue)
continuously replaced by stem cell divisions
epithelial cells
selective barrier that limits/aids substances in/out of body
protective surface that resists env influences
germinative cells
epithelial stem cells
located near basement membrane
connective tissue
few scattered cells surrounded by large amts of extracellular matrix
-specialized cells
-extracellular protein fibers
-fluid (ground substance)
simple squamous epithelium
cells are thin and flat
location: lines heart, blood vessels, alveoli of lungs
function: reduces friction, controls vessel permeability
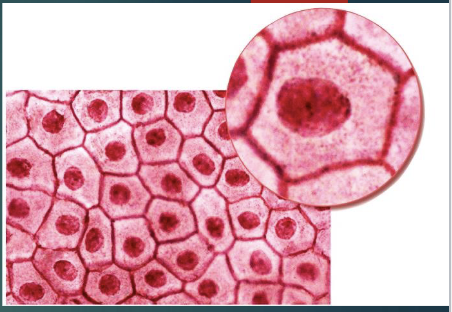
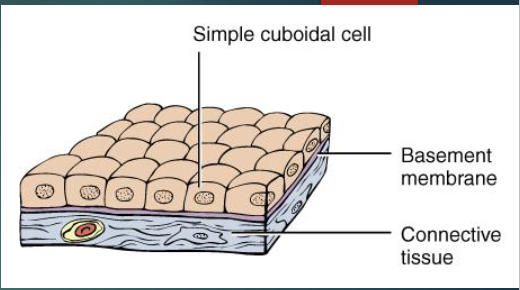
simple cuboidal epithelium
cells look like boxes
location: glands, ducts, thyroid gland
function: protection, secretion, absorption
nonciliated simple columnar epithelium
tall slender cells
location: stomach lining, intestine, gallbladder
function: protection, secretion, absorption
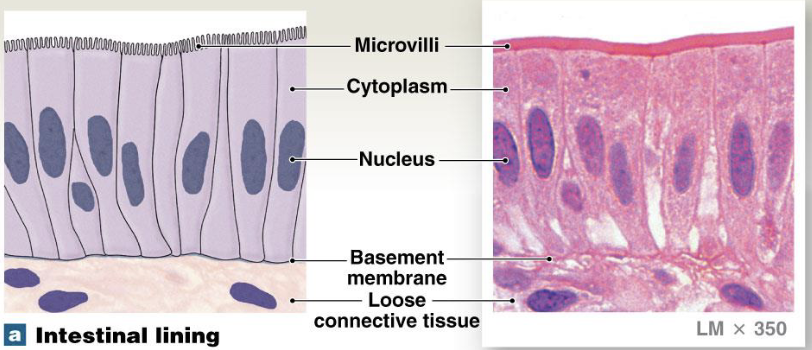
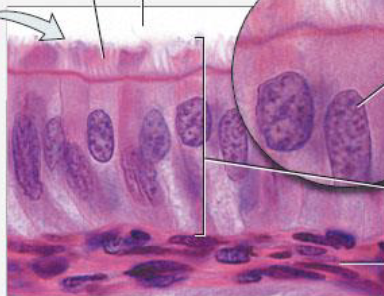
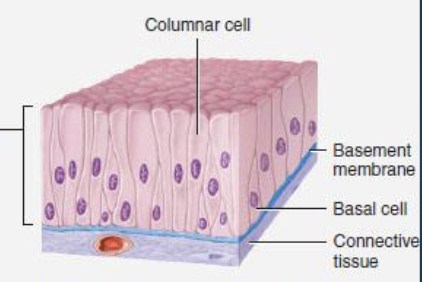
ciliated simple columnar epithelium
tall slender cells
typically have microvilli
location: uterine tube
function: move mucus + foreign particles to throat → cough
nonciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium
tall slender cells
nuclei at various levels, some cells don’t extend to apical surface
location: parotid gland duct lining
function: absorption and secretion
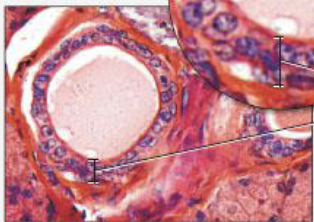
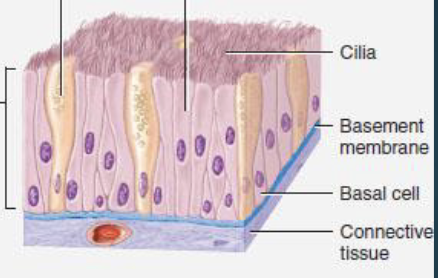
ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium
nuclei at various levels, some cells don’t extend to apical surface
appears stratified but not really, every cell touches basement membrane
location: trachea, bronchi, nasal cavity lining
function: protection, secretion, move mucus with cilia
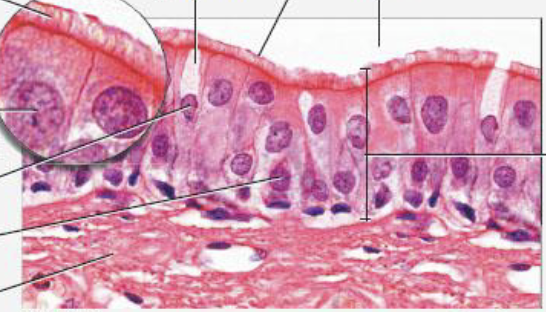
stratified squamous epithelium
found where mechanical stresses are severe
keratinized - skin (tough, water resistant)
nonkeratinized - mouth, throat, rectum, anus, vagina
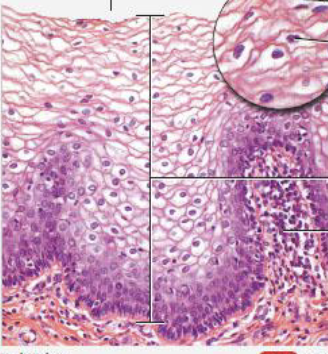
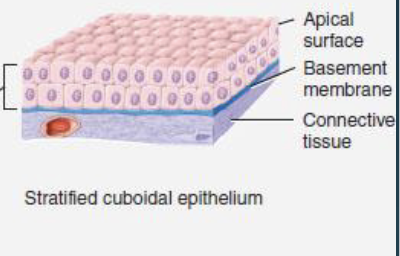
stratified cuboidal epithelium
has 2+ layers of cells
cells in apical layer are cube-shaped
location: esophagus, sweat glands, mammary glands
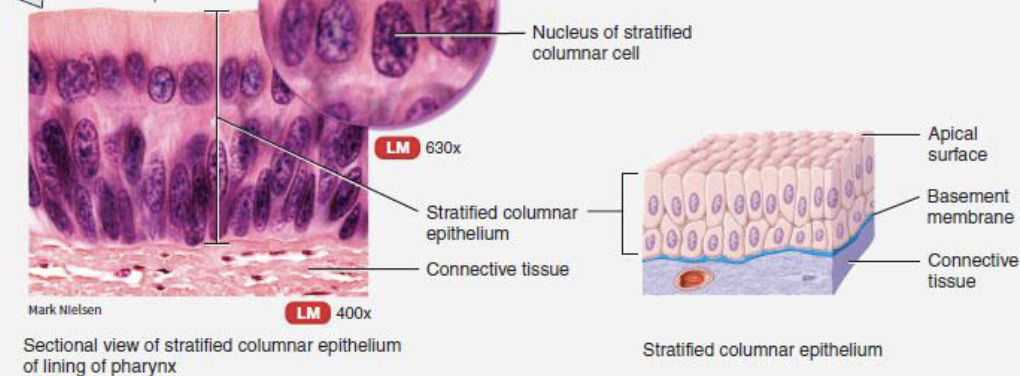
stratified columnar epithelium
basal layers are shortened, irregularly shaped cells, only apical layer has columnar cells
transitional epithelium
appears cuboidal when relaxed
appears squamous when stretched
location: bladder, pelvis, ureters
function: expansion and recoil after stretching
glandular epithelium
single cell or mass of epithelial cells adapted for secretion
endocrine + exocrine
matrix
combo of extracellular fibers + ground substances
largest volume of connective tissue
in the spaces bw connective tissue cells
never exposed to outside env
