Earths Climate Flashcards
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
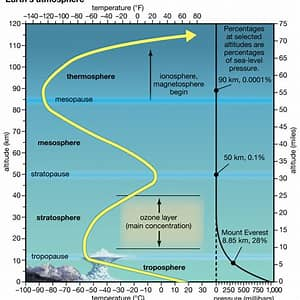
Troposphere
Where sulfur, pollution, and aerosols go Cools the planet briefly
Where all of the weather happens
Atmosphere
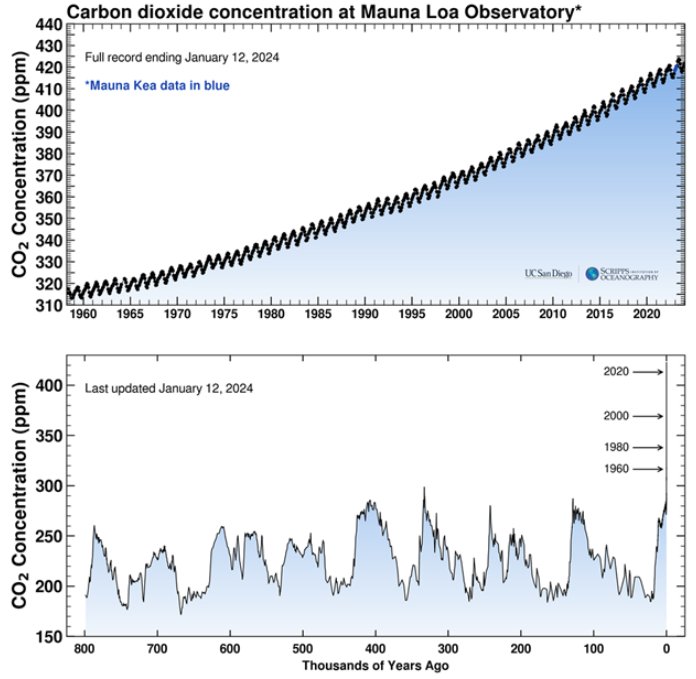
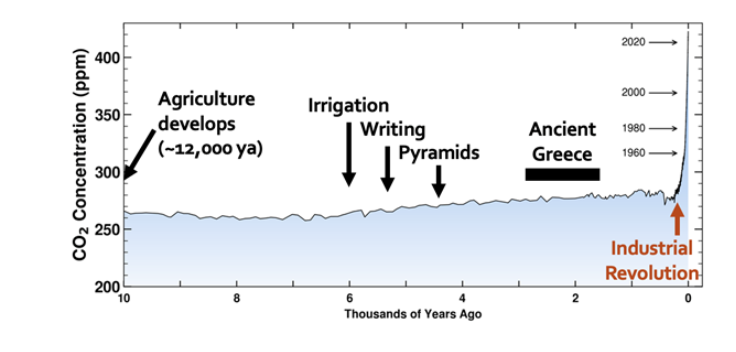
Current CO2 is 420 (double from the industrial revolution of 280 ppm)

Oceans
Phytoplankton hang out in the top part of the ocean to perform Photosynthesis
Phytoplankton are at the bottom of the ocean food chain
Ocean snow bringing CO2 into sediment
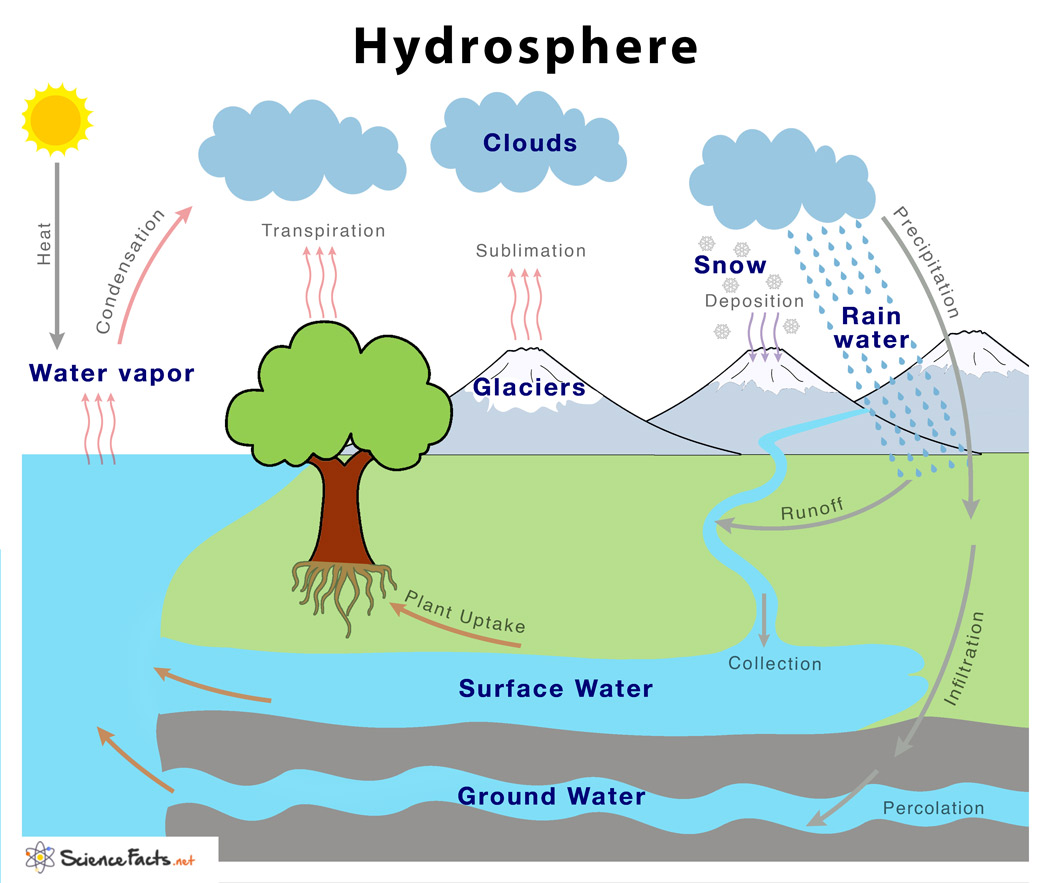
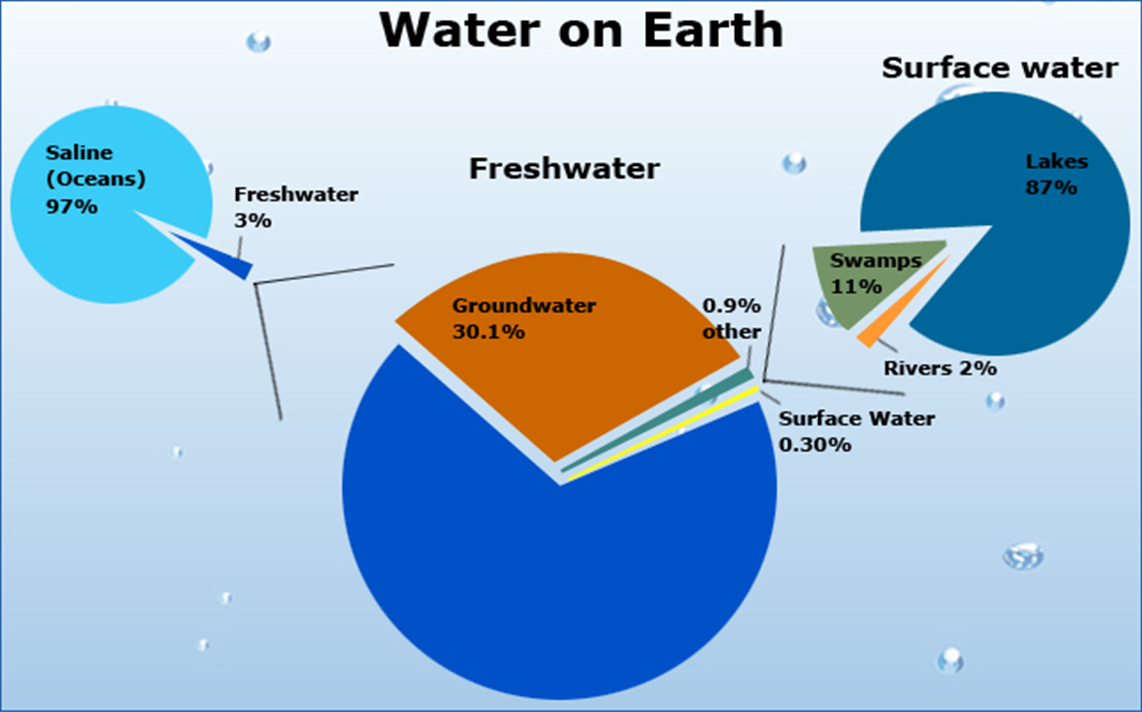
Hydrosphere
Water systems
Salt and fresh water
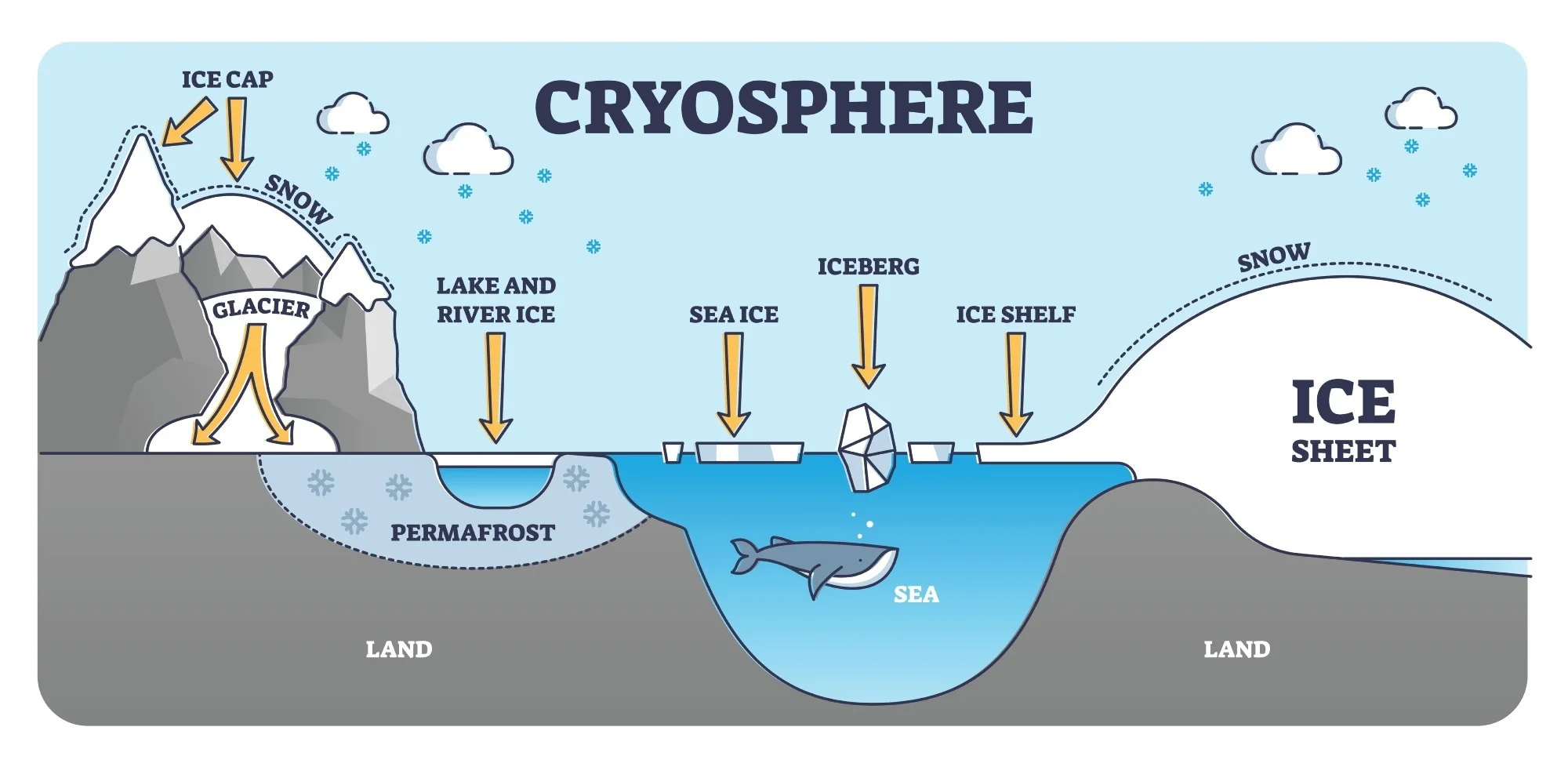
Cryosphere
