Case Management & Pre-Trial Hearings
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
When will the MC issue case management directions?
D issues not guilty plea to summary offence or not guilty to either way offence.
Issue directions after plea.
Directions issued before venue / allocation hearing if either-way offence.
What is the form called to record the standard directions? How much time is typically given to prepare for trial?
‘MC Trial Preparation Form’ (standard set of directions)
Parts 1-4 require PR and D to detail preparations;
Part 5 contains decisions / directions made by court.
8-weeks to prepare case; or
14-weeks if expert evidence.
Witnesses are important source of evidence at trial.
How does a solicitor secure their attendance?
Write to witness first to appear;
If negative / no response, apply for ‘witness summons’ (i.e. compel attendance).
Court grants ‘witness summons’ if…
Witness can give material evidence; and
Interests of justice to issue summons (s. 97, MC Act 1980).
If a D does call upon witnesses, what must they then do under s. 6C, Criminal Procedure and Investigations Act 1996? Is there a time limit?
Serve on CPS notice setting out names, addresses and DOBs.
Applies both to CC and MC.
Time limit = 28 days from when PR complies with s. 3, CPIA 1996.
S. 3, CPIA 1996 = PR discloses any material in possession that has not been disclosed to D. Reasonably considered capable undermine PR’s case.
True or False: The D must serve on the CPS copies of both its witnesses and expert witnesses statements.
False.
Only obliged to serve expert witness statements.
Is it necessary for all witnesses to attend trial?
No.
Evidence not in dispute; no requirement to attend.
May give s. 9, CJA 1967 statement.
Example - Assault case. Dr. examine and treat injuries. D does not deny hitting him; claims self-defence. Dr’s evidence not in dispute.
What is a s. 9, CJA 1967 witness statement? What are the requirements for it to be admissible?
(A). Signed and dated
(B). Contains declaration: ‘This statement is true to the best of my knowledge and belief and I make it knowing that if it is tendered in evidence…’.
(C). Copy has been served before hearing on other parties in case; and
(D). Minimum of 7-days from service to object. Court can extend time period to object.
What are the limits on what can be included under a s. 9 witness statement?
Limited to…
Evidence admissible only in oral evidence.
Matters not in dispute between parties.
Can I object to the admission of a s. 9 statement?
Yes.
Do so in writing within 7-days from service
Seek to challenge admissibility, cross-examine maker etc.
Both PR and D entitled use s. 9 method.
True or False: Documentary evidence (i.e. plans, photos) must be verified by a witness statement from a person who prepared them before admission to proceedings.
True.
What are some of the obligations outlined in ‘Transforming Summary Justice’ that the CPS must follow?
Publish IDPC on Common Platform minimum 5-days before hearing.
Promote engagement between D, PR and court (i.e. TEAMS).
Allow D’s solicitors time to prepare.
Early disclosure unused material in anticipated not guilty cases.
Ensure guilty plea (if one) for either-way offence issued at MC for max credit.
etc.
Cases sent to the Crown Court will be subject to a ‘plea and trial preparation hearing’ (PTPH) there.
Under s. 51(1), CDA 1998, when will the MC send offences that are not strictly indictable offences to the CC?
Either-way or summary offence appears related to offence triable on indictment; and
Re summary-only offence, its punishable by imprisonment, or involves disqualification from driving (s. 51(1), CDA 1998).

Before a D is sent to the CC for an offence triable only on indictment - what is the purpose of the MC’s hearing that takes place?
Purpose = Determine whether offence triable on indictment is charged; other related offences also send to CC.
Set date for PTPH at CC or preliminary hearing if necessary.
Remand on bail or in custody.
Issue standard directions to PR + D prior to PTPH at CC.
Issue notice specifying offences on trial.
Recap: In what instances will a D charged with an either-way offence who pleads not guilty be sent to the CC for trial?
Tried in CC if MC declines jurisdiction; or
D elects CC trial at allocation hearing.
When may a ‘linked summary offence’ be sent to the CC for trial?
