Biology 302- Chapter 5: DNA and Chromosomes
5.0(4)
Card Sorting
1/50
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 11:59 PM on 2/5/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
1
New cards
Who were James Watson & Francis Crick?
They were the men who helped discover the structure of DNA. They additionally revealed how DNa might be copied and encodes the instructions for making proteins.
2
New cards
Who was Rosalind Franklin?
She was a X-ray crystallographer who obtained excellent diffraction patterns of B-form DNA and discovered important basic facts about its structure.
3
New cards
How did scientists discover that DNA was the genetic material?
Fred Griffith performed an experiment using two strains of pneumococcal bacterium, a pathogenic s-strain and a non-lethal r-strain. When the living r-strain and the heat-killed s-strain were both injected in the mice, the mouse still died. Then the strain cells were isolated to find what caused the mouse to die. It was determined that the molecule that carries the heritable “transforming principle” is DNA.
4
New cards
What is chromatin?
It is the combination of DNA and proteins that make up the contents of the nucleus of a cell.
5
New cards
What are purines? What nucleotides do they consist of?
Purines are organic compounds with double ring structures. The purine nucleotides are Adenine and Guanine.
6
New cards
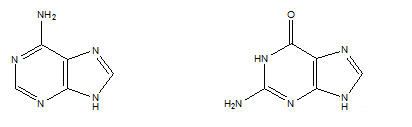
What is this an image of?
Purines, specifically guanine and adenine.
7
New cards
What are pyrimidines? What nucleotides do they consist of?
Pyrimidines are organic compounds with single ring structures. The pyrimidine nucleotides are Cytosine, Thymine, and Uracil.
8
New cards
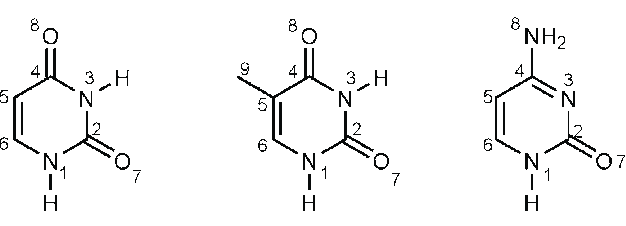
What is this an image of?
Pyrimidines, specifically thymine, cytosine, and uracil.
9
New cards
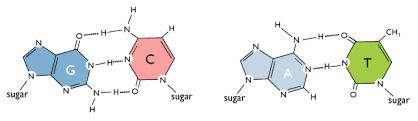
What are the nucleotides in DNA that bond together? RNA?
G forms a triple hydrogen bond with C, A forms a double hydrogen bond with T.
10
New cards
What is the bond that makes up the sugar-phosphate backbone of DNA? What type of bond is it?
It is the phosphodiester bond; covalent.
11
New cards
What is the difference between a nucleotide and a nucleoside?
\-tide = sugar-phosphate covalently linked to a base
\-side = sugar covalently linked to a base (no phosphate group)
\-side = sugar covalently linked to a base (no phosphate group)
12
New cards
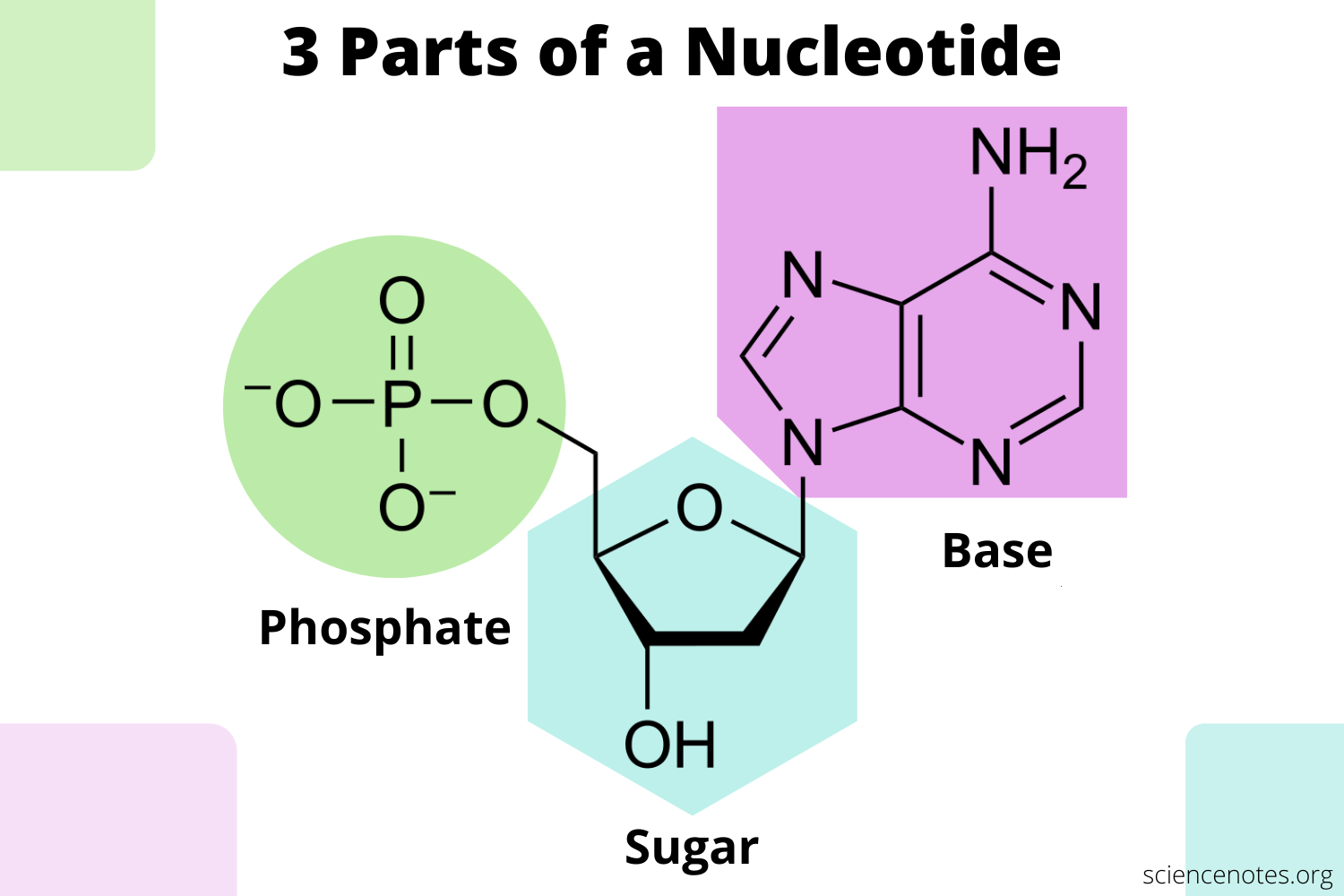
Identify the 5’ and 3’ ends on this nucleotide.
\
Bonus: what is this nucleotide’s base?
\
Bonus: what is this nucleotide’s base?