Ice caps and ocean ice
North hemisphere (formed in the late Cenozoic era)
South hemisphere (formed in the mid Cenozoic era)
Geosphere
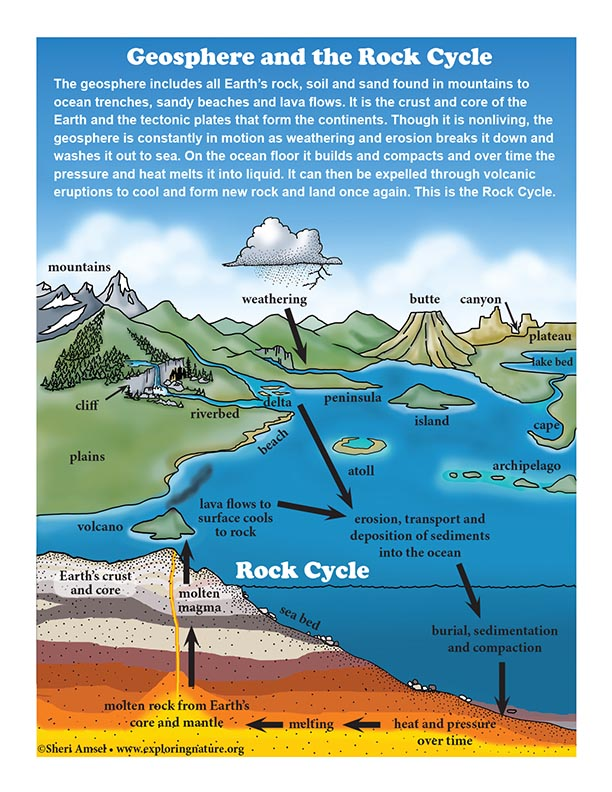
rock and earths systems
Silicate weathering
Limestone (CaCO3)
Quartz (SiO2)
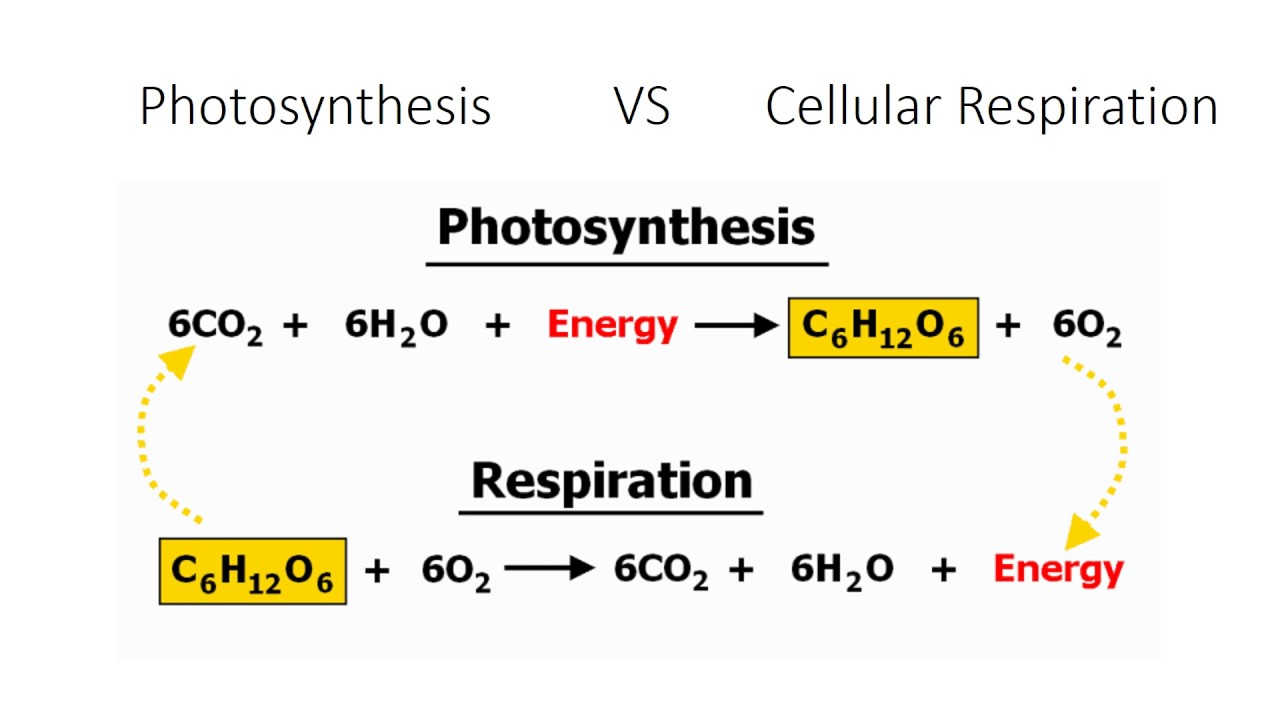
Biosphere
living systems (ecosystems)
Photosynthesis vs cellular respiration
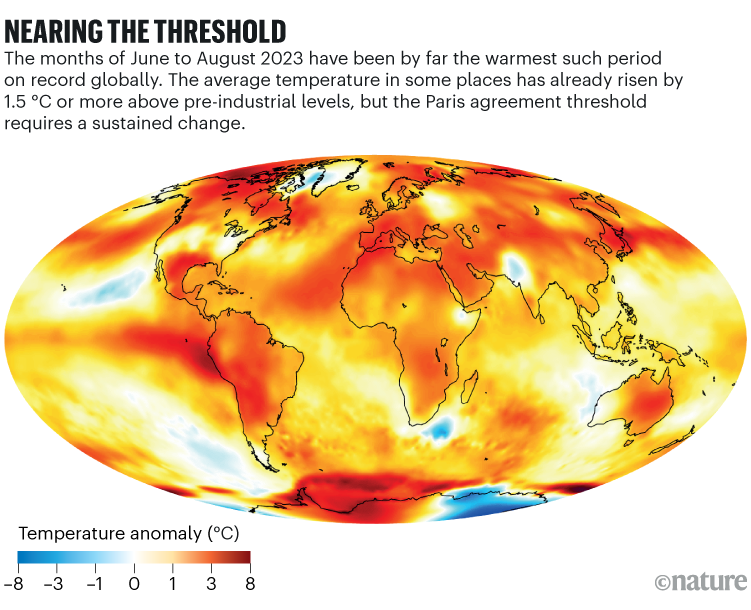
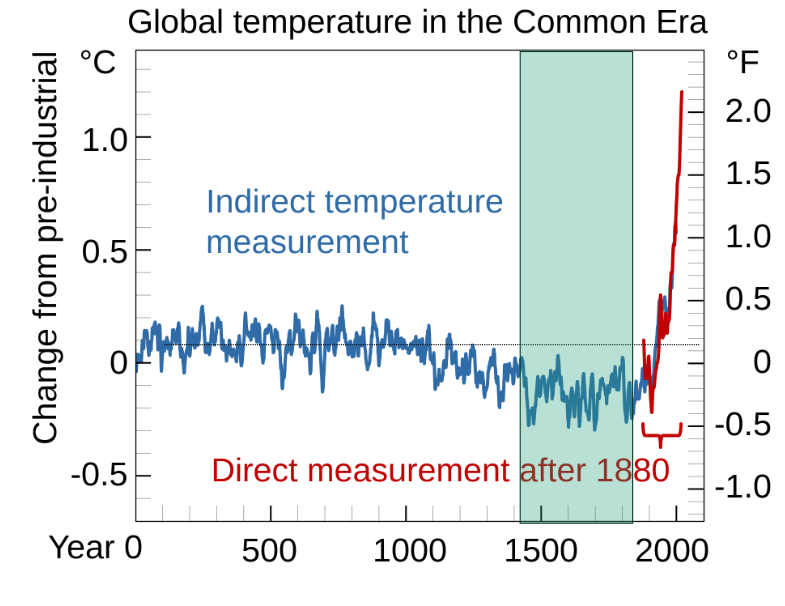
Climate Observations: Globally
2024 & 2023 were some of the hottest years globally
“pause” of temperature rise from 1940-1980 arousal pollution
The majority of CO2 was emitted mid the 1970s
1-1.5 Celsius warming since preindustrial times
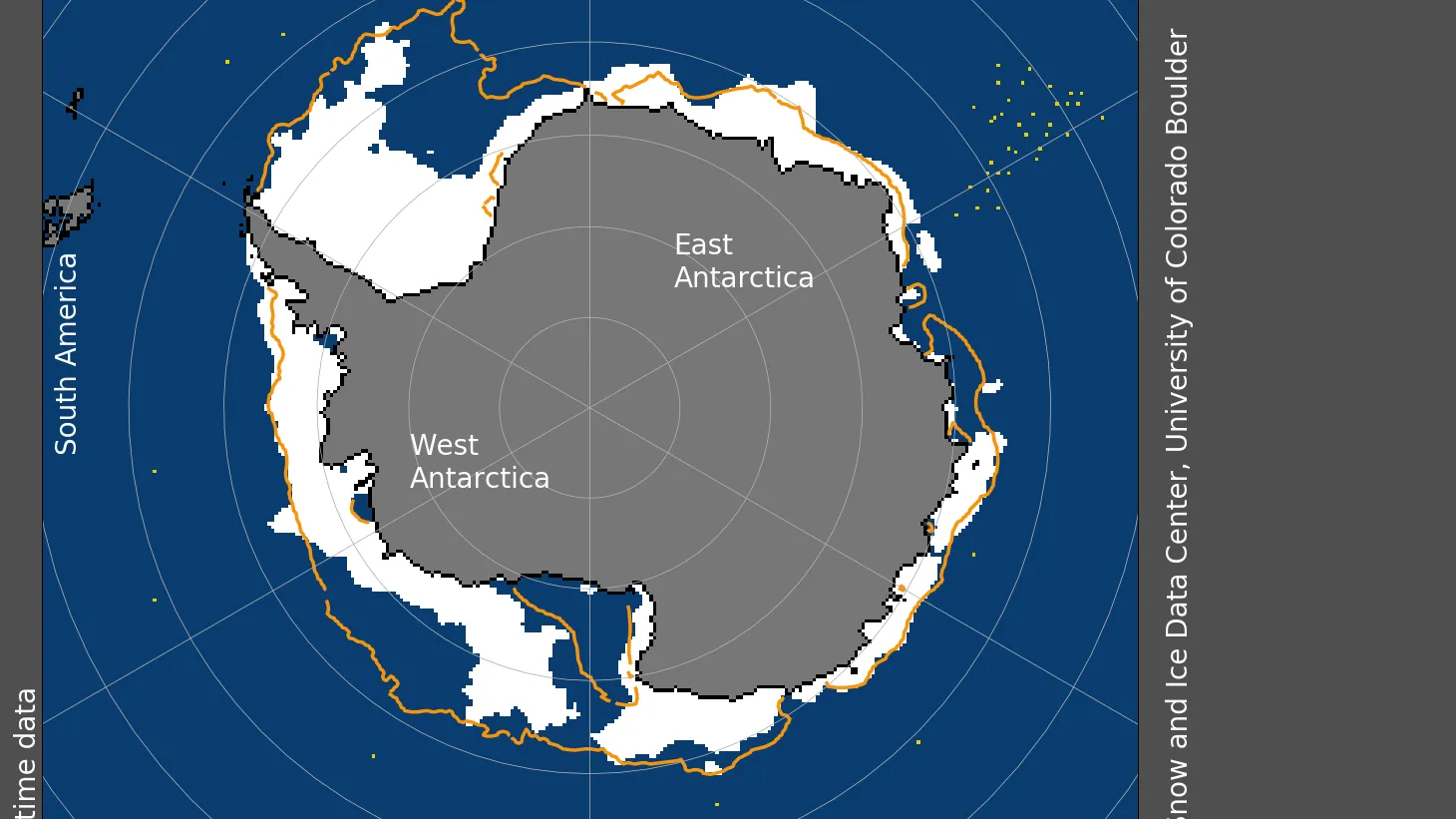
Climate observations: Cryosphere