Charged with either-way offence; may also be charged with summary-only offence too.
Can send to CC if summary-only offence founded on same facts as either-way offence or part series of offences.
Qualifying Offences: common assault, taking a conveyance without consent, driving whilst disqualified, criminal damage.

In what other circumstances may the MC send an either-way offence alongside a summary offence to the CC?
Summary offence is…
Punishable by imprisonment / disqualification from driving; and
Appears related to either-way offence.
S. 51, CDA 1998
What happens at the CC if…
(A). D is convicted of either-way offence + pleads guilty to the summary offence; or
(B). D is acquitted of either-way offence + pleads not guilty to summary only offence.
(A). CC can sentence for summary offence. Limited to MC powers.
(B). Summary offence must be remitted back to MC for trial (i.e. not ‘may’).

Sometimes a ‘preliminary hearing’ will be required.
Where does this take place? Why will this take place? When must it take place?
Occurs in CC for indictable offences only.
Rare cases only where…
Case management issues CC must resolve
Trial likely exceed 4-weeks.
Desirable set early trial date.
D under 18yo.
Likely guilty plea. D could be sentenced at it.
Must take place within 10 business days of date on which MC send to CC.
True or False: The 1st hearing in the CC will always be the PTPH.
False.
CC may hold a ‘preliminary hearing’ in certain circumstances.
Uncommon though.
What is the purpose of the PTPH? When must it be held?
Purpose = D enters plea. If not guilty; judge issues case management directions prior to trial.
PTPH must occur within 20 business days of MC sending to CC.
An arraignment occurs at the start of the PTPH.
What does this entail?
Counts on indictment put to D who pleads guilty / not guilty.
Jury not informed of guilty pleas. Why? Prejudicial.
A D may enter into an agreement with the CPS to plead guilty to certain offences in return for the CPS to not pursue others.
What is the result of this at the arraignment?
D pleads guilty to offences.
CPS offers no evidence on other counts.
Judge orders verdict of not guilty in response.
What other situation will lead the CPS to offer no evidence at the arraignment?
Further evidence has become available.
No longer reasonable prospect of conviction.
Judge order not guilty verdict.
Alternative - CPS request count ‘lies on the court file’.
Charges not terminated. Can reactivate with permission of court / court of appeal.
Why? New evidence, not in public interest to prosecute, D agree plead guilty other charges etc.
What occurs if the D pleads guilty at the arraignment?
Sentence immediately; or
Adjourn for pre-sentence reports (i.e. medical, probation) or D dispute factual allegations by PR witnesses.
Factual disputes resolved via ‘Newton hearing’.
I am about to enter a guilty plea at the PTPH.
Can I request the judge for an indication of sentence before I do this?
Yes.
Labeled an R v Goodyear indication.
Advanced indication of likely sentence if pleads guilty.
D must expressly request this.
Once given, D enters plea, indication is binding.
NOTE - Can do this at MC initial allocation hearing too. Can request indication; receive estimation then proceed to plead guilty or elect trial.
I have entered a not guilty plea at the PTPH.
What does the judge do next?
Considers if further directions necessary (on top of MC directions).
Fixes trial date or places on ‘warned list’ (i.e. cases awaiting trial; no dates).
What does the judge request from the D and PR to determine if additional instructions are necessary at the PTPH?
Require D and PR supply following:
Summary of case issues;
Details of witness numbers, estimate trial length.
Police interview transcripts require editing.
Defence statement served; issues with adequacy.
Whether PR serve additional evidence.
Whether dispute re disclosure adequacy of PR’s unused material.
Whether expert evidence called
Further directions needed for hearsay / bad character evidence.
Special measures required for any witnesses
Facts which can be formally admitted.
Points of law / issues re admissibility of evidence.
Dates of availability for witnesses and advocates.
True or False: Once a D enters a guilty or not guilty plea it cannot be changed.
False.
D enters not guilty plea can change this any time before jury return verdict. At court discretion.
D can enter guilty plea during trial if judge makes ruling on point of law / admissibility evidence deprives D of defence.