15% water, 30% collagen fibers, 55% mineral salts
functions of connective tissue
structural framework for body
transports fluids + dissolved materials
protects delicate organs
supports + interconnects other tissue types
stores energy reserves
defends body
embryonic (connective tissue)
mesenchyme
mucus
mature (connective tissue)
loose
dense
cartilage
bone
blood
collage fibers (connective tissue)
long, straight, unbranched
most common
flexible, yet strong
reticular fibers
branching, interwoven
made of collagen but arranged differently
forms network called stroma
stabilizes functional cells of organs
elastic fibers
branched, wavy
composed of elastin
can stretch and return to og length
loose (connective tissue)
packing material of body
fills spaces
cushions/stabilizes organs
supports epithelia
areolar tissue
adipose tissue
reticular tissue
dense (connective tissue)
majority of volume is made of collagen fibers
elastic tissue
irregular tissue
regular tissue
areolar tissue (loose connective tissue)
widely distributed
least specialized
has extensive blood supply
has all cell types and fiber types
adipose tissue (loose connective tissue)
adipocytes filled w triglyceride droplet cytoplasm
nucleus pushed to periphery of cell
white fat and brown fat
reticular tissue (loose connective tissue)
fine interlacing network of fibers → stroma to support parenchyma
location: liver, kidney, spleen
function: supporting framework
regular tissue (dense connective tissue)
shiny white extracellular matrix
mainly collagen fibers bundled with fibroblast
collagen fibers run parallel to each other
elastic tissue (dense connective tissue)
stretches organs, strong and can recoil to og shape after stretching
irregular tissue (dense connective tissue)
fibers form meshwork w no consistent pattern
can stand many stresses
perichondrium
periosteum
cartilage (connective tissue)
firm gel that has chondroitin sulfates complex w protein
chondrocyte
found in lacunae
found in chondroitin which makes cartilage
hyaline cartilage
appears in body as blue-white
most abundant
smooth surface for movement at joints, flexibility, and support
weakest type + can be fractured
elastic cartilage
chondrocytes in network of elastic fibers within extracellular matrix
perichondreum present
maintains shape, provides strength, elasticity
resilient + flexible
fibrocartilage
no perichondreum, very little ground substance, matrix is densely interwoven cartilage fibers
very durable and tough
bone
very little ground substance, has mix of calcium salts, reinforced w collagen fibers
steel = collagen fibers
concrete = mineralized matrix
has osteons that contain lamella, lacunae, osteocytes, canaliculi, and central canals
made of osseous tissue
levels of structure: gross, microscopic, chemical
osteocyte (bone cell)
mature bone cells found within lacunae
canaliculi