Decrease in sea ice from ice not staying frozen
Arctic is melting faster than the Antarctic
However, 2023 & 2024 shows sea ice swiftly disappearing
Contributes to sea level rise
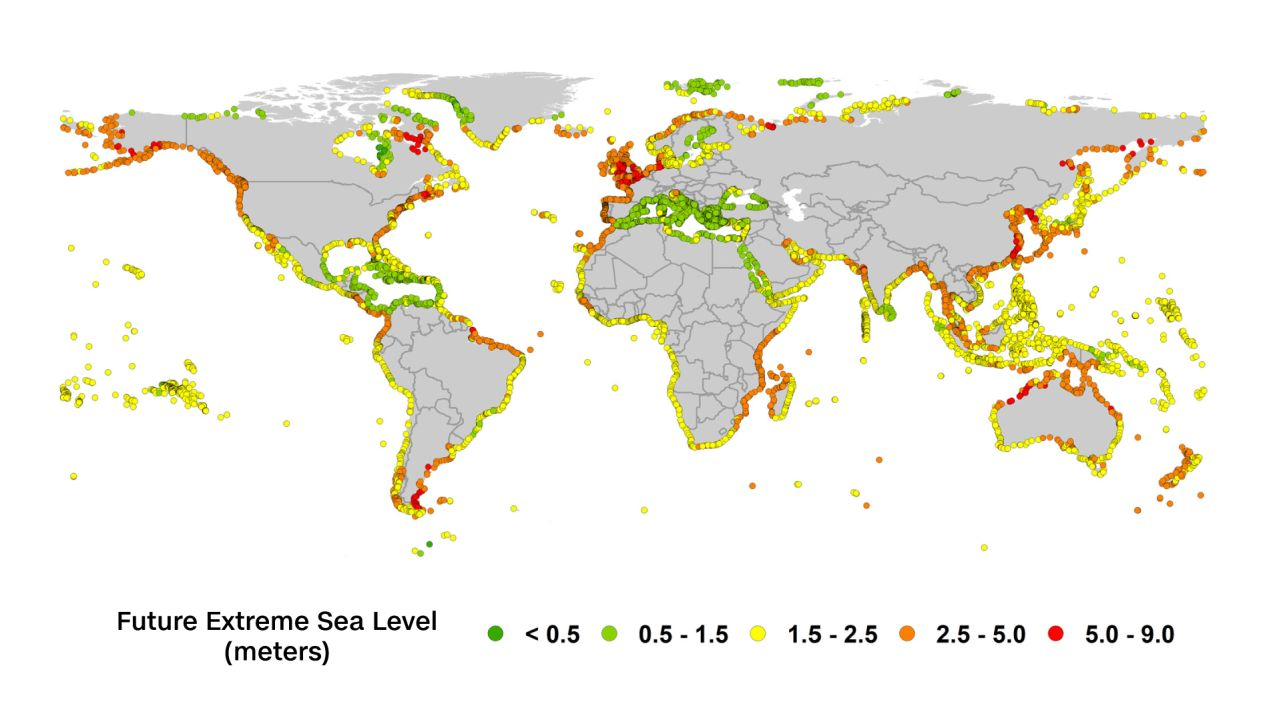
Climate observations: Sea level rise
Most of the rise is form thermal expansion (it literally getting physically bigger)
ice melting contributes to a change in sea salinity
Climate observations: Atmosphere
CO2 is rising swiftly
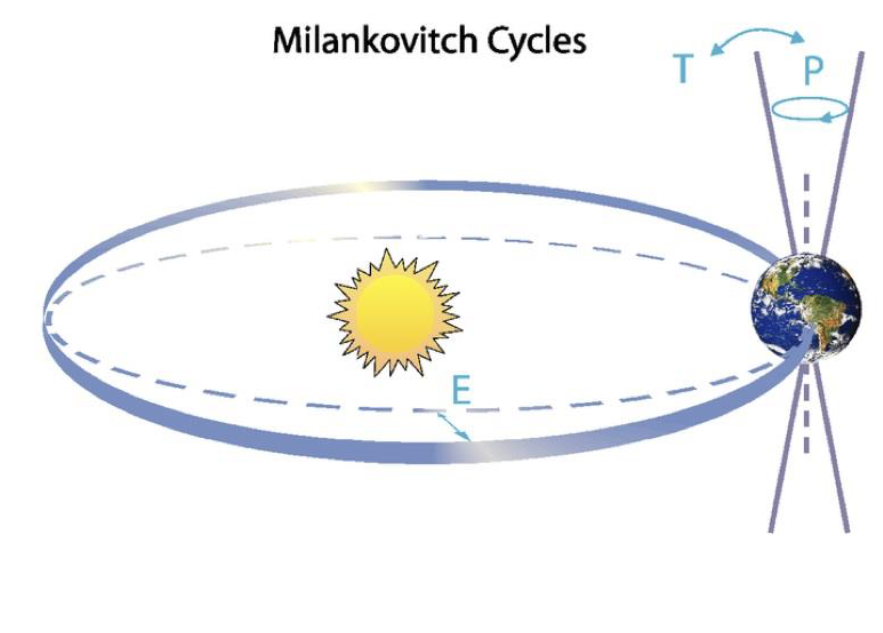
Milanovich cycles
Roughly 100,000 years long
Tilt
Eccentricity
Precession
Changes how much solar radiation earth receives
Shift recently in temperatures DO NOT line up with the Milinkovich cycles because we are “supposed” to be going into a cooler climate if so (BUT THATS NOT HAPPENING)