What is the test for the PR to disclose ‘unused material’?
S. 3, CPIA 1996
Disclose if ‘might reasonably be considered capable of undermining the case for the prosecution…or of assisting the case for the accused’.
Examples - Records of 1st description suspect by witness; D’s information provides innocent explanation for offence; material casting doubt witness reliability, confessions.

Is the CPS obliged to disclose further unused material after initial disclosure?
Yes.
May receive further evidence or in light of D’s defence statement.
S. 7A, CPIA 1996
Can the PR withhold disclosure of unused material after a request by D’s solicitor?
Maybe - depends if unused material is ‘sensitive’.
National security / intelligence
ID police informants, undercover officers.
Techniques / methods relied on by police.
Child witness material.
If above meets s. 3, CPIA 1996 threshold they must disclose unless CPS argues ‘public interest immunity’.
CPS must apply to court ex parte (i.e. without notice to D).
At court’s discretion.
When must a defence statement be served and to whom in the MC?
D’s solicitor has a choice to serve defence statement (rare they do).
Why? Issue statement to provoke CPS disclose more evidence.
Serve to CPS within 10 business days initial CPS disclosure unused material;
Send a copy to court;
Court may decide serve on co-accused (if >2 Ds)
Can request time extension from court.
When must a defence statement be served and to whom in the CC?
D does not have choice to serve a defence statement.
If not? CC can raise adverse inference.
Serve to CPS within 20 business days initial CPS disclosure unused material;
Send a copy to court;
Court may decide serve on co-accused (if >2 Ds)
Can request time extension from court.
What must the defence statement contain as required under s. 60, CJIA 2008?
Be a written statement:
Sets out nature and particular defences D is relying on (i.e. alibi, self-defence).
Indicates factual matters D disputes and why;
Outlines particulars of matters of fact D relies on for defence;
Indicates points of law (admissibility of evidence) D will pursue at trial; and
If alibi defence; provides name, address, DOB of witnesses
Are the defence under a continuing duty with regard to the defence statement?
Yes.
Must update if details change (i.e. witness comes forward support alibi).
S. 6B(3), CPIA 1996.
Does the D’s solicitor need to obtain the approval of the D for the defence statement?
Yes.
Because defence statements deemed approved unless contrary shown.
Keep D’s signed copy on file as proof.
^ Not mandatory, but good practice.
When may the CC draw an adverse inference with regard to the defence statement?
Occurs upon ‘faults’:
Fail to provide statement at all;
Late service;
Incomplete statement;
Statement inconsistent with trial defence;
Fail update statement.
Court or other party (PR / co-accused) with leave can draw inference. Need court’s permission. Does not arise automatically.

After serving a defence statement, what does it oblige the PR to do?
CPS reviews initial disclosure.
Examines if further unused material disclosable in light of statement.
Capable undermine PR’s case or assist D.
S. 7A, CPIA 1996

After serving a defence statement, can the D challenge the PR failure disclose unused material?
Yes. Can apply to court.
Challenge CPS failure re continuing duty to disclose in light of matters in defence statement.
Show reasonable cause PR has materials should have been disclosed.