connect osteocytes together
hairlike canals that connect osteocytes + lacuna to each other and to central canal
blood (fluid connective tissue)
plasma =watery matrix
cells = formed elements
RBC (erythrocytes), WBC (leukocytes), Platelets (thrombocytes)
arteries
carry blood away from heart
veins
carry blood to heart
capillaries
smallest vessels; site of exchange
lymph
forms when interstitial fluid enters lymphatic vessels
fluid returns to bloodstream
monitered by immune system
membranes
flat sheets of pliable tissue that cover body part
epithelial
-mucus
serous
-cutaneous
synovial
muscular tissue
has fibers that provide motion, maintain posture, produce heat
-skeletal
-cardiac
-smooth
skeletal (muscle tissue)
large cells w many nuclei
can’t divide
stem cells allow for partial repair
actin and myosin organized in striations
aka striated voluntary muscle
cardiac (muscle tissue)
cardiocytes - smaller than skeletal muscle
only one nucleus
intercalated discs - connections bw cells (ex. desmosomes, gap junctions)
very limited ability for repair
aka striated involuntary muscle
smooth (muscle tissue)
small, spindle-shaped cells w 1 nucleus
able to divide; regenerate after injury
actin and myosin arranged differently (no striations)
aka nonstriated involuntary muscle
neural tissue
neuron - longest cells in the body
can’t divide, poor ability for repair
3 regions: dendrites, cell body, axon
neuroglia - supporting cells
tissue repaid
replaces worn out, damaged, dead cells
epithelial tissue replaced by stem/undifferentiated cells
not all connective tissues can repair
muscle cells have limited repair
nervous cells repair is 50/50
fibrosis
formation of scar tissue
integumentary system
cutaneous membrane = skin
hair
glands (sudoriferous + sebaceous)
nails
sensory receptors
epidermis
superficial layer, has epithelial tissue
avascular, keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
many layers of cells
dermis
under epidermis
mostly dense irregular connective tissue
has nerves, blood/lymphatic vessels, hair follicles, oil and sweat glands
hypodermis
subq/subcutaneous fat makes up 80% of body fat
deep to skin
not part of skin, shares some functions
made of adipose tissue, some areolar tissue
anchors skin to underlying tissue
keratinocyte
specialized for producing keratin
melanocyte
produces melanin pigment
protects nucleus from UV damage
langerhans/dendritic cell
aka intraepidermal macrophage
immune cells
defense against microorganisms that penetrate upper layers
merkel cell
tactile epithelial cells
sensory receptors that sense touch
stratum corneum (layers of epidermis)
multiple layers of flattened, dead, interlocking keratinocytes
water resistant
permits slow water loss by insensible perspiration
stratum lucidum (layers of epidermis)
appears as glassy layer in thick skin only
stratum grandulosum (layers of epidermis)
