Biology: Chapter 13-14
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
What are the two domains of prokaryotes?
Bacteria and Archaea
Describe a prokaryotic cell
Small, does not have a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles, has genetic material and plasmids
How do cyanobacteria obtain energy? Are they autotrophs or heterotrophs?
They obtain energy through photosynthesis, making them autotrophs
What are the main characteristics of Archaea?
most are extremophiles, they can be found in humans and they have traits from both Bacteria and Eukaryotes.
What are the most abundant organisms on earth?
Bacteria
Define plasmid
small, circular piece of DNA in a prokaryotic cell
What are the three most common shapes of bacteria?
bacillus, coccus, spiral
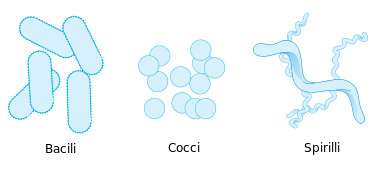
What is the purpose of the cell wall in prokaryotic cells?
to give extra protection to the cell
What is an endospore?
a spore that forms inside prokaryotic cells when the cell is under stress. (a tough structure that encloses the DNA and protects it)
How do prokaryotes reproduce?
Through binary fission, a type of asexual reproduction
Are viruses living things? Why or why not?
no, because they lack many of the characteristics needed to classify them as living things
What are viruses made of?
genetic material contained inside a capsid ( a protein coat)
What is the purpose of the envelope that surrounds some viruses?
It is used to avoid the host's immune system
What is a single virus called?
virion
What is the dormant state of a virus called?
latency
What are the three main processes of the lytic cycle?
1- infection of the host
2- the host replicates the virus' DNA
3- rupturing (lysing) the host so the viruses can spread. (this kills the host)
What is the lysogenic cycle?
It is another way for a virus to infect its host, but it doesn't happen immediately- the virus stays in a state of latency before the host replicates the virus' DNA
What shapes can viruses come in?
Helical, complex, and icosahedral
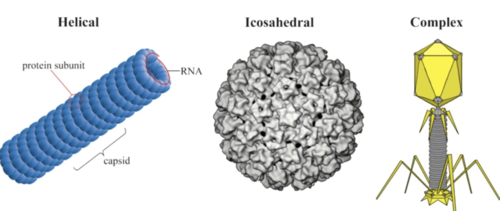
Define bacteriophage
a virus that infects bacteria
What domain are protists classfiied?
Eukarya
What are the three main types of protists?
protozoa, algae, molds (animal-like, plant-like, fungi-like)
What is a pseudopod? What type of protist uses it?
a temporary extension of the cytoplasm used for movement. Ameboids use pseudopods
Compare and contrast flagella and cilia
Cilia are small and usually many of them are on the protist. They move in a back-and-forth motion.
Flagella are long and usually there are one to three of them. They move in a spiral motion (like a propeller)
What type of offspring will binary fission produce?
a single offspring identical to the parent
What type of protist gets food by engulfing it?
Ingestive protists (ex: amoebas)
Define/describe protozoa
Protozoa are animal-like protists capable of movement (motility)
What will smile molds do when food is scarce?
they aggregate (the slime mold bunches together to become a slimy mass)
How are algae beneficial to humans?
They provide oxygen and are an important factor of oceanic food webs (which we can be apart of)
What domain and kingdom are fungi classified in?
Domain- Eukarya
Kingdom- Fungi
What is chitin? (for fungi)
a polysaccharide found in the cell walls of fungi
Define budding
a type of asexual reproduction in which the offspring pinches off from the parent, making two new identical cells (ex: yeast)
What is hypae?
filaments of multicellular fungi
Describe sexual reproduction in fungi
hyphae form two parents fuse, forming a zygospore
What is the purpose of spore production in fungus?
spores are how fungi asexually reproduce, so the more spores, the more offspring
List two important roles that fungi play for humans
Fungi are a source of food (ex: mushrooms, yeast)
Fungi are used in medicine (ex: penicillin, antibiotics)
What is mycelium?
mass of hyphae that makes up the body of a fungus
List two diseases in humans caused by fungi
Athlete's foot and ringworm
What is a mold?
type of protist that decomposes waste
What is the endosymbioc theroy?
that a smaller prokaryotic cell was engulfed by a large one, forming a mutually symbiotic relationship that eventually formed into protists.