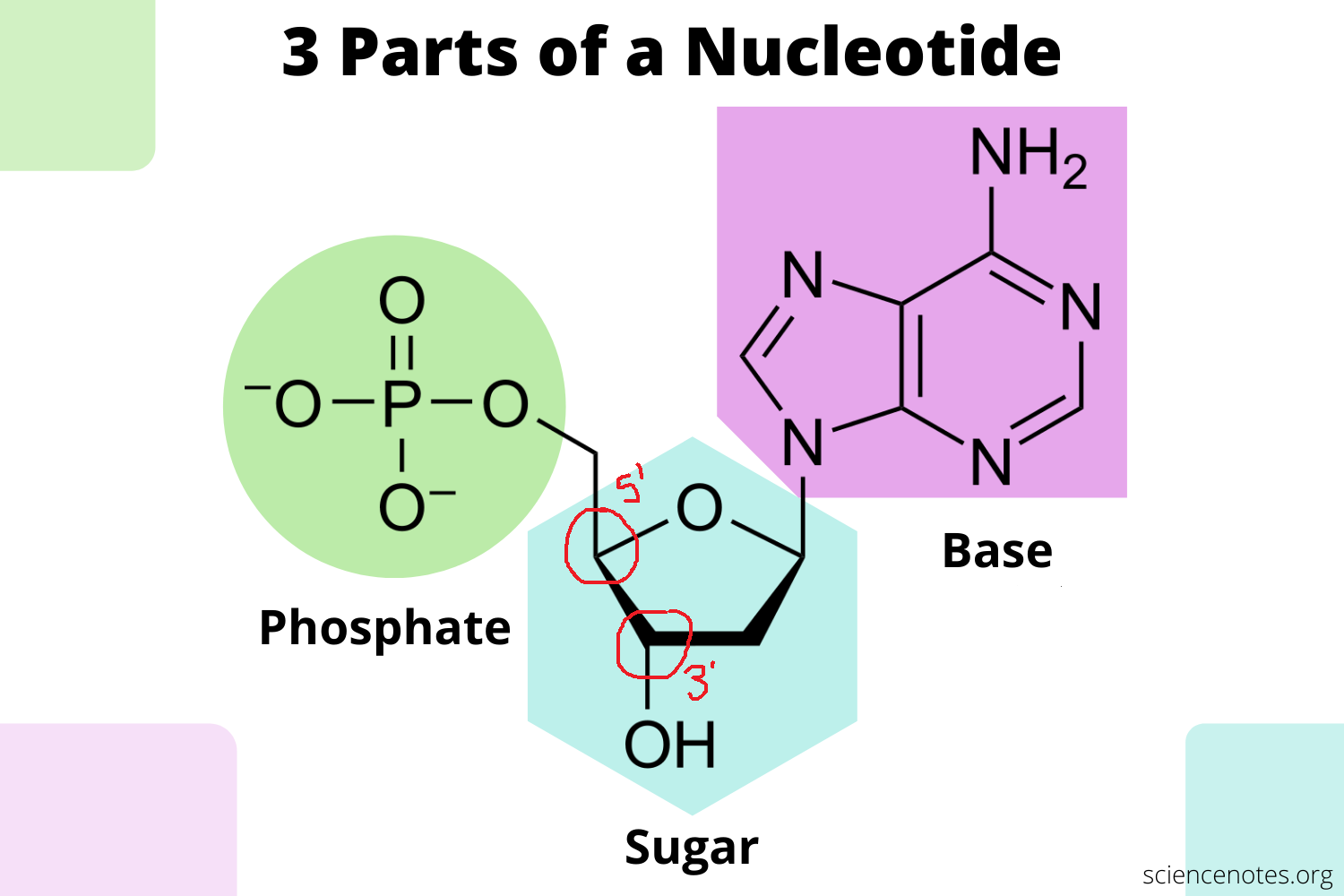
13
New cards
DNA strands run ______ to each other in the DNA molecule.
anti-parallel
14
New cards
![\[T/F\] Each groove in the structure of DNA is the same size.](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/654f079227c54d9ebb8260ac28a0bd28.jpeg)
\[T/F\] Each groove in the structure of DNA is the same size.
False. There is a major groove and a minor groove.
\
The image on the “term” side is over-simplified and neglects to show the difference in grooves.
\
The image on the “term” side is over-simplified and neglects to show the difference in grooves.
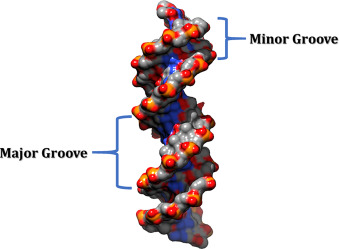
15
New cards
What is the name of the process of nuclear division?