keratinocytes make keratin
keratin fibers get thinner and flatter
cell membranes thicken and cells die
stratum spinosum (layers of epidermis)
keratinocytes bound by desmosomes
stratum basale (layers of epidermis)
deepest layer
attached to basement membrane
has stem/basal cells, melanocytes, + merkel cells
keratinization
newly formed cells slowly pushed up
accumulate more and more keratin
undergo apoptosis and then replaced
thin hairy skin
covers most body parts
thick hairless skin
covers palms, digits, and soles
papillary (layers of dermis)
areolar tissue thin collagen fibers
dermal ridges house capillaries, free nerve endings
reticular (layers of dermis)
irregular connective tissue
lots of collagen fibers → strength, resiliency
bind water, keep skin hydrated
elastic fibers → stretch-recoil fibers
extends into papillary layer + hypodermis to bind everything together
ceavage lines
tension
caused by many collagen fibers running parallel to skin - externally invisible
stretch marks
when dermis is extremely extorted
rapid weight gain or pregnancy
epidermal ridges + dermal papillae
more surface area for attachment to basement membrane → ridges in the skin (ex. fingerprints)
ridges on fingers + toes increase friction → secure grip + sense of touch
melanin
pigment formed by melanocytes in epidermis
pheomelanin - yellow → red
eumelanin - brown → black
skin color differs due to amt of melanin
darker ppl have more melanin
protects (epi)dermis from UV radiation
albinism
genetic condition causing absence of melanin production in skin, hair, eyes
hemoglobin
red pigment in RBC
carotene
orange pigment in epidermal cells
most apparent in light-skinned ppl
can be converted to Vit A
helps maintain epidermis + eye photoreceptors
UV radiation
can cause DNA mutation → skin cancer
destroys folate (folic acid)
necessary for Vit D production
cyanosis
bluish coloration of skin
lack of oxygen or extreme cold
easiest to see on thin skin (lips, under nails)
jaundice
too much bilirubin in skin (liver disorders)
yellowish coloration of skin
pallor
paleness of the skin
can be caused by shock, anemia, low blood pressure
erythema
redness of the skin
due to skin injury, inflammation, heat exposure, infection
sebaceous gland
oil gland
widely distributed
connected to hair follicles
secretes sebum, inhibits bacterial growth, softens hair + skin
inactive during childhood, activated by hormones during puberty (ex. androgens)
sudoriferous gland
sweat gland
all skin except nipples + external genitalia
eccrine + apocrine
myoepithelial cell
contract upon nervous system stimulation to force sweat into ducts
eccrine (sudoriferous gland)
most numerous
ducts connect to pores on skin surface
apocrine (sudoriferous gland)
mainly in hairy skin areas
ducts empty into hair follicles
ceruminous gland
modified apocrine gland in ear canal
mammary gland
secrete milk