Paleoclimate
Climate in the past
Using proxies such as
tree rings (now to 2000 years)
Ice cores (now to 800,000 years)
Marine sediments (now to hundreds of millions of years)
Tree Rings
Ice cores
marine sediments
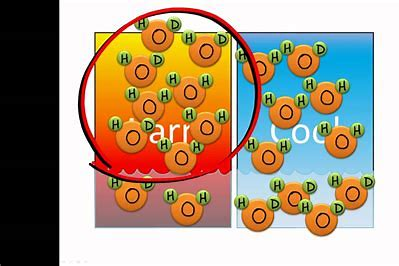
Isotopic fractionation
measured in ice cores and marine sediments
Hotter temperatures can evaporate “heavier elements” which go back into precipitation
Deuterium- heavy hydrogen
(shows in ice cores more when temp was high)
O18- heavy oxygen
(In ice more when temp is high)
(in ocean sediments when more when temps are low)
C13- Heavy carbon
(biosphere prefers lighter C12)
(low C13 in air shows more fossile fuels contribution)
Late holocene
Last 2000 years
Recent human and earth history
CO2 spiked
Holocene
Last 12,000 years
Coming out of the last glacial period with more climate stability
Agriculture invented 10,000 years
CO2 was stable
Plastiocene
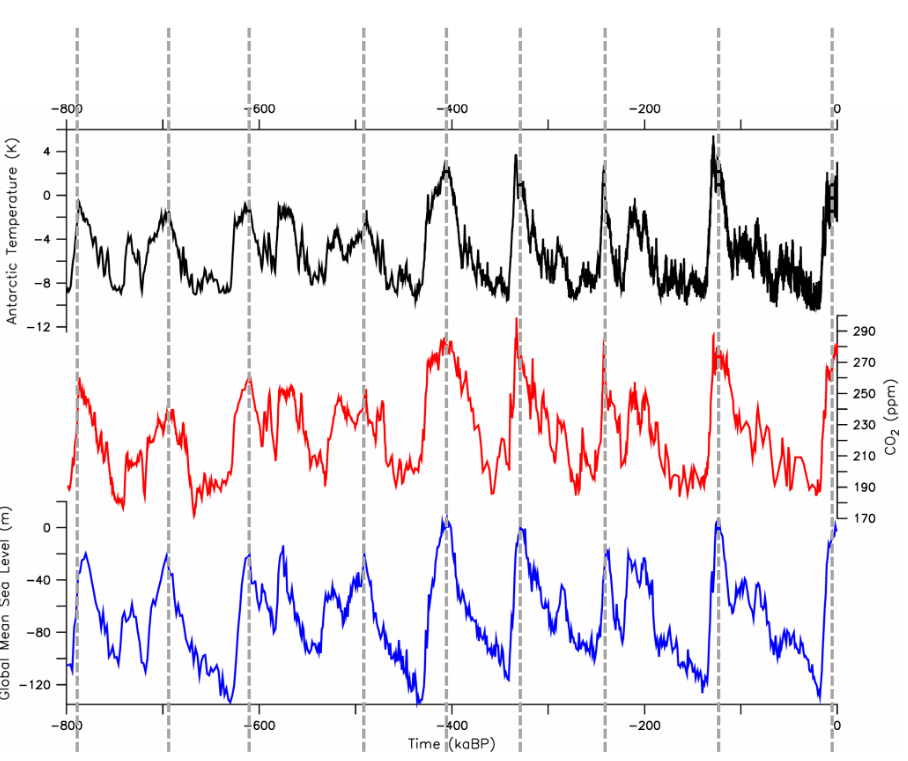
Last 2.58 million years
Ice ages and very variable climate
When temp is low, CO2 is low
Cold water dissolves more CO2 (think like a warm flat soda)
albedo loop
Cenozoic
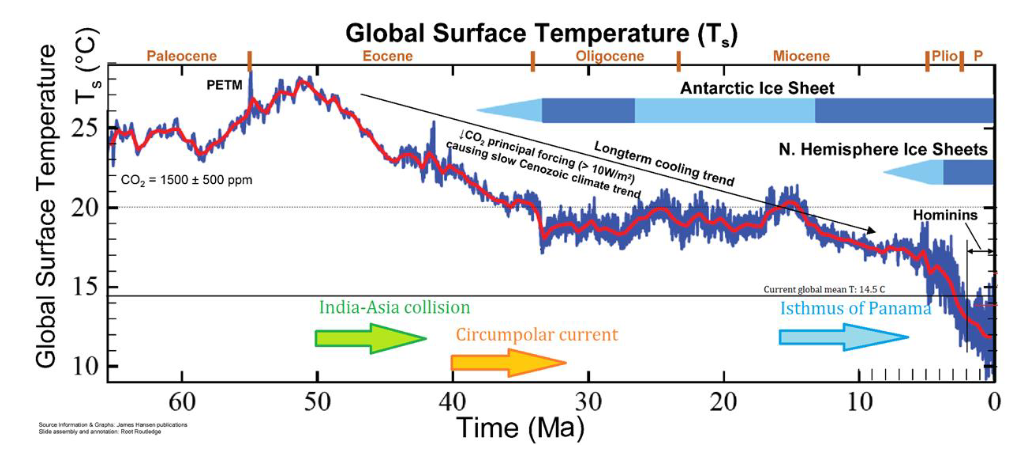
Last 66 million years
Started 15 Celsius hotter but started a downward temp trend due to silicate weathering
The silicate weathering is from the uplift of the Himalayas made from Africa bumping into India
PETM due to large volcanic eruptions spewing CO2 & blubbering basalt (carbon-rich sediments leading to temp rise) End permian