Mitosis
16
New cards
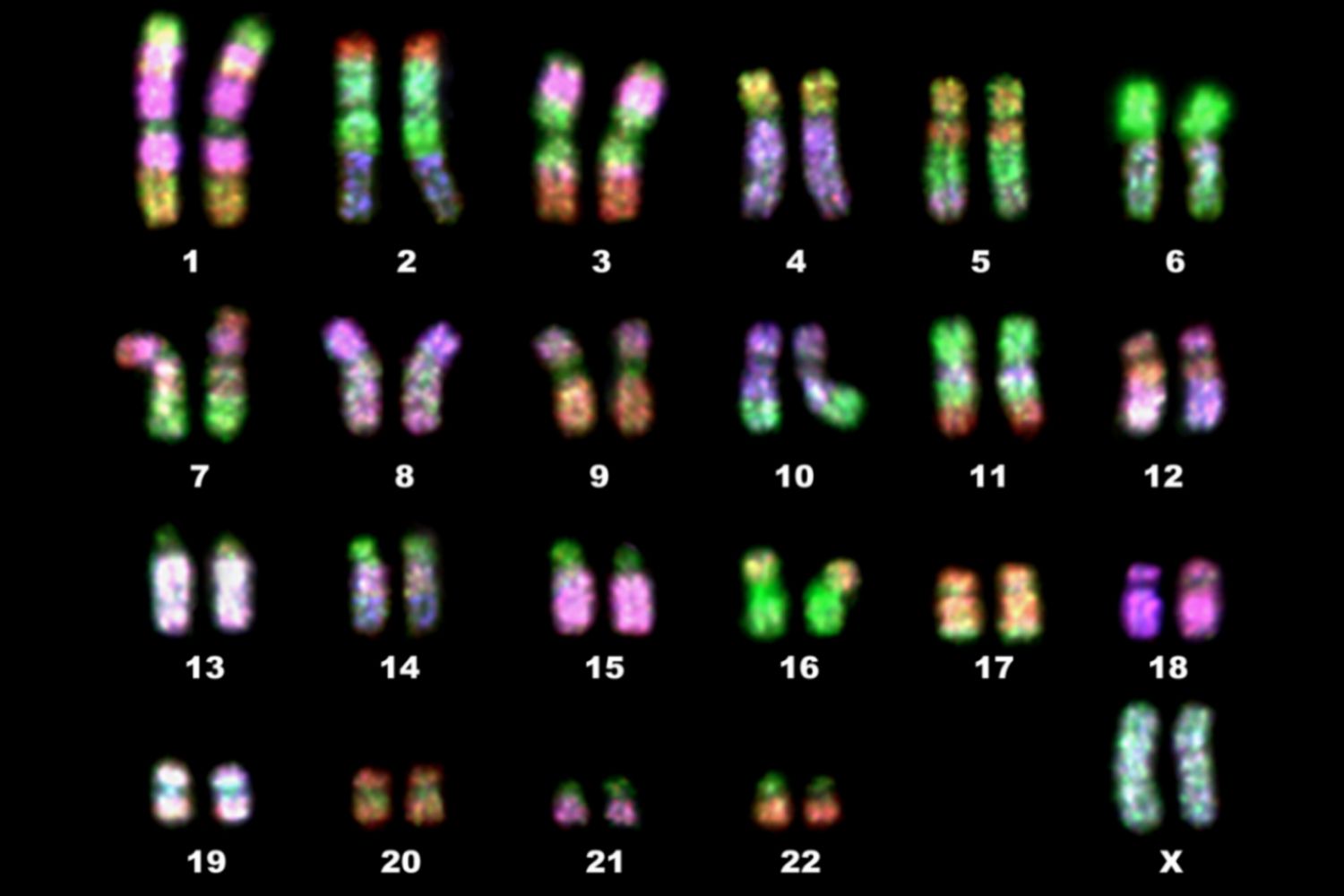
What is this an image of?
Homologous chromosomes that are numbered and arranged into pairs. This is called a **karyotype**.
17
New cards
\[T/F\] Abnormal chromosomes have little to no effect on our genome.
False, they are associated with some inherited genetic defects.
18
New cards
\[T/F\] Reciprocal chromosomal translocation is beneficial, as it ensures genetic diversity.
False. When reciprocal chromosomal translocation occurs, it causes an uncommon arrangement of chromosomes. It is typically associated with cancerous cells.
19
New cards
\[T/F\] Despite being called “junk DNA”, non-coding DNA actually serves a purpose.
True, though we do not have enough studies that show what the full range of their purpose is yet.
20
New cards
What is non-coding DNA?