Big flowchart
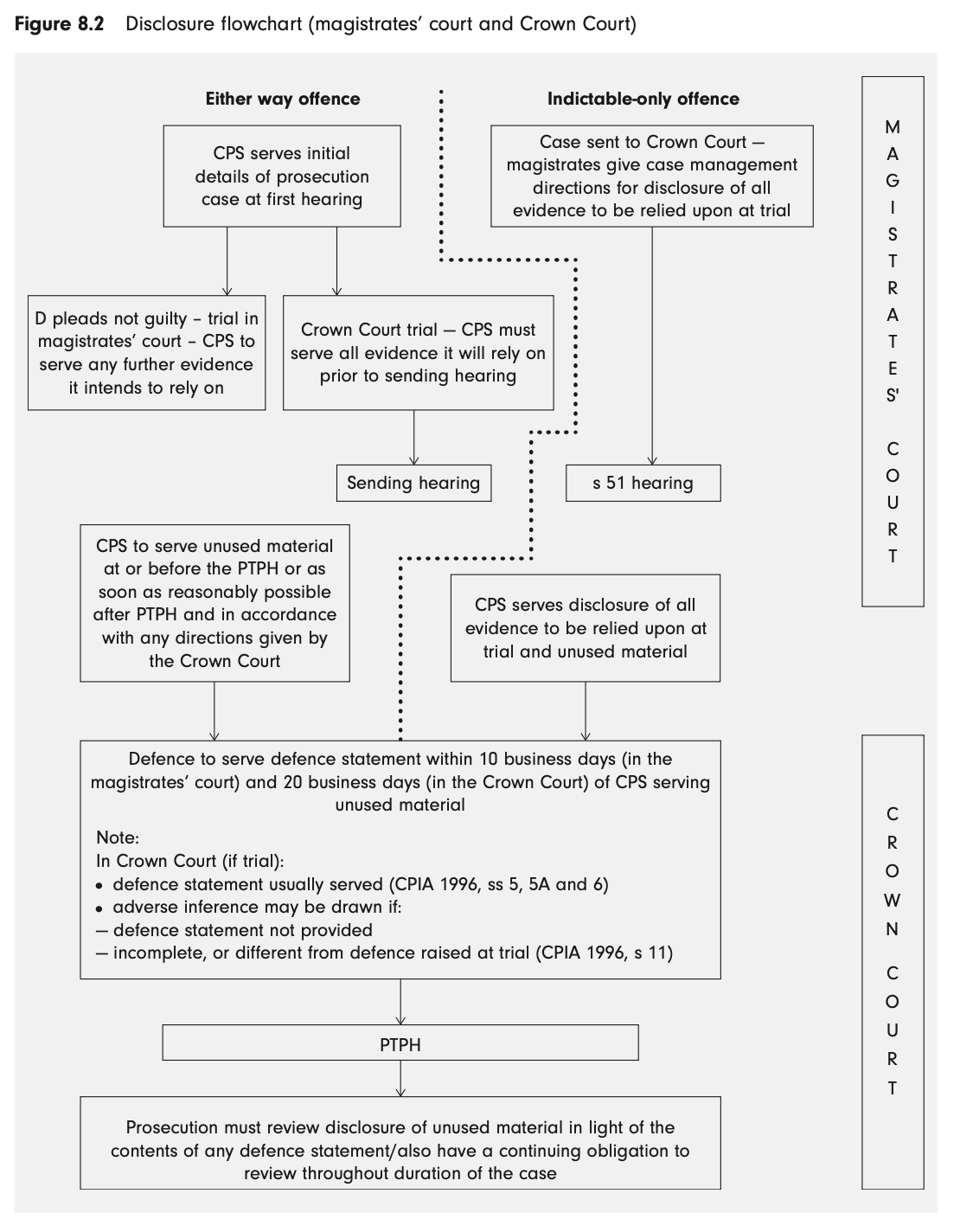
When must the CPS serve all evidence that it is relying upon if the case is being sent to the CC?
Must serve all evidence before the sending hearing where MC commits case to CC.
When does the CPS typically disclose ‘unused material’ for CC cases?
Typically serve at or before PTPH.
Otherwise as soon as is reasonably possible after PTPH.
Date when this occurs determines when D must serve defence statement.
What is the role of the ‘legal adviser’ in the MC?
Duties:
Reads out charge to D, informs D of plea before venue procedure, committal for sentence, requests indication of plea.
Takes notes of evidence for magistrates.
Advise on law and practice.
Can be present in room during deliberations.
Can ask questions of witnesses.
Cannot do:
Offer opinion on likely verdict. Only advise.
Will not announce verdict.
True or False: A witness must wait outside the courtroom before giving their evidence.
True.
Unless witness is a party to the case or expert witness.
ALSO - No requirement to state address at beginning of evidence unless relevant.