End cretaceous asteroid crashes into earth and releases aerosols (colder temps)
The circumpolar current is made from the Drake passage (south America and Antarctica) being opened. it’s a cold current keeping Antarctica frozen
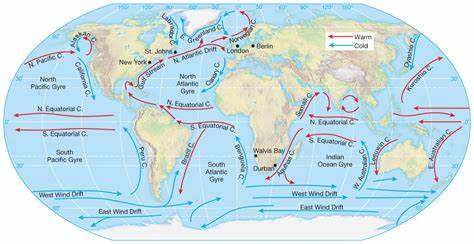
Ocean currents
Downwelling- colder, saltier water
Upwelling- hotter, lighter water
This contributes to the ocean carbon cycle
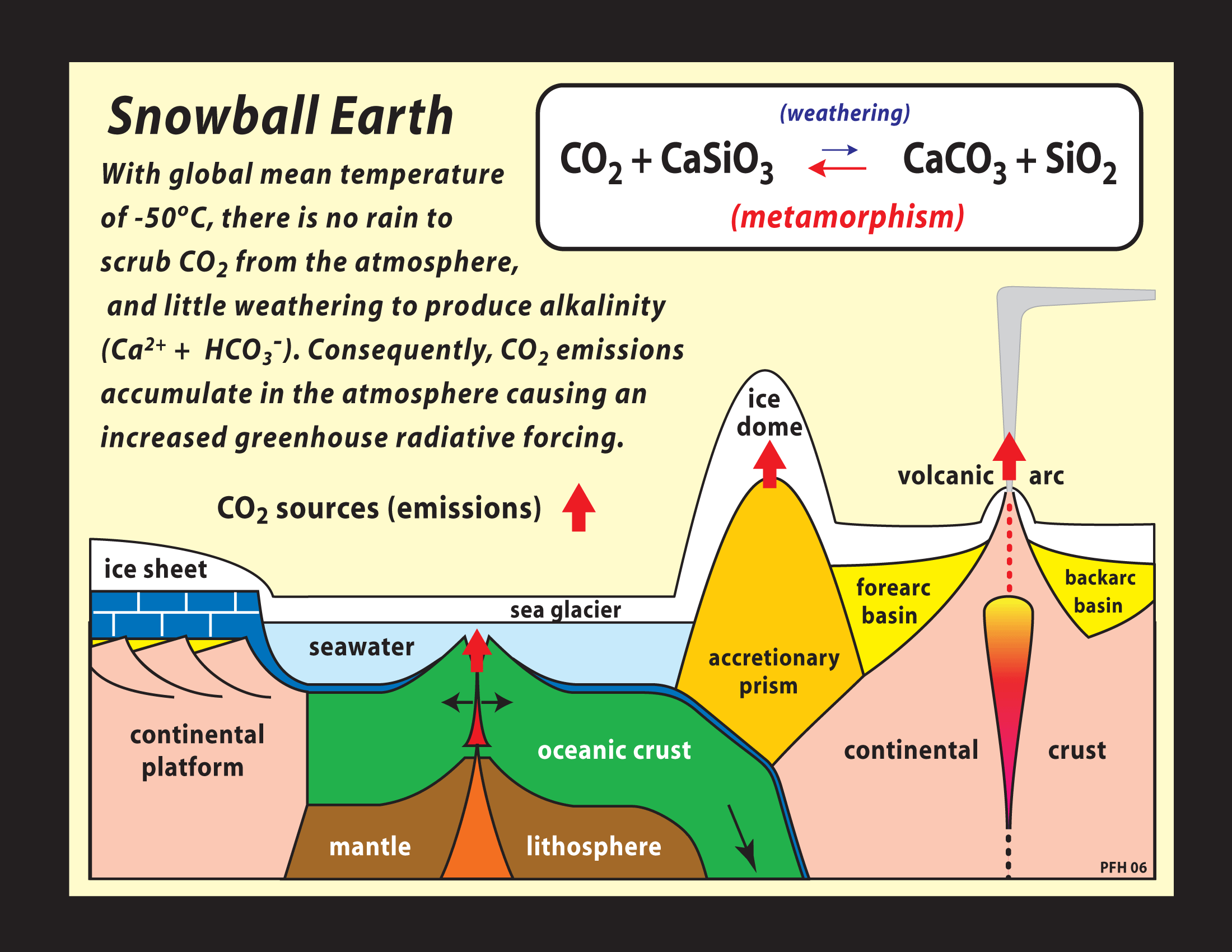
Snowball earth
Volcanic silicate weathering around the equator causing a cooling in that area via more rain
Cools into ice and ice reflects light back into space via Albedo effect
Brought back to life via CO2 volcanic activity
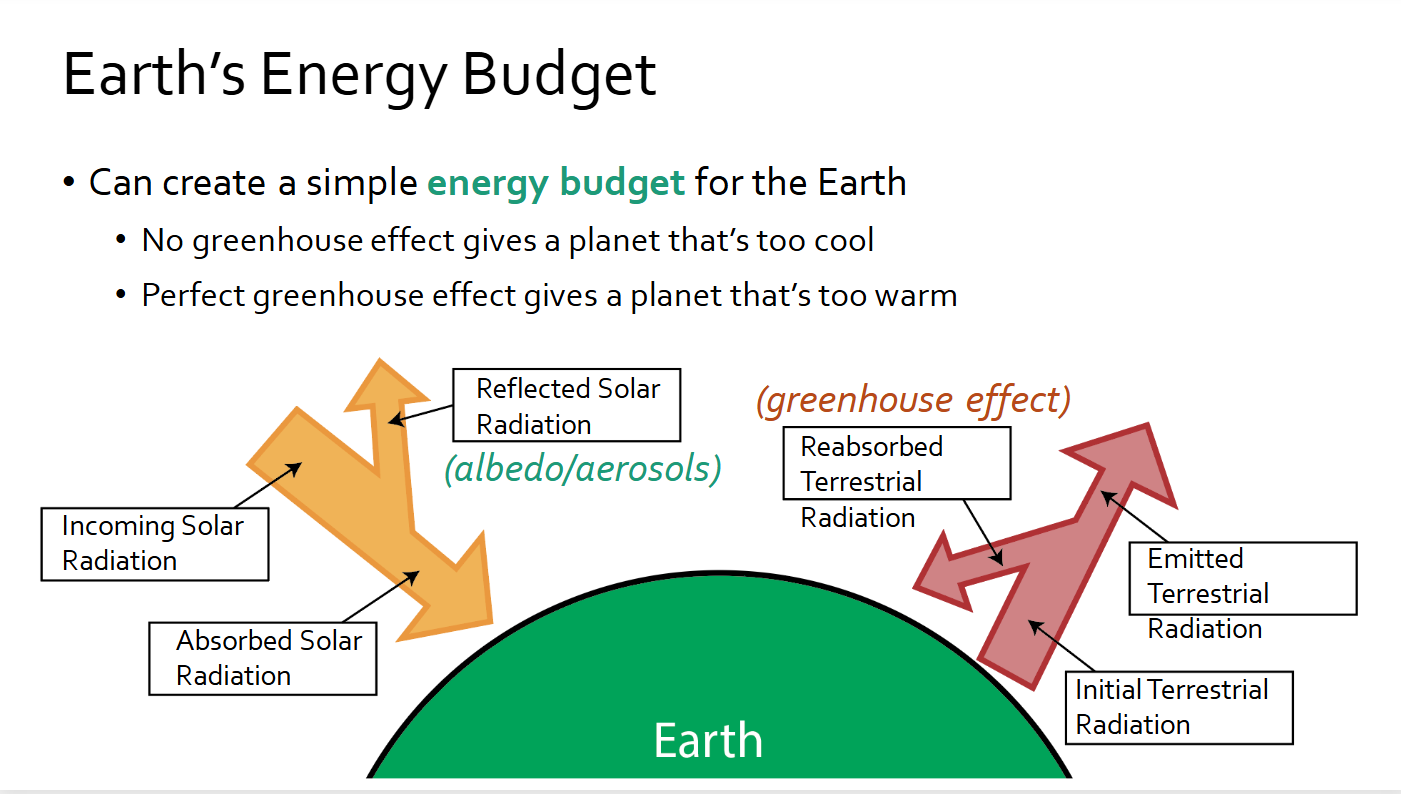
Energy budget