Non-coding DNA are sequences of DNA that do not encode protein. These sequences of DNA are __not__ biologically inactive, as the serve other purposes.
21
New cards
What is interphase?
It is the stage where a cell is preparing for cell division.
22
New cards
What is mitosis?
The division of the nucleus within the cell after the DNA has been replicated/doubled.
23
New cards
What occurs during the M-phase of a cell?
The chromosomes condense, gene expression largely ceases, and the mitotic spindle forms from microtubules and other proteins.
24
New cards
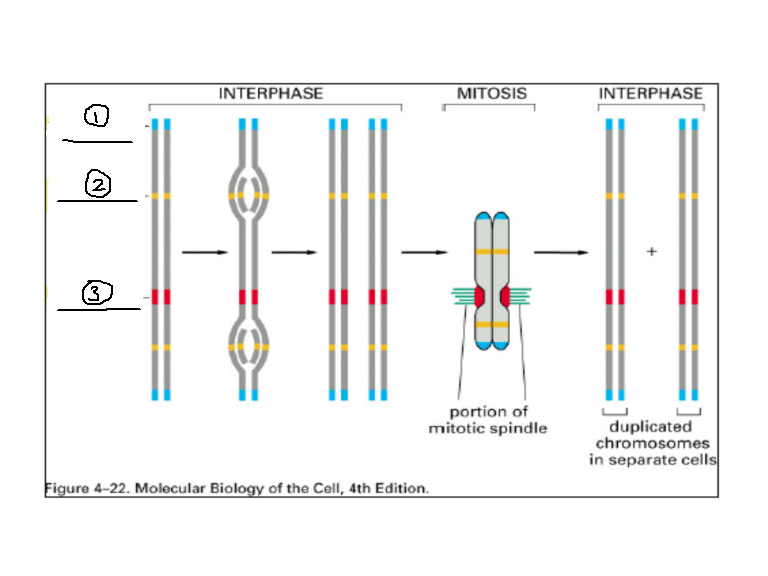
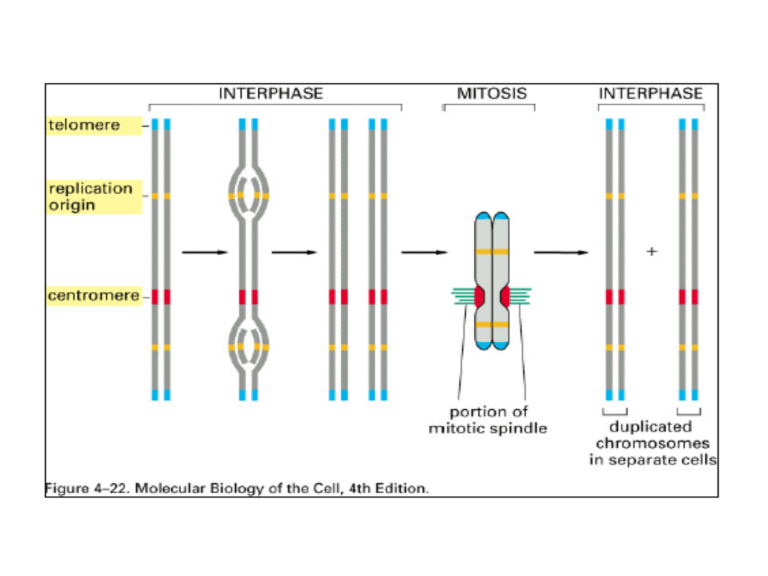
Identify numbers 1, 2, and 3 on the image.
1: telomere
2: replication origin
3: centromere
2: replication origin
3: centromere
25
New cards
The _______ is attaches the duplicated chromosomes to the mitotic spindle so that one copy/chromosome is distributed to each daughter cell when the cell divides.
centromere
26
New cards
______ contain repeated nucleotide sequences that enable the ends of chromosomes to be replicated and also cap the end of the chromosome to prevent mistaking it for being broken DNA that needs repair.
telomere
27
New cards
Interphase chromosomes occupy their own _______ _______ within the nucleus.
distinct territories
28
New cards
What is the nucleolus?