How much radiation earth takes in and how does the atmosphere interact with it
Ozone grabs UV light
Most of sunlight makes it to us
70% of light stays trapped via greenhouse gasses and warms the planet
Positive climate feedbacks
Amplified over time
Ice-Albedo reflecting light back into space making earth colder
Water vapor and methane causing more warming causing trapped material to repeat the process
Negative climate feedbacks
Dampens overtime
Ocean Gas exchange
Silicate weathering
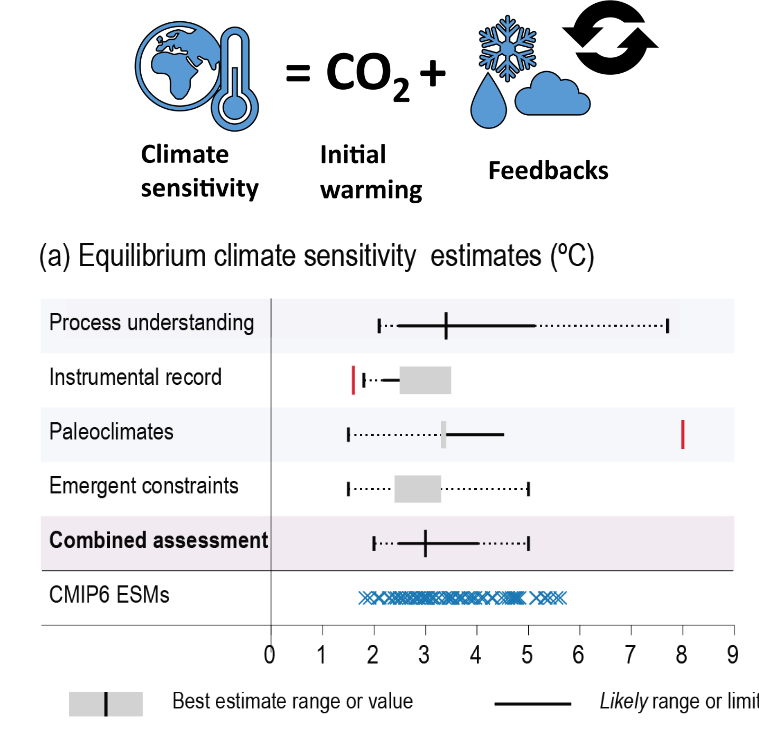
Climate sensitivity
Total amount of warming via radiative forcings (energy from the sun) + other relevent feedbacks
Equilibrium Climate Sensitivity is from CO2 doubling causing a raise in temp
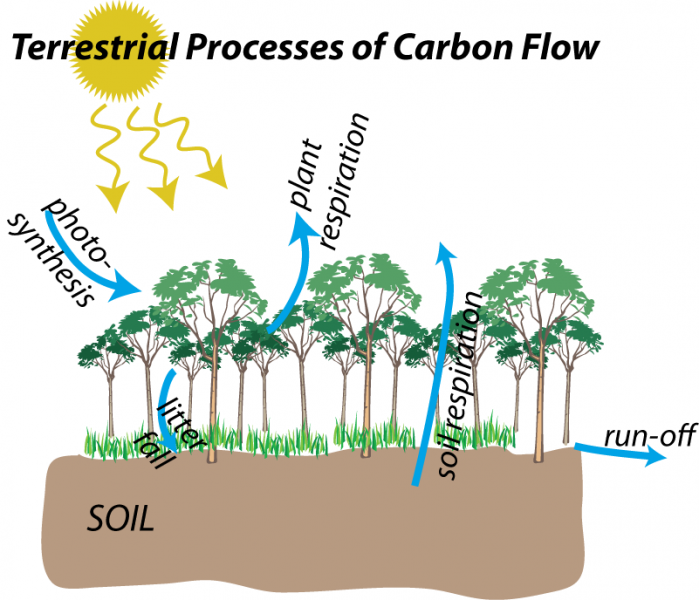