A non membrane-bound structure composed of proteins and nucleic acids found within the nucleus. It is the most prominent structure in an interphase cell.
29
New cards
What is heterochromatin?
It is tightly compacted chromatin. It is a gene-poor and is located mainly around the periphery, immediately under the nuclear envelope.
30
New cards
What are nucleosomes?
They contain DNA wrapped around a core of eight histone molecules.
31
New cards
What are histones?
histones are highly basic proteins abundant in lysine and arginine residues that are found in eukaryotic cell nuclei
32
New cards
\[T/F\] Chromatin is the complex of both classes of protein (histones and non-histone proteins) with nuclear DNA.
True
33
New cards
What are the aspects of the nucleosome core:
8 histone proteins: H2A, H2B, H3, and H4 (each x2)
The double-stranded DNA, 147 nucleotide pairs long, that winds around the histone octamer
The double-stranded DNA, 147 nucleotide pairs long, that winds around the histone octamer
34
New cards
What is the nucleosome?
A nucleosome core particle plus one of its adjacent DNA linkers (\~80 nucleotide pairs)
35
New cards
The 147 nucleotide pairs of DNA is wrapped around the nucleosome core:
a. 2.5 turns
b. 1.7 turns
c. 0.7 turns
d. 3.0 turns
a. 2.5 turns
b. 1.7 turns
c. 0.7 turns
d. 3.0 turns
1\.7 turns
36
New cards
What charge is the sugar-phosphate backbone of DNA?
negative
37
New cards
What charge is the histone?
positive
38
New cards
\[T/F\] The sequence of DNA matters when wrapping around a histone octamer.
False. It is based on charge, not nucleotide sequence.
39
New cards
The chromatin in human chromosomes is folded into __________?
looped domains
40
New cards
What is the name of the normal, non-packed chromatin in a chromosome?
a. homochromatin
b. heterochromatin
c. alochromatin
d. euchromatin
a. homochromatin
b. heterochromatin
c. alochromatin
d. euchromatin
euchromatin
41
New cards
What is methylation?
A chemical reaction in the body in which a small molecule called a methyl group gets added to DNA, proteins, or other molecules. This occurs for gene sequences via heterochromatin.
42
New cards
What is acetylation?
A reaction that introduces an acetyl functional group (acetoxy group, CH3CO) into an organic chemical compound. This occurs for gene expression via euchromatin.
43
New cards
What is the position effect?
The activity of a gene depends on its position along a chromosome.
44
New cards
K! 1) The specialized DNA sequences that cap the ends of eukaryotic chromosomes are called:
telomeres
45
New cards
K! 2) What structure in an interphase eukaryotic cell contains ribosomal RNA genes?
the nucleolus
46
New cards
K! 3) The DNA in eukaryotic chromosomes is folded into a compact form by interactions with:
proteins
47
New cards
K! 4) What statement about the nucleolus is **false**?
\
a. Nucleosomes are DNA wrapped around 8 histone proteins, plus linker DNA.
b. Nucleosomes can be seen in the electron microscope.
c. Nucleosomes are found only in mitotic chromosomes.
d. Nucleosomes represent a fundamental level of chromatin packing.
\
a. Nucleosomes are DNA wrapped around 8 histone proteins, plus linker DNA.
b. Nucleosomes can be seen in the electron microscope.
c. Nucleosomes are found only in mitotic chromosomes.
d. Nucleosomes represent a fundamental level of chromatin packing.
Nucleosomes are found only in mitotic chromosomes.
48
New cards
K! 5) How do chromatin-remodeling complexes work?
They use the energy from ATP hydrolysis to alter the chromatin structure.
49
New cards
K! 6) The tails of the core histone proteins can be chemically modified by the covalent addition of which chemical group(s)?
\
a. Acetyl
b. Phosphate
c. Methyl
d. All of the above
\
a. Acetyl
b. Phosphate
c. Methyl
d. All of the above
All of the above
50
New cards
K! 7) Histones are an example of a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein. \[T/F\]
False
51
New cards
K! 8) In interphase chromosomes, regions of the chromosome that contain genes being expressed are generally more compact. \[T/F\]
False