Terrestrial Carbon cycle
Fast processes (stays and leaves fairly fast)
Biological processes
Slow processes (stays and leaves fairly slow)
Silicate weathering
silicates + H2O + CO2 → dissolved ions → rivers → oceans → sequestered in ocean sediments/rocks)
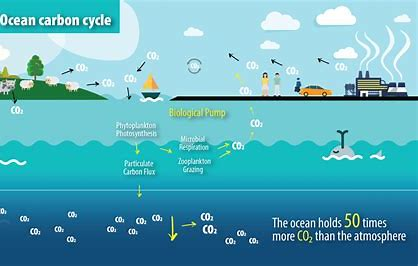
Carbon Cycle in Oceans
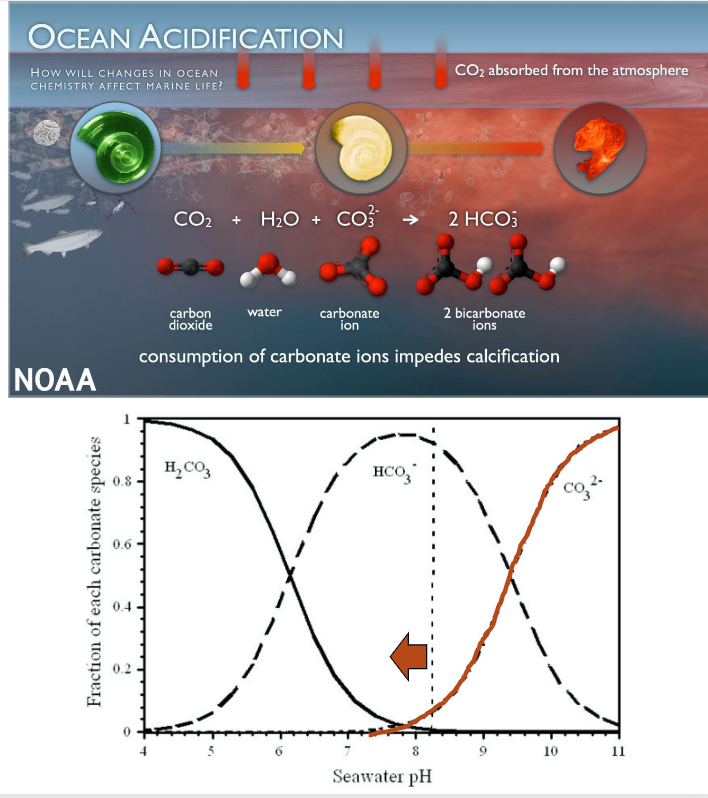
Ocean acidification
Ocean Atmosphere exchange
Calcifies role
Anthropogenic Carbon
We know because of
Economic data (countries physically telling us)
Carbon isotopes (fossil fuels have a low C13)
Atmospheric Oxygen concentration (less oxygen in the air)
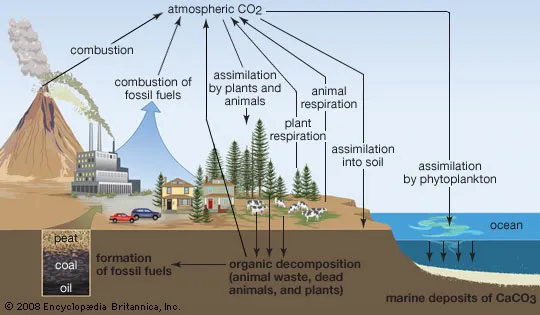
Summary
Humans put so much CO2 into the atmosphere
CO2 has doubled since pre-industrial PPMS
Greenhouse effect